When should you take a Gamma GT test?
- Comprehensive diagnosis of diseases caused by intra- and extrahepatic cholestasis;
- Comprehensive diagnosis of acute and chronic hepatitis;
- Comprehensive diagnosis of oncological diseases of the liver, pancreas, prostate;
- Monitoring liver damage while taking hepatotoxic drugs;
- Suspicion of alcoholic or non-alcoholic fatty liver disease;
- Preparation for surgery.
What affects GGT levels?
When deciphering the results of blood biochemistry for GGT, the age component should be taken into account - in infancy and childhood, enzyme levels exceed normal values for adults. Thus, the GGT value of 90 is within the normal range for newborns and infants aged 1-7 months. If such a concentration of the enzyme is detected in adults or older children, then increased activity of gamma-glutamyltransferase is diagnosed.
The gender of the subject is also taken into account: the rate of GGT activity in men is significantly higher than in women (the difference is up to 50% and is ensured by the influence of male sex hormones and the secretion of the enzyme gamma-glutamyltransferase by the prostate gland). A similar pattern begins to be observed after reaching puberty.
The results of the GGT enzyme test are also affected by:
- diet – excess salty, sweet foods;
- deficiency of vitamins and minerals;
- body mass;
- presence of bad habits – smoking, drinking alcohol, substance abuse;
- pregnancy (first weeks);
- drug therapy;
- use of hormonal contraception.
Detailed description of the study
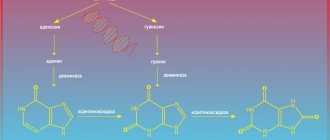
Gamma-glutamyltransferase (gamma-GT) is an enzyme that is present in tissues and organs that have the ability to secrete and absorb any substances. The highest concentration of gamma-GT is found in the liver and pancreas; This enzyme is also present in the intestines, kidneys, spleen, prostate, heart, but to a lesser extent.
The concentration of gamma-GT varies depending on the age and gender of the person.
An increase in gamma-GT activity in the blood serum reflects dysfunction of the liver and biliary system. Gamma-GT serves as the main marker of bile stagnation in the body - cholestasis. The advantage of the method is that the test is more sensitive for determining cholestasis than determining the activity of ALT and AST, and allows you to detect pathology earlier than other tests.
The main causes of cholestasis:
- Intrahepatic: Acute hepatitis of any origin (infectious, alcoholic, toxic, medicinal);
- Cirrhosis of the liver;
- Autoimmune liver diseases (primary biliary cholangitis, primary sclerosing cholangitis);
- Congenital malformations of the bile ducts;
- Vascular liver diseases;
- Cholestasis of pregnancy;
- Malignant and benign formations of the liver and intrahepatic bile ducts.
- Blocking of the common bile duct with a gallstone;
A manifestation of cholestasis is jaundice (yellowing of the whites of the eyes, skin, darkening of urine and discoloration of feces) and itching of the skin. In addition, weakness, loss of appetite, nausea, and heaviness in the right abdomen may be noted.
An increase in the level of gamma-GT in cholestasis is observed earlier and lasts longer than changes in other liver enzymes - alkaline phosphatase, alanine aminotransferase, aspartaminotransaminase.
Metabolic disorders in the liver - alcoholic and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease - also lead to increased release of gamma-HT into the blood. Often this is the only laboratory sign of changes in a given organ over a long period of time.
Alcohol has a damaging effect on the liver. Even a single dose of alcohol can lead to an increase in gamma-GT levels in the blood serum over several weeks.
Determination of the level of gamma-GT in blood serum is recommended for a comprehensive assessment of the condition of the liver and bile ducts in conjunction with indicators such as ALT, AST, alkaline phosphatase, and total bilirubin.
General information
GGT enters the blood only when cells are destroyed. Cell renewal is a natural process. This explains the presence of a small amount of enzyme in the blood in the absence of any pathologies. A significant increase in its concentration indicates the death of a large number of cells. The GGT assay is highly sensitive for cholestasis. If the normal flow of bile is impaired, the GGT level rises earlier than the ALP concentration. An increase in GGT is characteristic of many pathologies, so it is impossible to make an accurate diagnosis based on the results of one analysis. This requires a comprehensive examination.
The main difference between GGT and other liver enzymes is the activation of its production under the influence of alcohol. In people who frequently drink alcohol, the enzyme level may be elevated even if there are no liver pathologies. Also, an increase in indicators in healthy people can be caused by taking a number of medications (for example, paracetamol, antidepressants). Enzyme activity can be increased not only in case of problems with the liver, but also in pathologies of the pancreas, prostate and some other internal organs.
References
- Ivashkin, V.T., Shirokova, E.N., Mayevskaya, M.V. and others. Clinical recommendations of the Russian Gastroenterological Association and the Russian Society for the Study of the Liver for the diagnosis and treatment of cholestasis. - Russian Journal of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Coloproctology, 2015. - V. 2. - P. 41-57.
- Uspenskaya, Yu.B., Sheptulin, A.A. Clinic, diagnosis and treatment of intrahepatic cholestasis in pregnant women, 2021. - V. 27(4). — P. 96-101.
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: The diagnosis and management of patients with primary biliary cholangitis. J Hepatol., 2021. - Vol.67(1). — P. 145-172.
- Alcoholic liver disease: Clinical guidelines - Scientific Society of Gastroenterologists of Russia, Russian Scientific Medical Society of Therapists, 2021. - 38 p.
GGT - what is it?
Not all medical terms are understandable to people not involved in this field of activity. Meanwhile, explaining in simple terms what GGT is is not so difficult. GGT, GGT, GGTP, gamma-GT, γ-GTP are abbreviations for gamma-glutamyltransferase. This is the name of the microsomal enzyme found in cells. It ensures the occurrence of biochemical processes (acting as a catalyst), amino acid reactions, and is important for the metabolism of glutathione, the main antioxidant in the human body.
This enzyme has other names - gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase. This word is synonymous with the term gamma glutamyl transferase. You should be aware that any of the above abbreviations may be indicated in the prescription for biochemical analysis (GGT - short for English Gamma-glutamyltransferase, γ-GTP - for γ-Glutamyltranspeptidase).
Preparing to take the Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase test
The patient should be instructed about the preparatory measures by the attending physician. He tells you what factors (medicines, oral contraceptives) can distort the result of a biochemical analysis and what should be done to ensure that the data obtained during the study are reliable. Standard training includes:
- Ensuring blood donation on an empty stomach - it is advisable not to eat food for 8-12 hours, do not overeat at the last meal, avoid fatty, pickled, spicy foods, and smoked foods. Fasting for more than 14 hours is not recommended. You are allowed to drink water (still).
- Avoid physical activity, emotional stress, and stressful situations on the eve of blood collection.
- Abstain from drinking alcoholic beverages. The restriction period must be at least 3-5 days.
- Stop smoking – at least 30 minutes in advance. before the procedure.
Enzyme content standards
Normal values vary greatly by age. Laboratory test results should be interpreted based on the standards indicated on the GGT analysis form. Each laboratory, in accordance with internal regulatory standards, establishes and officially approves its reference ranges for a specific gender and age. The reason that the limits of norms may vary is due to differences in the equipment used and the blood analysis technique used. The content level is indicated in international units, designated IU or ED, per 1 liter of blood plasma. For reference, the table shows approximate data on the level of the GGT enzyme.
| Age | Reference limits (upper limit of normal) Female / Male |
| up to 6 months | 204 |
| 7-12 months | 34 |
| 2-6 years | 23 |
| 7-12 years | 19 |
| 13-17 years old | 38 / 52 |
| adults | 39 / 66 |
Reasons for reducing GGT
Deviation of the indicator from the norm to a lesser extent is less common; in most cases, this condition does not need correction. The doctor’s task is to cure the underlying disease that caused the decrease in the concentration of gamma-glutamyltransferase in the blood. If the result does not fall within the lower limits of the norm, this may be a consequence of:
- acquired or hereditary hypothyroidism – lack of thyroid hormone;
- autoimmune thyroiditis;
- lack of iodine in food;
- consuming large doses of ascorbic acid.
How is biochemical analysis for GGT/GGTP performed?
The biomaterial for research is blood serum (from 1 ml.). Venous and capillary blood is used. The sampling is performed from the vein of the elbow or another vein accessible for fixation. A tourniquet is applied above the puncture site, and the skin area is treated with an antiseptic. The collected whole blood is transfused into a test tube and then, subject to a certain temperature, delivered to a biochemical laboratory (within 2 hours).
During transportation and storage, care must be taken not to cause hemolysis of the blood sample. There are several methods for determining GGT activity; each laboratory uses its own method. The period for completing the study and issuing the result presented in numerical form is from 3-5 hours to 1 day. The form issued to the patient or doctor who wrote out the referral for biochemical analysis indicates the value obtained during the study, the unit of measurement and the variant of the norm.
What are the dangers of deviations from the norm?
A high level of the GGT enzyme in the blood is not dangerous in itself. A pathological process that provokes an increase in the concentration of gamma-glutamyltransferase poses a threat to human health and even life. This protein is the first to respond to the destruction of liver cells and blockage of the bile ducts. Moreover, to determine the level of danger, the following statement is true: the greater the deviation of the value from the upper limit of the norm, the more severe the disease.
If the analysis reveals a low concentration of GGT in the blood plasma, then there is no health risk in this case. But this result of blood biochemistry serves as a reason for diagnosing the functions of the thyroid gland, determining the level of thyroid-stimulating hormone produced by the pituitary gland and the main thyroid hormones - T3 and T4. They coordinate the work of the digestive, reproductive, cardiovascular and other systems of the body.
Enzyme level correction
Increased GGT activity indicates the development of the disease. The way to reduce the level of the enzyme in the blood plasma is to prescribe competent treatment to eliminate the provoking factor. Medicines and therapeutic procedures are prescribed by a doctor after a comprehensive examination of the patient (to eliminate the possibility of error) and an accurate diagnosis. If endocrine system dysfunction is not detected with low GGT, it is recommended to include iodine-rich foods in the diet as a treatment.
How you can lower GGT yourself

Doctors do not recommend trying to reduce the concentration of Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase by taking any medications or traditional medicine. Diseases that provoke an increase in this indicator in the blood are quite serious; they require timely and adequate therapy. This will help avoid worsening the disease. Only an experienced doctor can choose the right treatment tactics.
To speed up the process of normalizing the biochemical composition of the blood and improving treatment results, the patient can:
- exclude alcohol, smoking;
- reduce weight;
- eat enough, give up unhealthy foods (fried, smoked, flour, spices and pickles, soda);
- include more vegetables (pumpkin, carrots, spinach are healthy) and fruits (citrus fruits, apricots) in your diet;
- normalize the drinking regime, replace coffee and tea with clean water;
- take vitamins, mineral complexes (with the approval of a doctor);
- strengthen the immune system;
- to walk outside.
If you start treatment at an early stage of the disease, the prognosis is quite favorable.