At the Yusupov Hospital, doctors from the oncology clinic conduct a comprehensive examination of a patient who is suspected of having a malignant neoplasm. For instrumental procedures, we use the latest diagnostic equipment from leading global manufacturers. Laboratory studies are carried out using high-quality modern reagents. This allows you to determine the level of leukocytes in oncology.
Patients at the oncology clinic are advised by related specialists. An integrated approach to examining a patient makes it possible to establish a diagnosis of cancer at the initial stage of the tumor process, carry out radical treatment with the most effective medications and apply innovative surgical techniques.
Patients of the oncology clinic have the opportunity to undergo complex diagnostic procedures and get tested for cancer at leading research institutes with which the Yusupov Hospital cooperates. The research results are interpreted by doctors of the highest qualification category, candidates and doctors of medical sciences. Leading specialists in the field of oncology at a meeting of the Expert Council collectively establish a diagnosis and develop optimal tactics for managing the patient.
Why get tested for cancer?
Doctors note that Russian cancer patients seek help quite often already at the last, advanced stage of the disease, and, accordingly, with extremely low chances of cure. Scolding medicine, people themselves often treat their health quite negligently, ignoring preventive examinations and examinations, and sometimes, even at the first symptoms of the disease, they prefer self-medication and the advice of friends, wasting precious time. In addition, few of them are informed about what blood test shows oncology and whether the blood test changes in oncology.
Any oncologist can tell you that cancer is often preceded by a precancerous stage. Tumors, except skin cancer, affect internal organs, therefore they are invisible to the eye and may not manifest themselves in any way in the initial stages. Therefore, the sooner you begin to control the changes occurring in the body and directly in the blood, the sooner you can diagnose the onset of a serious pathology, thereby increasing the chance of recovery and life.
Oncologists at the Yusupov Hospital recommend undergoing a timely blood test for oncology if you suspect the presence of tumors. Verification of the diagnosis in the early stages significantly increases the chance of cure.
Make an appointment
Diagnosis of cancer at an early stage
Early diagnosis of cancer is critically important for every person, since this significantly increases the chance of successful treatment. For example, the five-year survival rate for early stages of squamous cell carcinoma is more than 90%, provided timely diagnosis and adequate therapy. Outcomes for patients with advanced stages of this cancer are much worse - in the presence of lymph node metastases, the five-year survival rate is only 25-45%. With T-cell lymphoma, the difference in outcomes is even greater: in the early stages, ten-year survival rates reach 97–98%, while in later stages it is only 20%.
Specialists from the American Cancer Society conducted long-term observations of the treatment outcomes of patients with melanoma, one of the most malignant skin cancers. It was found that the prognosis for successful treatment increases significantly when melanoma is detected in the early stages:
- Localized tumor that does not extend beyond the skin - 98%
- Regional spread with invasion of nearby lymph nodes - 64%
- Distant metastases in the lungs, liver and other organs - 23%
Similar figures can be found for any type of malignant tumor. For example, the five-year survival rate of patients with stomach cancer increases significantly when diagnosed early:
- Localized tumor that does not extend beyond the gastric mucosa - 68%
- Regional spread with invasion of nearby lymph nodes - 31%
- Distant metastases in the liver and other organs - 5%
All this speaks to the incredible importance of timely diagnosis of cancer, since only in this case can a high probability of successful treatment and a favorable outcome be guaranteed. Each person should not only regularly undergo a general examination of the body for cancer, but also independently pay attention to the first signs of cancer. After all, the body often signals problems - you just need to listen to it carefully.
In what cases should you take tests for oncology?
Any disruptions in the functioning of the body are reflected in the composition of the blood. In order not to miss the onset of malignant processes, which often occur asymptomatically, an oncology test should be carried out for the following disorders:
- inflammatory processes that cannot be treated, protracted chronic diseases;
- lack of response of the pathology to the action of drugs that previously contributed to the cure;
- a noticeable decrease in immunity;
- frequent increase in body temperature without objective reasons;
- a sharp decrease in body weight;
- inadequate reaction to odors;
- decreased appetite;
- unexplained pain;
- general weakness and malaise;
- the appearance of difficulties when swallowing food;
- prolonged cough that cannot be treated;
- uterine bleeding or unusual vaginal discharge;
- wounds and fistulas that do not heal for a long time;
- chronic constipation, the appearance of blood in the stool;
- deformations of the mammary glands;
- for preventive purposes (at least once a year).
changes in the color and shape of moles;
If the above symptoms appear, contact Yusupov Hospital. Doctors, using the latest diagnostic methods, will establish their true nature by checking the level of leukocytes in oncology.
What studies can show oncology?
1. Complete blood count - shows the total number of red blood cells, platelets, leukocytes and other blood cells. When the indicators deviate from the norm, this may indicate the presence of a malignant neoplasm.
2. Biochemistry. With its help you can find out the chemical composition of the blood. This analysis allows us to identify where a malignant tumor develops in the human body.
3. Tumor markers. This is perhaps the most accurate test for detecting cancer. As soon as malignant cells appear in the body and undergo mutation, they release tumor markers into the blood. Since the body does not accept such protein, it immediately begins to fight it. Each tumor has its own tumor markers, with the help of which the doctor immediately knows which organ was affected.
Preparing for a blood test for cancer
To obtain reliable test results, patients should adhere to certain recommendations before taking blood:
- 2 weeks before the test, stop taking systemic medications;
- 2-3 days before the analysis, exclude fatty and fried foods and alcoholic beverages from the diet;
- stop smoking 2 hours before blood sampling;
- 30 minutes before the procedure, bring your emotional state back to normal, avoid mental and physical stress;
- In order to avoid obtaining distorted results, do not conduct analysis immediately after performing other types of examination (laboratory or instrumental).
You can eat food before a general blood test, but it is better not to eat eight hours before the test. To obtain a correct, undistorted result of a biochemical blood test, fasting is recommended before the test (8-12 hours). It is allowed to drink liquid in the form of purified still water.
Is it possible to determine oncology using laboratory diagnostics of cancer?
A blood test may indicate an imbalance in the body and the need for additional research to identify the exact cause of the changes occurring. Indicators may change due to previous illness, alcohol abuse, smoking, pregnancy and many other conditions.
Not all tumor markers are specific. Oncologists at the Yusupov Clinic strongly recommend that patients not rush to conclusions, since only an oncologist can correctly interpret all test results if cancer is suspected.
Whether a general blood test will show oncology is a question to which it is impossible to give a definite answer. Clinical analysis is a basic study, the results of which can be used to judge certain disorders that require a more detailed examination. It is impossible to accurately determine the presence of malignant tumors. In case of unfavorable changes in blood composition, an experienced general practitioner will prescribe a blood test for cancer markers, which will finally confirm or rule out abnormalities in the general blood test for oncology.
Make an appointment
What tests will indicate cancer?
Self-examination of the body and a visit to a medical specialist are important criteria for timely diagnosis of cancer. However, there are a number of laboratory methods that can also help in identifying malignant tumors.
- A complete blood count is a common and even “routine” method that involves counting different types of blood cells. It can help suspect blood cancer if too many or too few of certain types of cells are detected, or if abnormal blood cells are present. A bone marrow biopsy may be ordered to confirm the diagnosis of cancer.
- Biochemical blood test - provides general information about the metabolism and functioning of internal organs: pancreas, liver, kidneys, gallbladder, etc. Certain changes in blood biochemistry may indicate the presence of a particular cancer, for example prostate.
- Plasma proteins - This test helps identify special proteins in the blood plasma called immunoglobulins. Their numbers may be increased in patients with multiple myeloma and other types of blood cancer.
- A blood test for tumor markers is classified as a clarifying test and cannot serve as the main method of detecting cancer.
Tumor marker tests are based on detecting chemicals produced by tumor cells in the blood. There is no universal test that can accurately indicate the presence of a particular cancer. This is because levels of these chemicals can also increase in some non-cancerous conditions. Below are the most popular tumor markers - which ones to take for prevention and what they can show:
- prostate-specific antigen (PSA) - prostate cancer;
- carbohydrate antigen 125 (CA-125) - ovarian cancer;
- calcitonin - medullary thyroid cancer;
- alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) - liver cancer;
- human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) - testicular and ovarian cancer.
CancerSEEK blood test is aimed at identifying malignant tumor cells circulating in the blood. It is also called liquid biopsy.
The above tests help the doctor suspect the presence of a malignant tumor in the body. However, to confirm cancer, a diagnostic biopsy is required - taking a piece of tissue from a suspicious area for histological examination. Only under a microscope can one reliably determine whether a particular formation is a malignant tumor, as well as determine the type.
A biopsy can be taken from the surface of the skin, mucous membranes, internal organs, muscles, bones, etc. In some cases, a diagnostic minimally invasive operation is performed using an endoscope.

Examination if a tumor is suspected
Oncologists begin examining the patient with questioning, examination, palpation, percussion, and auscultation. After the clinical study, a list of necessary tests and instrumental diagnostic studies is drawn up.
What tests show oncology?
In accordance with the location and size of the tumor formation, a clinical blood test shows cancer in cases where the level of leukocytes is increased, platelet and hemoglobin levels are decreased, and lympho- and myeloblasts are detected. A particularly alarming sign is an increased number of young (immature) forms of leukocytes.
Complete blood count: ESR indicators
The results of a general blood test for oncology show an increased ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate). However, an increase in this indicator is also observed in other pathologies, for the treatment of which anti-inflammatory and antibacterial therapy is prescribed. If such treatment is not effective and the ESR is still high, the patient may be suspected of having a malignant tumor.
However, these indicators are not absolute confirmation of the presence of cancer. For a more detailed study, a biochemical blood test is prescribed; in case of cancer, a test for tumor markers is prescribed.
How to check for cancer of the whole body?
At the Yusupov Hospital, laboratory assistants determine the number and ratio of tumor markers in biological fluids. Tumor markers are protein compounds (antigens) that are produced by cancer cells. They are present in small quantities in a healthy body. In the presence of a malignant tumor, the level of tumor markers increases. Determination of tumor markers allows:
- confirm or exclude the presence of a malignant tumor;
- identify suspected metastases from the cancer process;
- monitor the effectiveness of treatment;
- clarify the nature of the tumor (benign or malignant);
- evaluate the effectiveness of cancer treatment.
Depending on the expected location of the tumor, oncologists at the Yusupov Hospital take an individual approach to the choice of tumor marker:
- The level of CA 125 antigen is determined for endometrial cancer of the uterus or ovaries;
- If cancer of the digestive organs is suspected, the level of tumor markers CA 72-4, CA 19-9 is examined;
- The presence of a malignant breast tumor is indicated by an increased concentration of the tumor marker CA 15-3 in the blood;
- Identification of tumor markers CEA, NSE, CYFRA 21-1 may indicate the localization of a malignant tumor in the lungs and other organs;
- In liver cancer, the concentration of AFP-embryonic glycoprotein increases.
To perform the test, nurses draw blood from a vein on an empty stomach. The study is carried out several times to assess the amount and dynamics of cancer markers in the blood.

Tests for cancer cells
Based on the results of a biochemical blood test, one can judge the localization of the tumor formation, the stage of its development, the size of the tumor, and possible reactions of the body.
Due to the fact that the process of tumor growth is accompanied by the release of specific antigens depending on which organ it affects, the rate of increase in the amount of these antigens in the blood allows us to predict how quickly oncopathology develops and determine the prognosis. Often, thanks to the identification of tumor markers, pathology can be diagnosed before the appearance of clinical symptoms, that is, in the early stages of the disease, which, with adequate treatment, significantly increases the chances of recovery.
There are many other tumor markers, and new ones are constantly being created, with the help of which doctors at the Yusupov Hospital have the opportunity to identify other forms of malignant pathologies.
Make an appointment
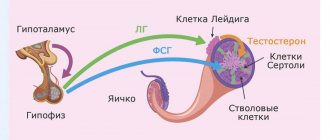
PSA level determination
PSA levels are measured to detect prostate cancer. Prostate prostate specific antigen (PSA). A small amount of the hormone enters the blood. With prostate cancer, the concentration of PSA in the blood increases several times. A high level of PSA in the blood may indicate the presence of an adenoma, a benign tumor of the prostate gland. Urologists recommend that all men over 50 years of age donate blood to determine PSA levels once a year. Patients whose immediate male relatives have had prostate cancer should visit a urologist upon reaching 30 years of age and have their blood tested for PSA.
Pap test for cancer
The study is performed if a woman is suspected of having cervical cancer. The gynecologist takes a smear and sends it to the histology laboratory. Using this study, it is possible to identify a precancerous condition, when the cells have not yet turned into malignant ones, but their structure has begun to change.
This test should be carried out three years after the start of sexual activity. In the future, the examination must be carried out once every 2 years, and upon reaching 50 years - once every 5 years. Two days before taking a smear, a woman should abstain from sexual intercourse, not use vaginal suppositories, douche, or use vaginal tampons. The result may be false if there is inflammation or infection of the genital organs.
Urine and stool analysis
A general urine test is informative for multiple myeloma. Laboratory technicians detect Bence Jones protein in urine. Elevated levels of creatinine and urea may indicate increased protein breakdown, cancer toxicity, or deterioration of kidney function.
A stool occult blood test can detect colon cancer in its early stages. This allows for radical treatment of the disease and improves the prognosis.
The first signs of organ cancer
All further information on how to determine cancer should not be taken as a mandatory criterion for the presence of cancer. Any of these symptoms in itself does not indicate the presence of a benign or malignant tumor in the body. However, these signs should cause caution and a subsequent visit to the doctor - only a qualified medical specialist, after a careful examination and a series of tests, can talk about the presence or absence of cancer.
Problems with urination - many men and women experience this as they age. Such problems include:
- Frequent urination, especially at night
- Sudden urge to go to the toilet
- Weak urination that lasts longer than usual
- Burning sensation during urination
- Urine leakage when coughing, sneezing, laughing, abdominal muscle tension, etc.
These symptoms can be caused by prostate hyperplasia or cancer in men, weakness of the muscular sphincter of the urethra in women, sexually transmitted infections in both sexes, etc. In any case, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Blood in the urine or stool is one sign of bladder, kidney, or colon cancer. However, bleeding can also occur with a urogenital infection or hemorrhoids. In any case, this condition is not normal, so you should make an appointment with a medical specialist: a urologist, surgeon or therapist.
Skin changes - special attention should be paid to moles and any other spots. A change in the color, size or shape of a mole is a reason to consult a doctor. You should also pay attention to the unreasonable darkening or lightening of any area of the skin. Your doctor may order a biopsy, which is removing a small piece from a suspicious area to be tested for cancer under a microscope.
Enlarged and/or painful lymph nodes - may be a reaction to a cold or to an inflammatory process in the lymph nodes, so-called lymphadenitis. However, in some cases, enlarged lymph nodes indicate cancer, so you should immediately visit your doctor.
Problems with voice and/or swallowing may be a sign of laryngeal cancer, which is especially common among active smokers. For diagnosis, the doctor may prescribe barium fluoroscopy, computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging, and other procedures.
Heartburn is a nonspecific symptom that in itself does not indicate the presence of a malignant tumor. However, progressive heartburn can occur with cancer of the esophagus, stomach or oropharynx.
Changes in the oral mucosa - the oral cavity should be examined especially carefully by active smokers. The presence of white, reddish or grayish plaques on the mucous membrane can be a sign of cancer and is a reason to visit a doctor.
Sudden weight loss - malignant cancer cells require a lot of energy to divide, which they take from food entering the body. Therefore, a significant amount of nutrients does not reach the necessary organs and tissues, and the person begins to quickly lose weight. If an unreasonable decrease in body weight is recorded, this may indicate cancer of the internal organs. Therefore, you need to make an appointment with a doctor as soon as possible.
Fever – In most cases, increased body temperature and fever indicate that the body is fighting an infection. But fever that persists or occurs regularly for no apparent reason may indicate blood cancer.
Breast changes - if a woman’s breasts have changed their structure or shape, or nodules or other formations have begun to be felt in the mammary glands, this is a reason to contact a medical specialist. Your doctor may order a mammogram, an X-ray test that can help detect breast cancer. Today, women around the world are taught to perform regular breast self-examination, which is an important method for the early detection of malignant tumors. However, there were 2,470 cases of breast cancer in men in Europe in 2021, so they should also be vigilant and check their breasts regularly for any changes.
Pain - as the size of a cancerous tumor increases, it begins to put pressure on surrounding structures: muscles, vascular bundles, nerve fibers, connective tissue capsule of organs, etc. This can cause pain, which in itself does not indicate the presence of cancer, but is a reason to visit a doctor .
| More information about diagnostics at Euroonko: | |
| Tumor markers for women | from 1380 RUR |
| Oncologist consultation | from 5100 rub. |
| Screening for cancer | from 12100 rub. |
Laboratory diagnosis of cancer
Tests of biological fluid for cancer do not always provide a clear picture, and the doctor is forced to resort to instrumental diagnostic methods. The Yusupov Hospital is equipped with the latest equipment from European, Japanese, and American manufacturers, which makes it possible to detect a cancerous tumor of any location at an early stage of the cancer process.
CT scan
Using computed tomography scanners, doctors obtain layer-by-layer images of internal organs. Modern equipment makes it possible to perform tomography of the whole body or one or several organs, regardless of the patient’s weight.
Magnetic resonance imaging
With the help of magnetic resonance imaging, doctors obtain an accurate image of internal organs, bones, and soft tissues using pulses of electromagnetic radiation and a magnetic field. The advantage of this diagnostic method is its harmlessness. When using modern devices, patients do not receive radiation exposure. Doctors usually conduct magnetic resonance imaging of the brain, spine, muscles, and joints.
Mammography
Mammography is used to diagnose breast tumors. Modern expert-class devices installed at the Yusupov Hospital make it possible to detect volumetric formations with a diameter of several millimeters. The study is safe and does not cause discomfort in women. It is carried out regardless of breast size. The research results are presented in digital images or on film. Mammologists recommend that women over the age of 40 undergo preventive examinations annually. To rule out the presence of a malignant neoplasm, you should visit a doctor and have a mammogram or ultrasound examination of the mammary glands.
Make an appointment
Scintigraphy
This is a method of radionuclide diagnostics using gamma rays. With its help, doctors detect malignant tumors 6-12 months earlier than using other laboratory and instrumental methods. During the study, it is possible to visualize even the smallest volumetric formations, determine their nature and exact location. Scintigraphy is used to study the skeletal system, brain, mammary glands, lymphatic system, salivary glands, heart, liver and kidneys.
The device can operate in scintigraphy mode of the whole body or targeted projection of certain areas. Using scintigraphy, oncologists evaluate the effectiveness of chemical and radiation therapy and determine the viability of implants in bone tissue. The procedure is not performed on pregnant women and patients whose condition is assessed as serious.
Ultrasound
At the Yusupov Hospital, functional diagnostic doctors perform ultrasound examinations using the latest expert-class devices. They allow you to see a clear picture and get a high-quality image. Differential diagnosis of soft tissue tumors is carried out using elastography, a method based on visualization of soft tissues, determination of their elasticity and other characteristics. Oncologists prescribe ultrasound examination of the following anatomical areas:
- Thyroid gland;
- Lymph nodes;
- Mammary glands;
- Hearts;
- Abdominal and pelvic organs;
- Prostate;
- Kidney.
Biopsy
Used to determine the nature of the tumor process. Surgeons obtain pieces of tissue that are sent to the laboratory for histological examination using the following techniques:
- Stereotactic trephine biopsy - used in the diagnosis of microscopic neoplasms with a diameter of 1-2 mm, which are located in the mammary glands;
- Ultrasound-guided fine-needle biopsy – used primarily to extract the contents of breast cysts;
- Trephine biopsy using ultrasound – performed using a biopsy gun;
- Vacuum aspiration trephine biopsy – allows you to obtain large fragments from tissues;
- Core needle biopsy – used to remove a large tissue sample;
- Incisional biopsy - involves excision of a piece of tumor under local anesthesia;
- Excisional biopsy is a mini-surgery during which the surgeon removes the entire tumor or excises part of it.
Pathological examination
Morphologists at the Yusupov Hospital conduct a pathological examination of pieces of pathologically altered tissue using special equipment.
Dermatoscopy
Using dermatoscopy, the nature of skin formations is determined. The study is necessary if there are a large number of pigmented moles on the skin, changes in their shape and color. It allows you to detect skin cancer and melanoma at an early stage.
How a cancer tumor manifests itself - the first signs
When tumor-like structures are detected, it is necessary to clarify their nature, whether they are malignant or benign. For this, a biopsy can be used, as well as various instrumental and biochemical research methods. If the malignant nature of the tumor is detected, additional types of cancer diagnostics may be prescribed.
The naming of a specific type of cancer is based on the organ of its original location. Even if the cancer metastasizes to other parts of the body, the name does not change. For example, with a breast cancer, they speak specifically of breast cancer, even if metastases are found in the lungs. Prostate cancer that has spread to the bone tissue is called metastatic prostate cancer.
Other common types of cancer include carcinoma, sarcoma and lymphoma. The names of these types of cancer also correspond to their initial location in the body. Carcinoma is a general term for tumors that arise in epithelial tissues, such as the skin or the lining of organs such as the uterus and lungs. That is, saying that a woman has a cancerous tumor of the uterus is the same as saying that she has carcinoma of the uterus. Likewise, a cancerous tumor of the stomach may be referred to as gastric carcinoma.
Tumors that arise in connective tissue, such as muscle or bone, are called sarcomas. Primary brain cancers are called gliomas, and malignant tumors that arise in the lymphatic system are called lymphomas. Tumors localized in the bone marrow are called leukemia.
The terms "cancerous tumor", "malignant neoplasms" and "malignant tumor" are used interchangeably. Not all tumors are malignant; many do not contain cancer cells. For example, lipomas, small fatty tumors, are often present in the skin. Benign tumors can sometimes cause pain and other problems, and sometimes require surgical removal. For some people, the terms “cancer” and “tumor” are used interchangeably, which is not true. In some cases, problematic structures can even be represented by ordinary scar tissue.
Screening and diagnosis of cancer tumors
One of the reasons why doctors recommend undergoing routine medical examinations is the possibility of detecting tumor-like structures in the early stages. Regular screening can improve the detection of cancer in the early stages of the disease. Cancer, when detected in the early stages of the disease, is usually easier to treat.
If, during a routine physical examination, the doctor suspects that he has discovered a cancerous tumor, he may order a cervical smear (to detect cancer of the uterus), a mammogram (to diagnose breast cancer), and other types of tests. A blood test may be ordered to assess the risk of developing prostate cancer, and a helical CT scan may be used to diagnose lung cancer.
A person's age, family history, and occupational history can largely determine the recommended frequency of routine medical examinations for the diagnosis of cancer. If diagnostic results deviate from the norm, they require careful study and the appointment of clarifying types of examination.
For example, results from a cervical smear may indicate the presence of abnormal cells in the cervix. Gynecological studies show that over time these cells can lead to cervical cancer, but this does not always happen. In such cases, the gynecologist may recommend more frequent cervical smears in order to monitor the situation and make an early diagnosis. In some cases, a cervical smear test can reveal cancer cells on the cervix. After this, tests to stage the cancer or a biopsy are usually ordered.
Some people see a doctor if they have certain symptoms that indicate they are at risk for cancer (breast lumps, changes in the color or size of a mole, severe headaches, etc.). If the doctor believes that these symptoms may be caused by the formation of cancerous tumors, a biopsy, a procedure used to diagnose cancerous tumors, may be ordered. If the biopsy shows the presence of cancer cells in the sample taken, the cancer is then staged. Staging consists of clarifying the location of the cancerous tumor, its stage and effect on the body. There are three important points to note regarding diagnosis:
- not high-quality screening methods have been developed for all types of cancer tumors;
- even with high-quality screening for some types of cancer, early diagnosis is not always successful;
- pathological changes identified during screening diagnostics do not always relate to cancerous tumors.
Diagnosis of the clinical stage
The clinical stage of a cancer tumor is established on the basis of a medical examination, blood tests and instrumental examination methods. These measures are necessary to diagnose the stage of the disease, develop suitable treatment for the cancer and provide a prognosis. In some cases, a biopsy may be required for a correct diagnosis. The list below indicates some of the features of diagnosing cancer tumors:
- Suspicious lumps or abnormal areas may be completely removed during a biopsy (for example, a specific lymph node or skin ulcer).
- A biopsy may involve taking samples of cells from a deep-seated lump (for example, if you suspect a cancerous tumor in the breast).
- Sometimes, for diagnostic purposes, an endoscope is used to remove a small piece of tissue from a specific organ. For example, if a stomach cancer is suspected, a gastroscope can be used, inserted into the cavity of this organ to take a tissue sample.
- If leukemia is suspected, cells are collected from the bone marrow.
- Diagnosis of cancer sometimes involves testing urine or sputum samples to check for the presence of cancer cells.
Biomarkers
A biochemical structure that characterizes a specific disease or the effectiveness of its treatment is called a biomarker. Prostate-specific antigen is a biomarker for the presence of prostate cancer. If a decrease in the VEGF biomarker is detected in patient samples after antiangiogenic therapy, this usually indicates that the cancer is being treated effectively.
Various types of blood tests can detect the presence in it of certain biomarkers that are actively synthesized by cancer cells. Normally, markers are present in the blood in small quantities. An increase in the concentration of a certain marker may indicate the formation of a certain type of cancer. Biomarker tests are also used during cancer treatment to determine the effectiveness of the therapy used. Scientists are constantly conducting research to identify new biomarkers. Below is a list of abbreviations for some of the most common tumor markers and some examples of the types of cancer that correspond to them:
- CEA - breast cancer, stomach cancer;
- CA 19-9 - stomach cancer;
- AFP and beta-HCG - germ cell tumors;
- OC-125 - ovarian carcinoma;
- PSA - prostate cancer.