A smear examination for oncocytology allows you to actively identify various diseases of the cervix. It is prescribed for specific indications and for preventive purposes for the early detection of malignant neoplasms and precancerous conditions. Thanks to the introduction of this method into practice, the percentage of advanced forms of cancer has significantly decreased.
- Indications for oncocytology of the cervix
- Preparing for the study
- How are smears taken for oncocytology?
- How is cervical oncocytology done?
- What does oncocytology of the cervix show and how to interpret the analysis
- Smear for oncocytology: studies during pregnancy
- Oncocytology for older women
Indications for oncocytology of the cervix
Since this is a screening test, a smear for oncocytology is performed on all women of reproductive age at least once every 3 years. If there is a gynecological pathology or a family history of cancer, the examination is carried out more often (the specific timing is set by the doctor). It is recommended to take oncocytology in the following cases:
- at the stage of preparation for pregnancy;
- if suspicious areas are detected on the cervical part of the uterus during a gynecological examination (hyperemic, bleeding, etc.);
- in the presence of genital warts, HPV infection, inflammatory processes and other background and precancerous diseases;
- for monitoring during and after specific treatment of cervical diseases;
- to clarify the diagnosis (if the level of oncological markers increases, if pathological changes are detected during ultrasound examination, etc.);
- if a woman has a high risk of developing cervical cancer (blood relatives had malignant tumors of the reproductive system, have chronic HPV infection, HIV, regular exposure to carcinogenic factors);
- if there are complaints (discharge from the genital tract that is atypical for age, contact bleeding, nagging pain in the lower abdomen, etc.);
- if a woman gave birth several times in a row, there were early (before 18 years of age) or complicated births;
- during the onset of menopause, especially when taking MHT (menopausal hormone therapy);
- with frequent changes of sexual partners;
- before installing an IUD (intrauterine device).
A smear for oncocytology is regularly performed for women with precancerous diseases (polyps, leukoplakia, erythroplakia, dysplasia).
How to overcome time?
What to do? - do women ask gynecologists in despair after receiving an atrophic type of smear? There is no need to despair, on the contrary, breathe a sigh of relief - thank God you don’t have cancer.
Hormone therapy is prescribed for hormonal changes during menopause.
. Such a correction will not turn back time, but will help maintain a healthy vagina and avoid inflammatory processes.
Your gynecologist-endocrinologist will determine which therapy you should use. Local treatment involves the use of ointments, creams and suppositories. It is used to prevent inflammation and restore damaged vaginal walls.
Systemic therapy, including tablets and capsules, is used when a woman develops cardiovascular pathology and osteoporosis. This decision is made by the doctor.
The female body gradually loses the strength to recover. Our task is to help ourselves and help in time to save life. Contrary to nature and time.
Preparing for the study
To get a reliable result when taking oncocytology, you must adhere to the following rules:
- on the eve and on the day of the study, do not douche, do not use sanitary tampons, vaginal suppositories, tablets, creams, lubricants and other means;
- 2-3 days before taking a smear, refrain from sexual intercourse;
- you cannot take the test during menstruation, a few days before and after it;
- 2 hours before the test do not urinate;
- Extended colposcopy cannot be done earlier than 48 hours before oncocytology.
It is also advisable to exclude any unfavorable factors (stress, hypothermia, etc.) on the day of the examination. If a woman is taking any medications, the doctor should be informed about this in advance. In case of an acute inflammatory process in the vagina, a smear for oncocytology is not taken. The test is performed only after anti-inflammatory therapy.
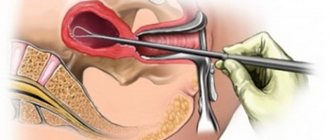
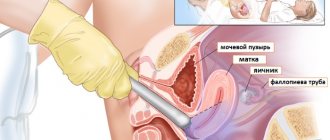
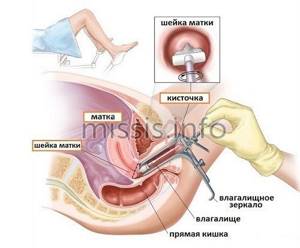
How are smears taken for oncocytology?
The study is carried out during a routine appointment with a gynecologist. The woman sits in a gynecological chair. The doctor inserts a special speculum into the external genital tract to gain access to the cervical part of the uterus. The biomaterial is taken separately from the vaginal area of the cervix and the cervical canal (inner part) using special medical instruments (brush, spatula).
As a rule, the patient does not feel pain during the taking of smears. Hypersensitive individuals may experience short-term minor discomfort. As a rule, an analysis for oncocytology is carried out in conjunction with a bacteriological study of vaginal microflora and HPV testing. Often, smear collection is combined with other procedures (follow-up colposcopy, etc.).
The resulting material is sent to the laboratory for study. Its fixation occurs using one of the standard methods used in oncocytology:
- the biomaterial is applied to sterile glass, then fixed with a special solution and stained, followed by examination under a microscope (PAP test, Papanicolaou method);
- a removable brush with epithelial particles is placed in a special tightly closing flask, the study is carried out using special equipment (liquid oncocytology).
On average, taking a smear takes 10-15 minutes. Glasses and flasks must be marked. They indicate the study number, patient data, sampling site (ecto-, endocervix).
How is cervical oncocytology done?
The resulting smears are studied in the laboratory. For Pap staining, the evaluation is performed by staff using a microscopic examination. If there are a lot of cells and they are layered on top of each other, it is not always possible to draw correct conclusions, so laboratory doctors recommend repeating the test.
Liquid oncocytology is more informative, since biological samples are more “clean” (there is no accumulation of cells, blood elements, etc.). They are prepared and processed by a special computerized system. If necessary, biological material can be subjected to additional diagnostic methods, for example, immunohistochemical analysis. Therefore, it is liquid oncocytology that is considered the standard in the diagnosis of cervical diseases, in particular cancer.
What does oncocytology of the cervix show and how to interpret the analysis
The doctor evaluates the result of the smear for oncocytology. Approximately 10% of tests taken using the Papanicolaou method for one reason or another show an unreliable picture (there were errors during the collection of biomaterial, incorrect transportation, etc.). Good quality samples are graded according to the international Bethesda scale. The latter is not only descriptive, but also determines further medical tactics.
There are the following interpretations of a smear for oncocytology:
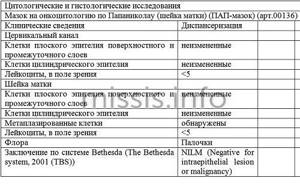
- NILM: no pathological changes, no treatment required.
- LSIL: the smear revealed mild lesions of the squamous epithelium within the mucous layer, which corresponds to a low risk of developing malignant tumors of the cervix, a characteristic picture for HPV infection and GIN-I dysplasia are determined.
- HSIL: significant changes in the epithelial layer are diagnosed, classified as GIN-II and GIN-III dysplasia, that is, atypical cells are detected, which corresponds to a high risk of cervical cancer, therefore further examination and treatment are required.
- GIS: a smear confirms the presence of invasive cancer, the patient is sent for consultation to a gynecological oncologist at a specialized institution.
The Bethesda system also uses the following terms: ASC-US (there are atypical cells, but a specific answer cannot be given due to the unsatisfactory quality of the biological material) and ASC-H (ambiguous result requiring repeated analysis).
Decoding a smear for oncocytology according to Papanicolaou includes five gradations:
- Stage I - cytological picture is within normal limits;
- Stage II - there are inflammatory changes, further examination and treatment are carried out;
- Stage III - a smear for oncocytology shows the presence of a small number of locally changed cells with disturbances in the structure of the nucleus and cytoplasm, which requires a comprehensive examination by the attending physician and additional diagnostic tests;
- Stage IV - malignant degeneration of cellular structures is diagnosed, which indicates severe dysplasia or the development of an oncological process in the cervix, the patient is sent to undergo additional clarifying procedures to confirm the diagnosis (colposcopy, collection of biological material for histological examination, etc.) with subsequent appointment adequate treatment.
- Stage V - a smear for oncocytology confirms the presence of a large number of altered epithelial cells, which largely indicates the presence of an oncological process in the cervix.
One should take into account the fact that each of the ten tests determines the norm. However, doctors advise taking smears at least once every three years, even in absolutely healthy women.
Age-related cell destruction
There are several types of cells that reflect their development:
- Superficially keratinized
- large cells with a small nucleus. - Intermediate
- the overall cell size is smaller. - Parabasal
- the cell size decreases, and the nucleus increases. - Basal cells
are the atrophic type of cells.
Cell atrophy is their almost complete destruction
. They decrease in volume and their functions are impaired. The greater the atrophy, the larger the nucleus of these cells. It occupies almost the entire cytoplasm.
Cause and result
What is the reason for the atrophy of cells taken for cytological analysis from the epithelium of the cervix?
They lack the female hormone estrogen to grow and mature. Estrogen improves blood supply to the vaginal epithelium, promotes the formation of lactic acid and maintains an acidic environment.
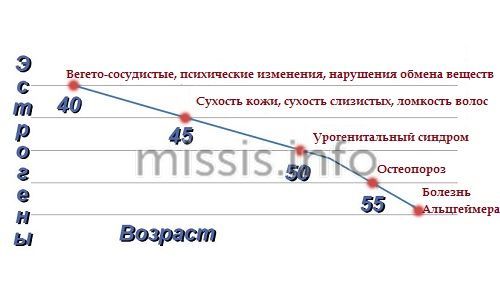
It is the acidic environment that favors the proliferation of beneficial lactobacilli - Doderlein bacilli. In the opposite case - as a result of the appearance of cellular denerates in the tissues of the female organs - there is a proliferation of leukocyte cells and a decrease in protective Doderley bacilli.
The vagina is literally open to infection and subsequent inflammation. Hence the appearance and development of bacterial vaginitis.
Pap smear to determine estrogen levels
It turns out that a cytology smear helps determine not only gynecological problems, but also the general condition of a woman’s body. After all, the level of estrogen affects, for example, the development of osteoporosis. There are 4 levels of the female hormone, each of which tells about the processes in a woman’s body:
- Severe deficiency:
only atrophic cells and leukocytes were found in the epithelium. - Moderate deficiency:
the presence of atrophic, intermediate and leukocyte cells.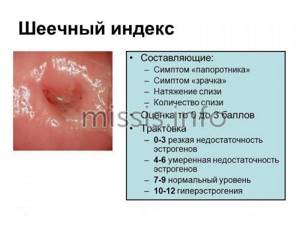
- Moderate deficiency:
the presence of only atrophic and intermediate cells. - Normal estrogen saturation:
only keratinized cells are present.
Hormonal imbalance is typical for older women who entered menopause several years ago.
Moreover, such a phenomenon is taken for granted. If the atrophic type of smear appears in a young woman, then this is a reason to contact the gynecologist again.
Experts believe that an egg is viable for several days, and in order to successfully plan conception, you need to know how long sperm live in the vagina. Read more in the article: “how long do sperm live in the vagina.”
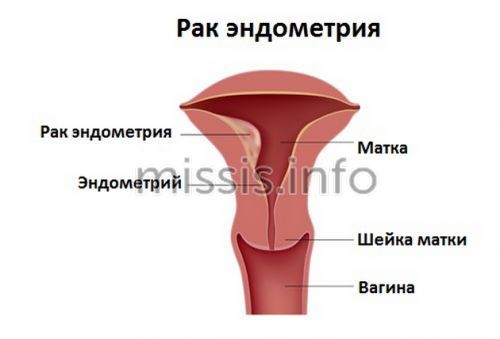
Suspicion of cancer
Atrophied cells in their structure resemble parakeratosis.
These are pathological keratinized tissue particles that signal the appearance of neoplasms, possibly malignant. Therefore, this phenomenon is called pseudoparakeratosis. Once you are diagnosed with cancer, get tested again.
Oncocytology for older women
Despite the fact that in women with the onset of menopause, the risk of developing cervical diseases decreases, a smear for oncocytology is a mandatory test when visiting a gynecologist’s office. If the patient has undergone this study over the past three years, and no pathological changes in the structure of epithelial cells were detected, then in the postmenopausal period it is recommended to repeat the test once every two years.
Provided that the smear was performed irregularly, or there were deviations in its interpretation, doctors advise doing the analysis every year. If the results are negative within three years, repeated studies are not carried out.
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78
Cytology smear
An external examination of the female genital organs, even with the help of modern technology, does not provide the same guarantee in diagnosing the disease that analyzes of biological material provide. One of them is a cytology smear, which has several names, including a smear for atypical cells.
Cytology is a science whose object of study is the cell, its composition, physiological activity and behavior
.
It is interesting that each age has its own characteristics and changes in cellular composition. The material for study is taken using a small disposable brush from the surface of the uterus. Several cells taken from a woman will tell you about the condition of the genital organs in a simple and accessible way. They take into account what size, what shape the cells are, how many there are and how they are located. The main goal is to detect atypical cells in time
in order to identify malignant tumors in the early stages. Therefore, this analysis is often called oncocytology.
You have taken a smear and within 24 hours the result will be known, which may or may not please you. After all, it is after cytology that the terrible diagnosis of cancer is made. But if you have an atrophic type of smear, what does this mean?
Gardnerellosis causes active reproduction of an anaerobic bacterium - gardnerella. It is found in limited quantities on the vaginal mucosa, but sometimes its growth increases, which leads to inflammation and disruption of microbiocenosis. Read more in the article: “Gardnerellosis: causes of occurrence in women.”