Attention!
The information in the article is for reference only and cannot be used for self-diagnosis or self-medication. If you notice any symptoms of the disease, contact your doctor.
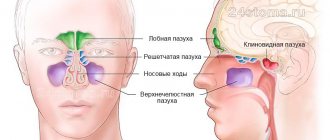
Sinusitis is an inflammatory lesion of the mucous membrane lining the inner surface of the maxillary sinus.
The disease manifests itself as headache, discomfort in the paranasal area, as well as symptoms of general intoxication. The disease is acute or chronic. It affects adults and is detected in older children. Sinusitis has an ICD code of J32.0
Types of sinusitis
The division of sinusitis into forms is determined by the nature of the course, the causes of occurrence and the localization of the pathological process. The lesion can be bilateral or unilateral.
Purulent
A variant of sinusitis in which bacterial infection of the mucous membrane of the maxillary sinuses occurs. These spaces are filled with pus. The pathological process involves one or both sinuses. With purulent sinusitis, the patient experiences pain in the middle part of the face. This type of pathology is that pus in the sinuses can provoke inflammation of the membranes of the brain.
Catarrhal
With this type of sinusitis, infiltration of the mucous membrane lining the sinuses occurs. It is manifested by edema, accompanied by the release of serous-mucosal fluid in moderate quantities. With catarrhal sinusitis, the mucous membrane is hyperemic and congested. There is parietal thickening of the choroid plexuses in one or both sinuses. Often, bilateral catarrhal sinusitis occurs immediately.
Odontogenic
It is characterized by the presence of inflammation of the sinus mucosa, which is caused by the penetration of the pathogen from the main source of infection. It is located in the upper jaw area. The most likely source of infection in odontogenic sinusitis is a diseased tooth. This occurs in those people who have structural features of the jaw. The apexes of the roots of their teeth are located immediately under the mucous membrane.
Bilateral
This variety is characterized by damage to the paranasal sinuses on both sides. It is less common than unilateral lesions. Bilateral sinusitis has a more severe course compared to unilateral inflammatory process. It often takes a chronic course.
Spicy
This form of the disease is detected in patients more often than others. Acute sinusitis is characterized by its occurrence as a complication of an acute respiratory viral infection. Edema quickly forms in the sinuses and exudate accumulates. Clinical manifestations of the disease occur at lightning speed. It lasts no more than three months. Then the manifestations of the disease disappear.
Chronic
This form is a complication of acute sinusitis. It occurs when the disease is untimely, incorrectly treated or terminated prematurely. Chronicization of the process is facilitated by: deviated nasal septum, hypertrophied adenoids, proliferation of polyps, and the presence of a tumor in the nasal cavity.
Contraindications
Conditions in which x-rays of the sinuses cannot be taken:
- pregnancy;
- severe (terminal) condition of the patient (coma, decompensated cardiovascular or respiratory failure);
- strong mental agitation;
- acute situations requiring surgical intervention (massive bleeding, open pneumothorax);
X-ray contrast examination of the paranasal sinuses is contraindicated in:
- allergies to iodine;
- lactation;
- nosebleeds.
It is not recommended to do an X-ray of the sinuses of a child under 7 years of age, except in situations where the examination is prescribed for health reasons, for example, in case of traumatic damage to the bones of the facial skull. But in general, the advisability of x-raying the child’s sinuses depends on the age of the patient. More precisely, from the age at which the final anatomical formation of the nasal sinuses occurs. Thus, ethmoiditis can occur immediately after birth, sinusitis - after 3 years, frontal sinusitis - in a child over 5 years old, sphenoiditis - starting from 10 years.
Causes of sinusitis
It becomes acute due to the development of complications of viral infections affecting the nasopharynx. This occurs due to swelling of the mucous membrane, due to which the opening for communication between the sinus and the nasopharynx begins to narrow. Exudate accumulates in its cavity. Excellent conditions are created for the growth of bacteria.
Main reasons:
- allergic rhinitis;
- chronic runny nose;
- vasomotor rhinitis.
Against the background of decreased immunity, the patient may develop acute inflammation of a fungal nature. Acute sinusitis can be quickly managed with adequate therapy.
Reasons for becoming chronic:
- presence of bronchial asthma or allergic rhinitis;
- frequent respiratory infections;
- permanent residence in conditions with polluted air;
- polyps and tumors in the nasal cavity;
- deviated nasal septum;
- abuse of vasoconstrictor drops;
- smoking;
- dehydration of the body;
- taking drugs that reduce immunity.
Symptoms and signs of sinusitis
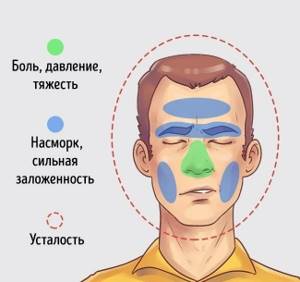
Sinusitis has clear characteristic symptoms. The main manifestation of the disease is pain, which is localized in the middle third of the face and paranasal region. Pain with sinusitis has its own characteristics. Their intensity increases in the evening, and in the morning they are practically absent. How does sinusitis manifest?
Symptoms of acute sinusitis
- headache with sinusitis is bursting, intense;
- signs of general intoxication are noted: general weakness, nausea, feeling of weakness;
- body temperature rises;
- lacrimation and photophobia are noted;
- nasal breathing is difficult;
- the sense of smell with sinusitis is impaired;
- Nasal discharge may be clear or purulent.
If the process has spread to the periosteum, swelling of the orbital area and cheeks on the affected side is noted. In children, the symptoms of sinusitis are pronounced. Signs of general intoxication prevail over local signs of inflammation.
Symptoms of chronic sinusitis
- body temperature rises slightly, often this sinusitis in adults occurs without fever;
- increased weakness and fatigue;
- headache of a bursting nature, worsening in the evening;
- decreased sense of smell;
- a cough with a small amount of sputum is possible;
- constant runny nose.
Sinusitis in adults without symptoms
Without any symptoms, sinusitis often occurs in elderly and weakened people. The only manifestations of the disease may be increased weakness and fatigue, but this is attributed to other health problems.
Sinusitis without symptoms is dangerous due to its complications. The infection spreads to other organs. Therefore, if you suspect a disease, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Sinusitis without fever
The presence of a temperature reaction is a manifestation of the body’s fight against infection. If immunity is reduced, then this does not happen. The temperature remains normal. Sinusitis occurs without it in chronic forms.
Sinusitis without runny nose and nasal congestion
The infection occurs without a runny nose if caries has dissolved the oral septum and penetrated inside. This is facilitated by injuries to the facial bones and a curved nasal septum.
Diagnosis of sinusitis
Before treating sinusitis, the patient must be carefully examined. The patient is examined as follows:
- The doctor first examines the patient's medical history and complaints.
- He examines the nasal cavity and the projection site of the paranasal sinuses. Performs palpation of the soft tissues of the face
- During rhinoscopy, using a special device, the doctor examines the nasal mucosa. Finds its swelling and hyperemia.
- An ENT doctor uses special tests to examine the respiratory and olfactory functions of the nose.
- Diaphanoscopy is used to illuminate the sinuses. With unilateral sinusitis, darkening of half the face is recorded.
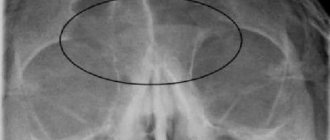
- X-ray examination provides a clear image of the paranasal sinuses. Sinusitis in the picture is visible as darkening of the sinus.
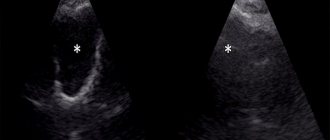
- Ultrasound examination can determine the presence of fluid.
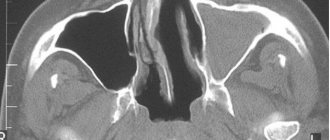
- CT and MRI are performed if tumors, polyps and cysts in the sinuses are suspected, complicating the course of the disease.
- A diagnostic puncture is performed to study the exudate for subsequent determination of the causative agent of the disease during bacterial culture.
- Endoscopic diagnostic methods are used to study the condition of the mucous membrane of the maxillary sinuses during examination.
- Laboratory diagnostic methods: blood for HIV, immunoglobulins, immunogram.
If necessary, additional diagnostic methods are used to clarify the diagnosis.
Preparation for the procedure
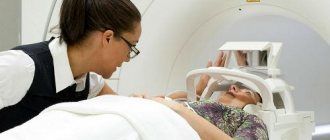
Before starting the procedure, you must remove your outer clothing, metal and other jewelry, earrings, piercings, and remove dentures. Next, you need to tell the doctor whether similar procedures have been performed previously, whether there are dental implants, fractures of the nose or facial bone.
During the diagnosis, the patient must stand still and not move. He should rest his nose and chin on the stand of the X-ray machine, which has been previously adjusted to the patient’s height. After this, the doctor will take several pictures from another room and give further instructions to the patient. During the procedure, the patient will sometimes need to hold their breath for a few seconds (no more than 10 seconds). The radiologist will take pictures in two projections, and sometimes while lying down.
The whole procedure will take about 10 minutes.
Treatment of sinusitis
How to cure sinusitis? Now there are several effective methods that allow you to get rid of it.
When the mucous membrane is inflamed, the maxillary sinus is filled with exudate, which can be very viscous. He doesn't leave on his own. He has to be evacuated. One of the treatment methods is puncture of this cavity.
Puncture of the maxillary sinus
Puncture of the maxillary sinus is a puncture of its wall using a sharp instrument. This is necessary to evacuate the inflammatory contents. It is often used for drainage of sinusitis, in case of accumulation of viscous contents inside the sinus that does not come away on its own. It cannot be extracted by other methods.
Puncture for sinusitis quickly alleviates the patient’s condition immediately after evacuation of the inflammatory exudate. The sinus is also punctured when the patient’s condition is threatened by a breakthrough of purulent exudate into the surrounding tissues with the development of irreversible consequences (meningitis, otitis media, encephalitis, sepsis).
Stages of the procedure:
- The puncture is performed in the area of the lower nasal passage using a special needle with a curved and beveled tip.
- Under visual control, it is inserted into the lower nasal passage. Here the bone is of minimal thickness, which makes the puncture easier. The needle rests on his arch. The depth of its penetration is up to 2.5 cm.
- The needle is advanced to the outer edge of the orbit. Using a syringe, the doctor evacuates the contents of the sinus and rinses it with antiseptic solutions.
- After the procedure, the patient is placed on his side for half an hour. Make sure that the solution leaves the sinus cavity.
Methods for treating sinusitis without puncture
It is preferable to treat without puncturing the sinus, since with this method of treatment there are often complications - bleeding, vascular thrombosis, etc. There are other methods that are effective for this disease.
The use of antibiotics for sinusitis
Antibiotics for sinusitis of bacterial origin are the means of choice. Several of these groups of these drugs are used for treatment. The most commonly used drugs are penicillins, fluoroquinolones, macrolides, and cephalosporins. The doctor chooses the drug for treatment.
Healing procedures
Less invasive techniques are used for treatment. They are used for sinusitis to rinse the sinuses.
The following methods are used:
- "Cuckoo". The patient is placed on the couch. Then, using a tube, the antiseptic is applied into one nasal passage, and a tube is placed in the other to pump out exudate from the sinuses.
- Balloon sinuplasty. Gas is pumped into the sinuses - it expands the lumen of the anastomosis. Then the contents of the sinuses are removed.
The procedures provide effective treatment for sinusitis. The techniques make it possible to remove inflammatory exudate from the sinuses without punctures. They are so safe that they are used to treat sinusitis during pregnancy.
Physiotherapy
It is used in complex therapy in the treatment of sinusitis. The techniques activate biochemical processes and restore metabolism.
For treatment use:
- electrophoresis;
- radio wave therapy;
- ultrasonic influence;
- UHF.
Physiotherapeutic methods in combination with other types of therapy can significantly speed up the healing process.
Drug therapy
In addition to antibacterial agents, other drugs are used. To do this, use the following means:
- antihistamines - help relieve tissue swelling;
- vasoconstrictor sprays and drops - they facilitate nasal breathing;
- glucocorticoids – reduce the manifestations of allergies, have an anti-edematous and anti-inflammatory effect.
Success in treating the disease depends on a rational combination of all treatment methods. If conservative treatment for sinusitis is ineffective, surgery is performed. During a maxillary sinus, the sinus is opened and the pathological contents are removed.
What can you do at home?
Treating sinusitis at home is dangerous. You should not self-medicate. Home treatment is used to alleviate the condition before going to the doctor. Let's look at what you can do at home for sinusitis.
Nasal drops for sinusitis
These remedies for sinusitis have a local effect. They must be supplemented with general-effect drugs.
The following drops are used:
- vasoconstrictors – relieve tissue swelling, normalize nasal breathing;
- antiseptics – inactivate pathogenic microorganisms that provoke inflammation;
- antibacterial drops – have a bactericidal effect;
- mucolytics - thin the pus in the sinuses and facilitate the removal of mucus.
These remedies are a good addition to the main treatment.
Nasal rinsing
How to rinse your nose with sinusitis? Solutions for rinsing the nasal cavity help remove contents from the sinuses. Rinse the nose for sinusitis to moisturize the mucous membrane. To do this, use ready-made solutions that are sold in pharmacies - Humer, Dolphin, Aqua Maris. You can rinse your nose with saline solution or furatsilin solution.
Inhalations
Inhalations are recommended for the treatment of chronic sinusitis. The easiest way is to use steam procedures. Inhalations for sinusitis are best done using a nebulizer. It sprays medicinal solutions in the form of fine particles. They penetrate well into the sinuses.
Painkillers and antipyretics
At high temperatures above 38C0, you can take antipyretics. They will help bring her down. If you have a headache, painkillers can temporarily relieve it.
Self-massage
- Before the session, thoroughly wash and dry your hands. Movements should be light.
- The wings of the nose are gently massaged with the pads of your fingers. Pinch the tip of the nose.
- Knead the area of the nasolabial folds. Then gently rub the cheek area.
- Then they move on to stroking the bridge of the nose. Massage the area of the outer corners of the eyes.
The procedure is performed in no more than five minutes. Massage can be done up to five times a day.
Before using massage, you should consult your doctor.
Where to take an x-ray of the sinuses
A radiologist or therapist will refer you for examination if the patient’s snot does not stop for a long time. X-rays of the sinuses for sinusitis are done in district clinics, hospitals, private clinics and diagnostic centers. The cost of an examination in 1 projection is 1300 rubles, in several - from 1800 rubles. List of diagnostic centers in Moscow where they do x-rays of the nose:
- SM clinic;
- Best Clinic;
- Clinic "Family Doctor;
- AMS Medicine;
- Medkvadrat.