Home > Encyclopedia of Oncology > Tumor markers for women
Tumor marker tests for women are becoming increasingly popular due to their effectiveness in diagnosing cancer at an early stage. For example, depending on the marker, malignant pathology can be determined several months before the clinical form appears. And this is more than 90% of the success rate of future treatment. It is also an effective prevention of relapses and metastases.
Some tumors can grow for a long time without any symptoms and then quickly metastasize.
Good news
Medicine does not stand still. Experts are looking for and finding new ways of prevention, diagnosis, treatment and rehabilitation.
Today, oncology is no longer a death sentence: over the past 30 years, cancer survival has doubled. And the point here, of course, is not only about modern powerful medicines or the skill of the surgeon. If you consult a doctor when the signs of the disease have already become obvious, the chances of recovery are sharply reduced. After all, the presence of clinical symptoms indicates late stages of cancer.
The secret of effective treatment of any tumor lies in early diagnosis, that is, in identifying the disease at the preclinical stage, when there are no obvious symptoms of malignant neoplasms, but the harmful process has already begun. This latent period can last from several months to several years. It is difficult to recognize the disease at this stage, but modern laboratory and instrumental methods make this possible. Early treatment in most cases leads to complete recovery of the patient.
How to donate blood for tumor markers
In order for testing for tumor markers for women to be effective and reliable, it is very important to follow simple rules for preparing for the test:
- At least 8 hours before the test, do not eat food or drink coffee, tea, or juices. Only clean water without gas is allowed, including on the day of the examination.
- Stop taking any medications 3-4 days before the test. This should only be done in consultation with the doctor who is seeing the patient and who prescribed them.
- Stop drinking alcohol and smoking at least 12 hours before the start of the study. It is advisable to stop using 3-5 days in advance.
- On the eve of the visit, do not undergo examination by doctors or any type of diagnostics. Also, do not visit a massage therapist.
- Moderate physical activity (especially for fitness enthusiasts).
- Try not to face stressful situations.
In general, the preparation rules are similar to those that are relevant for taking a biochemical blood test.
To check the norm of tumor markers for women, blood (in some cases, urine and puncture) is taken from a vein using a syringe and transferred to a test tube, which is marked with the appropriate symbols.
The collected blood is processed in a special device. This is necessary to separate serum from blood plasma. Antibodies are introduced into the resulting sample, the reaction of which will be the result of the analysis.
After completion of the research, the data is entered into a protocol, which is given to the patient. Please note that tumor markers for women are deciphered by a specialist from the laboratory in which the analysis was carried out.
As a rule, to obtain an accurate result, the doctor prescribes a group of tumor markers, or this group is selected after the first study on one indicator, which produced controversial results.
You can undergo the examination in independent laboratories equipped with modern equipment. In such institutions there are no queues and comfortable reception conditions. In addition, in most of them the price of tumor markers for women in St. Petersburg is affordable for the majority. We also recommend that you pay attention to getting tested in Israel, where laboratories are equipped with the latest technology. If indicated, do not delay diagnosis and treatment. Cancer is curable!
Who needs tumor marker determination and when?
ONCE EVERY 2-3 years
- After age 40 as screening tests for early diagnosis of cancer if you have no obvious risk factors.
ANNUALLY
- If your blood relatives had cancer.
- If you suffer from precancerous diseases.
- If you have previously been treated for cancer.
- If you are at risk for developing cancer (for example, you work in hazardous working conditions) or have bad habits (long-term smoking, alcohol abuse).
ONCE EVERY 3-4 MONTHS
- If you are concerned about - causeless weight loss, - unexplained increase in body temperature, - chronic fractures, - enlarged lymph nodes without objective reasons.
- To determine the dynamics of the condition after radiation therapy, drug or surgical treatment.
- For early prediction of possible relapses.
What tumor markers does a woman need to test?
Tumor markers for women are specific protein compounds, some of which are produced by the body and are always present in a certain amount, while others are the product of pathological neoplasms and, accordingly, are a signal for possible cancer.
An increase in the level of tumor markers in the body does not always mean cancer. These proteins can increase due to inflammation, pregnancy, menstruation, and other reasons.
Since diagnostics based on the amount of these substances is highly effective in identifying pathologies, you should know which tumor markers to give for prevention to a woman who is suspected of having primary or recurrent cancer.
Consult with an Israeli specialist
Today, nine markers are used in clinics:
| Alpha fetoprotein | is produced by the body and normally should not exceed 5.8 IU/ml. The same level is found in healthy men. If it grows, we can talk about disorders in the body. |
| HE-4 | is also produced by the body, but at different periods of life its norm differs: in premenopause - no more than 70, in postmenopause - no more than 140 ng/ml. This tumor marker for women has the highest specificity, therefore it is effective in diagnosing cancer when other markers have not changed in their quantity. |
| REA | is present in the body, and its norm fluctuates in the following range – 0-5 ng/ml. |
| SA 15-3 | breast marker. The risk of developing cancer occurs when its level is above 22 IU/ml. |
| SA 72-4 | if its amount does not exceed 6.9 U/ml, then everything is in order. His minimal height is a reason to continue examination for possible cancer of the stomach and ovaries. Also used for the dynamics of disease treatment. |
| SA-125 | The tumor marker norm for women is a maximum of 35 IU/ml. It is a marker of the ovaries, pancreas, uterus and fallopian tubes, rectum, stomach, liver, lungs. It is most effective in combination with the HE-4 marker. |
| MSA (mucin-like associated antigen) | is present in the blood, and its norm is a maximum of 11 IU/ml. An increase in the rate can be caused by a cancerous tumor in the mammary gland. |
| SCC (squamous cell carcinoma antigen) | in an amount of 2.5 ng/ml is considered normal. In case of growth, there is a suspicion of the development of a malignant tumor in the epithelial tissues of the cervix. |
| hCG | The hCG tumor marker in women is known as a marker of pregnancy, as it rises as soon as conception occurs. Its norm in a non-pregnant position is 5 IU/ml (produced by the pituitary gland). If it increases significantly, there is a risk of serious disorders in the body. |
Tumor markers for women are measured in nanograms per milliliter (ng/ml) and in international units (IU/ml).
Tumor marker CA 19-9
tumor marker of the pancreas, gall bladder, marker of pancreatic carcinoma. A blood concentration of 40 IU/ml or higher is considered pathological. Elevated levels of this marker are a poor prognostic sign in patients with colon and rectal cancer.
Increased CA level 19-9:
Pancreas cancer,
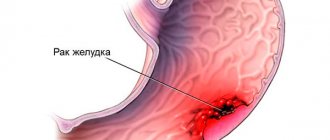
Stomach cancer,
Colon cancer,
Rectal cancer
Gallbladder cancer
Tumor marker CA 15-3 (Mucin-like glycoprotein)
or breast tumor marker. An indicator of the course of the disease and the effectiveness of therapy for breast carcinoma. Normally, the level of CA 15-3 is 0-22 U/ml. Tumor marker CA 15-3 is effective in determining relapses. Some elevation of the marker may also occur during pregnancy.
Increased SA level 15-3
Breast carcinoma (a particularly high level is observed in late stages and in the presence of metastases),
Bronchogenic carcinoma,
Stomach cancer,
Liver cancer,
Pancreas cancer,
Cancer of the ovaries, endometrium, uterus (late stages of tumor development).
Is it necessary to undergo additional diagnostics if the result is questionable?
In the body of a healthy person, tumor markers are present in a certain amount; even a slight increase in them indicates the need for examination. Therefore, it is better not to take risks and undergo additional diagnostics.
The cheapest and most accurate examination method is ultrasound. Tumors are clearly visible on ultrasound of the pelvis, abdominal cavity, and mammary glands. If you suspect cancer, you should get checked by ultrasound, take a second test for tumor markers, and only then go for an unpleasant biopsy or an expensive MRI.
CEA tests
CEA or cancer embryonic antigen is produced by cells of the digestive tract of the embryo and fetus. The substance is practically absent in the blood of healthy adults and pregnant women. CEA serves as a tumor marker; even a slow increase in its concentration in the body can indicate the development of cancer.
Why do you need a CEA analysis?
Tests for tumor markers are relevant for the purposes of early diagnosis, monitoring of therapy, and the course of the disease in certain tumors. The most popular analysis is CEA
acquired as a tool for detecting rectal and colon cancer, as it is characterized by the greatest sensitivity. Also, the concentration of the substance may increase with cancer of the ovaries, breast, stomach, prostate and so on, metastases to the bones and liver (but the level of sensitivity is lower).
CEA analysis is prescribed for the following purposes:
- Diagnosis, control over treatment of malignant tumors.
- Confirmation of the effectiveness of radical treatment of malignant neoplasms. After surgery to remove a tumor, the CEA tumor marker returns to normal within a couple of months at most; regular tests allow the patient’s further condition to be monitored, with the help of which a relapse is detected in a timely manner.
- Evaluation of the effectiveness of conservative treatment of malignant neoplasms.
- Early diagnosis of cancer recurrence.
Indications for CEA analysis
A study to determine the tumor marker CEA may be prescribed if the patient is suspected of having cancer:
- rectum, large intestine;
- mammary gland;
- pancreas;
- lungs;
- stomach;
- ovaries.
This analysis is also a tool for diagnosing metastases of tumor tissue in the bones and liver. Detect metastases by analyzing the tumor marker CEA
allows approximately 3-6 months before the first clinical signs occur in the patient.
How is CEA analysis carried out?
The analysis is carried out using the immunochemiluminescent method. The object for research is venous blood. It is recommended to take the test in the same laboratory if the purpose of the test is to monitor the effectiveness of treatment. Different laboratories use different research methods, which leads to different results of decoding CEA.
It is important to know
Even if the concentration of the carcinoembryonic antigen CEA in the patient’s body is outside the normal range (in one direction or another), this is not yet considered a reason for diagnosing the patient with cancer. This result is a reason to continue the examination. The CEA indicator often rises above the norm with frequent smoking and drinking alcohol.
How to prepare for CEA analysis
Preparation for a test for cancer embryonal antigen is a prerequisite for obtaining correct results. Before taking a blood test for the CEA tumor marker, the following requirements must be met.
- Two weeks before donating blood for antigen, it is necessary to suspend treatment with medications, as they can cause CEA values to deviate from the norm. If you cannot stop treatment, you must notify your doctor.
- The concentration of the colon cancer tumor marker CEA may increase in the patient’s body not only due to the presence of cancerous tumors, but also due to other diseases (liver cirrhosis, pneumonia, chronic hepatitis, autoimmune diseases, pancreatitis, and so on). The doctor must know about all the diseases that the patient has or has recently had.
- Some medical procedures can also lead to a deviation of the CEA value from the norm. If 7 days before donating blood for analysis, the patient underwent an MRI, X-ray or ultrasound examination, CT scan, etc., the doctor should know about this.
- Three days before the test, you should not drink alcohol, allow significant physical activity (it is better to refrain from sports activities), sexual contacts, or emotional stress.
- A couple of days before the study, you need to carefully prepare your daily menu, abstaining from spicy, fatty, and rough foods.
- A blood test for this tumor marker is taken on an empty stomach. Within 12 hours before the test, it is prohibited to eat or drink sweetened drinks (coffee, juice, tea). You are allowed to drink only non-carbonated clean water, the quantity does not matter.
Before analysis
A blood test for CEA must be taken in the morning, from 7 to 11. The patient is advised to come to the laboratory in advance, rest, sit for half an hour, and adjust emotional balance. It is advisable to abstain from cigarettes 3 hours before the test.
Tumor markers for breast cancer
Markers CA 15-3 (carbohydrate antigen CA 15-3), CA 27-29 (carbohydrate antigen CA 27-29) indicate the development of breast cancer. This type of tumor is a common cancer among women worldwide, accounting for more than 15% of all cancer cases among women.
Not all breast cancers cause elevated levels of CA 15-3 because some types of cancer cells do not produce excess amounts of the antigen. The level of CA 15-3 increases significantly in the blood when metastases spread beyond the breast, and can also be an indicator of hepatitis and cirrhosis of the liver, tuberculosis, sarcoidosis, etc.
CA 27-29 is specific for breast cancer, but can also be found in colon, stomach, liver, lung, pancreatic, ovarian and prostate cancers. Testing for this tumor marker is not used to diagnose the disease. It is limited to the following two functions:
- Monitor the progression of metastatic breast cancer with increasing values corresponding to progressive disease.
- Monitoring the treatment of metastatic breast cancer with a decrease in values corresponding to a positive treatment result.
In clinical practice, a combination of tests for CA 15-3, CA 27-29, CEA is applicable to monitor the dynamics of breast cancer development.
Serum Her-2/neu is used for disease prognosis. In about 1 out of every 5 cases of breast cancer, the cancer cells have a gene mutation that causes an excess of the Her-2 protein.
Tumor marker CA 125
The main marker of ovarian cancer and its metastases. Normally, the concentration of tumor marker in the blood is 0-30 IU/ml. Elevated CA 125 levels, more than 30 IU/ml, may indicate malignant diseases:
ovaries (mainly),
uterus (inner layer - endometrium),
mammary gland.
pancreas (in combination with CA 19-9)
Preparation:
Fasting is when at least 8 hours (preferably at least 12 hours) pass between the last meal and the blood draw.
Physiologically, an increase is observed during pregnancy and during menstruation.
How often should you get tested?
Currently, less than 20% of ovarian cancers are detected in the early stages before they spread beyond the affected area. The main reason they go undetected is that the symptoms of ovarian cancer are quite nonspecific. The need for a reliable method for early detection of this disease in asymptomatic women continues to motivate scientists to conduct new research. At the same time, regular physical examinations, pelvic examinations, blood screenings, as well as understanding family history and studying the dynamics of symptoms are important.
- Once a year, it is necessary to take tests for female tumor markers for those who have a family history of malignant tumors in various organs.
- Screening should be carried out with the same regularity for women who have been diagnosed with benign tumors, such as fibroids or fibroids, or tumor-like formations, such as cysts. Women outside the risk group are recommended to be tested once every few years.
- For those who have undergone cancer therapy, the dynamics of the level of tumor markers in the blood must be carried out at strict intervals: every month during the first year, every two months during the second year, every three months during the next three years. Further research is sufficient to carry out 1–2 times a year.
Can tumor markers be trusted?
Do elevated levels always indicate the presence of a tumor process? The reason for deviations from the norm does not always lie in malignant cells, especially if the indicators were exceeded once. The indicator of tumor markers is affected by chronic inflammatory processes, hormonal changes in the body, as well as benign tumors (however, the indicators will be slightly increased). It is for this reason that tumor marker tests are more often used to monitor the treatment of cancer patients, rather than for the primary detection of cancer. How accurate is tumor marker analysis? Can he be trusted? Tumor markers can be trusted, but it is worth remembering that this analysis, like any other, is not 100% accurate and is used in conjunction with other diagnostic methods to make a diagnosis. Only your attending physician can interpret the result. What to do if the test result is abnormal? In this case, after some time the doctor will prescribe a repeat test to confirm or refute the first result. If it is confirmed, you may have to make an appointment at the oncology clinic, as well as undergo additional examinations (ultrasound, MRI, etc.). In other words, tumor markers will not miss the onset of a tumor process, but may give an overestimated result against the background of other diseases in the body.