What tumor markers show and how to get tested correctly
Analysis for tumor markers allows you to:
• find out whether the patient is at risk; • roughly identify the affected organ; • suspect a relapse of oncology;
When receiving test results for tumor markers, special attention should be paid to:
• for increased performance; • appears to have elevated tumor markers.
Changes in indicators indicate that there are deviations from the norm in the human body, including progressive cancer cells. The main advantage of the analysis is that tumor markers show the presence of cancer in the early stages, which is very important for the effectiveness of treatment.
What are the indications for the need for analysis?
Testing for oncology is mandatory for all persons over 50 years of age who have a hereditary predisposition and are employed in enterprises whose activities involve chemicals and toxic substances (primarily workers with extensive work experience).
Timely testing makes it possible to identify tumor markers for cancer of the pancreas, stomach, esophagus and other organs at an early stage, which increases the risk of recovery.
In addition to the above, the main indications for analysis are:
- Primary and prognostic examination of the oncological process in the stomach and intestines, as well as their mucous sides.
- Checking the effectiveness of ongoing treatment procedures.
- Observation after treatment and prevention of relapse and metastases.
Rules for taking the analysis:
- blood is donated from a vein on an empty stomach, excluding food intake 8 hours before the procedure; — analysis is carried out until 11 a.m.; - three days before the test, stop drinking alcohol and junk food, reduce physical activity; - on the day of the analysis, smoking and taking medications are prohibited; - when taking a PSA test, abstain from sexual intercourse for seven days.
Tumor markers are found in the blood and urine of children, young, adults and elderly patients. In most cases, such an analysis shows the presence of cancer cells six months earlier than other diagnostic methods.
It is important that tumor markers show even the slightest changes and help solve the following problems:
1. Monitoring the effectiveness of therapy, which allows in some cases to change the treatment regimen or change medications. 2. Monitoring tumor recurrences, monitoring the appearance of new metastases. This will help you start re-treatment on time and not miss the disease. 3. The analysis will help decide which therapy methods should be used. 4. A tumor marker helps to assess the extent to which an organ is affected by cancer cells and the degree of progression, which helps to select a more adequate treatment regimen. 5. The analysis helps to assess how remission is progressing and make a prognosis for the patient’s life expectancy.
What can distort the result
Sometimes it happens that the data obtained may be somewhat distorted. Most often, this happens when all recommendations regarding preparation for a blood or feces test are not followed.
Also, unreliable data may occur if a specialist makes mistakes during the examination of the obtained biomaterial.
In addition, a false positive result may occur when taking the test at the time of development of acute inflammation or in chronic pathologies at the acute stage. Antigens can increase with diseases such as flu, bronchitis or dental problems.
Who needs analysis and when?
Screening tests should be carried out 1-2 times a year for those patients who have a genetic predisposition, benign neoplasms, suspicious papillomas and moles. Other people can be tested no more than once every two years, and also:
• after severe nervous strain; • when living in unfavorable environmental conditions; • under other circumstances that may cause cancer.
People are recommended to do screening tests more often:
• with a diagnosis; • with a treated malignant tumor; • upon initial detection of a neoplasm; • before and after surgery; • during a course of therapy.
Those who have recovered are recommended to check their tumor marker levels within 3 years after treatment is completed:
1. First year – every month. 2. Second year – once every two months. 3. Third year – once every three months. Subsequent years are analyzed every six months. Before screening, the patient must visit an oncologist, who will find out which markers need to be tested for.
What tumor markers are used to diagnose stomach cancer?
CA-19-9
This marker is produced by epithelial cells of the gastrointestinal tract. Accordingly, in tumors originating from these cells, the level of CA19-9 increases significantly. The indicators change most with pancreatic cancer, but can also increase with cancer of the colon, liver, bile ducts and gallbladder, pancreatitis, and cystic fibrosis. Thus, given the low sensitivity and specificity, this indicator is not used for self-diagnosis and monitoring.
REA
CEA (carcinoembryonic antigen) is a protein, a tissue marker of oncopathology. It is used in the diagnosis of colon tumors, but can also be effective in stomach cancer. Normally, its levels are extremely low, but in the presence of a malignant neoplasm, its level increases sharply.
SA 72-4
CA 72-4 is a glycoprotein that is located on the surface of the epithelium of the gastrointestinal tract during human intrauterine development. In adults, it appears with colorectal cancer, stomach cancer and other malignant tumors. However, in 6.7% of patients, its increase was also detected in the presence of benign tumors.
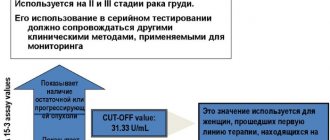
Sensitivity for stomach cancer is 40-46%, and the higher the tumor marker, the more widespread the malignant process, i.e. there is a correlation with stage. After radical removal of cancer, the CA value of 72-4 returns to normal within 3-4 weeks. As for metastases, this tumor marker for stomach cancer is more sensitive than CEA or CA 19-9. The determination of CA 72-4 is carried out to assess the chances of survival in patients with an established diagnosis of gastric carcinoma. The higher the tumor marker, the higher the stage of the disease.
REA

The CEA marker is secreted mainly by the digestive tract of the fetus. In adults, the substance is found in the blood in minimal quantities.
Normal: up to 6.3 ng/ml. A slight increase in CEA norms is determined in smokers. With high marker levels, there is a risk of neoplasms in the following organs:
- digestive tract; - mammary gland; - prostate; - liver; - lungs.
CEA analysis is recommended if:
• shortness of breath, causeless cough; • appearance of a visible tumor; • chronic fatigue; • unreasonable loss of strength; • sweating; • prolonged increase in body temperature; • weight loss; • appearance of new moles; • loss of appetite or complete reluctance to eat with attacks of nausea and vomiting; • disturbances in the functioning of the digestive tract.
Where can I donate tumor markers?
To undergo such tests, it is better to choose specialized clinics. Therefore, it is advisable to consider medical institutions that have the necessary equipment and qualified specialists who are able to correctly interpret test results.
In this case, the patient will be able to get the correct diagnosis the first time, and he will not have to waste personal time on additional research. You can also get tested at regular municipal clinics. But practice shows that after these examinations, patients turn to specialized institutions for a retake.
Elevated tumor marker (PSA)
PSA is a protein secreted by the prostate gland. A tumor marker will help identify a prostate tumor, adenoma. The analysis is used to monitor therapy.
Normal: up to 4.1 ng/l. If the norm is exceeded, then tumor markers indicate the presence of malignant pathology in the prostate. Experts recommend that men over 50 years of age be tested for prostate-specific antigen annually. This will help identify prostate diseases in the early stages, which will simplify therapy and make it as effective as possible.
To properly prepare for the analysis, you need to:
• stop eating food 10 hours in advance; clean, still water is recommended, other drinks are excluded; • you need to stick to a diet for two days; • you should not play sports and put as much stress on yourself as possible for several days. • seven days not to be sexually active.
What are gastrointestinal tumor markers?
Tumor markers of the gastrointestinal tract are protein compounds formed in cancerous tumors.
They also talk about problems in the tract that require further investigation and treatment. The information content is quite high, but not sufficient for a clear diagnosis. It cannot be said that a patient has cancer based on an increase in the number of tumor markers of the stomach and other digestive organs. After all, their level can increase with compactions of a non-oncological nature. Pathological protein compounds, if present, can be detected in the blood and urine. If they exist and there are a lot of them, this is a serious reason to undergo a full examination in a specialized institution.
Since oncology of the digestive system is common and cases of detection of tumors in young people are becoming more and more frequent, diagnosis becomes especially necessary and should be as informative as possible in order to identify the pathology at the time of its inception or at least at the stage of early development.
In this case, the chance of recovery is much higher than if the detection is recorded later. Consult an Israeli specialist
AFP analysis: detailed characteristics
Alpha fetoprotein or AFP is a tumor marker used to detect liver cancer. The antigen is characterized by increased sensitivity, the concentration of AFP in the body increases in 95% of patients with liver cancer. Moreover, in half of the cases, the increase in this substance occurs 2-3 months earlier than the first symptoms of the disease appear. AFP analysis is used
and for the purpose of diagnosing other diseases.
What is this - AFP?
AFP is a glycoprotein that is produced in the fetal gall sac, intestinal epithelium and fetal liver. The tumor marker is directly involved in its full development. In the body of adults, the antigen is absent or present in minimal quantities. A slight increase in the tumor marker value may indicate liver pathology, a serious increase may indicate a poorly differentiated tumor, liver cancer. A sharp increase in AFP is characteristic of cancer of the gonads and liver; this study is highly informative for certain tumors of the ovaries and testicles.
Donating blood for AFP tumor markers is prescribed as an additional diagnostic tool if the patient is suspected of having tumor processes in the gallbladder and bile ducts, but in such a situation the analysis is combined with a test for CA 19-9.
Problems solved by AFP analysis
Analysis for the tumor marker alpha-fetoprotein
solves several problems.
- Testing for AFP tumor markers is used for prenatal diagnosis of abnormalities in the development of the unborn child. This may be anencephaly (a pathology in which part of the fetal brain is simply missing), failure of the neural tube, chromosomal abnormalities and other pathologies, which will be indicated by a deviation in the level of AFP concentration in the body of the expectant mother from the norm.
- Donating blood for AFP tumor markers is necessary to diagnose liver cancer (primary hepatocellular carcinoma). (Carry out if indicated).
- AFP testing can detect testicular teratoblastoma.
- Testing for this tumor marker is a tool for diagnosing poorly differentiated tumors.
- The analysis is carried out to detect liver metastases (tumors of various locations).
- AFP testing is a mandatory step in monitoring the effectiveness of cancer treatment.
When is an AFP test prescribed?
A doctor may order an AFP test for a patient in the following situations.
- During a comprehensive examination with a high probability of tumor development (chronic hepatitis, liver cirrhosis, lack of alpha-antitrypsin).
- If the doctor suspects liver damage in a patient due to tumor metastases.
- Before, during and after treatment for certain cancers.
- As part of monitoring the condition of patients who have undergone tumor removal.
- An AFP test can be prescribed in the 2nd trimester of pregnancy (that is, 15-21 weeks), this is an important tumor marker for women.
- Testing for the tumor marker AFP is advisable for pregnant women who have undergone chorionic villus sampling and amniocentesis in early pregnancy.
When performing an AFP test, the patient's blood is examined, which is taken from a vein. The examination is carried out in the morning. The cost and timing of obtaining test results for AFP tumor markers depend on the specific laboratory.
How to prepare for AFP tests
The accuracy of the results of a blood test for AFP is guaranteed if the preparation for the study is followed.
Test results for AFP tumor markers may deviate from the norm not only due to the presence of diseases in patients, but also due to the use of monoclonal antibody drugs. A decrease in the blood concentration of AFP in a pregnant woman can also cause insulin-dependent diabetes.
In order to avoid receiving erroneous test results for the level of AFP tumor markers, the patient must warn the doctor about all the medications he is taking and about all the diseases present. If the patient takes large doses of biotin (exceeding 5 mg per day), an AFP test can be performed only 8 hours after the last use of the drug.
Other preparation rules
Preparing to donate blood for tumor markers involves the following steps.
- 10 days before the blood test for AFP, the patient is recommended to adhere to a certain diet, refusing fatty and fried foods, eggs, chocolate, and confectionery. The menu should be dominated by vegetables, fruits, and cereals.
- It is important to donate blood for AFP testing in the morning and on an empty stomach. If it is not possible to take the test in the morning, you must wait at least 5 hours from the moment of your last meal. Drinks allowed are pure water without gas.
- Three days before the analysis, it is advisable to stop physical activity. It is recommended to devote more time to rest.
- You need to stop drinking alcohol 3 days before; you can start abstaining from cigarettes approximately two hours before the test. Sexual contacts are not recommended for two days.
- If, in agreement with the attending physician, the patient's medication has been suspended, ideally you should wait about 10 days after discontinuation.
- If the purpose of testing for AFP markers in the body is to monitor the effectiveness of treatment, it is best to choose the same hours and the same laboratory for donating blood.
- Medical procedures (instrumental, x-ray examination, massage, etc.) can also distort the results of blood tests for AFP.