Understanding how tubal laparoscopy is performed will help a woman understand how to properly prepare for the procedure and avoid unwanted anxiety before treatment.
Reproductive services use advanced endoscopic equipment. The laparoscopy procedure is performed by specialists with extensive practical experience, who have specialized in the use of endoscopic techniques and regularly improve their qualifications on the basis of the best medical organizations in the Russian Federation and abroad. Preparation for the study is carried out on an individual basis, taking into account previous diseases, the patient’s condition, and the results of a comprehensive examination.
Diagnostic laparoscopy of the fallopian tubes
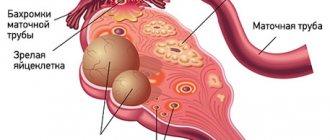
According to statistics, approximately 40% of cases of infertility in couples are caused by diseases of the female reproductive system. Very often (about 40%) the cause is tubal obstruction. Hence the logical answer to the question: “Why is tubal laparoscopy done?” The procedure allows you to visualize the uterine appendages (fallopian tubes and ovaries), assess their condition, and accurately determine the real cause of infertility. Modern endoscopic equipment makes it possible to examine the internal organs in detail in good lighting, enlarge the image to study small details, which provides high information content and diagnostic value of the study.
In addition to assessing the patency of the fallopian tubes, laparoscopy is the “gold” standard for diagnosing endometriosis, a condition in which elements of the uterine mucosa (endometrium-like cells) are found in atypical places (tubes, ovaries, retrocervical space, peritoneum, etc.). Ultrasound is not always informative in identifying this disease, especially when it comes to superficial lesions.
Indications for diagnostic laparoscopy of the fallopian tubes for infertility
The procedure is a surgical intervention associated with certain risks, so many patients are interested in: “When is tubal laparoscopy done?” The study is not routine and is used in cases where the causes of infertility could not be established using simpler methods. A doctor may suspect tubal pathology after performing an ultrasound or hysterosalpingography. For example, adhesions in the near-pipe area, defects and unevenness in the wall structure can be detected.
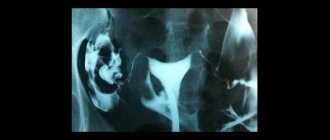
During laparoscopy, a visual assessment of the condition of the fallopian tubes is made. After introducing methylene blue into the uterine cavity, you can directly assess the degree and time of its entry into the abdominal cavity, which is an objective method for diagnosing tuboperitoneal infertility.
The method is also used in cases where, after a full examination, identification and correction of possible causes of infertility, conception does not occur. Laparoscopy helps in diagnosing endometriosis, especially those forms that are not visible on ultrasound.
Therapeutic laparoscopy is used to treat the following pathological conditions:
- ectopic pregnancy;
- hydrosalpinx (accumulation of fluid in the pipe as a result of the formation of adhesions against the background of an inflammatory process that is resistant to conservative treatment);
- purulent salpingitis (accumulation of pus against the background of an infectious-inflammatory process, usually caused by bacteria);
- tubo-ovarian abscess (complication of advanced infectious and inflammatory diseases);
- endometrioid ovarian cysts and other forms of endometriosis that are subject to surgical treatment.
Progress of the operation
Diagnostic intervention or treatment takes about 40 minutes and is performed under general anesthesia. This method allows you to check patency using a dye solution.
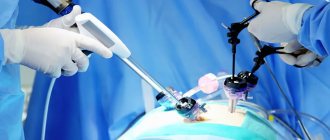
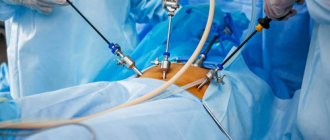
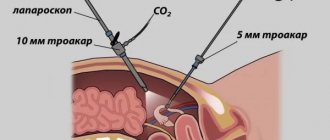
For examination, punctures (most often two) are made in the abdominal wall, through which special devices are inserted. To make visualization clearer, a small volume of carbon dioxide is pumped into the abdominal cavity. One incision is used to insert a laparoscope (a tube with a lens and an eyepiece that displays an image on the screen), the second is used to insert a manipulator, which is used to displace organs and carefully examine them. After the procedure, stitches are placed on the puncture sites.
Contraindications to diagnostic laparoscopy of the fallopian tubes for infertility
Laparoscopy of the uterine appendages is not performed in the following conditions:
- cachexia (depletion of the body);
- blood pathologies;
- bleeding disorders;
- cancerous tumors;
- severe somatic pathologies (in the decompensated stage);
- acute inflammatory processes in the body.
In other pathological conditions (diabetes, hypertension, metabolic disorders), the possibility of conducting the study is determined on an individual basis. The main thing is adequate correction of the underlying disease.
What should you not eat after surgery?
There are no obvious contraindications to eating any product, the only question is the quantity. If possible, you should, if not exclude from your diet, then minimize the consumption of sweets and fatty foods, since these are the foods that make it difficult for your body to absorb calcium.
Separately, it is worth paying attention to products that not only make it difficult for new calcium to enter the body, but also wash away existing calcium. At the top of this list is sweet soda, so it’s best to forget about it altogether during recovery. It is also advisable to limit the amount of coffee and black tea you drink, as the caffeine they contain also leads to calcium loss.
Preparation for the procedure
Before laparoscopy of the fallopian tubes, a woman is shown a clinical examination to assess their patency. Comprehensive diagnostics is necessary to exclude contraindications, as well as to prevent complications during and after the intervention. The examination is carried out no later than 2 weeks before surgery and includes:
- laboratory tests (general and biochemical blood tests, coagulogram, screening for infections, determination of group and Rh factor, smears for vaginal microflora, general urine test, PCR for COVID-19);
- instrumental procedures (electrocardiography, fluorography, ultrasound scanning of the pelvic organs);
- consultations with doctors (therapist, anesthesiologist).
Comprehensive diagnostics allows you to objectively assess the condition of the patient’s body, eliminate contraindications to surgery and anesthesia, foresee risks, and also take preventive measures in a timely manner. During the consultation with the gynecologist and anesthesiologist, it is important to provide complete information about your health status. The doctor must be aware of the patient’s lifestyle, as well as medications that the patient takes regularly or occasionally. Some of them may affect blood clotting and should be canceled in advance.
In the presence of extragenital pathologies, consultations with highly specialized specialists are indicated (if necessary, with additional examination). When an acute or chronic disease is detected, preparation for surgery involves complex treatment. In this case, laparoscopy is postponed until the patient’s condition stabilizes. Preparing for surgery involves following a diet for 2-3 days. Avoid foods that are difficult to digest and stimulate the formation of gases in the intestines, namely:
- fatty meat and fish;
- seeds;
- berries with seeds;
- baked goods;
- milk, cream;
- mushrooms;
- legumes;
- raw vegetables;
- alcohol;
- carbonated drinks.
It is allowed to eat cereals, lean meat and fish, and vegetables after heat treatment. You can drink water, tea, coffee, compotes. The last meal should take place 8-10 hours before surgery. On the day of laparoscopy, eating and drinking liquids is prohibited. A fasting pause is necessary to avoid the development of aspiration syndrome during general anesthesia.
In preparation for surgery, it is necessary to cleanse the intestines with a double enema (in the evening and in the morning). For these purposes, it is more convenient to use special microenemas with fast-acting laxatives. Before laparoscopic surgery, a hygienic shower is indicated.
What can you eat after surgery?
After fractures and operations on joints, ligaments and tendons, you can eat almost anything, but you need to monitor the quantity and pay special attention to foods that contain elements necessary for recovery. Below is a list of the main products from which you can get the necessary substances.
Protein . This element is the main building material in our body, so foods rich in it simply need to be included in your diet. With sufficient protein intake, you can significantly reduce the likelihood of infectious complications and get enough amino acids necessary for the synthesis of collagen, the main component of connective tissue. Main sources of protein: lean meat, fish, chicken, eggs, soy, seafood, legumes, nuts, spinach and artichokes.
Calcium . This is an essential mineral that is no less involved in the process of bone repair than protein. At the same time, calcium is necessary not only for your bones, it has a huge impact on the proper functioning of the heart, muscles and nervous system. The best sources of calcium: dairy products, fish (especially sardines), hard cheese, seeds, sesame seeds, almonds, hazelnuts, soybeans, cottage cheese, garlic, parsley.
Cellulose . It will not have a direct effect on the healing process, but will improve your digestion and reduce the likelihood of constipation, which is almost inevitable with low physical activity and regular use of painkillers. Fruits, grains, vegetables, legumes, avocados, almonds, whole grain pasta, and bran are rich in fiber.
Carbohydrates . In order for the proteins you consume to be used for the construction of new material, and not spent on basic metabolism, you will need to take care of a high content of carbohydrates in your diet. As your physical activity increases, be sure to increase your carbohydrate intake. The most useful sources are: rice, oatmeal, beans, beets, carrots, buckwheat and bananas.
Zinc . This element takes a significant part in collagen synthesis, accelerates regeneration and strengthens weakened immunity. The easiest way to get zinc is from beef, pork, turkey, red meat, chicken, nuts, legumes, and cereals.
Iron . Most operations are accompanied by blood loss, and iron-rich foods are needed to restore the level of hemoglobin and red blood cells in the blood. These foods include: red meat, liver, eggs, nuts, vegetables, apples, pomegranates, raisins, plums, figs.
Magnesium . This element plays an important role in many biochemical processes in the body, and a lack of magnesium can lead to disruption of the cardiovascular system. Food sources of magnesium include: spinach, pumpkin seeds, beans, sesame seeds, almonds, cashews, and navy beans.
Omega-3 . Fatty acids have a strong anti-inflammatory effect, cleanse the walls of blood vessels from cholesterol, improve blood viscosity and stabilize blood pressure. Available sources: tuna, salmon, red caviar, fish oil, lard, tofu, walnuts.
Phosphorus . Phosphorus strengthens bone tissue and is responsible for the body's absorption of minerals and vitamins, including B vitamins (which in turn are responsible for energy production). Where to get it: beef liver, salmon, sturgeon, halibut, turkey, chicken, eggs, beans, nuts, bran, pumpkin, peanuts.
Vitamin D. We can talk about the benefits of vitamin D endlessly; some experts today even call it a “protoharmone.” In the context of recovery after surgery, vitamin D improves the absorption of calcium and phosphorus through the intestinal wall. Sources: herring, salmon, sardine, tuna, egg yolk, cod liver, sturgeon caviar, red caviar, fermented milk products, butter, beans.
Vitamin C. Significantly accelerates the synthesis of collagen fibers, strengthens capillary walls, helps the functioning of the immune system (in particular, it is responsible for the synthesis of interferons). Contained in the following products: cabbage, broccoli, bell pepper, orange, melon, lemon, pineapple, berries, dill, sorrel, spinach, rose hips.
B vitamins . These vitamins take part in bone growth and are responsible for the delivery of important substances and microelements. Vitamins B6 and B9 promote collagen synthesis. You can replenish the norm of vitamins of the group with salmon, poultry, beef liver, eggs, milk, nuts, spinach, beans, cereals, seeds, yeast.
Technique for laparoscopy of fallopian tubes
Diagnostic laparoscopy is performed in the first phase of the cycle. For pain relief, general anesthesia is usually used. How the operation of laparoscopy of the fallopian tubes is performed (the order of manipulations) largely depends on the nature of the pathological changes identified during the study.
Stages of implementation, step-by-step description of the procedure
- Immersion in anesthesia. It is possible to administer the drug intravenously or endotracheally after induction of anesthesia.
- Preparation of the surgical field. Involves treatment with antiseptic solutions to prevent infectious complications.
- Introduction of tools. In the abdominal area, 3 small incisions up to 1 cm long are made, through which an endoscope, a channel for introducing surgical instruments, and a tube for supplying gas (Veress needle) are inserted into the abdominal cavity. The need to create another additional channel is determined during the intervention process after assessing the degree of complexity of the clinical case.
- Diagnostics. The doctor visually examines the uterus, ovaries, tubes and surrounding areas. An endoscope is a rigid tube with lighting and optical systems. The device transmits the image to the monitor. To improve visualization of hard-to-reach areas, nearby tissues are moved apart in an atraumatic manner.
- Therapeutic manipulations. Depending on the identified changes, diagnostic laparoscopy can be combined with medical operations to eliminate adhesions around the fallopian tubes, tuboplasty (restoration of patency), partial or complete removal of the tubes (salpingectomy), removal of endometriotic lesions, checking the patency of the fallopian tubes after manipulation (by insertion into the uterine cavity a special catheter through which a colored solution is injected), if necessary, an anti-adhesion gel is injected into the abdominal cavity, etc.
- The final stage. Upon completion of diagnostic or therapeutic procedures, the instruments are removed and the incisions are sutured with atraumatic needles. After healing, barely noticeable scars up to 1 cm long remain on the skin.
How long does tubal laparoscopy take?
The patient’s time in the operating room depends on how the fallopian tubes are performed and what additional manipulations are performed. The diagnostic process usually takes up to half an hour. Since the procedure often takes on a therapeutic nature, the average time of laparoscopy is 40-50 minutes. When performing reconstructive manipulations and complex radical interventions, the operation can last several hours.
Laparoscopy of fallopian tubes under anesthesia
The procedure requires the use of general anesthesia, which temporarily suppresses the activity of the nervous system. Throughout the operation, the anesthesiologist monitors life support parameters (pressure, respiratory and heart rate, etc.)
To perform tubal laparoscopy, endotracheal anesthesia is used (with intubation and connection to a ventilator). Mask anesthesia is used in cases where the duration of the operation is precisely known.
The patient falls into deep sleep within the first seconds after the injection of the drug and does not feel anything. During the intervention, the depth of anesthesia is adjusted. If necessary, medicated sleep is prolonged with additional doses of medications.
The optimal method of pain relief is selected by the anesthesiologist after a detailed examination of the patient.
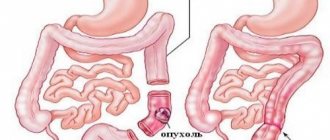
Removal of the fallopian tube during laparoscopy
Removal of the fallopian tube during laparoscopy is called salpingectomy. Diagnostic manipulation takes on the character of a radical operation if:
- hydrosalpinx - accumulation of fluid in the cavity of the pipe;
- pyosalpinx - purulent inflammation of the tube;
- tumors.
In these conditions, there may be no prospects for restoring the functional state of the pipe. In order to prevent complications, as well as in preparation for IVF, a decision may be made to remove it. Otherwise, the risk of ectopic pregnancy increases due to impaired peristalsis of the tube.
If one of the tubes is lost and the remaining one is in satisfactory condition, reproductive function is preserved. It takes about 3 months for the body to fully recover (the exact period depends on the volume and complexity of the intervention).
Rehabilitation period after laparoscopy of ovarian cyst
The period after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst is approximately one month, after which the woman can completely return to her normal lifestyle. It is believed that the key to successful rehabilitation lies in strict adherence to all advice and recommendations given by the attending physician. The golden rule for successful recovery of a woman’s body after laparoscopy is:
- Limitation of physical activity;
- Temporary refusal to play sports;
- Temporary restriction of sexual activity;
- Temporary refusal to wear tight underwear made of synthetic materials;
- Refusal to visit a sauna, bathhouse, public swimming pool, solarium;
- Refusal to take hot baths;
- Do not sunbathe in direct sunlight.
Consequences after the procedure
The woman’s condition after the intervention depends on the characteristics and duration of the operation, the method of pain relief, and the initial state of health. Upon recovery from anesthesia, hallucinations, delirium, weakness, nausea, and vomiting are possible. These phenomena pass within 1-3 hours. Anesthesiologists at SM-Clinic use the latest generation drugs for pain relief, which minimizes the risk of side effects and ensures good tolerability of anesthesia.
Laparoscopy carries minimal risk of complications. In the early postoperative period (1-3 days), doctors carefully monitor the patient’s condition in a hospital setting. During laparoscopic surgery, carbon dioxide is injected into the abdominal cavity. Pressure on the internal organs provokes moderate aching pain in the diaphragm and chest. The gas is removed upon completion of the intervention, the remains are utilized by the body. To make the process go faster, after 8 hours the patient is recommended to get up and move slowly around the ward. Early activation also prevents the development of adhesions and promotes normal bowel function.
If the patient’s condition is satisfactory, the patient is discharged the next day or 2-3 days after laparoscopy. Upon discharge, the doctor gives recommendations regarding the rehabilitation period and its duration, and prescribes medication.
Normal consequences of laparoscopy are:
- wounds in the abdominal area (after complete healing they become almost invisible);
- moderate increase in body temperature on the first day after surgery;
- moderate aching pain in the lower abdomen;
- mucous or bloody discharge from the genital tract;
- delay of menstruation (from several days to 3 weeks).
Painful sensations can last up to 5 days, wounds heal within 2 weeks. Spotting bloody discharge from the vagina can be observed for up to 10 days.
After discharge, the woman must follow the doctor’s instructions and carefully monitor her condition on her own. The following symptoms are reasons to urgently contact a gynecologist:
- redness of wound edges;
- discharge of pus;
- pain in the stomach;
- increased body temperature;
- profuse bleeding from the genital tract;
- unpleasant odor of discharge;
- prolonged feeling of weakness, drowsiness.
The postoperative period is the time from the start of surgical procedures until the patient’s ability to work is restored. The duration of this stage after diagnostic laparoscopy usually does not exceed 10 days.
Advantages of laparoscopic technique
- The abdominal incisions are only 0.5-2 cm long (the open technique involves an incision 15-20 cm long).
- Less severe pain syndrome.
- After surgery, less time is required for rehabilitation in the hospital.
- There is a very low probability of the formation of postoperative hernias, inflammation, suture dehiscence and adhesions.
Laparoscopic treatment method
General anesthesia
Operation time - 40 minutes
Recovery in hospital - 2-3 days
Cost of the operation: from 26,000 rubles.
Possible complications after the procedure
The laparoscopic technique eliminates serious tissue damage, so the risk of complications is minimal and ranges from 0.7-7%. The following adverse effects are extremely rarely recorded:
- damage to internal organs when installing trocars or performing surgical procedures (with the proper experience of the surgeon, practically does not occur);
- bleeding as a result of incomplete coagulation of blood vessels (possibly during radical and reconstructive plastic surgeries);
- vein thrombosis (occurs as a result of improper preoperative preparation or the characteristics of the patient’s body);
- subcutaneous emphysema (develops when gas accumulates under the skin);
- adhesive process (re-formation of synechiae is possible if the intervention technique is violated, organ damage, or improper rehabilitation);
- infectious and inflammatory processes (result from incomplete examination, improper preparation for surgery or violation of recommendations during rehabilitation);
- obstruction of the fallopian tubes.
The list of possible complications after laparoscopic operations is minimal. And with proper preparation of the patient, correct performance of laparoscopy and competent rehabilitation, they practically do not occur. The risk of consequences is lower than with open operations.
Complications of anesthesia described in the literature may include swelling of the larynx, impaired ability to breathe, heart attack, and pneumonia. An individual approach to the selection of anesthesia, the use of modern drugs and methods of anesthesia, as well as careful monitoring of the patient’s condition reduces the risk of complications to a minimum.
Diet after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst: what to exclude from your menu
During the period of recovery of the body after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst, women are strictly prohibited from consuming alcoholic beverages, coffee and various carbonated drinks. Instead, you should consume compotes, fruit drinks, herbal teas, and home-made juice.
Among other prohibited foods during the diet after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst, the following should be listed:
- Fatty food;
- A variety of canned food, marinades, pickles, smoked meats;
- Hot spices, herbs, sauces and ketchups, mustard, seasonings;
- Raw fruits;
- Chicken eggs;
- Sweet products and baked goods: chocolate, cakes, custard pies, baked goods. Bread in small quantities is allowed to be consumed starting from the third day after surgery.
After laparoscopy, it is advisable to eat frequently and in small portions, that is, follow a balanced diet. The recommended frequency of meals is 6-8 times a day.
Yusupov Hospital is a European center that provides high-quality therapeutic and surgical care. The clinic performs operations in all areas of modern surgical gynecology. All patients who give preference to the Yusupov Clinic receive effective comprehensive treatment, consultation from many of the center’s leading specialists in various fields of medicine and, most importantly, highly qualified care. To make an appointment please call.