Price list Doctors clinic
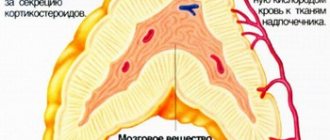
The adrenal glands are a paired organ that produces hormones important for adaptive, protective mechanisms. The latter provide the body’s natural reactions to stress, loads, and environmental changes. They control thermoregulation, water-electrolyte balance, blood vessel tone, metabolism, and the production of collagen fibers. In addition, they are responsible for the body’s reaction during inflammatory processes and the intake of allergens. Testing the function of the adrenal glands allows you to prevent dysfunction of many organs and systems.
Diseases of the adrenal glands can manifest themselves either by an increase or decrease in the level of hormones produced. In some cases, the synthesis of one hormone is impaired, in others, the pathology extends to all hormones. In both cases, it is necessary to take measures to correct the condition.
When should you take an ACTH test?
- Sudden and pronounced change in weight.
- Migraine, back pain.
- Fatigue, lethargy, apathy, depression, insomnia.
- Acne in adults.
- Increased body hair in women, disruption of the menstrual cycle.
- Hyperpigmentation of the skin in areas not exposed to ultraviolet radiation.
- Early onset of puberty.
- Deviation from the norm in the concentration of cortisol in the blood.
- Treatment with glucocorticosteroids for a long period.
- Suspicion of pituitary adenoma.
- Diabetes.
- Osteoporosis, discomfort, bone pain, crumbling teeth.
- Infertility.
Aldosterone
Aldosterone is a hormone of the adrenal cortex that affects the human kidneys by controlling water-salt balance (sodium, potassium concentrations). Under the influence of this substance, chlorine and sodium are retained by the renal tubules, resulting in a reduction in the excretion of fluid in saliva and urine, and the removal of potassium from the body is activated. Aldosterone ensures the maintenance of blood pressure; if its concentration increases, problems arise such as decreased muscle tone, high blood pressure, the appearance of edema, convulsions, and heart rhythm disturbances.
Indications for analysis:
- the patient is suspected of having adrenal insufficiency;
- high blood pressure is present;
- diagnosis of adrenal hyperplasia, adrenal adenoma;
- orthostatic hypotension;
- suspicion of primary hyperaldosteronism.
Detailed description of the study
ACTH is a pituitary hormone, the most important regulator of the function of the adrenal cortex.
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) is a chemically active protein. It is produced by the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland.
With the bloodstream, the hormone reaches the target organ - the adrenal glands. By acting on their cortical layer (superficial part), adrenocorticotropin stimulates the release of adrenal hormones - cortisol, cortisone, corticosterone. Corticotropin indirectly affects the release of adrenaline, female and male sex hormones.
Biochemical and physiological effects of adrenocorticotropin:
1. Resisting stress. In situations of overstrain (emotional and physical overload, cold) it increases the concentration of the steroid hormone cortisol, which helps mobilize the body's resources.
2. Effect on brain structures. The psychoemotional state of a person depends on the increase or decrease in ACTH concentration. Lack of the hormone leads to depression, memory impairment, and suppression of cognitive functions.
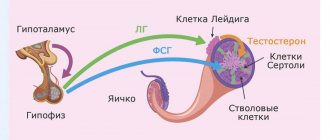
3. Stimulation of the production of sex hormones. Under the influence of ACHT, the adrenal glands increase in volume and produce more progesterone, estrogen, and testosterone.
4. Participation in the process of cholesterol synthesis, which is necessary for the construction of cell walls, the formation of vitamin D, and red blood cells.
5. Increased skin pigmentation. Adrenocorticotropic hormone stimulates melanocytes, which produce the pigment melanin.
6. Regulation of weight, muscle volume. Adrenocorticotropin affects the increase or decrease in appetite, the removal of fat from subcutaneous tissue, and is involved in the regulation of glucose metabolism (accumulation of glycogen in muscles). Stimulates the release of insulin from pancreatic beta cells (along with other regulatory factors). Activates the absorption of amino acids and glucose into muscle tissue. The main causes of disruption of corticotropic hormone production:
- diseases of the pituitary gland: decreased (hypofunction) or increased (hyperfunction) activity;
- disruption of the adrenal cortex;
- abnormal external secretion of corticotropin due to the presence of a tumor in the body (ectopic corticotropin production syndrome, EPS).
DEA-s
DHEA-c is an androgenic, steroid hormone that is produced by the adrenal cortex. This substance is required by the human body for the formation of estrogen and progesterone. Excessive amounts of DHEA-s can cause spontaneous miscarriage, fraught with fading and termination of pregnancy.
Indications for testing for the hormone DEA-c:
- adrenogenital syndrome;
- recurrent miscarriages;
- fetal hypotrophy;
- tumors in the adrenal cortex;
- delayed puberty;
- diagnostics of the fetoplacental system (for pregnant women).
On average, the execution time is one or two days.
References
- Nazarenko G.I. Clinical assessment of laboratory research results / G.I. Nazarenko, A.A. Kishkun - M.: Medicine, 2006 - 543 p.
- Allen MJ; Sharma S. Physiology, Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH) March 3, 2021 URL: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK500031/ (accessed 01/10/2020)
- Fish S., MD Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH), October 2019 URL: https://www.hormone.org/your-health-and-hormones/glands-and-hormones-a-to-z/hormones/adrenocorticotr… ( access date 01/10/2020)
How to prepare for tests for adrenal hormones
Tests for adrenal hormones are an effective medical tool, the use of which allows you to effectively diagnose a huge number of diseases. Of course, the test results will be as reliable as possible only if the patient takes the rules of preparation for them responsibly and strictly follows them. Therefore, you need to be interested not only in the cost of blood tests, but also in the preparation rules. So, what should and should not be done before testing for these substances?
The rules for preparing for research vary, depending on what specific type of analysis we are talking about, this is of paramount importance. As a rule, doctors prescribe DHEA-c, total cortisol and aldosterone.
Preparation for analysis for DEA-s
If a patient is to take a blood test for the level of the hormone DEA-c, first of all, he needs to avoid physical stress and emotional turmoil three days before the tests, reduce the level of physical activity (preferably, completely abandon it), and not smoke too often. It is recommended to donate blood on an empty stomach, do it in the morning, from 8 to 11. If it is not possible to donate blood in the morning, you can reschedule the test for another time, avoiding eating 6 hours before it.
Also, before taking a blood test for this hormone, it is recommended to stop taking the following medications: oral contraceptives, hydrocortisone, diprospan, dexamethasone, estrogens, prednisolone. When donating blood, be sure to inform the nurse that you are taking medications that may affect the concentration of hormones.
Preparing for a total cortisol test
When planning to take an analysis for the concentration of the hormone cortisol in the blood, it is very important to refrain from taking opiates, estrogens, and oral medications. If stopping treatment for one reason or another is not possible, you should definitely discuss this problem with your doctor. In addition, it is not recommended to smoke, play sports, or allow physical activity the day before the test.
Preparing for an aldosterone test
It is advisable that the patient, whom the doctor has recommended to take a blood test for aldosterone levels, follows a low-carbohydrate diet for two weeks before collecting biological material; the amount of salt is not limited. Also, before carrying out the analysis, intense sports exercises and stressful situations should be completely excluded, since such factors can cause such a temporary phenomenon as excessive concentration of aldosterone.
In addition, in preparation for a urine or blood test for adrenal hormones, it is advisable to stop taking medications that can affect the exchange of potassium and sodium ions in the body. These are all kinds of antihypertensives, diuretics, estrogens, oral contraceptives, steroids. It is best to consult your doctor about taking a break from treatment.
Thyroid hormones
Tests for thyroid hormones (TG) are performed to diagnose diseases of the endocrine system and metabolic disorders. Based on the test results, additional studies are prescribed that will help clarify the diagnosis and create the most effective treatment program.
In the medical offices of the Health Laboratory CDC, you can take a blood test (thyroid hormones) to study indicators such as:
- TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone),
- TZ (total triiodothyronine),
- T3 St. (free triiodothyronine),
- T4 (total thyroxine or tetraiodothyronine),
- T4 St. (free thyroxine or tetraiodothyronine),
- TG (thyroglobulin).
The general list of indicators that include a hormonal blood test is determined by an endocrinologist.
Where to get tested for adrenal hormones in St. Petersburg
All this is just general information; only a professional doctor (endocrinologist, gynecologist) can correctly decipher an analysis for adrenal hormones. You can take such tests in St. Petersburg and get specialist advice on the results at the Diana Clinic.
CLICK TO SIGN UP
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter
Study of exogenous pancreatic function
Laboratory diagnosis of the pancreas includes tests for the main hormones and enzymes produced by this organ. Such substances are markers of the condition of the gland. An increase or decrease in their concentration indicates the presence of serious pathologies.
The pancreas is one of the main organs of the human endocrine system. It regulates metabolism in the body and the functioning of the digestive system.
Most often, laboratory diagnostics of the pancreas is prescribed to patients with gastrointestinal disorders. In this case, special attention is paid to the pancreatic elastase indicator. To assess its concentration, it is necessary to conduct a stool test.
Patients who have elevated sugar levels need to take a blood test for insulin. This will allow you to determine the type of diabetes and select the optimal treatment.
If laboratory diagnostics show an increase in the concentration of the hormone, it is necessary to undergo a proinsulin test. Insulin synthesis occurs by breaking down this substance. An increase in proinsulin levels may indicate the presence of insulinoma, a malignant tumor of the pancreas.
When the proinsulin molecule breaks down, the hormone and enzyme C-peptide are formed. The substances are synthesized in equal volumes, so the concentration of C-peptide allows us to determine the level of insulin secretion. The analysis is prescribed for insulin-dependent patients. The amount of C-peptide does not change under the influence of artificially synthesized hormones. Diagnostics allows you to assess the condition of the organ even while taking insulin.
Laboratory diagnosis of pancreatic functions - a comprehensive study. Check with your doctor for the order of tests and preparation rules.
results
Reference values:
- adrenaline: 10 - 85 pg/ml;
- norepinephrine: 95 - 450 pg/ml;
- dopamine: 10 - 100 pg/ml.
Catecholamine levels may be increased by:
- pheochromacytoma;
- myocardial infarction;
- traumatic brain injury;
- ketoacidosis in patients with diabetes mellitus;
- neuroblastoma;
- paraganglioma tumor;
- chronic alcoholism;
- manic-depressive psychosis in the manic phase.
Catecholamine levels may be reduced if:
- acute and chronic renal failure;
- underdevelopment of the adrenal medulla;
- manic-depressive psychosis in the depressive phase.
Stomach hormones
Analysis of stomach hormones allows you to determine various diseases of this organ. In the laboratory of the CDC “Health Laboratory” they check the gastrin content in the blood. The compound is the most significant marker in determining Zollinger-Ellison syndrome. An increase in hormone levels is found in 93% of patients. The concentration increases due to the tumor of the cells that produce gastrin.
An increase in concentration also indicates:
- chronic atrophic gastritis,
- megaloblastic anemia,
- stomach ulcer,
- stomach cancer.
Analyzes show an increase in secretion under stress, increased levels of glucocorticoids, and intake of prostaglandin biosynthesis inhibitors. During the study, the formation of “stress” stomach ulcers and gastritis caused by non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs becomes clear.
A decrease in the level of the stomach hormone is observed after a gastrectomy or with hypothyroidism - a lack of compounds produced by the thyroid gland.
The results of tests for stomach hormones are used in the differential diagnosis of diseases leading to an increase in gastrin levels. For this purpose, preliminary stimulation with calcium chloride or secretin is used.
The concentration of the stomach hormone is directly related to the circadian rhythm and food intake. From three to seven o'clock in the morning the amount of the substance reaches its lowest value, increasing during the day and after meals.
The blood test must be taken in the morning, on an empty stomach. The material for research (microanalysis) is blood with EDTA. You can donate biomaterial at any of our offices or at home.
Complexes with this research
Metabolic profile RUR 5,900 Composition
Adrenogenital complex Analysis of excess male hormones in a woman RUR 2,560 Composition
Expanded anti-aging diagnostics in postmenopause Expanded monitoring of age-related changes during postmenopause RUB 29,230 Composition
IN OTHER COMPLEXES
- Advanced women's anti-aging diagnostics RUB 28,680
- Three important indicators for a man RUB 1,810
- Advanced male anti-aging diagnostics RUB 33,710
- Anti-aging diagnostics in postmenopause RUB 12,630
- Women's anti-aging diagnostics RUB 12,070
Adipose tissue hormones
Hormones of adipose tissue are involved in energy and other types of metabolism. The laboratory can test the level of leptin, a compound that regulates body weight. If the body is genetically unable to produce sufficient amounts of the hormone, severe obesity may occur.
In other cases, the content of the substance in the blood increases with the addition of adipose tissue and decreases with weight loss. Normally, the level of the hormone in adipose tissue is involved in the formation of hunger. A decrease in the amount of the substance after severe weight loss leads to increased appetite and weight gain.
Leptin tests help assess the possibility of developing type II diabetes. It has been established that an excessive amount of leptin leads to disruption of insulin production and the emergence of resistance of adipose tissue to its effects. Insulin does not act on the liver and because of this, glucose levels rise.
Excessive amounts of leptin increase the risk of thrombosis. Blood clots are formed by the interaction between the hormone and the sensitive ends of platelets - the cells responsible for blood clotting.
A decrease in hormone levels is one of the factors in amenorrhea, which develops due to anorexia and bulimia. Lack of connection is also typical during excessive physical activity.
Determining the level of adipose tissue connection is important in diagnosing pathologies of the heart and blood vessels. It is known that the amount of the hormone affects the development of these diseases, regardless of other prerequisites, such as high cholesterol or smoking