Cervical cytology is a cytological study that evaluates the condition of the uterine epithelium and identifies cells with changes in structure (atypical).
Atypical cells include cells with mild, moderate or severe dysplasia, and cancer cells. They differ from each other in the severity of structural changes. Annual cytological screening is indicated for women aged 21 to 69 years. The exception is virgins and women after hysterectomy. To do this, two methods are used to fix and study the cervical epithelium. During the examination, the performance, composition and structure of cells obtained from the patient’s biological material are assessed. They are compared with normal values.
In what cases can a doctor prescribe cytology?

This usually occurs when indications are identified during a preventive examination, for example, when the characteristics of the tissues of the cervical canal change. Indications for cervical cytology may include:
- Human papillomavirus;
- Pathologies of the endocrine system;
- Diabetes;
- A course of hormonal medications;
- Deviations in the reproductive system;
- Diseases of the genital area;
- Various vaginal discharge;
- Cervical erosion;
- Cancer of the genitourinary system;
- Abortion or miscarriage;
- Preparing for pregnancy.
As a rule, cytological examination is not prescribed for girls under 18-20 years of age who are not sexually active. This is due to the low accuracy of such a survey.
How is cytology deciphered?
In the past, cytology results were described using the following groups: from I, which indicates everything is normal, to V, which means cervical cancer. Now groups, that is, the description of cytology results using the Papanicolaou system, are a thing of the past. Since 2001, Europe has used the much more precise Bethesda System (TBS), using uppercase letters A, B, C, D, etc., Roman numerals, and possibly lowercase letters.
For example, AI means the smear can be assessed, AII means the result is questionable - the smear is illegible, but is still being assessed, AIII means the smear cannot be assessed. This occurs when the laboratory determines that the swab was collected incorrectly, was not secured correctly, dried out during transport, etc., and cannot be reliably tested. It also happens that the patient has an infection, and there are a lot of inflammatory cells in the smear, so they blur the image.
For example, B is the general smear characteristics that determine whether a Pap smear is normal (BI) or not (BII). The best cytology is AI, BI.
The following letters are notes about brush strokes or roughness. Very important: an incorrect result does not necessarily mean cancer! This only tells the doctor that he should look more closely at the abnormal cells.
The study commentary also includes abbreviations for the English names of the abnormal conditions, for example, ASC-US - atypical squamous cell of undetermined meaning.
What does preparation for research include?
Two days before taking a smear, it is necessary to avoid drinking alcoholic beverages and try not to take medications - the latter can blur the picture of the condition of a woman’s body. It is recommended to limit sexual contact and avoid douching, and not to use perfumed products for intimate hygiene.
As a rule, gynecologists prescribe cytology in the period from 14 to 25 days of the cycle - 5 days before or after menstruation.
Attention! The doctor may reschedule the collection of a smear for cytological examination if there is a suspicion of acute inflammation!
Who should get Pap smears more often?
There are times when a test needs to be repeated because, for example, the result is ambiguous or false due to inflammation.
If during a cytological examination cells with an abnormal structure are detected at least once, the cytology is not checked by another cytology, because the next result can reassure the patient when it is time to act. It should be remembered that the classic Pap test has a sensitivity of about 60%.
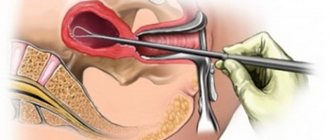
How is a cytological examination of the cervix performed?
Despite the name, which sometimes scares patients, cytology is painless and quick. To obtain biological material, the doctor does not need to cut the mucosal tissue.
Taking a smear for cytology proceeds as follows:
- The doctor directs the patient to the gynecological chair;
- Treats the intimate area with antiseptic compounds;
- Using special instruments (for example, viewing mirrors), the vagina is expanded, gaining access to the cervix;
- A thin layer of tissue is carefully scraped from the cervical canal, including the area at the beginning of the uterus if necessary.
After collecting a smear, the biological material is sent to the laboratory, where employees study the structure and condition of the cells.
Making a diagnosis after the study
The transcript of the study results contains information for a specialist and is not a final diagnosis. It is difficult for a patient without special education to understand highly specialized terms. This information cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-medication, therefore, with any test results, you should consult a gynecologist.
If the test results are positive, the patient may be prescribed a repeat test and additional diagnostic methods:
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs;
- extended colposcopy;
- cervical biopsy.
- bacterial sowing;
- PCR diagnostics.
Types of research
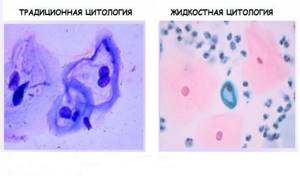
Cytology is divided into types based on the method of collecting and preserving biomaterial. In the case of standard cytology, it is taken and placed on laboratory glass, onto which a special composition is applied to prevent drying out.
An alternative is liquid-based cytology, which uses a special disposable cytobrush. With its help, the doctor makes a scraping and then places it in a test tube with liquid. The liquid is a colored catalyst or a neutral composition.
After the tube with the biomaterial arrives at the laboratory, it is placed in a centrifuge. Under its influence, the process of separation of the cells of the upper layer of the cervical mucosa from each other occurs. This can significantly improve diagnostic accuracy and reduce the risk of errors.
Liquid cytology eliminates the possibility of biological material drying out and helps to increase its shelf life - the study does not have to be carried out in the near future after collection. If necessary, the smear can be sent for other research procedures.
Types of tests
Screening can be carried out using the traditional or liquid method. In a traditional test, biological material is applied to laboratory glass and dried at room temperature. Disadvantages of such diagnostics:
- some biological material remains on the specialist’s instruments and gloves;
- the method does not include a filtering step;
- the cells on the glass are distributed unevenly, forming several layers.
Such features of the study may affect the reliability of the result.
Liquid technology avoids many problems related to the quality of smears. With this technique, the sample is examined in full. The samples taken are placed in a test tube with a stabilizing medium. Thus, the shelf life of the material is extended to several months. Using a centrifuge, the material is filtered, which increases the information content of the result.
During the study, various methods of staining preparations are used:
- Papanicolaou test (Pap test);
- according to Romanovsky;
- according to Gram.
All methods are based on staining of certain cellular structures, which makes it possible to identify different types of epithelium and distinguish healthy cells from malignant ones.
How to behave after the procedure?
After the procedure, it is recommended to abstain from intimate life, the use of vaginal tampons and douching for 1-2 weeks.
Minor bleeding may occur for 1-2 days after the test.
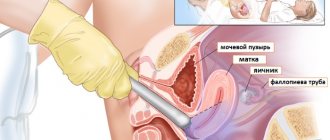
Collection of biomaterial from the cervical canal
Adequate collection of biomaterial from the cervical canal ensures that squamous epithelial cells will be present in it upon microscopic examination of the stained specimen. Transformation zones (the area of transition of squamous epithelium to glandular epithelium) and glandular epithelium in sufficient quantities. Why is it important? Because the transformation zone is the area (“storms and unrest”) that is the target for the development of neoplastic changes.
The reason for the inadequacy of the material for the study may be initiated by the patient herself with improper preparation (use of vaginal suppositories, ointments and other medicinal substances, it is necessary to exclude coitus on the eve of a visit to the gynecologist). Otherwise, the reason for the inadequacy will be noted by the cytologist on the form when forming a cytological conclusion. In the case of using the liquid cytology method, the description of the cytological picture of the specimen will contain only squamous epithelial cells in the absence of glandular (cylindrical) epithelium.
If the specialist took a smear improperly, then the cytological examination will be uninformative. The procedure will need to be repeated!
So which method of cytological examination will be more informative? Traditional (PAP test) or liquid (LC) test?
The table below presents some distinguishing criteria for these methods.
| Indicators | PAP test | J C |
| Microscopy | According to the rules of microscopy of cytological preparations | According to the rules of microscopy of cytological preparations |
| Morphological criteria for interpretation of cytological examination | Developed and well studied | Not currently developed |
| Clear classification | Yes, elements of the Bethesda classification have now been added to it | Certain elements of the Bethesda classification |
| Standard form for conclusion | Designed by | Not always |
| Qualified specialists | A lot has been prepared | Units |
| Insurance | Available in the compulsory medical insurance system | No |
| Cost of the method | Low | High enough |
| Diagnostic performance | Up to 96% | Highly effective for identifying atypical and cancer cells |
In fact, there is no significant difference in which method the smear was taken. Each of them has its own advantages and disadvantages.
Whatever method of cytological examination you choose with your doctor, their essence is to identify abnormal smears.
Of course, the formation of a cytological conclusion is influenced by the qualifications of the specialist (cytologist) who examined the material from the cervical canal of the cervix. Therefore, you have the right to ask who and in what laboratory the smear examination will be carried out. “In cytology, the obvious is easy to diagnose. But not everything is so obvious.” Therefore, it is necessary to emphasize that the cytological conclusion is not a diagnosis, but only a significant link in the formation of a clinical diagnosis. Cytological methods for any localization are limited. The decision to take material (biopsy) for histological examination is made only by the attending physician based on the identification of pathological changes in the cervical mucosa in the cytological specimen and the results of colposcopy.
Online consultation with a gynecologist
Online consultation
During the consultation, you will be able to voice your problem, the doctor will clarify the situation, interpret the tests, answer your questions and give the necessary recommendations.
After analysis
After liquid cytology, it is recommended to observe sexual rest for a week. It is not recommended to use tampons or douche. The presence of bleeding (slight) in the first days after the test is normal. If there is prolonged heavy discharge and other disturbing symptoms, you should consult a gynecologist.
The liquid cytology method is capable of identifying: precancerous conditions, malignant changes in the early stages. Also, the diagnostic results will help you select effective treatment and then evaluate its effectiveness.
Features and advantages of the technique
BD SurePath™ technology based on liquid cytology was officially approved by the FDA in the USA in 1999. Since 2011. widely used throughout the world and recommended in Russia.
Scraping is carried out with a special Rovers Cervex brush. Once collected, the tip is placed into a vial containing BD SurePath Special Liquid Media. The study uses all cells, including those remaining on the brush. Thanks to this, the technology is characterized by a maximum number of cells in the sample, which is 2-3 times higher than the number of cells in a traditional smear. The BD PrepStain concentrates the cells, then automatically spreads the cells in a thin layer onto the glass and automatically stains them. To view samples, a special imaging system with automatic analysis is used, BD FocalPointTM GS - high-precision optics with artificial intelligence, which analyzes all cells for more than 300 indicators. The system then aims a high-precision microscope, through which a specialist cytologist looks, at cells that differ from normal ones. Thus, cell analysis occurs twice: by the intelligent high-precision BD FocalPoint system and by a person. This approach ensures the highest quality of diagnosis of changes and pathologies of the cervix.
Advantages of BD SurePath™ technology: 1. The use of a special combined brush, which ensures the collection of biomaterial material from the endo-, ectocervix and transformation zone. 2. The biomaterial is placed in BD ShurePath liquid transport medium, and all collected cells are preserved. 3. A standardized preparation can be prepared with a small number of cells - up to 5000. A typical traditional smear contains from 8000 to 12,000 cells. 4. The automated BD FocalPoint™ system provides a quick overview of the entire specimen area. With conventional cytology, only a few hundred cells can be seen. 5. The system marks all atypical areas for examination by a cytologist, reducing the number of uninformative samples from 24% to 0.13% compared to traditional cytology. 6. Only part of the biomaterial contained in the vial is used; the remainder can be used for repeated analysis, screening for HPV infection or for diagnosing urogenital infections.
Where to take liquid cytology in St. Petersburg, price
Such tests are done in gynecological clinics. The price of liquid cytology is almost the same everywhere, so you need to give preference to quality. You can trust the analyzes only if they were taken by an experienced gynecologist, and the study of atypical cells itself was carried out in a modern laboratory.
You can take a smear for liquid cytology in St. Petersburg at our Diana clinic. At low prices, we guarantee a professional approach and reliability of the analyzes. In our medical center you can get advice from an experienced gynecologist and, if necessary, an oncologist.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter
When is it appointed?
Liquid cytology may be prescribed by doctors in the following cases:
- Routine medical examination. It is recommended to carry out once a year after the start of sexual activity;
- If you suspect cervical cancer.
- When planning pregnancy;
- For infertility;
- In case of disturbances, disruptions of the menstrual cycle;
- Long-term use of oral contraceptives, hormonal drugs that stimulate oncology;
- Selection of method of protection;
- Gynecological pathologies of viral origin (genital herpes, papillomavirus infection, viral hepatitis, HIV);
- To evaluate the therapy performed.
Most often, liquid-based cytology is performed to diagnose precancerous conditions. If cancer of the female reproductive system is suspected, this is a mandatory examination. The accuracy of the procedure is 95% and allows you to detect cancer at an early stage.