Author
Timofeeva Veronika Leonidovna
Leading doctor
Gynecologist
until September 30
We're giving away RUR 1,000 for all services per visit in September More details All promotions
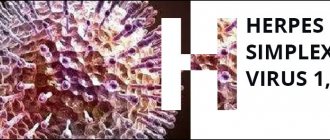
Herpes test
allows you to determine the presence of the herpes virus in the body.
Today, several types of herpes virus are known. The most common herpes simplex virus (HSV) type I, manifested in the form of characteristic rashes on the face and oral mucosa (the so-called “cold on the lip”), HSV type II (genital herpes, which is characterized by a rash on the genital mucosa organs), as well as herpes zoster (herpes type III).
Herpes can be transmitted in various ways - through direct contact (domestic contact), by airborne droplets; intrauterine infection is possible. At the same time, it is typical to become infected with herpes through sexual contact, which is why herpes is included in the list of STDs (sexually transmitted diseases). Herpes is also one of the ToRCH infections, which group together diseases that can cause harm to the fetus during pregnancy.
The herpes virus is not always active. It can be present in the body for years without causing any obvious symptoms and becoming active only when the immune system is weakened.
It is believed that the majority of the world's inhabitants are infected with the herpes virus (according to some estimates, up to 90%). This is why it is so important to determine whether you are a carrier of the virus. If not, you should be especially attentive to the threats of possible infection - this will allow you to maintain the health potential that you possess.
A herpes test is carried out for each specific type of virus. Knowing whether a given type of herpes virus is present in the body or not, the doctor receives the necessary information to diagnose diseases and assess the general condition of the body.
Today, medicine does not yet have means that can completely defeat herpes. But it is quite possible to suppress the activity of the virus or prevent it from becoming active. Therefore, testing for herpes is a component of many comprehensive examinations, and in case of suspected herpes, it is necessary for an accurate diagnosis and prescribing an adequate course of treatment.
When is a herpes test prescribed?
A herpes test is usually prescribed:
- in the presence of symptoms characteristic of a herpes infection - in order to confirm their herpes nature, as well as in order to determine what type of virus they are caused by;
- when planning pregnancy - for both partners;
- during pregnancy;
- newborns with maternal infection;
- in order to determine whether the herpes infection was transmitted through contact with an infected partner.
Herpes simplex - symptoms and treatment
The incubation period for the acquired form lasts 2-14 days. Most often, it cannot be installed due to lack of manifestation.
Herpes simplex in children usually occurs as stomatitis and gingivitis - the temperature rises, fever, general intoxication, focal hyperemia (redness) of all mucous formations of the oral cavity, pain when chewing, increased salivation. Small children refuse to eat due to pain. In a short period of time, small vesicular rashes appear at the site of hyperemia, which quickly open, leaving behind painful erosions - aphthae. Regional lymph nodes enlarge and become painful. Over time, the immune system strengthens and the symptoms gradually regress without any traces of damage. Relapses are rare.
When the skin is affected (mainly in adults), vesicular rashes often appear around the mouth, wings of the nose, and sometimes on the torso and buttocks. The rash consists of small vesicles with serous contents on a slightly hyperemic skin background. Subsequently, they open and dry out, after which crusts form without a trace.
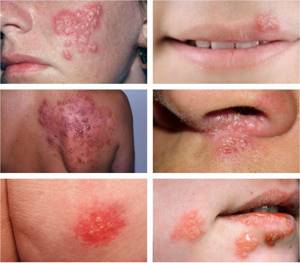
Sometimes the bubbles merge into quite large bubbles. Often their contents fester, oozing forms, and a secondary streptococcal or staphylococcal infection (staphylo- and streptoderma) occurs.
General health, as a rule, does not change. Sometimes the regional lymph node may be slightly enlarged and painful. In general, the process rarely lasts more than a week.
With severe immunodeficiencies, the infection may take a more widespread (generalized) course. In this case, a syndrome of general infectious intoxication occurs and internal organs are affected: the liver and spleen are enlarged, the nervous system is affected (meningoencephalitis, encephalitis and meningitis), as well as the lungs, kidneys and other organs. With relapses of a chronic infection, patients sometimes feel mild discomfort and tingling in the area of future rashes.
With genital herpes, rashes appear on the skin and mucous membranes in the genital area and perineum. They are usually accompanied by soreness, hyperemia of the surrounding tissue, enlargement and tenderness of the inguinal lymph nodes. The frequency of relapse depends on the individual characteristics of the immune system.
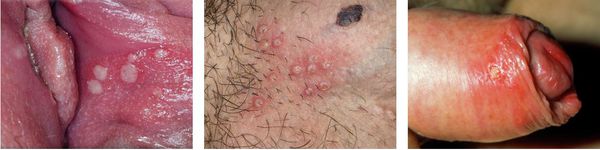
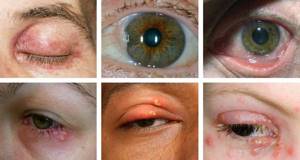
With ophthalmoherpes - eye herpes - unilateral lesions are more often observed due to the transition of the primary process to the organ of vision, i.e., a secondary lesion occurs. Keratitis, blepharoconjunctivitis, iridocyclitis, uveitis, chorioretinitis, optic neuritis and other manifestations may be observed.
A very unusual form of manifestation of herpes simplex is known as Kaposi's eczema herpetiformis - eczema herpeticum. As a rule, it occurs in people who have any skin disease or predisposition to it (dermatosis or “problem skin”). In this case, intoxication and high body temperature are observed, herpetic blisters appear everywhere, quite abundant and closely spaced, periodically merging, sometimes with hemorrhagic impregnation. In some cases, they suppurate, then they open, dry out and form a solid crust. When the rash is completely treated with green paint, the patient’s skin takes on the appearance of crocodile skin. The disease is often quite severe and can lead to death.
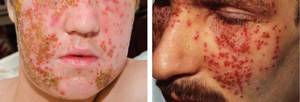
During pregnancy, the child becomes infected:
- before birth - in 5% of cases (primary infection and ascending infection during this period are rare);
- during childbirth, i.e. when passing through the natural birth canal - in 95% of cases.
With primary infection of a pregnant woman in the first trimester or with ascending infection of the fetus, malformations often develop that are incompatible with life, or a miscarriage occurs, especially when infected with type II herpes virus, which is the infecting agent most often - up to 80% of cases.
When a pregnant woman is infected in the second and third trimesters, the risk of injury to the child is about 50%. At the same time, the liver and spleen enlarge, specific inflammation of the lungs, jaundice, metabolic disorders, malnutrition, meningoencephalitis, anemia and more occur. After birth, it can occur either in an asymptomatic subclinical form or have severe disabling consequences - blindness, severe damage to the central nervous system, deafness [1][2][6][8][11].
Interpretation of tests for antibodies to herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2
• IgG is elevated in chronic herpes infection. If antibodies to herpes IgG increase by more than 30% when repeated testing after a time interval of 10 days, you can think about activation of the infection. If the titer of IgG antibodies to the herpes virus decreases during repeated studies, this indicates the success of treatment and the “extinction” of the infection.
Elevated IgG antibodies to herpes may indicate an intrauterine infection or the likelihood of its development. If the study was first performed during pregnancy, then it is not worth judging the probability until repeated studies are carried out. If IgG antibodies to herpes simplex virus types 2 and 1 were detected in the blood before pregnancy, then the likelihood of intrauterine infection is low.
• IgA appears in the blood 14 or more days after infection with the herpes virus and is not critical in diagnosis.
• IgM class - the first antibodies that appear after infection with herpes simplex virus types 2 and 1 within two weeks. A positive test result makes one think about an acute herpetic infection or the activation of a chronic one. In the latter case, IgM does not always appear in the blood serum; here the concentration of IgG antibodies to herpes is of greater importance.
A negative test result may indicate no infection. However, the same test result occurs in the first days of herpes infection or with a chronic inactive infection.
What the analysis shows
Herpes, belonging to the first type, manifests itself as blisters filled with liquid localized on the mucous membranes, lips and tongue. The second type affects the mucous membranes of the genital organs. The third type causes chickenpox and shingles.
The fourth type affects the tonsils, causing severe forms of sore throat.
The fifth type is dangerous because it remains dormant in the body for a long time, and when activated, it affects internal organs.
The sixth type - provokes the development of lymphosarcoma and lymphoma. The seventh type is manifested by symptoms of chronic fatigue. The eighth type - accompanies Kaposi's sarcoma in HIV-infected people.
The study confirms the presence or absence of the herpes virus in the body. The blood is tested for antibodies and parts of the virus.
Types and routes of HSV infection
The content of the article
Herpes is a common infection that affects people of all ages. Most of those infected have already developed the disease in some way, and some people become virus carriers, spreading the disease. Infection with herpes occurs through sexual and household contacts, in utero or during childbirth from a sick mother, as well as through breast milk.

The herpes virus (HSV) remains in the human body for life, periodically being dormant (from a month to several years) or active, causing small rashes on the mucous membranes, which subsequently merge, forming crusty ulcers. With an extremely low level of immunity, a generalized form of herpes occurs with damage to internal organs.
There are 8 types of infection. The viruses are interrelated and can be detected simultaneously in one patient. Most often, two types of viruses are detected in humans:
- Type 1 virus - herpetic fever (oral herpes) - most often appears on the lips, but can also cause the genital form. Transmitted orally. The infection affects 67% of people.
- Type 2 virus - genital and anal herpes - the virus affects the genitals (genitals), causes herpes in newborns and the disseminated form - herpes zoster, spreading over the face and body. Transmitted sexually. 11% of people are infected.
The first type of herpes in most cases affects a person in preschool age, the second type - with the onset of sexual activity. The prevalence of household infection is extremely high, since the virus persists for a certain time on household items, door handles, and wet surfaces.
Why do tests for herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2?
Herpes simplex virus types 2 and 1 not only cause cosmetically unpleasant rashes. It also causes severe pain (for example, along the nerve trunks in the area of the rash), general weakness and damage to the central nervous system.
Therefore, it is important to know about the presence of this virus in the body in order to ensure the necessary prevention of exacerbations of infection and timely, comprehensive treatment. These measures will prevent complications associated with the active progression of herpes infection.
The danger of herpes simplex virus types 2 and 1 is that against the background of decreased immunity, from which no person is immune at different periods of life, the infection is activated. The activity of the virus can lead to serious complications such as damage to the facial, auditory and other cranial and spinal nerves.
Herpes simplex virus types 2 and 1 can seriously threaten a pregnant woman and her unborn child. Intrauterine infection occurs with serious consequences for the nervous system. Reactivation of the infection during pregnancy can lead to its pathological course or premature termination.
Diagnostics
Tests for antibodies to herpes simplex virus 2 and 1: IgG, IgM
Given the high frequency of infection, antibodies to the herpes simplex virus are found in the vast majority of people (more than 90%) around the world. However, the antibody titer and its change over a certain period can provide much more information important for the treatment of herpes simplex virus types 2 and 1.
Antibodies to herpes simplex Ig M and Ig A do not remain in the blood for long - approximately 1-2 months. The only type of antibodies to herpes simplex virus 1 and 2 that persist in the blood throughout life is IgG.
Antibodies to herpes simplex Ig M are markers of primary infection. During primary infection with herpes simplex virus types 2 and 1, the IgG titer may increase. If the tests were taken at an interval of 10-12 days, the titer of IgG antibodies to the herpes virus can increase fourfold.
In the case of recurrent infection, antibodies to herpes simplex virus 1 and 2 IgG are very high. This indicates constant antigenic stimulation of the body. The exacerbation of the disease is also indicated by the appearance of IgM in the blood serum.
Determination of DNA of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2
The study is carried out using a highly sensitive PCR (polymerase chain reaction) technique. The DNA of the virus is determined by examining a scraping from the urethra, collecting morning urine or cerebrospinal fluid. If the analysis revealed DNA fragments of herpes simplex virus type 2 or 1, this indicates the presence of a herpes infection. If viral DNA is not detected, it means that it is not present in the sample taken, or is still present there in a concentration below the sensitivity limit of the test.
In Lab4U, using laboratory methods, you can accurately determine the presence of herpes simplex virus types 2 and 1, as well as get an impression of the course of the infectious process and possible complications. All this provides the doctor with valuable information that helps in diagnosis and choice of treatment regimen.
Herpes viral infections “under the guise” of other diseases
The basis of 45-50% of cases of gastrodoudenitis and gastric ulcer is an infection caused by the Epstein Barr virus (herpes type 4), and the basis of multiple sclerosis is the herpes simplex virus type 6 and cytomegalovirus (herpes type 5). Inflammatory diseases of the female reproductive system (cervicitis, etc.) are based on herpes simplex virus types 1, 2, Epstein-Barr virus, cytomegalovirus. But, unfortunately, it often happens that we treat the consequences of the virus without fighting the virus itself. And the disease returns again.
“They treat concomitant pathology, while local immunity decreases, and against this background pathogenic flora (bacterial, fungal) begins to develop; it is useless to treat it - everything comes back again, since it is based on a long-term viral infection,” explains infectious disease doctor Yuliy Bunov. “Unfortunately, there is little information about the treatment of these infections. It is generally accepted that immunoglobulin M is an indicator of an acute infection or exacerbation of this infection, and the presence of immunoglobulin G indicates that the infection was suffered a long time ago and antibodies to it remain. It should be borne in mind that antibodies to these viruses do not protect the body, as in some other diseases.
In addition, foreign studies have proven that immunoglobulins M are present only during primary infection, then we will not see them anymore, but this does not mean the absence of infection. In three years of working with herpes viral infections, I have seen immunoglobulin M in adults only twice, although there are many different patients. Therefore, you need to look at everything comprehensively, starting with a general blood test with leukemia formula. It shows how lymphocytes behave - during viral infections they increase. Platelets may decrease, monocytes may increase slightly, but the main thing is an increase in lymphocytes.
Many people rely on the PCR method (a method for detecting the DNA of the virus itself). But the PCR test for DNA depends on what test systems are purchased. If they are not highly sensitive, then he will not detect it, and the person is left without treatment. Recently I saw a woman who had been examined for three years; all this time she had been bothered by constant low-grade fever and weakness. During this time, she visited many doctors for consultations and underwent many examinations. I recommended that she take a blood test for four types of herpes viral infections, and the results revealed a high titer of antibodies to cytomegalovirus. After the prescribed treatment, the temperature returned to normal and the patient feels much better.
What symptoms may indicate herpes viral infections “under the guise” of other diseases? • signs of chronic fatigue syndrome, • causeless low-grade fever (above 37 and below 38).
In these cases, it is necessary to take a general blood test with leukemia and pay attention to the level of lymphocytes and monocytes. If they are elevated, then it is worth taking an ELISA and PCR blood test for 4 viral infections and understanding which of them causes this pathology: Epstein-Barr virus, cytomegalovirus, herpes simplex virus types 6 and 7. Remember that these viruses can cause both hepatitis and polyarthritis. If small joints hurt and swell and all rheumatic tests are negative, then it is also worth taking tests to detect herpes viral infections.
The danger of these viruses is that they are all oncogenic - in the future they can cause cancer of anything. In addition, they contribute to the development of atherosclerosis, as they have tropism (this is the ability of cells to ensure the reproduction of certain viruses) to the mucous membranes. By damaging the inner lining of blood vessels, viruses contribute to the formation of atherosclerotic plaques.
Once entering the body, these viruses remain in it forever, can be in “sleep mode” and are activated if the immune system weakens.