Home — For the public
- Map of medical organizations
- Vaccination
- Clinical examination
- Fluorography
- Addresses and opening hours of clinics
- Emergency rooms
- Oncology
- Where to take an HIV test
- Healthy child's office
- Services
- Prevention of CVD
- Disease Prevention
- World Patient Safety Day
- Newspaper "Medical News"
- specialist
- School of Health
— Disease prevention
- HIV infection
- All about vaccination
- All about proper nutrition
- Hepatitis
- Flu
- Dementia
- Schoolchildren's health
- STD
- Tick-borne encephalitis
- Whooping cough
- Measles
- Legionellosis
- Meningococcal infection
- Oncology
- Acute intestinal infection
- Pediculosis
- First aid
- Pneumococcal infection
- Pneumonia
- Prevention of rabies
- Dependency Prevention
- Rotavirus infection
- Diabetes
- Cardiovascular diseases
- Injuries
- Tuberculosis
- Tularemia
- Physical activity
- Obstructive pulmonary disease
- Exotic infections
- Ecology
- Why is swimming in ponds dangerous?
- HIV infection
- Express help
- HIV is not a death sentence
- HIV prevention
- Interesting about HIV
— HIV is not a death sentence — HIV: the first symptoms, stages and development of the disease
The insidiousness of HIV and the consequences of infection with it is nothing more than the carelessness of the people themselves. Yes, indeed, HIV infection is a serious disease. To date, there is no vaccine against it and it is completely incurable. But with timely diagnosis and subsequent HAART (highly active antiretroviral therapy), the life expectancy of HIV-positive patients is no different from the average. Medicines taken throughout life inhibit the development of HIV infection and people live to a ripe old age - 70 - 80 years. Following the recommendations of specialists, they lead a normal lifestyle - work, get married, travel and even have healthy children. The main thing is to recognize the first signs of the disease in time and seek help.
The first signs of HIV infection
Self-medication is a bad habit. When we feel unwell, we diagnose ourselves and prescribe medications, thereby ignoring the symptoms in the early stages of HIV infection. And at this time, the virus is already actively attacking the cells of our immune system and destroying it. The following signs indicate the progression of the process.
- Enlarged lymph nodes - in the neck, groin, armpits.
- Candidiasis (thrush), including in the oral cavity.
- Night sweats.
- Prolonged diarrhea.
- Unreasonable nausea and vomiting.
- A sharp decrease in body weight.
- Fever.
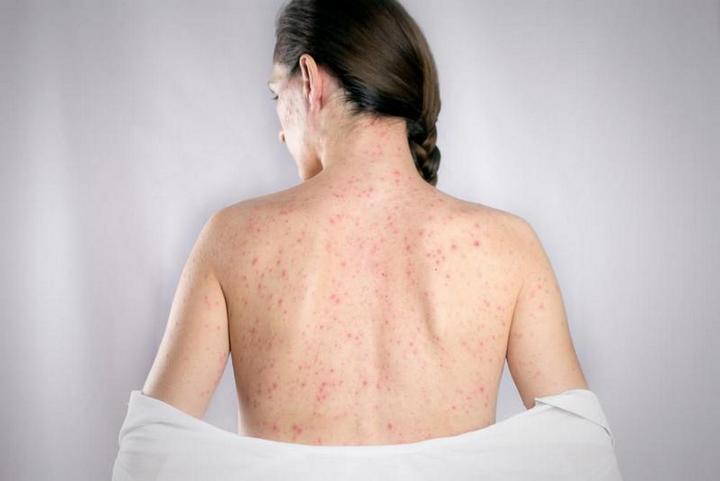
- Skin rashes.
Very often, the first symptoms of HIV infection resemble ARVI and flu. The patient is feverish and experiences muscle pain and headaches. His joints ache, the mucous membranes of his mouth and pharynx become inflamed. But soon all the unpleasant symptoms go away on their own and the next stage of HIV infection begins, when the disease does not show itself in any way.
“If a friend suddenly turns out to have…HIV”
The clinical picture of HIV infection is very complex and cannot always be recognized in the initial stages. Most often, patients perceive the first symptoms as simple chronic fatigue or do not notice them at all for many years.
How does the disease progress?
Experts note four stages of HIV infection: HIV and AIDS Incubation period Primary symptoms Secondary type of disease AIDS (last stage) A large number of infected people for many years do not even suspect that they have long been infected. In some cases, the period from the onset of the disease to AIDS can take up to 10-15 years. The main signs at the initial stage may be enlarged lymph nodes in the neck, in the groin area, on the collarbone, but not everyone attaches importance to these visible symptoms and does not rush to see a doctor, but in vain. Over time, an infected person may notice that his immunity weakens, and he begins to catch colds frequently, chronic diseases constantly worsen, and his health worsens. All this says that the body’s protective functions are destroyed, and the person is approaching death, which can occur even with a normal cough or runny nose.
How dangerous is HIV?
Everyone knows that HIV is a serious disease that is currently completely untreatable. But with the right attitude towards the disease and following all the doctor’s recommendations for therapy, you can live a long, normal life as a healthy person. The main danger of this infection is that it can be transmitted from person to person and does not actively manifest itself for a very long time, which leads to loss of time, which is very important in this case. Methods of transmission of the disease include: unprotected sexual intercourse, piercing and tattoos, which were done with unsterile instruments, the use of one injection needle by a group of people, medical error, that is, transfusion of contaminated blood, unsterility of surgical and other instruments from a sick mother to a child, HIV is not transmitted through everyday contact, through touch. , dishes, clothes, appliances, toilet, bath, etc. Therefore, you should not make outcasts out of infection carriers, they are non-infectious to some extent. An undiagnosed disease is dangerous because a person who does not know about his HIV status can infect his sexual partners, will not be able to stop the destructive process in time with the help of drugs, and will simply die. The asymptomatic course of the initial stage of the pathology is due to the fact that in the first months after the infection enters the body, special antibodies are produced that suppress the first signs. Primary signs Experts say that in women the virus in the initial stages manifests itself much more acutely than in men. This is due to the fact that in the vaginal fluid of representatives of the fairer sex there is a small presence of beneficial microbes, unlike the opposite sex, so the risk of receiving an unpleasant diagnosis is much greater. We can say that the main symptoms manifest themselves in the same way in both sexes, but in women there are some specific manifestations: Signs of HIV frequent pain in the pelvic area the menstrual cycle is disrupted unpleasant discharge from the vagina, in the form of mucus, the lymph nodes in the groin area are noticeably enlarged signs of anorexia appear, which accompanied by weight loss, nausea and vomiting, lack of appetite during menstruation, health critically worsens, nervousness, bad mood, hysterics, nervous breakdowns.
If there are at least some of these signs, then you should definitely go to the clinic and undergo a full examination, passing all the tests, including blood tests for hormone levels and HIV infection, and better yet, without waiting for health problems, periodically, find out your status at least once a year using express tests.
HIV in men is a dangerous viral disease that currently cannot be completely cured. Has several routes of infection. It predominantly affects men of reproductive age. Transmission from mother to fetus is possible. In this case, the symptoms of the disease will appear in childhood. Symptoms Treatment for HIV in men proceeds somewhat differently than in women, although the manifestation of the disease is largely identical. Infection, as a rule, occurs through sexual contact with a sick person, but there are also other ways: through donor blood transfusion; when using used and unsterilized medical needles (drug needles) or other medical instruments. The likelihood of infection depends on the state of the immune system - upon contact with any body fluids of a virus carrier, it is quite high. In addition, the likelihood of infection increases in cases where a healthy person has open wound surfaces - abrasions, cuts, etc., where blood or other fluids of an infected person can get in. Scientists have not yet established what determines the likelihood of people becoming infected with the virus, but some people do not get sick even if the virus enters their body. But unfortunately, this happens quite rarely. SYMPTOMATICS Symptoms of HIV in men depend on the stage of the disease. The first stage is the incubation stage, which can last from several weeks to several months. At this stage, even laboratory diagnostics (taking blood for antibodies) cannot detect the virus in the human body, so it is meaningless. At the same time, at this stage, a person may show signs of the presence of the virus in the body, which include: an increase in body temperature to subfebrile levels; weakness; increased fatigue. Of course, the first signs of HIV in men do not contribute in any way to making a correct diagnosis. Therefore, the incubation period develops into a latent period - a period of hidden manifestations of infection. There is another symptom that a person may experience after contracting an infection - the appearance of rashes that can be localized either throughout the body or in the genital area. Such rashes usually have a strange color and make a man pay attention to them, but they disappear literally after a few days, so the stronger sex believes that they have recovered, and they do not go to the doctor.
Despite the absence of pronounced symptoms during the incubation period, the risk of infecting others is quite high, since a man becomes dangerous from the moment the virus enters the body. At the second stage, the disease makes itself felt with symptoms of a viral infection: sore throat and sore throat, which occurs due to inflammation of the lymphoid tissue of the tonsils; an increase in temperature to febrile levels, which does not respond to antipyretic drugs; enlargement of regional lymph nodes (initially in the upper half of the body, then in the lower); the appearance of a cough; night sweats; Sometimes there is aching joints and muscle pain.
There are contraindications. Consult your doctor. The risk of infecting others at this stage is very high, since the virus spreads through secretions (blood, semen). One of the obvious manifestations of the disease at this stage is prolonged diarrhea, which leads to disruption of the supply of nutrients to the man’s body and a sharp decrease in body weight (by 10% or more). Lymphadenopathy in HIV At the third, latent stage of the disease, which can last up to 3 years (and sometimes decades, depending on the initial state of the person’s immunity), the viral infection has no manifestations. However, the likelihood of infecting others is still high. At this stage, a man’s immune system begins to collapse, which leads to frequent colds and other inflammatory and infectious diseases. The symptom of lymphadenopathy also persists - and the lymph nodes increase from 1 to 5 mm and can be either painless or slightly painful. Also at this stage, a man may develop a characteristic brownish-blue rash on his body, which may rise slightly above the surface of the skin. It goes away without treatment after a few days, but may persist for a long time or be completely absent. The last stage is the stage of development of AIDS. Signs of HIV infection in men at this stage indicate the development of severe immune disorders. All organs and systems of the body fail, a person easily catches infectious diseases that are difficult to treat, tumors can form in his body, etc. The likelihood of infecting others with the virus at this stage is reduced, since the person already realizes that he is suffering from a serious illness and may pose a threat.
The immune system of the human body has an important task: to protect it from various types of diseases. The strength and strong connection of cells create a reliable shield that an insidious virus can destroy. In order to start therapy on time, it is necessary to know the signs of HIV in women. The danger of infection lies not only in its destructive effect, but also in its ability to “sleep” for a long time before taking on a progressive form. A woman does not even always realize the presence of the virus in her body, infecting others, but preventing HIV infection could save many lives. Routes of transmission of HIV infection Contact of a healthy person with a carrier of HIV infection is not always dangerous. The risk of infection exists even with a single contact, even with constant contact; the type and amount of biological fluid containing HIV infection is considered a more significant factor. In a woman who tests positive for HIV, the concentration of the virus depends on the stage of the disease. If we talk about the ways of transmission of infection through contact with biological fluid, then according to the degree of probability of HIV infection, the following should be distinguished: maximum (through blood, breast milk, cerebrospinal fluid, sperm); minimal (through sweat, saliva, tears, sputum, urine).
Signs of HIV transmission in women through natural infection appear when the maximum concentration of biological fluid with the virus enters the blood or mucous membranes, for example, during sexual intercourse or the birth of a child. The artificial route of HIV transmission comes down to invasive procedures of a different nature - from the administration of intravenous drugs or blood transfusions for medical reasons to tattooing, hardware cosmetic procedures or manicures if the instruments were poorly processed. The first symptoms of infection in women. How long does it take for HIV to appear? This is the most common question that arises for all people, regardless of gender, in a dangerous situation. The insidious virus has a destructive effect, but the protracted form of its manifestation is no less dangerous. According to some medical data, HIV infection can remain in the body and not manifest itself in any way for more than ten years!
Women can learn that the virus has begun to multiply by the following first signs:
- A sudden, often without reason, rise in temperature to 40 degrees, which cannot be brought down for a week or more.
- Headaches, muscle weakness, sweating. Enlarged lymph nodes (neck, armpits, groin).
- Anorexia.
- Nausea, cramps, vomiting. Painful menstruation, profuse mucous discharge.
Stages of the disease and their symptoms:
A characteristic feature of HIV infection in women is the absence of symptoms. Some signs of the virus may not appear at all, but others appear as additional ones, because a weakened immune system is not able to cope with the effects of other pathogenic microorganisms. How long does it take for symptoms of HIV infection to appear? Before obvious signs appear, the virus can lie low for a long time, or only manifest itself partially, so many women are not even aware of the presence of the disease.
The stages of disease development in women who become infected with HIV look like this: Incubation. The average duration of the stage from the moment HIV enters a woman’s body until the first symptoms appear is about three months, sometimes up to a year. From the moment of infection, there is active reproduction of the virus with subsequent spread throughout the body, but HIV does not yet pose a threat to the woman’s immune system. Primary. This stage of the disease lasts about three months. A characteristic sign of the spread of the virus is the appearance of antibodies. Symptoms in women are mild; HIV carriers often pass this phase without showing the main signs of the disease. Secondary. If the disease progresses slowly, the average duration of this phase is about seven years. Symptoms of HIV infection begin to manifest themselves gradually; there are very rare cases when a girl or young woman is susceptible to the rapid development of the disease. Rashes appear on the skin, fever is noted, and pharyngitis begins. Enlarged lymph nodes, liver and diarrhea are characteristic external symptoms that are signs of HIV in women. Third. The progressive, acute phase of HIV disease is characterized by significant depletion of the immune system, which leads to the manifestation of secondary infection. The duration, as well as the severity of the disease, depends on the individual characteristics of the organism. Other infections or the diagnosis of cancer aggravate the clinical picture of the development of HIV disease, although with proper treatment remission is not excluded. Fourth (AIDS). The irreversible stage of the spread of HIV infection, when any methods of antiviral therapy in combination with treatment of secondary diseases cannot help the patient. The patient will have to undergo a maintenance course from several weeks to a couple of months, since a cure for AIDS has not yet been found. The onset of the irreversible stage of HIV infection is indicated by extensive fungal infection of the skin, pneumonia, hepatitis, candidiasis, and ulcerative formations on the mucous membrane. To detect HIV infection and make a correct diagnosis, multiple studies are carried out. The absence of characteristic symptoms of HIV disease is no less dangerous than an erroneous diagnosis, so an infectious disease specialist will definitely order laboratory tests to detect antibodies. In the early stages of the disease, HIV tests are not always able to detect infection, so women need to be retested after a few weeks, even if the first result is negative. If the diagnosis of HIV infection itself is carried out in the laboratory, then an infectious disease specialist must make a diagnosis based on data, examination and anamnesis. If a specialist suspects signs of HIV, he will invite the woman to register to monitor her health. In order to monitor your health and not miss the possible development of HIV infection, once every six months you will have to take tests for your viral load, immune status, or take a course of antiretroviral drugs.
Ultrasound diagnostics doctor O.V. Fedotova
Stages of HIV infection
HIV is a human immunodeficiency virus. Penetrating into the body, it attacks the cells of the immune system, which causes the development of HIV infection - a slowly progressive disease. Without adequate treatment, it develops into AIDS - acquired immune deficiency syndrome. A clear distinction between these concepts helps to understand what happens to the human body at each stage of the disease.
| Disease stage | Duration | What happens in the body | Symptoms |
| Window period | from 2 to 12 weeks (with weakened immunity – 12 – 24 weeks) | the so-called incubation period, when infection has already occurred and the virus attacks the cells of the immune system | no symptoms |
| Acute phase | 3 to 6 weeks from infection | the virus actively replicates, the viral load increases, which is accompanied by a violent reaction of the body | see the first signs and early stages of HIV infection |
| Latent period | on average – 8-10 years | a conditional balance is established between the rate of HIV reproduction and the response of the immune system | there is an increase in lymph nodes, there are no other symptoms |
| Pre-AIDS | 1-2 years | cellular immunity is suppressed | relapses of herpes, candidiasis, stomatitis |
| AIDS | without treatment – 1-2 years | the terminal stage of HIV infection, when the person’s immune system is practically destroyed | tumors and opportunistic infections that cause the development of tuberculosis, meningitis, encephalitis, pneumonia and other HIV-associated diseases |
Thus, from the moment when the first signs of HIV infection appear until the moment when the disease enters the latent stage, very little time passes. It is very important not to miss this period of time, since for the next few years (8-10 years) the person will live, feel normal and not even suspect that he is sick with HIV infection. At the same time, it infects other people during unprotected sexual intercourse. But most importantly, he wastes precious time. After all, without treatment, the inevitable stage of development of HIV infection occurs - AIDS.
Route of transmission and risk groups
HIV is transmitted in several ways:
- Unprotected sexual intercourse – people (heterosexuals and homosexuals) have a high risk of frequently changing sexual partners and practicing unprotected sexual intercourse. Anal sex is the riskiest due to the most sensitive mucous membrane, followed by vaginal and, less commonly, oral sex.
- Through blood and its derivatives - repeated receipt of donor blood and other blood products through transfusion. It is rare today due to the introduction of mandatory testing of blood products.
- Reuse of injection syringes by drug addicts – People who share drugs and use injection kits after others are at high risk.
- Through an infected mother to a child - during pregnancy, childbirth and breastfeeding.
The ways in which HIV is NOT
transmitted:
- air;
- general contacts - handshakes, hugs, kisses on the cheek;
- intimate contact without sexual intercourse - kissing, caresses;
- contact with objects - on a bus, train, school;
- use of public toilets, saunas, swimming pools, showers;
- coughing, sneezing, skin contact with tears or saliva;
- treatment in hospitals, medical and dental clinics, subject to standard hygiene measures;
- providing first aid while observing standard hygiene measures;
- massage, physiotherapy, ear piercing, piercing, subject to standard hygiene measures;
- scratches and bites from pets (dogs, cats);
- insect bites;
- care for people living with HIV and AIDS, subject to standard hygiene measures.
Development of the disease: from infection to AIDS
Human immunodeficiency virus belongs to the family of retroviruses. At its core, it is a virion - a particle consisting of an envelope and a protein-nucleic acid complex. Outside the host cell, it shows no signs of biological activity. But as soon as the HIV virion attaches to a living immune cell (T-lymphocyte), it merges with it and transfers its genetic information to it. An immune cell infected in this way is unable to perform its functions and is a favorable environment for the replication of virions - HIV begins to create its own copies. New viral particles bud off, enter the bloodstream and find a new host cell. The old virus-carrying cell dies, and new T-lymphocytes are targeted. And so on ad infinitum! Until the immune system is completely destroyed. During this time, the human body goes through all stages of the development of the disease.
- HIV enters the body - infection with the virus.
- Virions begin to attack T-lymphocytes - the incubation period.
- The number of replicated virions increases sharply – the acute phase.
- The rate of HIV reproduction is balanced by the body's immune response - the latent stage, in which there are no symptoms.
- The number of replications increases, and the number of healthy T-lymphocytes steadily decreases - the immune system does not perform its functions and AIDS develops.
Thus, infection and HIV infection are not fatal to humans. Antiretroviral therapy (HAART) suppresses the activity of the virus, limiting the progression of the disease. In fact, the patient is constantly in the latent stage and leads a normal lifestyle.
HIV tests, prices, when to get tested
According to testing standards, blood for HIV is donated three times after the threat of infection - 3, 6 and 12 months from the moment of suspected infection. It is not at all necessary to do this at home using pharmacy tests or in private clinics. The best decision would be to contact the AIDS CENTER, which is in every city, and describe the situation to the doctor. The doctor will decide whether emergency prevention of HIV infection is needed (antiviral drugs are prescribed) or whether there is no threat to health. Examination and treatment when visiting such a center are free of charge.
Victoria Druzhikina
Neurologist, Therapist
You can donate blood yourself in a private clinic; the average cost of the test is 400 rubles.
Life expectancy with timely detection of the virus and early initiation of therapy does not differ from the life expectancy of a person without HIV infection. Without treatment, the condition enters the AIDS phase, which is approximately 5-10 years before death.
This article has been verified by a current qualified physician, Victoria Druzhikina, and can be considered a reliable source of information for site users.
Bibliography
1.https://aidsvolgograd.ru/wp-content/uploads/2017/08/Clinical-protocols-HIV-2017.pdf 2. https://pharmacta.ru/d/2015-10-30_4994.pdf https: //www.rcrz.kz/docs/clinic_protocol/2015/Therapy/Infectious%20diseases/3%20HIV%20u%20adults.pdf
Rate how useful the article was
4.3 12 people voted, average rating 4.3
Did you like the article? Save it to your wall so you don’t lose it!
How long do people live with HIV?
In this case, everything depends on three important factors - the timing of the diagnosis, the treatment performed and the general health of the patient. The statistics on HIV infection and AIDS provide the following figures.
- Timely diagnosis and subsequent HAART – life expectancy is 20-50 years.
- Detection of HIV infection in late stages and subsequent HAART – 10-40 years.
- Undiagnosed infection without treatment – 9-11 years.
- AIDS without treatment – 6-9 months.
An equally important factor influencing the life expectancy of HIV-infected patients is the general state of health and immunity. Naturally, people with strong immunity, who do not have chronic diseases and congenital pathologies, will live longer. At the same time, a weakened body is less resistant to the virus. Therefore, in addition to HAART, all HIV-positive patients are recommended to have a healthy lifestyle and proper nutrition. They must protect themselves from infectious and colds. Strengthen your immune system, take care of your body and undergo regular examinations.
Treatment regimens and cost of therapy
According to WHO protocols and National clinical guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of HIV infection in adults in the Russian Federation, the initial regimen recommended is tenofovir + lamivudine (or emtricitabine) + efavirenz. If contraindicated or unavailable, then zidovudine + lamivudine + efavirenz, zidovudine + lamivudine + nevirapine, tenofovir + lamivudine (or emtricitabine) + nevirapine
To increase the effectiveness of treatment, drugs are combined, but this increases the risk of negative consequences - toxic effects on the liver and kidneys. The result of treatment is assessed by the dynamics of the immune status.
In general, therapy for HIV infection appears to be effective. It has been proven that it helps prolong life, returning it almost to its original level. The level of protective cells in the body increases, which prevents the development of infectious, viral, and fungal processes. The earlier the disease is detected and treatment started, the higher the chances of a favorable outcome.
The average cost of treatment per year ranges from 20 to 370 thousand rubles; if you have a compulsory medical insurance policy, SNILS and a passport, the purchase is carried out at the expense of budget funds.
Preparations have been developed that allow you to take 1 tablet in the morning instead of a whole handful. A vaccine is also being developed to completely eradicate the virus. They are not yet available for use, tests are being carried out.
How to test your body for HIV?
To do this, you need to know your HIV status. To determine it, indirect and direct tests are carried out to detect antibodies to HIV and the virus itself. To carry out the tests, you need to donate blood for an HIV test. You can do this anonymously!
How long after can a test be carried out if there was a risk of infection?
You can donate blood for analysis 2-3 weeks after the fact of possible infection. However, it is necessary to take into account that due to the individual characteristics of the immune system of a particular person, the test result may be unreliable, since the number of antibodies to HIV will still be too small for an accurate diagnosis of the disease.
How long does it take for HIV infection to appear in the blood?
To obtain a reliable test result, it is necessary that at least 3 months have passed since the infection. In rare cases, the appearance of antibodies characteristic of HIV takes longer - 4-6 months.
If the result is negative after 3 months, is it necessary to do a repeat test?
If a negative result was obtained, but you are sure of the infection, then it is better to repeat the test after 6 months.
How does the disease manifest itself after a month?
After 1 month, the first bright symptoms of HIV, as a rule, are muffled, and the pathology continues to progress and destroy the immune system from the inside. HIV infection can manifest itself with the following symptoms, which initially appear sporadically, and over time develop into permanent conditions:
- prolonged colds and exacerbation of chronic ones;
- headaches and migraines (read about other possible causes of headaches here);
- increased fatigue and insomnia (a somnologist and neurologist will help you cope);
- depression and a feeling of apathy (consulting a psychologist will help you cope);
- digestive disorders and rapid loss of muscle mass;
- persistent diseases of the genitourinary system (thrush, endometriosis, erosion, and so on);
- exacerbating manifestations of herpes simplex and genital;
- damage to the skin and mucous membranes by multiple or single ulcers, pustules, rashes (for treatment, consult a dermatologist);
- ENT diseases, aggravated by manifestations of a painful cough (consults ENT);
- muscle pain and aches;
- increased sweating and dizziness (other causes of dizziness are described here).
The listed first signs of HIV in women can be either single or join each other, acquiring multiplicity, and have both mild and more pronounced manifestations.
If at the very beginning of infection the disease could not be recognized even by a blood test, then after 1 month a test for HIV infection shows the real picture. It is important not to ignore the first warning symptoms of HIV that occur at an early stage, especially if a woman is included in the so-called “risk group”:
- underwent a blood transfusion;
- got a tattoo, piercing;
- often changes sexual partners.
A woman should be wary of the duration of the symptoms that arose at the initial stage or the illogicality of their appearance (for example, digestive disorders without the slightest change in diet).
It should be remembered that when the first signs of HIV infection occur, in specialized AIDS prevention centers you can take both a rapid HIV test and a detailed laboratory analysis on a completely anonymous basis.