Red blood cells are the main parameters of urine analysis along with leukocytes, which show the general condition of the urogenital tract. Any doctor pays special attention to them, since increased values of this indicator have diagnostic value.
An increase in red blood cells (erythrocyturia) in women is a pathological and alarming sign that requires further examination and observation, since it is undesirable to start such a process.
Let's take a closer look at what is the normal rate of red blood cells in a urine test in women, and what are the reasons for an increase in their level?
Don't self-medicate! Be sure to consult with a qualified healthcare practitioner. The information is for informational purposes only and does not replace medical care.
What are blood cells responsible for and how to find out their level
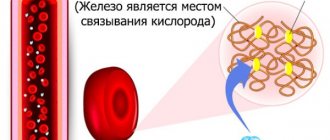
Red blood cells are specific blood cells that respond to areas of inflammation and infection. From a biological point of view, their role in the body is invaluable.
They ensure the delivery of oxygen to organs , tissues, muscles, and, as a reverse function, transport carbon dioxide to the lungs. This is how the body breathes and nourishes itself.
Red blood cells, like other blood cells, are formed in the bone marrow , and then they begin to actively participate in the hematopoietic system. Their average period of activity is 4 months, and then cell breakdown occurs in the liver and spleen.
Red blood cells cleanse the body of toxins and other harmful substances that cause intoxication, so they cleanse the blood in a specific way.
During inflammation and disease, the concentration of cells begins to increase sharply. This can be observed in urine tests, blood tests, swabs from the throat, nose, urogenital tract, etc.
Erythrocyturia is detected where inflammation or infection is localized.
An increased level of red blood cells in a woman’s urine indicates a pathology of the urogenital tract, which requires treatment.
to check the presence and number of red blood cells in a woman’s urine.
To do this, you need to do the following laboratory tests:
- general urine analysis;
- analysis according to Nechiporenko.
If the patient needs to find out the general level of data, then a clinical blood test is best suited for this, which accurately calculates their concentration together with erythrocyte indices.
However, there is no direct connection between the level of red blood cells in the blood and urine , so it is necessary to conduct a full examination of the organs of the urogenital tract.
According to the reference values of many laboratories, red blood cells should be absent in a woman’s urine or their level should be no more than 3 in the field of view (p/zr), everything else is not the norm.
Do you know how many times a day women need to wash themselves?
How to do Kegel exercises for women? Useful recommendations are in this article.
You can learn about the treatment of urinary incontinence in women here in the article.
Norms of red blood cells in urine
| Patient | Number of red blood cells in the field of view |
| Women | No more than 3 (up to 5) |
| Men | No more than 1-2 |
| Children | 1-2 |
| Newborns (up to 1 month) | Up to 4 (due to the functional immaturity of the glomerular membrane) |
Factors influencing the result
- Overheating of the body (working in a hot shop, visiting a solarium or bathhouse, prolonged exposure to direct sunlight, etc.);
- Heavy physical activity and emotional stress;
- Intense sports training;
- Alcohol abuse (causes microspasms of renal vessels);
- Excess of acidic foods and drinks, spicy and spicy foods in the daily diet;
- Long-term treatment with ibuprofen, methenamine, sulfonamides, anticoagulants, vitamin C.
Temporary erythrocyturia, provoked by one or more of the above factors, is regarded as a variant of the norm.
With repeated OAM and exclusion of influencing factors, red blood cells in the urine should normalize. Important! The interpretation of the results is always carried out comprehensively. It is impossible to make an accurate diagnosis based on only one analysis.
Risk factors, why the disease occurs
Erythrocyturia does not always mean a pathology that needs to be treated immediately. Often the reason is a normal physiological process, but with severe symptoms this will not be the norm.
The doctor first needs to listen to the patient and ask questions to distinguish between physiology and pathology.
Why are there increased red blood cells in a woman’s urine, what is the reason? A physiological increase in indicators is possible under the following conditions:
- menstruation;
- alcohol intoxication;
- severe stress;
- uncontrolled use of anticoagulant drugs;
- increased physical activity;
- abuse of hot and spicy foods.
A significant increase in these cells is possible if a woman donates biomaterial during menstruation .
Despite douching and following the rules for collecting the analysis, cells still end up in the urine and can be detected in large quantities.
This is a physiological norm, but when interpreting the results, the doctor may not know about it .
In this case, it is most informative to conduct laboratory tests after the end of menstruation.
In other cases, physiological erythrocyturia may be quite insignificant.
More often, various pathologies become the cause of increased red blood cells in a woman’s urine. The doctor evaluates all the indicators of the analysis, and only then makes diagnostic conclusions.
These cells rarely increase in isolation from other parameters, but still they make it possible to identify urological abnormalities.
Pathological erythrocyturia is possible with the following diseases:
- infection of the genitourinary system (cystitis, urethritis, colpitis);
- urolithiasis disease;
- traumatic injuries to the bladder or kidneys;
- neoplasms of the urogenital tract;
- kidney diseases (pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis, nephritis, nephrotic syndrome);
- arterial increase in pressure of renal origin;
- pathological bleeding from the uterus;
- gynecological diseases (cervical erosion);
- decrease in platelets in the bloodstream (thrombocytopenia);
- blood clotting diseases (hemophilia).
The final cause of the increased content of red blood cells in a woman’s urine must be determined by a doctor, and for this purpose additional examinations are often prescribed.
Complaints and symptoms can help in diagnosing the disease and speed up the process of describing the clinical picture.
SOS signals from our body, blood in urine in women:
Increased values (hematuria)
Highlight
- mild hematuria (microhematuria): up to 20 red blood cells in the field of view;
- moderate: 20-200 red blood cells;
- severe (macrohematuria): more than 200 red blood cells in the visual field.
Hematuria is diagnosed by the presence of more red blood cells in the urine and is of three types: somatic, renal, renal associated and postrenal.
1. Causes of somatic hematuria:
- hemophilia (blood clotting disorder due to decreased production of clotting factors);
- thrombocytopenia (decreased platelet count, provokes increased bleeding);
- hemoglobinuria (presence of hemoglobin in the urine);
- intoxication of the body with waste products of bacteria and viruses (causes dysfunction of the glomerular membrane of the kidneys);
- poisoning with medications, chemical reagents (benzene, aniline, etc.), snake and spider venom, mushrooms, etc.
2. Renal hematuria, related to the activity of the kidneys, is divided into glomerular and extraglomerular:
Glomerular is combined with proteinuria, erythrocyte casts and altered erythrocytes in the urine, the color of the urine is brown, occurs with:
- Benign familial hematuria
- Glomerulonephritis
- Alport syndrome (hereditary nephritis)
- IgA nephropathy
Extraglomerular is also combined with proteinuria, but there are no red blood cell casts in the urine, the color of the urine is reddish or pink:
- Tubulointerstitial nephritis
- Polycystic kidney disease
- pyelonephritis (infectious inflammation of the kidneys, provokes increased vascular permeability);
- oncological processes (a cancerous tumor proliferates and grows into the vessels of the kidneys, causing bleeding with unchanged red blood cells entering the urine);
- kidney stones (stones block the renal collecting system, which can lead to vascular damage and bleeding);
- hydronephrosis (stretching of the kidney due to impaired urine outflow);
- kidney injury (rupture, penetrating knife or gunshot wound, illiterate surgical intervention complicated by bleeding).
3. Postrenal, related to the urinary tract:
- cystitis (inflammation of the bladder);
- urolithiasis (a stone in the urethra or bladder injures the mucous membrane, causing bleeding);
- tumor processes (cancer of the bladder, urethra, prostate, uterus or ovaries leads to vascular proliferation and bleeding);
- injuries of the genitourinary organs;
- prostatitis (inflammation of the prostate);
- Benign prostatic hyperplasia;
- urethritis (inflammation of the urethra) in men and women;
- pathological uterine bleeding, in which blood from the vagina can enter the urine during urination;
- cervical erosion (violation of the integrity of the cervical epithelium, which leads to damage to blood vessels).
Also, red blood cells in the urine can appear as a result of:
- cardiovascular diseases: heart failure, myocardial infarction, hypertension;
- taking anticoagulants;
- infectious and inflammatory diseases: mononucleosis, tuberculosis, tonsillitis, malaria, severe forms of influenza;
- autoimmune disorders (systemic lupus erythematosus);
- varicose veins of the bladder neck.
Erythrocyturia in pregnant women and after childbirth
An increased number of red blood cells in the urine of pregnant women is also not normal .
The reasons for this condition lie in the pathologies described above, but do not forget that while carrying a child, the body begins to function differently.
What do red blood cells in urine mean in pregnant women? The growing fetus puts pressure on the bladder, uterus, and ureters, so congestion and vascular disorders in the genitourinary area begin .
This is a favorable environment for the development of bacteria, but for a healthy body without chronic pathologies this will not be a problem.
There may be a slight increase in indicators (microhematuria) , which does not cause discomfort. However, severe erythrocyturia requires treatment and emergency medical measures.
Chronic diseases of the genitourinary system during pregnancy in a woman can worsen, as indicated by high rates. More often these are kidney diseases (pyelonephritis) that require treatment.
The pregnant woman is sent to the hospital, where, if possible, she undergoes the following procedures:
- “positional treatment” to restore urine outflow;
- ureteral catheterization;
- puncture nephrostomy in severe cases (drainage of urine using a catheter);
- kidney decapsulation (removal of the affected area of the kidney);
- removal of the kidney in the most severe cases.
In case of advanced renal pathologies, the pregnancy has to be terminated , so it is necessary to immediately consult a doctor and not start the inflammatory process.
During gestation, urolithiasis (sand, stones) also occurs, but in this case the treatment will be simply therapeutic, which includes increased water consumption.
After childbirth, high levels of red blood cells in the urine of women are a pathology, as this indicates inflammatory changes in the urogenital tract.
Changing hormonal levels have no effect on red blood cells, so ideally they should not increase under any circumstances .
People often ask: when should you get your period after giving birth? You asked - we answer!
Read about contraindications to ultrasonic facial cleansing in our article.
This publication will tell you about the treatment of rosacea on the face at home.
Symptoms
Typically, erythrocyturia is rarely asymptomatic , and women immediately notice pathological changes in themselves. Symptoms vary depending on where the inflammatory process is localized and in which organ.
The color of the urine begins to change. If with slight erythrocyturia (microhematuria) this may not be noticed, then with a pronounced increase blood appears.
In some cases, the urine takes on a very dark shade , which should alert you.
All this requires finding out the reasons, but usually everything is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- frequent urination;
- pain during or after urination;
- fever, general malaise;
- weakness, headache;
- pain in the back or sides;
- renal colic;
- lack of appetite or nausea;
- increased blood pressure;
- blood in the urine (gross hematuria);
- bloody discharge from the vagina.
Minor erythrocyturia may be asymptomatic. But usually this is due to improper collection of biomaterial, so this issue needs to be given special attention.
Such nuances can greatly distort the results of the study, since tests must be taken in a sterile container and only after a thorough toilet of the genitals. Only a doctor can determine the final cause of the disease by prescribing additional examinations.
These indicators increase together with protein and leukocytes , which accurately indicates the infectious nature of the disease. Therefore, in no case should symptoms that appear be ignored.
Why is this condition dangerous?
The danger is not the increased indicators, but the pathology that caused their increase. We need to find out what caused erythrocyturia . Without treatment, various complications and more serious pathologies are possible.
Asian Female Doctor taking note on checklist paper.
For example, kidney diseases (pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis, nephritis) can transform into chronic diseases or kidney failure.
Urolithiasis has a tendency to relapse and further develop, since sand, without proper removal, begins to transform into large stones, causing consequences.
Untreated cystitis, in turn, can constantly recur , reducing the quality of life, so it is necessary to begin medication measures as quickly as possible.
A possible complication is a malignant tumor in the genitourinary organs, which begins to progress.
Blood in the urine appears constantly, as well as other symptoms, which are not helped by various antibiotics and painkillers. In this case, surgery and chemotherapy are required.
The danger of erythrocyturia in the development of the following diseases:
- chronic pathologies of the urinary tract (cystitis, pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis, etc.);
- renal failure;
- increase in stones in the urinary tract;
- malignant/benign tumor, cyst of the urinary tract or pelvic organs;
- persistent arterial hypertension;
- nephrotic syndrome;
- functional pathologies of the bladder and kidneys.
A full examination and consultation with a doctor is necessary, who will prescribe treatment and prevent the development of complications. Therefore, you cannot delay going to the doctor .
2. Reasons
It is obvious that the main causes of erythrocyturia are associated, first of all, with the pathology of the urogenital (genitourinary) system. These are diseases such as:
- oncological process;
- urolithiasis disease;
- inflammation of parenchymal renal structures (glomerulonephritis, pyelonephritis);
- cystitis and any other infections of the urinary tract and/or reproductive organs;
- kidney injury;
- microtrauma of the urinary tract due to certain medical procedures (for example, catheterization, bougienage, etc.);
- long-term therapy with “blood thinning” anticoagulant drugs in inappropriately large doses;
- arterial hypertension with stretching and thinning of the walls of the blood vessels of the kidneys;
- acute intoxication, poisonous snake bite;
- autoimmune connective tissue diseases (systemic lupus erythematosus);
- a group of diseases of the circulatory system under the general name “hemorrhagic diathesis”, which are accompanied by a tendency to bleeding and hemorrhage.
Visit our Therapy page
Which doctor should I contact, diagnostic methods
The cause of erythrocyturia can be eliminated using modern medicine, but clinical manifestations must be noticed in time.
with urinary tract diseases :
- urologist;
- nephrologist;
- gynecologist.
These doctors can be contacted both in public and private medical organizations.
A urologist deals with genitourinary pathologies, and a nephrologist specializes only in kidney diseases and dysfunctions.
A gynecologist treats diseases of the pelvic and genitourinary organs, since in women everything is interconnected.
Often gynecological diseases and sexually transmitted infections cause inflammation of the urinary tract, but then treatment becomes more difficult. The patient has to be observed by several specialists who use different approaches to treatment.
In private clinics there is a urogynecologist who deals with such problems. Therefore, it is best to find such a specialist to avoid progression of the disease and improper therapy.
If erythrocyturia is detected in the analysis, the doctor pays attention to other indicators and symptoms. An increase in protein and red blood cells often indicates a renal origin of the pathology, and a normal increase in cells and the presence of salts means urolithiasis.
In most cases, further examination is required, which includes diagnostic measures :
- Urinalysis according to Nechiporenko, where leukocytes, red blood cells and casts are counted as accurately as possible.
- Urine culture for microflora with sensitivity to antibiotics.
- Ultrasound of the bladder, ureters and kidneys, where you can visually see stones, tumors and foci of inflammation.
- Repeated OAM.
- Blood biochemistry (urea, creatinine, free nitrogen, uric acid) for the diagnosis of renal failure.
- Cystoscopy and biopsy in severe cases (instrumental examination of the urethra and bladder walls).
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs and colposcopy.
- X-ray of the kidneys.
- MRI or CT scan of the urinary tract.
These are studies that are necessary to establish the cause of erythrocyturia. Initially, it all depends on the patient’s condition and symptoms. Therefore, the doctor will not always prescribe a long list of diagnostic procedures.
Do you know why uterine fibroids are dangerous? Find the answer to the question in this article.
You can learn about the cost of hirudotherapy from this publication.
Don't know which epilator to choose for the bikini area? We'll tell you! A review of the devices is here in the publication.
Urinalysis according to Nechiporenko: indications, preparation, standards
No medical examination is complete without a urine test. A general urine test is perhaps one of the most frequently prescribed tests. And this is not just a tribute to medical tradition: using this method, you can obtain data valuable for making a diagnosis, prescribing and monitoring treatment. But sometimes a general analysis is not enough.
In what cases is a urine test according to Nechiporenko prescribed? What kind of research is this? What is it for? Let's figure it out.
Urinalysis according to Nechiporenko - what is it?
If in a general urine analysis some changes were identified that make it difficult to make unambiguous diagnostic conclusions, then to clarify and detail them, a urine test according to Nechiporenko may be called.
It is performed with a microscope. In this case, the number of leukocytes, red blood cells, and so-called cylinders in 1 milliliter of urine is calculated.
Why is a urine test according to Nechiporenko prescribed?
Indications for its implementation vary. It is used to identify various inflammatory processes in the urinary system (kidneys, bladder, urethra); for the purpose of assessing kidney damage in a number of systemic diseases; to distinguish between urinary tract diseases; for the purpose of monitoring treatment.
Pyelonephritis: what is this disease and how to treat it? Urologist at Clinic Expert Kursk says:
Devyatkin Alexander Alexandrovich
What does the Nechiporenko test show?
A significant number of red blood cells may indicate damage to any part of the urinary system.
An increase in the number of leukocytes is observed during local inflammatory, infectious processes, etc. In such cases, it is additionally necessary to perform a urine test for the presence of bacteria in it.
In addition to erythrocytes and leukocytes, the study of cylinders is important. What are they? These are accumulations of protein that form from cells and cellular debris when the properties of urine change. The place of their formation is the renal tubules. There are several types of cylinders (epithelial, hyaline, etc.)
What are the reasons for the increase in this or that indicator?
Increased red blood cells in the urine. Looking for reasons
The number of red blood cells increases with urolithiasis; trauma, tuberculosis and kidney tumors; glomerulonephritis, severe pyelonephritis, etc.
The number of red blood cells can also increase in pathologies not directly related to the kidneys. These include hemophilia, benign prostatic hypertrophy, leukemia (leukemia), congestive heart failure, systemic lupus erythematosus and a number of others.
Following Queen Victoria's gene: what is hemophilia? The head of the hemostasis study group of the department for optimizing the treatment of hematological diseases of the Center named after. Dmitry Rogacheva, Doctor of Medical Sciences
Zharkov Pavel Alexandrovich
Leukocytes are elevated. Why?
An increase in their number in the urine is observed in acute pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis, cystitis, kidney tuberculosis, bladder neoplasm, etc.
Cystitis: symptoms, diagnosis and treatment. Read more
Casts in urine. What does it mean?
Depending on their type, their number increases with intense physical activity, glomerulonephritis, heavy metal poisoning, acute and chronic renal failure, emotional stress, kidney damage due to diabetes, kidney tuberculosis, etc.
Ultrasound or MRI for kidney disease? The chief doctor of MRI Expert Yelets, Vladimir Vladimirovich Tulinov, tells
Preparation for urine analysis according to Nechiporenko
For 12 hours before the test, do not eat spicy, salty foods, as well as foods that change the color of urine (for example, beets, carrots).
For 48 hours before urine collection, stop taking diuretics (only after agreeing on this with your doctor).
How to properly collect urine for analysis according to Nechiporenko?
First, the external genitalia are toileted. An average portion of morning urine is collected.
How many days does it take to prepare a urine test according to Nechiporenko?
It depends on the workload of the laboratory. As planned - 1 working day.
Can urine for analysis be stored in the refrigerator?
The urine sample must be fresh. However, if the situation does not allow you to donate urine immediately before the test, you should store it in the refrigerator at a temperature of +2...+8°C. The total time of storage and delivery to the laboratory is no more than twelve hours from the moment the material is taken. It is necessary to clarify all these nuances in advance in the laboratory, clinic, etc., where the analysis will be carried out.
How to read the analysis correctly? Urine sample standards according to Nechiporenko
Normally the indicators are:
— leukocytes: 0 — 2000/ml
— red blood cells: 0 — 1000/ml
- cylinders: not detected
You can sign up for the study here or in the contacts section
Historical reference
This analysis was proposed by the Soviet military surgeon, urologist-oncologist Alexander Zakharovich Nechiporenko.
The birthplace of the future doctor was the Volyn province of the Russian Empire (today the Zhytomyr region of Ukraine).
A year before the start of the Great Patriotic War, Alexander Zakharovich graduated from the Kiev Medical Institute.
In the first years after the war, he trained in the field of thoracic surgery at the leading educational institution for training military doctors - the Leningrad Military Medical Academy.
Since the mid-60s he has been working at the Rostov Medical Institute at the Department of Surgery.
In 1967, Nechiporenko became the scientific director of the oncourological department of the Research Institute of Oncology and Medical Radiology in Rostov-on-Don. For more than 10 years he was the head of the urology course at the Medical Institute of Grodno (Belarus).
He is a pioneer of the method of removing the bladder for bladder cancer and removing lymph nodes for malignant neoplasms of the testicle.
He passed away in November 1980 at the age of 65.
Features of therapy
Treatment depends on the underlying disease that caused the increase. It is necessary to establish a diagnosis and then prescribe treatment, which includes the following methods:
- combination drug therapy;
- diet;
- local procedures (bladder installation with medicinal solutions, catheterization, etc.);
- physiotherapy (laser, ultrasound therapy);
- immunomodulation;
- surgical intervention.
For infectious erythrocyturia of any origin, antibacterial therapy is predominantly used in conjunction with urological antimicrobial drugs (Palin, 5-NOK, Nevigramon, Urotractin, Canephron, Negram, Uroflux, Phytosilin, etc.).
These are herbal and synthetic medicines that, together with antibiotics, eliminate foci of infection.
The type of antibiotic is selected according to laboratory tests : culture of microflora of urine, urethra, vagina, PCR scraping from the urogenital tract, etc.
Herbs are used as additional treatment: bearberry, calendula, knotweed herbs, madder, etc. But they should be used only after consulting a doctor.
Infectious diseases can often recur, so immunomodulatory therapy is used , which restores the mucous membrane of the walls of the bladder and urethra. These can be either special preparations or ordinary installations.
For urolithiasis, antibiotics are ineffective, so doctors prescribe a strict diet as treatment.
As well as medications that remove stones and sand (Cyston, Fitosilin, Canephron, Urolesan), antispasmodics (No-shpa, Baralgin, Arpenal).
If significant erythrocyturia appears in the analysis, it means that the stones have injured the walls of the bladder and urethra. In this case antimicrobial drugs are prescribed to restore the mucous layer.
Large stones are removed using a procedure called lithotripsy, which is performed instrumentally through the bladder.
Sometimes this is done using conventional ultrasound, which destroys medium-sized stones.
If the cause of erythrocyturia lies in gynecological diseases (colpitis, cervical erosion), then local treatment is carried out (vaginal suppositories, douching, ointments) and instrumental techniques (laser therapy, cryotherapy, radio wave surgery).
With malignant tumors of the urinary tract, a significant increase is observed. This pathology is best treated in the initial stages. The tumor is removed surgically.
If the tumor is concentrated in the bladder , then transurethral electroresection of the bladder is performed, where malignant or benign tumor cells are removed.
In the later stages of the disease, the bladder and tumor are completely removed (cystectomy).
Renal tumors are operated on laparoscopically and are often excised along with the kidney (nephrectomy).
For minor tumors, partial preservation of the kidney (resection) is possible.
Diet
Diet plays an important role in the treatment of urological and nephrotic diseases. The patient is not recommended to abuse hot, spicy, fried foods, or drink alcoholic beverages.
Drinking plenty of fluids (at least 2-2.5 liters per day) is necessary for any inflammatory process of the urinary tract.
It is also advisable to quit smoking , as it increases the risk of developing cancer and other urological pathologies.
A special diet is necessary for urolithiasis. The correct diet is selected based on what types of salt crystals are detected in the TAM. These can be phosphates, oxalates and urates.
If phosphates are present (phosphaturia), you should avoid fried foods (fish), dairy products, eggs, and liver.
Detection of oxalate salts (oxalaturia, ammonium salts) requires avoidance of foods rich in vitamin C.
The following products should not be consumed:
- citrus fruits, apples;
- broths;
- cocoa, chocolate;
- greens, salads, sorrel;
- ascorbic acid;
- tomatoes;
- beet;
- nuts;
- berries;
- beans and beans.
Detection of urate salts (uraturia) requires a complete restriction of deli meats, broths, coffee, chocolate, hot and spicy foods.
For any urolithiasis, it is necessary to drink fluids intensively, as this helps remove crystals and stones.
In this case, herbal infusions (rose hips, madder, birch buds, calendula) are also useful, which dissolve sand and calculi of the urinary tract.
With a proper and balanced diet, erythrocyturia should disappear, as well as the accompanying symptoms of the disease.