Hormonal levels change almost immediately from the moment of conception. The first trimester (1-12 weeks) the embryo develops very intensively. Obstetric pregnancy begins from the moment of ovulation, and actual pregnancy begins from the 3rd week, when the fertilized egg reaches the uterus through the fallopian tubes and attaches to the endometrium.
At this moment, the tissue of the fetal egg begins to secrete hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin), which will be present in the body throughout the entire gestation. This protein hormone will be responsible for maintaining the hormonal levels responsible for favorable conditions for fetal development.
It appears in urine within a few days after fertilization, and many modern test strips are based on a reaction to hCG and a change in the color of the strip. Also, this hormone is used to detect an ectopic or multiple pregnancy even before it is visualized by an ultrasound machine. HCG peaks at 6-7 weeks from the moment of conception, then the concentration drops, but remains in the woman’s blood until childbirth.
Important hormones during pregnancy: how they affect a woman’s body and appearance
Starting from the 6th week, CSM - chorionic somatomammotropin - begins to be produced. Thanks to the interaction with estrogen, milk ducts develop, and due to progesterone, glandular tissue increases in pregnant women, and with it the size of the breasts.
No wonder they say that pregnancy rejuvenates a woman. Human chorionic gonadotropin promotes cell renewal, increases the concentration of thyroid hormones, and accelerates metabolism. If a woman does not have problems with the thyroid gland, it seems to blossom: the skin color becomes brighter, minor imperfections disappear, small wrinkles are smoothed out. But with a certain hormonal imbalance (lack or excess of T3 or T4), the appearance of the pregnant woman worsens, acne appears, the skin becomes covered with spots and irritations.
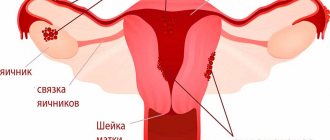
Progesterone and estrogen are produced by the corpus luteum, a temporary gland formed at the site of a ruptured follicle after ovulation, and support the endometrium. The onset of pregnancy largely depends on the required amount of estrogen (more precisely, the hormones estrone, estradiol and estriol). It is responsible for the blood supply to the endometrium and maintains the normal internal mucous membrane of the uterus. Subsequent development of the embryo also depends on the required amount of this hormone.
Progesterone is a derivative of cholesterol compounds from the blood. The hormone ensures that the mother’s immune system does not begin to reject the embryo as a foreign body. Progesterone prevents contraction of the uterus and is responsible for the growth and stretching of the uterine muscles.
- An increase in estrogen leads to the retention of excess fluid, and the pregnant woman develops edema. The hormone also leads to the accumulation of excess fat in the subcutaneous layers, so during pregnancy some women “spread it.” Improved blood supply leads to the appearance of spider veins and the growth of moles. Skin sensitivity increases and excessive pigmentation appears. Mood swings are also caused by excess estrogen, which causes depression.
- Progesterone relaxes smooth muscles, preventing uterine contractions. But at the same time, the intestinal muscles relax, the woman suffers from constipation and heaviness in the stomach. Softening of connective tissues leads to the appearance of stretch marks, as well as dry skin and acne.
The tandem of estrogen and progesterone prepares the mammary glands for lactation, dilates the ducts, but does not allow milk to form until birth. When a baby is born, the level of these hormones drops, prolactin affects the ducts, and the woman produces colostrum - the very first milk.
A drop in progesterone leads to spontaneous miscarriage. Fetal malformations and infections reduce estrogen (estriol) levels, also causing embryo rejection. Pregnant women have blood tests for estrogen and progesterone every 2 weeks. Changes in the levels of these two hormones indicate pathology of embryo development.
Hormone production
The endocrine system consists of the following endocrine glands:
- pancreas, thyroid, thymus and parathyroid glands;
- adrenal glands;
- ovaries;
- pituitary;
- hypothalamus.
The blood carries the hormones produced throughout the woman’s body. Any malfunctions in the functioning of this system can lead to problems with conceiving a child, uterine fibroids, polycystic ovary syndrome and other possible diseases.
It is very easy to disrupt the fragile system of hormonal balance in the body. Daily stress, fatigue, lack of sleep, past illnesses, bad habits, taking certain medications - this is not a complete list of what can have a negative impact on a person’s hormonal status.
Hormones by trimester of pregnancy
In the 1st trimester of pregnancy, it will be very important to determine the level of alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) - a specific protein that is produced by the membrane of the fertilized egg. It plays a huge role in the development of the baby: it ensures the delivery of protein material for the growth of embryonic cells, protects the fetus from the influence of the mother’s estrogens, maintains normal blood pressure in the baby, suppresses immune cells and prevents the embryo from being rejected.
An AFP test is taken from the 5th week of pregnancy. Low levels lead to the birth of a baby with pathologies, and an increase in levels above normal leads to miscarriage or premature birth in the future.
Thyroid hormones T3 and T4 also change during pregnancy. Due to the increase in the amount of progesterone, the thyroid gland is activated. At the same time, more selenium-containing protein, which binds free thyroxine, is released into the blood. For this reason, in the 1st trimester, T4 levels fall below normal.
T3 in the 1st trimester, on the contrary, increases. Lack of triiodothyronine poses a threat to the mother's life. There is a risk of giving birth to a baby with pathologies, because until 12 weeks the embryo compensates for the need for T3 at the expense of the mother. In this case, the doctor prescribes drugs based on a synthetic analogue.
Considering the vital importance of thyroid hormones, it is advisable for a woman to know her hormonal levels before pregnancy, otherwise any deviation can lead to serious consequences.
Start of article HERE
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter
When are blood tests for hormones indicated?
Hormonal examinations for hormones during gestation are prescribed if there are the following indications:
- Suspicions of pathologies of pregnancy (persistent menstrual dysfunction, history of miscarriages). In such a case, the concentration of hormones such as cortisol, prolactin and progesterone is checked;
- Partial placental abruption or threatened miscarriage. Hormones are checked 2 times a week in the period from 5 to 13 weeks by determining the concentration of hCG in the blood;
- High probability of developing genetic and congenital anomalies of fetal formation (Down syndrome, hydrocephalus, neural tube pathologies). To monitor hormone levels, two biochemical tests are prescribed (in the 1st and 2nd trimesters). In this case, a triple analysis is carried out: examination of the level of alpha protein, free estriol and hCG.
Based on the published materials, the following conclusions can be drawn:
- Patients with microadenomas (<10 mm) can be observed once every trimester, because the tumor usually does not increase in size;
- While patients with macroadenomas (>10 mm) and patients receiving drug treatment for <1 year before conception should be monitored monthly for symptoms indicating an increase in tumor size (headache and visual disturbances);
- If they occur, it is necessary to perform an MRI without contrast;
- If the tumor size increases, it is necessary to begin therapy with dopamine agonists (bromocriptine or cabergoline);
- If drug treatment is ineffective, surgical intervention may be performed after the first trimester;
- These women should be advised not to breastfeed.
LH (luteinizing hormone): what is it? Functions, tasks and norms
Luteinizing hormone is produced by the pituitary gland. This hormone is extremely important for the female body. It stimulates the production of estrogen, plays an important role in regulating progesterone levels, and thanks to LH, the cyclicity of menstruation is regulated.
Emotional stress, oral contraceptives, surgical interventions, taking certain medications - all this can have a negative impact on the level of LH in the blood.
How to get tested for luteinizing hormone levels?
If the cycle is regular, then it should be taken 6-7 days after the start of menstruation, but if not, any other day. You need to stop doing physical activity a day, stop smoking an hour, and try to calm down before taking tests. In case of acute illnesses, testing should be postponed to a later date.
What are the norms of the above-mentioned hormone in the female body?
- 1 – 12-14 days of the cycle – 2-14 mU/l
- Days 12-16 of the cycle – 24-150 mU/l
- 16-before the first day of the menstrual cycle – 2-17 mU/l.
Estradiol: concept, functions in a woman’s body, norms
Estradiol is a female sex hormone that is synthesized in the ovaries and is “responsible” for female beauty.
What is the role of the hormone estradiol in the female body?
Estradiol takes part in the formation of the body according to the female type, regulates the cyclicity of menstruation, takes part in the development of secondary sexual characteristics of women, and takes part in the maturation of the egg in the ovaries.
Factors that negatively affect the level of the hormone estradiol in a woman’s blood:
- liver diseases and sexual diseases;
- taking certain medications;
- heavy physical activity;
- diets, fasting, weight loss;
- bad habits.
How to get tested for estradiol levels?
The test must be taken on an empty stomach, the last meal should be no later than 8 hours ago. A day before the test, exclude fatty, fried foods, alcohol in any form, and, of course, smoking from your diet. Do not take the test after X-ray exposure or physiotherapeutic procedures. Be sure to inform your doctor about the day of your monthly cycle.
The norms of the hormone estradiol in a woman’s blood according to the phases of the menstrual cycle:
- follicular phase (menstruation) – 68-1269 pmol/l
- ovulatory phase (10-13 days of the cycle) – 131-1655 pmol/l
- luteal phase (20-22 days of the cycle) – 91-861 pmol/l
- postmenopausal period - less than 73 pmol/l.
Choosing a clinic for testing and interpretation of results
If future parents are thinking about a baby, then we are talking about conscious pregnancy planning. If the long-awaited pregnancy does not occur, the doctor will most likely order hormonal tests. LH, FSH, estradiol, prolactin, progesterone, testosterone, T3 - free (triiodothyronine), T4 (thyroid-stimulating), antibodies to TSH - this is the list of hormones that you will most likely have to test.
It is not enough to perform a reliable analysis; you also need an experienced reproductive specialist who will correctly interpret the results and give professional advice.
Hyperandrogenism in women: treatment
Not every woman with signs of androgenism needs treatment, since many successfully give birth to several babies. The need for treatment arises when there is a threat of miscarriage or infertility that appears against the background of androgenism. However, choosing therapy to block pregnancy is quite difficult - since the range of medications is not very wide. Temporary synthesis or exposure to androgens is necessary; glucocorticoid hormones are used for this, since no others can be used during pregnancy. According to the mechanism of action, they suppress the function of the pituitary gland, which is located in the brain of a special endocrine gland that controls the production of androgens. This reduces the stimulus to the adrenal gland to synthesize androgen and lowers its level in tissues and blood plasma. The dosage is selected by the doctor based on the level of the problem based on the results of laboratory tests. Usually they start treatment with the minimum possible dosage and monitor their well-being.
Naturally, women are afraid to use hormones, especially in the first weeks of pregnancy, during the period when the baby’s main systems and organs are formed, worrying about the birth of a child with disabilities. However, it has now been unequivocally proven that these drugs do not affect the development of the child, and many children born after such therapy are now giving birth to children themselves. Therefore, reviews for the treatment of hyperandrogenism in women are usually only positive. But all the same, tablets are prescribed only according to strict indications and with precise adherence to doses. All drugs today carry a warning for pregnant women, and doctors prescribe medications based on clinical trials conducted, as well as experience with the drugs. If there is the slightest doubt, therapy will be canceled.
Our clinic conducts a detailed study of patients, based on the results of which the most gentle, but at the same time effective course of treatment is prescribed. Therefore, the expectant mother does not have to worry about her health or the condition of her baby.
How is diagnosis carried out?
This condition can be confirmed using laboratory analysis - identifying the number of active male sex hormones in the plasma. The study is carried out when there is a threat of interruption, as well as during examination. But it is not easy to identify them - partially active metabolites can be detected in daily urine. This is a fairly simple and very revealing research technique, although tedious. The level of a special composition is determined in the urine. This testing has not lost its relevance since the beginning of its discovery.
Changes in the pituitary gland during normal pregnancy
- The shape and size of the pituitary gland changes throughout life: a slight increase is noted during puberty and reproductive age (reaching a maximum of 10 mm).
- During pregnancy, the cells of the anterior pituitary gland undergo various changes: In response to increased estrogen concentrations, the number and size of lactotrophs increase, which in turn leads to an increase in the size of the pituitary gland.
- Reduction in the number of gonadotrophs.
- Thyrotrophs and corticotrophs – no changes
- During pregnancy, production of growth hormone (GH) by the placenta and a secondary increase in insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) leads to suppression of somatotroph function.
During pregnancy:
- Normally, the pituitary gland increases in size;
- GH and IGF-1 levels also increase (secondary to increased placental GH);
- In most cases, microadenomas do not increase in size;
- Increasing the levels of GH and IGF-1 does not have a significant negative effect on blood pressure and carbohydrate metabolism in the mother;
However, patients with acromegaly require careful monitoring:
- Women receiving long-acting somatostatin analogues should be switched to short-acting drugs when planning pregnancy;
- All medications should be discontinued once pregnancy is confirmed;
- Women with macroadenomas should have their visual fields checked monthly;
- If symptoms or visual field impairment occur after the first trimester, an MRI without contrast should be obtained;
- If the tumor size increases, it is necessary to begin therapy with dopamine agonists (bromocriptine or cabergoline);
- The use of the drug is limited to only two indications: tumor growth and headache;
- If drug treatment is ineffective, transsphenoidal surgery may be performed in the second trimester;
- Women with microadenomas should be monitored every three months;
- Women who experience tumor growth during pregnancy should be advised not to breastfeed.
Source : Laway BA. Pregnancy in acromegaly. Therapeutic Advances in Endocrinology and Metabolism
. 2015;6(6):267-272. doi:10.1177/2042018815603927.