Published: 01/30/2018 Updated: 04/06/2021
Unlike menopause in women, the decline in hormone levels in men occurs gradually. Starting from about 40 years of age, the level of testosterone in the blood drops by 1-2% per year, and by the age of 60 it can decrease significantly. However, the ability to conceive in 50% of men remains even at an older age (in women, menopause indicates a complete decline in reproductive function).
What are the dangers of changing androgen status? First of all, the development of serious diseases and conditions that significantly worsen the quality of life. This is due to the fact that biologically hormones have an effect on various target organs.
Normal hormone levels in men
| Dihydrotestosterone | 250 – 990 pg/ml |
| Testosterone | 345 – 950 ng/dl |
| Sex binding globulin | 13-70 nmol/l |
| FSH | 1.37 - 13.58 mEdl |
| LH | 2 - 9 mU/l |
| Estradiol | 16 – 73 pg/ml |
| Prolactin | 2.5 - 15 ng/ml |
| Progesterone | 0.35 – 0.63 nmol/l |
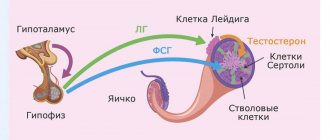
Hormonal regulation of spermatogenesis
Prolactin
Norm:
73-407 honey/l.
Prolactin is a hormone produced in the pituitary gland and affects the functioning of the mammary glands. It is he who plays a decisive role during lactation in women. However, its amount depends on the amount of other sex hormones.
Ilya Baskin
trainer, vice-champion in classical bodybuilding
Another opponent of testosterone is the hormone prolactin. From an emotional point of view, it does not cause irritability and tearfulness, like estradiol, but apathy, lethargy, melancholy, and drowsiness. The most famous and nasty consequence of increased prolactin is considered to be gynecomastia. This is an accumulation of fat and water near the mammary glands, which turns the male breast into a semblance of a female one. This disease is sometimes caused by a genetic predisposition, but is most often seen in people who are overweight, lack physical activity, and in athletes who have used anabolic steroids.
Since the hormones prolactin and estradiol compete with testosterone, recommendations for reducing them coincide with indications for increasing testosterone. But it is important to understand that their excessive reduction cannot be called correct - these are necessary hormones.

Fitness like a man: 6 sports accounts on Instagram
FSH analysis in men
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) is produced by the pituitary gland ; it is one of the main hormones, without which the ability to conceive is lost. FSH
promotes normal functioning of the testicle and epididymis, activates spermatogenesis and estradiol production.
In an adult man after 21 years of age, the normal FSH level in the blood is 0.95-11.95 mU/l.
Increased levels of FGS can occur with chronic renal failure, pituitary cancer, reproductive dysfunction and orchitis. Reduced levels - with excess weight, pituitary dysfunction, taking anabolic hormones and fasting. For diseases of the reproductive system, in particular infertility, a blood test for FSH is basic. Before the tests you should not drink alcohol, smoke or exercise. Blood is taken from a vein three times within half an hour.
Estradiol
Norm:
40-161 pmol/l.
Just as testosterone is found in small doses in women, estradiol is found in the bodies of men. Although elevated levels of this hormone can lead to the same consequences as low testosterone, its levels should not fall below normal.
Ilya Baskin
trainer, vice-champion in classical bodybuilding
In contrast to the main male hormone testosterone, there is also the main female sex hormone - estradiol. In a positive way for a man, it affects the condition of the skin, teeth, nails, the strength of bones, joints, resistance to diseases and infections. However, an increased level negatively affects libido, swelling, emotional state, and fat deposition, primarily on the female principle, for example, on the hips.
Increased estradiol is caused by the same factors as decreased testosterone. It also negatively affects health: decreased libido, increased frequency of injuries, illnesses, infections. In general, estradiol is a kind of stop tap; its task is to psychologically restrain you in order to protect your health.
Analysis for prolactin in men
Prolactin is synthesized by the pituitary gland and affects a man’s ability to conceive. The task of prolactin is to stimulate the body's immune defense, regulate spermatogenesis, participate in the formation of secondary sexual characteristics and influence weight. The normal level of prolactin in the blood of a healthy man is 50-400 mU/l.
The amount of the hormone may increase for the following reasons:
- Heavy physical activity before donating blood;
- Insomnia;
- Fasting before donating blood (12 hours or more);
- Excessive protein intake before testing;
- Stress;
- Chronic pain;
- Pituitary diseases;
- chronic renal failure;
- Thyroid dysfunction;
- Treatment with antidepressants, beta blockers and antihypertensive drugs;
- Drug use.
Hyperprolactinemia manifests itself as decreased potency, infertility, decreased levels of male hormones, depression, insomnia, the development of diabetes mellitus, osteoporosis, gynecomastia and excess weight gain. The level of prolactin decreases due to diseases of the pituitary gland, while taking certain medications. Before taking the test, you should not worry, work hard, have sex, go to the sauna, drink alcohol or smoke.
Hormonal profile (complex) for men
This profile provides a basic assessment of a man's hormonal status. Regulation of the male reproductive system begins in the cerebral cortex and hypothalamus, which send signals to the pituitary gland, the regulator of all endocrine glands in the body. To ensure the functioning of the genital organs, the pituitary gland produces follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), luteinizing hormone (LH) and prolactin. The next level of regulation is the testes, where androgens are synthesized. The main androgen is testosterone; without it, spermatogenesis and the formation of a male physique are impossible. Normally, hormonal regulation ensures the formation of a male body capable of procreation. Problems associated with hormonal dysfunction are more often identified during the reproductive period (male infertility, impotence) or during puberty. Also, hormonal disorders can be secondary: against the background of various diseases and excessive physical exertion, when taking anabolic steroids.
What is included in the complex?
FSH - follicle-stimulating hormone - ensures full spermatogenesis: it affects the formation, development and function of the testes and seminiferous tubules, stimulates the production of androgen-binding proteins (SHBG), which deliver testosterone to the epididymis, ensuring proper maturation of sperm.
– luteinizing hormone – under its influence testosterone is synthesized in the testicles.
Prolactin - in men, enhances the effect of LH and FSH, is responsible for metabolic processes in the testicles, affecting spermatogenesis. Increased prolactin leads to infertility
TSH is a thyroid-stimulating hormone that regulates the function of the thyroid gland, which has a direct effect on reproductive function.
Free testosterone (includes determination of total testosterone, free testosterone, SHBG and free androgen index). Testosterone is the main male hormone, the total fraction consists of free testosterone - biologically active and associated with proteins - sex hormone binding globulins (SHBG). It is important to analyze these fractions simultaneously.
In what cases is a hormonal profile for men usually prescribed?
- Suspicion of male infertility (inability to conceive with regular unprotected sexual activity for more than a year). A spermogram is also usually examined
- Changes in sexual activity
- erectile disfunction
- Disorders of sexual development in boys
- Assessment and dynamic monitoring of sex hormone levels in thyroid diseases and diabetes mellitus
- For men taking anabolic steroids
- Routine examination of hormonal status
What do the test results mean?
The results of laboratory tests are assessed as a whole by the attending physician, who has information about the patient and the results of other studies.
Test deadlines.
1-2 days.
How to prepare for the analysis?
Venous blood is donated in the morning on an empty stomach before 11 am. It is recommended to avoid heavy physical activity the day before.
Analysis for hCG in men
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is produced in men by the testes; the normal hCG level is 2.5 mU/ml.
The main task of hCG is to activate Leydig cells in male embryos; Leydig cells produce testosterone.
Elevated levels of hCG in men may indicate the development of a cancerous tumor of the reproductive or digestive system. Rules for donating blood for analysis to determine the level of hCG: 12 hours before, do not eat, do not drink water, do not get too cold, do not engage in sports or heavy physical work, and avoid stress.
Diseases associated with decreased testosterone levels
- Cardiovascular pathology. It occurs on average 3-5 times more often in men than in women. The relationship between arterial hypertension and low testosterone levels has been proven.
- Atherosclerosis. It is a “provocateur” of strokes and heart attacks.
- Metabolic syndrome. Reduced testosterone levels contribute to weight gain and obesity.
- Erectile disfunction. Both hormonal imbalance and extra pounds have a combined effect.
- Osteoporosis. Against the background of androgen deficiency, bones become more fragile - there is a high risk of fractures even with a normal fall.
Indications for analysis
There are many indications for the analysis, and therefore it is one of the most common after a general blood test. When determining the causes of infertility in a family, an analysis of hormonal status is one of the first to be carried out, since it allows you to obtain maximum information in a short time. In addition, the following indications for the study are identified:
- the risk of the presence of neoplasms in the testicles - to identify the functioning of the sex glands;
- the presence of disturbances in the functioning of the adrenal glands - if necessary, to identify the degree of disturbance;
- obesity – in the absence of obvious reasons for this;
- skin inflammations, including acne in adolescence, which are not eliminated with traditional medications;
- developmental disorder of boys and adolescents, in which there is excessively early puberty or its significant delay;
- the presence of swelling and swelling in the area of the genital glands - for an unknown reason.
An analysis will also be required if there are disturbances in the functioning of the thyroid gland. This allows you to evaluate the functioning of the entire endocrine system, which often suffers with thyroid pathologies.
ALT/AST
Norm:
41 / 37 U/l.
Basically, the level of these enzymes depends on the work of the liver; when it is destroyed, they enter the blood. Therefore, elevated levels of ALT and AST may indicate hepatitis, liver cirrhosis, myocardial infarction and other diseases.
Ilya Baskin
trainer, vice-champion in classical bodybuilding
ALT/AST are enzymes that take part in the metabolism between cells. In the event of destruction of internal organs, primarily the liver, they enter the blood, and by their concentration in the serum, doctors determine problems with the organs.
As a rule, elevated levels indicate liver problems. You should not self-medicate - in such cases it is better to consult a doctor. The only thing you should do for sure is to give up alcohol.
What to do if there are deviations from the norm
If the amount of a particular hormone is outside the normative range, the doctor will prescribe additional tests. Along the chain, they will check the condition of organs related to its synthesis and transformation: brain glands, testicles, adrenal glands, liver, thyroid gland.
If it is not possible to eliminate the cause of hormonal imbalance, for example, with Klinefelter syndrome, then hormone replacement therapy is prescribed.
What is hormone replacement therapy and how testosterone levels affect the male body, says doctor Andrey Egorov
Autoantibodies
Autoimmune antibodies (autoantibodies) are formed when autoimmune disorders develop in the body. Autoimmune reactions are a pathological response of the human immune system to components of the body’s own tissues. They can manifest themselves in the production of antibodies to phospholipids, DNA fragments, thyroid factors, etc. In obstetric and gynecological practice, such disorders are considered within the framework of antiphospholipid syndrome. Autoantibodies cause an increase in blood coagulation, the development of microthrombosis in the placental vessels, implantation disorders, uteroplacental insufficiency, intrauterine growth retardation syndrome, and fetal death.