Home – For patients – Useful articles – Gynecology – Smear in gynecology
A smear is one of the examination methods in gynecology, which allows you to identify some diseases of the female genital area (bacterial vaginosis, thrush, vaginitis, sexually transmitted infections, cervical tumors, etc.). Obtaining a smear is a procedure during which the doctor scrapes the mucous membrane of the internal genital organs (vagina, cervix, cervical canal, urethra), which is then examined under a microscope. There are 2 main types of smear: flora smear (study of microbes found in the scraping) and cytology (study of cervical tissue taken during scraping).
1. Smear on the flora.
A flora smear (general smear, bacterioscopy) is a laboratory microscopic examination that allows you to determine the nature of the microflora of the vagina, cervical canal or urethra (urethra). Microflora is the entire spectrum of “beneficial” and pathogenic microbes of any organ. The microflora of the female genital organs is represented mainly by lactobacilli, which maintain an acidic environment in the vagina, which prevents the proliferation of pathogenic microbes. Violation of the vaginal microflora is characteristic of diseases such as bacterial vaginosis, candidiasis (thrush), and vaginitis.
Description of the consequences of the disease
It is rare, but it happens that Candida yeast fungi penetrate the placental barrier, contributing to intrauterine infection of the fetus. But basically, a child becomes infected with thrush at the time of birth, when he moves through the birth canal affected by the fungus. Infection during childbirth can cause severe damage to the skin and mucous membranes, and the membranes of internal organs.
Candidiasis is dangerous not only for the unborn child, but also for the pregnant woman herself. Fungi negatively affect the condition of the tissues of the vagina and birth canal, helping to reduce their strength and elasticity. Therefore, immediately at the time of birth, the risk of serious injuries increases, which can cause heavy blood loss and other complications.
In addition, untreated vaginal candidiasis often causes the progression of erosive processes in the uterus. Erosion can subsequently negatively affect women's health and cause infertility.
In what cases is it recommended to take a flora smear?
A microflora smear is performed for the purpose of diagnosing and preventing inflammatory diseases of the female genital area (usually, if nothing bothers the woman, once every 6 months), and for diagnostic purposes in the presence of the following symptoms:
- Pain or discomfort in the lower abdomen.
- The presence of pathological discharge from the genital organs.
- Itching in the genital area.
- Pain during sexual intercourse.
A smear for flora is recommended for all women planning pregnancy, as well as after long-term treatment with antibiotics or drugs that reduce immunity (corticosteroids, antitumor drugs, etc.).
A smear on the flora allows you to identify sexually transmitted diseases: gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, as well as bacterial vaginosis (violation of the ratio of beneficial and pathogenic bacteria in the vagina).
Cost of treating candidiasis in women
The cost of treating candidiasis in a medical setting is the most conservative and affordable. Before prescribing a treatment plan, our specialists will conduct a thorough examination, study in detail the results of the diagnostic examination, assess the general health of the pregnant woman, and only then select an effective therapeutic regimen, which will allow you to quickly and safely get rid of the infection and prevent the disease from becoming chronic.
You can find out how much it costs to treat vaginal candidiasis at the Healthy Family medical clinic by calling +7 (495) 185 93 07 or ordering a call back. Our administrators will contact you and answer all your questions.
Flora smear during pregnancy.
During pregnancy, due to changes in the body's hormonal levels, the risk of various inflammatory diseases of the vagina is especially high. The presence of an inflammatory process in the genital tract can have serious complications such as miscarriage, premature birth, infection of the child during childbirth in the presence of specific pathogens. In this regard, a pregnant woman is recommended to undergo a smear test for flora at least 3 times during pregnancy: when first visiting a doctor, at 30 weeks of pregnancy and at 36-37 weeks. An additional smear test for flora may be prescribed if there are complaints of itching, burning in the genital area and a change in the nature of the discharge (unpleasant odor, change in the color of the discharge, or its quantity). Interpretation (decoding) of a smear for flora during pregnancy is carried out according to the same parameters as in non-pregnant women. During pregnancy, a slight excess in the content of leukocytes in the smear is acceptable (up to 15-20). Collecting material for a smear during pregnancy is completely safe for the fetus.
2. Smear for cytology.
A cytology smear (for atypical cells) is a laboratory microscopic examination that is carried out for the purpose of early diagnosis of cervical cancer. Pap smear tests evaluate the size, number, shape, and arrangement of cervical cells to help identify precancerous lesions and cervical cancer.
The danger of candidiasis in pregnant women
If the treatment of candidiasis in women during pregnancy is correct and timely, neither she nor the unborn child is in any danger in terms of health. It’s another matter when the disease progresses, and the pregnant woman refuses to take the medications prescribed by the doctor for fear of harming the fetus. But it is worth noting that the modern pharmaceutical market sells many antifungal drugs that are allowed to be used already in the early stages of pregnancy. They effectively destroy fungal infection and at the same time do not have any effect on the growth and development of the fetus.
Do's and don'ts
Quite often, swelling occurs in the third trimester of pregnancy. To prevent them and alleviate your condition, eliminate smoked and salty foods, reduce your intake of fats and sugar. These substances retain fluid in the body. On the contrary, you should not reduce the amount of water you drink: this will further provoke swelling. Control weight gain, eat more vegetables and fruits.
If swelling does not subside within 3 days, your blood pressure rises, or your weight increases unexplained, consult your doctor immediately. These are symptoms of gestosis in pregnant women - a condition that is life-threatening for the mother and fetus.
Is it possible to speed up labor?
We recommend that you do not resort to “folk” and sometimes dangerous methods of bringing the long-awaited event closer. Avoid lifting heavy objects, taking castor oil, or taking hot baths as this can cause rapid labor, bleeding, and other complications.
If the baby is in no hurry to be born, then medical stimulation in the maternity hospital is the safest way.
Nutritional features in the 3rd trimester
When the stomach drops, the heaviness in the stomach and heartburn go away, a woman’s appetite improves, and a desire arises to eat “something harmful and forbidden.” We advise you not to get carried away; additional stress on the liver and pancreas is completely unnecessary now. No, one cake will not harm you and your baby, but you should know when to stop.
Eat as before, in small portions. To get the vitamins and minerals you need, include the following foods in your diet:
- fresh vegetables and fruits, leafy greens;
- fermented milk products and eggs;
- nuts, dried fruits, vegetable oils;
- lean meat and fish;
- oatmeal, brown rice, millet, buckwheat and other grains.
Limit your consumption of potatoes, confectionery and flour products - sources of simple carbohydrates. Avoid alcohol, carbonated drinks, fried and smoked foods.
Meat, fish and eggs must undergo sufficient cooking. Avoid soft-boiled eggs or medium-rare steak. This will protect you from listeriosis, an infection that has serious consequences for the fetus.
How to test for gonococci
A smear is taken from the suspected location of the inflammation. The doctor determines it based on symptoms. Bacteria often affect the urethra. Therefore, clinical material is taken from the cervix and vagina. If gonococci have affected the mucous membrane (eyes, nasopharynx), then the collection is carried out with cotton swabs.
How is a smear taken for gonococci in women? Before sampling, the urethra is massaged. As a result, discharge comes out of the urethra, which is taken for analysis. Often during the study, the material is Gram stained. This makes bacteria visible. Negative and positive microorganisms are distinguished by staining.
Symptoms of bacterial vaginosis
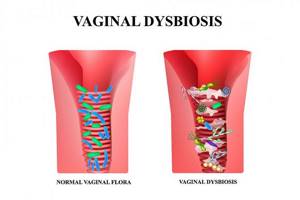
With BV, vaginal discharge (leucorrhoea) becomes whitish-gray, has a liquid consistency or resembles a cheesy mass. They have an unpleasant fishy odor, and their total volume increases significantly compared to the norm. The long course of the disease leads to the fact that the leucorrhoea acquires a yellow-greenish tint and becomes thicker and more stretchy. The patient may also experience burning, itching and discomfort during urination, and rarely pain in the lower abdomen in the suprapubic region.
Depending on the woman’s general well-being, there can be both an acute course of the disease and an asymptomatic one, when the patient does not even suspect that her health is not all right. It occurs as a monosymptomatic course of the disease, i.e. The only concern is the discharge, as well as the polysymptomatic one, when there are many symptoms of the disease. The diagnosis of BV is established on the basis of data from clinical and special laboratory research methods.iv The material for assessing the state of the vaginal flora is a smear from the posterior fornix and cervix. Regular visits to the gynecologist and timely treatment of the disease are required in all cases, even if there are no symptoms of the disease and nothing bothers the woman.
Treatment of bacterial vaginosis
Therapy for BV is most often carried out with antibacterial drugs. This approach in some cases allows to relieve the symptoms of BV, but does not lead to a complete cure. This happens because antibiotics also suppress the remaining lactobacilli, so vaginal dysmicrobiocenosis is aggravated. The acidic environment of the vagina, which is normal, is also not restored with this treatment. Antibacterial therapy, especially long enough, can also lead to decreased sensitivity to antibiotics. Those. Over time, antibacterial drugs may be powerless even to eliminate the symptoms of the disease.
The main difficulty in treating bacterial vaginosis during pregnancy lies in the fact that in most cases, bacteria in the human body do not exist in isolation, but in the form of organized communities - biofilms. Active cooperation between microorganisms and their tight adhesion to the vaginal mucosa increases their survival and allows them to successfully resist the effects of various drugs. This makes frequent relapses of the disease possible. It is obvious that for effective treatment of BV in modern conditions, not only antibiotics are needed, but also agents that enhance immunity and probiotics. Both of these groups of drugs can help restore vaginal microbiocenosis.
As practice shows, it is especially difficult to draw up a treatment plan and select medications for the treatment of pregnant women. There are many medications that are potentially dangerous to the fetus. In this regard, it is very important when prescribing medications to expectant mothers to seriously assess the possible benefits and risks of taking medications during all trimesters.v If the patient is concerned about bacterial vaginosis during pregnancy, it is permissible to use only those drugs whose instructions indicate the safety of their use for treatment of pregnant women.
List of tests during the first trimester of pregnancy (0–14 weeks)
Women are required to register with the antenatal clinic before 12 weeks. At the initial appointment, the gynecologist will conduct an examination, collect anamnesis and prescribe blood tests:
- General.
- Biochemistry.
- For antibodies of classes M, G to rubella viruses, herpes, cytomegalovirus, and toxoplasma (TORCH panel).
- Coagulogram.
- For blood type, Rh factor.
- For syphilis, hepatitis B and C, HIV.
- For sugar, for glucose tolerance.
- Double test (PAPP-A + hCG). Allows you to detect pathologies such as Edwards, Patau, and Down syndromes.
In addition, you will need to undergo a urine test, PCR for chlamydia, gonococci, mycoplasma, and microscopic examination of vaginal discharge.
Causes and routes of infection
Gonococcal infection is a sexually transmitted disease that is highly contagious. Representatives of the fair sex often fall into the risk zone. Gonorrhea is rare in men. This is due to the anatomy of the genitourinary system. More often, the infection is transmitted sexually (oral, vaginal and anal sex). There are other causes of gonococci in a smear in women:
- using someone else's washcloths;
- wearing dirty laundry for a long time;
- contact with objects and clothing of an infected person;
- use of a public toilet and swimming pool (sauna, bathhouse);
- using dirty dishes;
- swimming in stagnant water;
- sharing a towel;
- kisses with the patient.
First of all, inflammation affects the vagina, as well as the urethra. Inflammation of the rectal mucosa, eyes and nasopharynx is possible.
Other examinations
Test results alone do not allow us to form a complete picture of the health status of the woman and child. Therefore, pregnant women are prescribed other examinations:
- Ultrasound. A woman will have three ultrasound screenings: at 10–14, 20–24, 32–36 weeks.
- ECG. This needs to be done when a woman registers.
- CTG (cardiotocogram) is performed weekly from 32 weeks. CTG shows fetal heartbeat and movement, uterine contractions.
- Doppler study. Conducted at 30–32 weeks. Allows you to understand whether the baby receives enough oxygen and nutrients through the placenta.
Examination by specialized specialists is no less important. In the first trimester, you need to visit an otolaryngologist, dentist, ophthalmologist, endocrinologist, and also a therapist. In the third trimester, there will be a second consultation with a therapist and an ophthalmologist - their conclusion is important, for example, when determining the method of delivery (natural birth or cesarean section).
Throughout pregnancy, it is necessary to visit a gynecologist: once every 3 weeks in the first trimester, once every 2 weeks in the second, once a week in the third.
Remember that when carrying a child, it is important not only to undergo prescribed studies and tests in a timely manner, but also to carefully follow the recommendations of doctors. Thus, women are advised to pay attention to nutrition, avoid stress, and walk in the fresh air more often.
THIS IS NOT AN ADVERTISING. THE MATERIAL WAS PREPARED WITH THE PARTICIPATION OF EXPERTS.
Complexes with this research
Women's reproductive health 3,710 RUR Composition
Entry into IVF Examination when a woman enters the IVF procedure 23,020 RUR Composition
Women's safety Preventive examination of the pelvic organs RUB 1,960 Composition
IN OTHER COMPLEXES
- Examination during pregnancy. 3rd trimester 9,620 RUR
- Examination during pregnancy. 1st trimester 16,690 RUR
- Pregnancy planning. Cervical screening and STIs RUB 4,700
- Women's check-up No. 2 6,700 RUR
Causes of bacterial vaginosis

Among the main reasons that lead to the development of BV is the hormonal changes in the body that usually accompany pregnancy. Hormonal imbalance, which is often observed during pregnancy, changes the secretion of cervical mucus, which increases the pH level. This causes disruption of the normal microflora of the vagina and the proliferation of opportunistic microorganisms, which are characteristic of the norm, but with an increase in their population and under conditions of increased stress on the female body, they can lead to the development of the disease.
Also, the appearance of BV in pregnant women is caused by the same reasons that are responsible for the development of this disease in women who are not expecting a child. For example:
- Systemic and local antibiotic therapy. Antibacterial drugs are not able to act selectively on the body, which means that while fighting pathogenic bacteria, they are also detrimental to beneficial microflora in a variety of body systems - wherever the antimicrobial components of the drug enter along with the blood and lymph flow.
- Treatment with hormonal and cytostatic drugs. These medications can also disrupt the normal vaginal microflora.
- Hormonal imbalances. Hormonal levels are affected not only by pregnancy, but also by some chronic diseases, including diabetes. This disease affects the composition of the vaginal epithelium and the properties of its cells, which can negatively affect a woman’s well-being.
- Intestinal dysbiosis. Changing the species composition of intestinal bacteria can lead to similar changes in the reproductive organs.
- Malformations of the genital organs. Congenital disorders can negatively affect the vaginal microflora.
- Neglect of basic hygiene rules. Excessive zeal is also harmful - it is not recommended to use antiseptics or antibacterial soap on a regular basis.