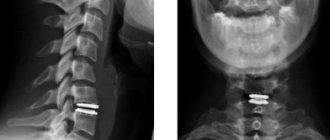
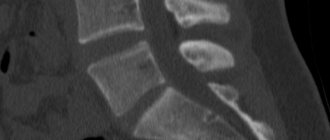
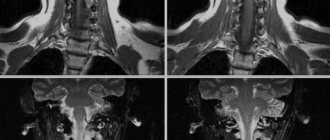
Computed tomography of the lumbosacral spine is the most informative research method for many pathologies. The tomograph perfectly visualizes bone structures, vertebral bodies, and can be used to examine in detail the condition of the spinal canal, intervertebral discs, ligaments, and the spinal cord.
Thanks to innovative equipment - a multislice computed tomograph, diagnosing diseases such as tumors, hematomas, fractures, inflammatory processes and many other pathologies of the spinal region is not difficult.
CT scan of the lumbosacral spine is most often used to assess the condition of the ligamentous apparatus and intervertebral discs. Sometimes the cause of troubles for patients who come with complaints of “lumbago” in the back and legs is inflammatory processes that are located in the thoracic spine. Therefore, to obtain a complete picture of the disease, an extended computed tomography of the spine is sometimes used: the lumbosacral region with simultaneous examination of the thoracic region.
The Yusupov Hospital is the most progressive medical institution in Moscow, and therefore computed tomography of the lumbar spine is carried out by the best specialists in Russia using the most modern equipment. The European status of the clinic allows it to serve patients of all segments of the population. The Yusupov Hospital boasts a huge number of grateful clients who, thanks to competent diagnostics, were diagnosed at the earliest stages.
Main indications for computed tomography of the lumbosacral spine
Computed tomography is applicable in all areas of medicine. It has virtually no contraindications and after the study, patients can return to their previous lifestyle.
Basically, computed tomography of the lumbosacral spine is prescribed in the following cases:
- Intervertebral disc herniation and discopathy;
- Spinal hemorrhages;
- Anomalies of vertebral development;
- Various types of spinal tumors (benign and malignant, metastasis);
- Vertebral fractures;
- Spondylosis;
- Germination of neoplasms of neighboring organs into the vertebrae;
- Osteoporosis;
- Spinal stenosis;
- Rheumatic lesions of the spinal column (ankylosing spondylitis);
- Osteochondrosis;
- Vertebral instability.
At the Yusupov Hospital, computed tomography is performed even in emergency cases, when diagnosis is a vital procedure. A team of doctors is ready to assist patients at any moment. At such moments, it is especially important to obtain a competent and quick opinion from a specialist.
Features of CT with a contrast enhancer
Best materials of the month
- Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- Antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: how effective are they?
- The most common "office" diseases
- Does vodka kill coronavirus?
- How to stay alive on our roads?
To clarify some changes, such as formations, for example, in the lumbosacral region, radiocontrast agents are used. The basis of such drugs is iodine.
Before carrying out a procedure using radiocontrast agents, a test for the body's sensitivity to iodine-containing solutions must be performed.
The presence of an allergic reaction is a contraindication to the procedure. A sharp deterioration in the patient's condition due to the administration of a contrast agent is the basis for interrupting the diagnosis.
A radiocontrast agent is administered to the patient intravenously. The images are deciphered by a qualified specialist - a radiologist - at the end of the scanning procedure.
Is it dangerous to perform a computed tomography scan of the lumbosacral spine?
Computed tomography involves exposing the patient’s body to x-rays, but their dosage is so small that this method does not pose any harm, much less a threat to life. This is a completely safe diagnostic test, which, under certain indications, can be performed even on children. Thanks to modern equipment and hardware and software systems, radiation exposure is biologically determined. Computed tomography can be performed even several times a year, and is not dangerous for the patient’s body.
At the Yusupov Hospital, doctors are worried about the health of their patients. And therefore, during absolutely all studies there is an anesthesiologist who carefully monitors the tomography, especially if it is carried out with a contract substance.
Advantages and features of CT
In terms of information content, CT is not inferior to MRI. Moreover, computed tomography is preferable for assessing the condition of bone tissue. Also, CT becomes the method of choice if the patient has such contraindications to MRI, such as the presence of metal foreign bodies, implants, etc. in the body.
X-ray and ultrasound compared to computed tomography are less accurate and not always reliable. In addition, the radiation dose from a CT scan is significantly lower than from a traditional X-ray examination.
What should be the preparation before a CT scan of the lumbosacral spine?
If a computed tomography scan is performed without the use of a contrast agent, the patient does not need special preparation.
If your doctor has prescribed you a CT scan of the lumbosacral spine with contrast, you should have with you:
- Referral from a specialist;
- An extract (from the clinic or hospital where you were examined);
- Images and conclusions of previous examinations (this applies not only to computed tomography, but also to other methods);
- Conclusion of related specialists (if there are concomitant diseases).
Preparing for the study
No special preparation is required for CT scanning. Immediately before the scan itself, the patient must remove all metal elements, including dentures and hearing aids. If implants are present, the patient must notify the radiographer who will perform the procedure.
Failure to follow these recommendations negatively affects the quality of the images obtained and may lead to an incorrect diagnosis.
Before the scan, the patient changes into clothing provided to him by the medical facility.
How is a CT scan of the lumbosacral spine performed?
To conduct a computed tomography scan of the lumbosacral spine, the patient is invited to go to a special diagnostic room in which the device is located. The patient must remove all metal objects, including jewelry, metal parts on clothing, removable medical devices, and a mobile phone, only after which the patient can lie down on the mobile table.
During scanning, a special ring will rotate around the table, and the table itself will move in a horizontal plane. In this case, the patient must remain absolutely motionless so that the computer images are clear and free of interference.
During the diagnostic examination, only the patient will be in the office, and the medical staff will monitor the procedure through the wall (or through glass); the images at this moment will be shown to the doctor on the computer monitor as they are scanned. The patient will also be heard through a feedback device, so if a person becomes ill during the tomography, doctors will be able to quickly provide him with first aid.
Contraindications
Computed tomography is contraindicated in pregnant women, patients weighing more than 150 kg, and people with severe mental disorders. For children, the procedure is prescribed in emergency cases strictly according to indications. CT with contrast is not allowed for people with an allergy to iodine, impaired liver and kidney function, or severe diabetes mellitus. Lactation is not included in the list of contraindications, however, after the examination, the woman will have to skip breastfeeding twice, since contrast agents penetrate into the milk.
Which study is better - MRI or CT (MSCT or SCT) of the lumbosacral spine?
Since multislice computed tomography is aimed at visualizing bony and hollow structures, this method is ideal for diagnosing the spine. Multislice computed tomography perfectly displays not only the external, but also the internal structure of the spinal column.
The detail of structures is so high on modern tomographs that doctors use the images to evaluate the integrity, direction and thickness of the bone beams under study, and thanks to new computer applications, densitometric indicators (bone density) can be seen in absolute values.
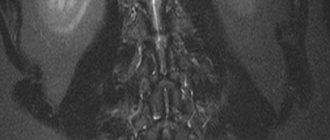
Computed tomography also perfectly determines the pathology of the spinal cord, diseases of the spinal canal (demyelinating processes (multiple sclerosis), developmental anomalies), oncological processes, hemorrhages in the spinal cord with arteriovenous malformation and many other disorders.
At the Yusupov Hospital you can undergo a CT scan of the lumbar spine, the price of which will be from 8,350 rubles, depending on the selected area and the use of contrast agent.
The Yusupov Hospital employs real professionals who save the lives of patients every day.
Indications for CT scanning
The diagnostic procedure is indicated for patients who have a history of chronic diseases or congenital pathologies of the spinal column. There are diseases that can provoke degenerative processes of the vertebrae or ligamentous elements; severe infection in the body; injuries; chronic back pain.
CT is also a mandatory diagnostic method when preparing a patient for surgery.

Other indications for referral to computed tomography are:
- intervertebral disc herniation or suspicion of it;
- rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis;
- pinched nerve;
- back injury;
- congenital pathologies of the spinal column;
- neoplasms in the lumbosacral region;
- impaired mobility and sensitivity of the legs;
- hemorrhage in the spinal cord;
- acute back pain, which is accompanied by an increase in body temperature.
Computed tomography, in comparison with other diagnostic methods (for example, radiography), allows you to see all layers of the lumbosacral region from different angles. The images even show developing pathological processes that cannot be seen with other studies.
Additionally, the specialist assesses the condition of not only the spinal column, but also nearby organs. This comprehensive approach makes it easier to make an accurate diagnosis and greatly increases the patient’s chances of a full recovery.
Decoding the results obtained
In order to make a diagnosis using computed tomography data, it is necessary to describe the pathological changes that are present in the obtained images. A radiologist or radiation diagnostics doctor is engaged in decoding. Any information about previous examinations and treatment that the patient can provide can help the doctor. After decoding, the patient receives photographs on digital media or printed on film, as well as a doctor’s report certified by signature and seal.
How the research works
During the scan, the patient is placed in the tomograph tunnel. Before doing this, he needs to remove all metal objects. When the tomograph ring rotates around the extendable table, numerous layer-by-layer images are created. To ensure that the images are not distorted, you must remain still during the procedure. The procedure is absolutely painless and lasts from 5–10 minutes to half an hour (for examination with contrast).
After the scanning is completed, the resulting images are processed on a computer, deciphered by specialists and given to the patient along with a medical report.
What does it show?
Diagnostics allows you to examine the spinal column and surrounding soft tissues from different angles, viewing them completely in depth. As a result of the procedure, the information transmitted by the tomograph is processed by a computer, after which layer-by-layer images of the studied parts of the spine and soft tissues are printed in different sections. This allows you to study them in detail, identify any pathological formations and displacements, and other disorders.
Computed tomography guarantees high clarity of the resulting images, which distinguishes it from less informative x-rays.
CT scan of the spine shows:
- Texture, structure, density of bone tissue. Any damage, tumors and pathological changes (including spinal osteochondrosis, metastases);
- Spinal canal and intervertebral foramina;
- Vertebral processes;
- Spinal cord.
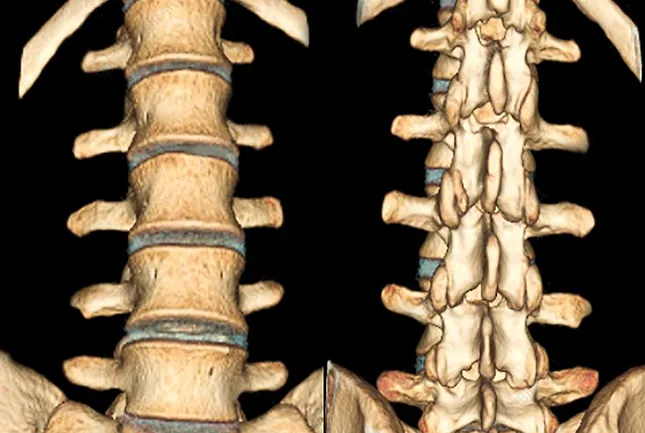
What diseases will a CT scan of the spine show, and in what cases is it better to do an MRI? Let's look at it in this article.