16.07.2020 41706 0
The sixth week of pregnancy according to obstetric calculation is the fourth embryonic week. This means that about 28 days have passed since conception. At this stage, most women no longer just guess about their new status, but have official confirmation in the form of a positive pregnancy test and/or a gynecologist’s report. But this is not enough for the expectant mother. It is important for her to know what to do, what is happening to her body, how the baby is developing and what changes to expect during this period.
Interesting Facts
| Options | Indications |
| Time from conception | 4 week |
| Period by month | 6 weeks |
| What month | 2 |
| Dimensions and weight of the fetus | 2-4 mm, 1.3-1.5 g |
| Uterus dimensions | A little more than normal |
| Pregnant weight | Depends on the severity of toxicosis |
Your baby is the size of
Black peppercorn
2-4mm Size
1.3-1.5 g Weight
The sixth week of pregnancy is a special period when the formation of the baby’s brain, as well as the chorionic villi - the future placenta - begins. What else happens to mother and baby at this stage? What can already be seen on an ultrasound? How to prevent the development of complications?
Let's sort it out in order and start with the counting method. 6 weeks is how many months, what trimester and how much time has passed since conception? Our calendar is compiled in accordance with obstetric dates, that is, the beginning of pregnancy is considered the first day of the last menstruation. Thus, you are now in the sixth obstetric week, or you have 1.5 months of gestation, or 4 weeks from conception, which corresponds to 1 trimester.
Changes in a woman's body
External signs
. At this stage, the belly continues to retain its pre-pregnancy shape, so the happy position will not be visible either externally or in the photo. But the expectant mother may notice other changes. Under the influence of hormones, the amount of pigment in the skin increases. Women prone to hyperpigmentation may develop freckles or age spots, a darker stripe down the middle of the abdomen, and visibly darker and rougher nipples and areolas. Many women are pleasantly surprised to notice that their skin has become radiant and their hair has become especially silky.
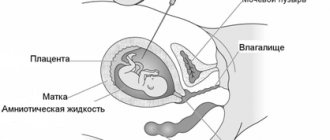
Enlarged uterus.
The baby grows, and the uterus grows with him. In the sixth week, it increases to the size of a large plum, which still does not affect the contours of the figure. And if a woman notes that her favorite jeans have become slightly tight at the waist, then this is not due to an increase in the size of the uterus. Most likely, changes in appetite during pregnancy, decreased physical activity, or hormonal changes led to slight weight gain or swelling.
Hormonal changes.
Hormones control the course of pregnancy, and this is not an exaggeration. For example, progesterone, the main participant in this process in the early stages, is responsible for ensuring that pregnancy is not only established, but also maintained. True, this same hormone can slow down intestinal motility, which manifests itself as constipation. And other pregnancy hormones often cause emotional swings when the expectant mother experiences unreasonable sadness, joy or irritation (and this is all within a short period of time). Hormones can also affect libido: temporarily reduce it to almost zero or, conversely, increase the sexual appetites of the expectant mother.
Feelings of the expectant mother
Increasing the level of progesterone, necessary for the maintenance and development of pregnancy, affects the woman’s well-being.
Extreme fatigue and mood swings
At 6 weeks pregnant, you may feel completely exhausted, even after minor normal exercise. Then suddenly you feel euphoria, then again complete decline. During this period, headaches and dizziness may appear. This condition can be improved with proper nutrition: make sure your diet contains enough iron-containing foods. A good night's sleep is also important. If you can afford to take a nap during the day, it is priceless.
Nausea
A very individual symptom. Some people don’t feel it at all, while others suffer from toxicosis until the 3rd trimester. Nausea can be triggered by smells or hunger, but sometimes it occurs on its own. Eat small meals, keep unleavened flour products on hand for an easy snack, and spend more time in the fresh air. And don't despair. It will soon pass!
Frequent urge to urinate
The uterus increases in size and puts pressure on the bladder. You will want to go to the toilet more often. Unfortunately, this is inevitable. Don't deprive yourself of fluids, but plan your routes taking into account the possibility of visiting the WC.
Breast condition
Due to increased blood flow, the mammary glands swell slightly, increasing in size. The skin becomes more sensitive, and the areola may darken. These are physiological changes of pregnancy that do not have negative consequences.
Vaginal discharge
Normally they should be transparent white, with a sour odor. If you experience brown, pink, or cheesy white discharge, consult your doctor immediately. This is a symptom of threatened miscarriage, as well as thrush and other inflammatory diseases.
It is important!
Nausea and vomiting are experienced by approximately 70% of pregnant women, usually occurring in the first trimester of pregnancy*.
The severity of toxicosis varies widely. An expectant mother may experience nausea only from the taste of a certain product, only in the morning or only in hot weather, etc. But attacks of severe nausea can be overcome by any strong smell, even from one that she previously liked (from her favorite perfume, the aroma of fresh baked goods and etc.).
Increased fatigue.
A growing fetus needs energy. But he is completely dependent on the mother, so she has to share her resources with the baby. If a woman has no problems with her health, and her lifestyle can be called healthy, then such energy consumption is not very noticeable. But if a pregnant woman suffers from toxicosis, often experiences stress or is exposed to physical exertion, then the feeling of fatigue and drowsiness is quite pronounced.
Frequent urination.
Frequent urge to urinate can be observed already in the very early stages of pregnancy. This is due to both hormonal changes in the body and an enlarged uterus, which irritates the bladder.
Mood swings.
Again, hormones are to blame. In most cases, the body adapts to its new status, and mood swings stop or become less pronounced. But in the first trimester, the expectant mother needs to be prepared for the fact that emotions will not depend on objective circumstances. Causeless euphoria and sadness can replace each other just like that and several times over a short period of time.
New taste preferences
. The need for a pregnant woman to eat something strange has become almost a legend. But this phenomenon has a completely understandable explanation. A woman's body becomes a vessel in which new life develops. And this life requires a variety of substances that are not always fully present in the diet of the expectant mother. With such an irresistible need to eat something unusual, the baby signals his own needs. Doctors recommend listening to such signals. But if they are too frequent and urgent, then it makes sense to reconsider your diet and adjust your diet in general.
What does an embryo look like at 6 weeks?
The size of the fetus at this stage is about 2-4 mm. He's like a pomegranate seed. The rudiments of arms and legs appear, the tail disappears, the skull and brain, upper and lower jaws, eyes, nose, mouth and ears are formed.
Internal organs develop rapidly:
- the intestinal tube will turn into the stomach, small and large intestines;
- the rudiments of the genital organs are formed;
- red blood cells, leukocytes and other blood cells appear;
- The heart already has 2 atria and a ventricle. On an ultrasound, you can hear it beating and count 120-140 beats per minute.
Features of embryo development
The 5th week of pregnancy corresponds to the beginning of the second obstetric month, i.e. From the moment of implantation of the fertilized egg into the endometrium, about 29-35 days pass. In an ultrasound photo, a 5-week embryo looks like a small cylinder 6-7 mm long. During this period of pregnancy, it is possible to distinguish the buds of the arms and legs, as well as the auricles and nasal slits of the embryo.
Starting from the 5th week of gestation, the formation of the pancreas, upper respiratory tract and liver occurs. It is during this period that the child’s heart makes its first beats, and the circulatory system continues its active development. In the last days of the fifth week of pregnancy, the rudiments of the bone marrow, the thyroid gland and individual elements of the musculoskeletal system are formed.
With the help of transvaginal echography, it is possible to distinguish between the eye sockets and the development sites of the inner and outer ear. Due to the underdevelopment of soft tissues, it is impossible to determine the sex of the child in the early period of gestation. However, the umbilical cord and individual elements of the endocrine system are clearly visible in the photographs.
Analyzes and research
If you register for pregnancy in the sixth week, you will receive a long list of tests. You will have to donate several tubes of blood to find out:
- hemoglobin and sugar levels;
- progesterone and hCG content;
- concentration of bilirubin, liver enzymes, fibrinogen;
- HIV, AIDS and STD status;
- your Rh factor, blood type and evaluate your coagulation system;
- presence/absence of hepatitis and TORCH infections.
The doctor will also conduct an external examination, measure your height, weight, pelvic volume, and blood pressure. From the 6th week of pregnancy until delivery, you need to take a general urine test weekly.
What will an ultrasound show?
An ultrasound can confirm pregnancy, determine the number of embryos and their correct location in the uterine body. This is important, because diagnosing an ectopic pregnancy in time means preserving the woman’s reproductive functions.
Pregnancy in an unknown place
Pregnancy in an unknown location is a term used to describe a transient condition of early pregnancy during which ultrasound does not reveal MB and the adnexa are normal—in other words, “normal” pelvic ultrasound findings. At this stage, the three main possibilities include early MB, occult ectopic pregnancy, and complete spontaneous abortion. Unfortunately, serum beta-hCG levels alone do not reliably differentiate between these possibilities.
.
In the case of a positive pregnancy test with low beta-hCG levels, it may be too early to visualize the site of blastocyst implantation. Despite a number of studies reporting a discriminatory beta-hCG level (the value above which an intrauterine ulcer is consistently visualized in normal pregnancies on ultrasound) of 1000–2000 mIU/ml (1000–2000 IU/L), the validity of the discriminatory level in exclusion of a viable pregnancy is less than initially reported. For example, studies have reported cases of fetuses with cardiac activity on follow-up ultrasound after an initial ultrasound that did not detect PU with beta-hCG levels greater than 2000–3000 mIU/mL (2000–3000 IU/L). In addition, multiple pregnancies result in higher beta-hCG levels at any gestational age compared with those in singleton pregnancies. Although the chance of an ectopic pregnancy increases significantly with an empty uterus and higher beta-hCG levels, especially if the level is above 3000 mIU/ml (3000 IU/L), the chance of a viable ectopic pregnancy is still 0.5%.
Thus, in a patient who is hemodynamically stable and has a pregnancy in an unknown location, it is less risky to wait, monitor beta-hCG levels, and ultrasound than to presumptively treat an ectopic pregnancy.
By explaining the limitations of this technology, healthcare providers can help patients appreciate the uncertainty of the diagnosis and the need for appropriate follow-up. As Doubilet and Benson (2010) so eloquently state: “Above all, do no harm.”(*I think this principle can be safely dated earlier than 2010 - primum non nocere - as it refers to the so-called oath Hippocrates).
Alarming symptoms and possible complications
One of the main dangers of the first trimester is ectopic pregnancy. The growth of the embryo in the fallopian tube leads to its rupture. This can happen as early as 5-6 weeks. It is impossible to determine the pathology on your own: all the symptoms coincide with intrauterine pregnancy.
However, you should be alerted to sharp nagging pain in the lower abdomen and lower back, as well as bleeding, which is often breakthrough, that is, sudden. At this time, it is important to provide immediate medical attention, since excessive blood loss can be fatal.
Another possible complication of the sixth week is intrauterine death or fetal death. It occurs due to hormonal disorders, infections, problems with the blood coagulation system, and chromosomal disorders in the embryo. The condition can be recognized by the following symptoms:
- spotting dark bloody discharge;
- severe weakness and fever;
- lower abdomen hurts;
- soreness of the mammary glands disappears;
- A blood test will show a decrease in hCG levels.
Terminology
Accurate interpretation of ultrasound findings in the first trimester requires the use of appropriate and consistent terminology, as outlined in Doubilet et al. (2013). The criteria for viable and non-viable MBs are simple. However, MB of unknown viability is a broad category and can lead to confusion. To be precise, MB of unknown viability can apply to normal pre-embryo development situations with cardiac activity, including empty PU (PM with a yolk sac but no embryo), and PU with a yolk sac and an embryo smaller than 4 mm but without cardiac activity. activities. The second category of unknown viability is used when there is evidence of miscarriage (signs of poor prognosis). The authors of the publication found that using the term MB of unknown viability is more appropriate in this case because it conveys a sense of alertness. Alternatively, for small uterine ulcers, it is preferable to use the term “early intrauterine uterine ulcer at __ gestational age” instead of urinary tract of unknown viability, with a recommendation for follow-up ultrasound to confirm normal pregnancy development.
Pregnancy in an unknown location has several scenarios, and the authors encountered these scenarios while applying this terminology to their patient population. If the results of pelvic ultrasound are almost normal, a differential diagnosis of “very early MB”, “non-visualized ectopic pregnancy” or “complete spontaneous abortion” is provided. When vaginal bleeding and thickening of the heterogeneous endometrium occur, the authors used the term “pregnancy in an unknown location, the most likely scenario is spontaneous termination of pregnancy.” Detection of an area of low-resistance arterial trophoblastic flow may be useful to confirm the site of intrauterine implantation in these situations. However, spectral Doppler ultrasound should not be used in the first trimester if normal viable MB is likely (*And I keep hearing that these recommendations are often ignored...). The third scenario is vague intrauterine fluid accumulation. While intrauterine PO and early MB may be most likely, the differential diagnosis also includes a decidual cyst and localized intrauterine fluid. Thus, in these situations, it is recommended to monitor beta-hCG levels and control endovaginal (*transvaginal) ultrasound after 7-10 days.
Nutrition and exercise
We advise you not to indulge in salty foods, even though you really want to. Excessive salt consumption causes fluid retention and swelling. Avoid fast food: it contains a lot of salt and sugar. It's better to switch to homemade food when you know exactly what it's made from.
In the absence of contraindications, we welcome any physical activity during the 6th week of pregnancy. Walk, walk, swim in the pool, do yoga - all this is very useful and safe for you and your unborn child.
Recommendations
Remember every second that your baby is sensitive to any external influence. Do not take any medications without your doctor's permission, try to avoid stress, get plenty of rest and eat well.
It is best if you eat food in fractions (eat often, but in small portions). At 6 weeks of pregnancy, it is necessary to include complex carbohydrates in the diet, which are beneficial for the digestive system. To do this, eat legumes, cereals, pasta, garden herbs, zucchini, cabbage, bell peppers, apples, peaches, grapefruits, cherries. Avoid all edible “harmful” foods, but do not forget to consume foods that contain calcium (milk, cheese, cottage cheese, kefir, etc.).
Continue taking your vitamin/mineral supplement (if you are vomiting, take your vitamins when you are least nauseous). Weigh yourself regularly and monitor your blood pressure: if it is slightly low, there is no need to worry, but if it is elevated, this is a reason to be wary. By the way, not only various diseases, but also nervous experiences can increase blood pressure, so you need to learn to calm down and relax.
Checklist for the sixth week of pregnancy
- You can already register with a antenatal clinic or enter into a contract for pregnancy management in a private center.
- Start learning breathing exercises: it will help reduce stress levels and will be very useful during childbirth.
- Control your body weight: normally, the weekly gain should not exceed 600-700 grams.
- Spend 40-60 minutes a day outdoors, preferably away from highways.
- If you have a cold or ARVI, do not take any medications without a doctor’s prescription and read the instructions carefully.
- If you suddenly feel dizzy, try to quickly sit down or lean on something. If conditions recur frequently, check your hemoglobin level.
- To prevent constipation, drink more water, eat fiber-rich foods, and exercise. All this stimulates intestinal motility.
If you have the opportunity to delegate some of your household tasks to someone and take a little nap, do it without a twinge of conscience! The first trimester is a difficult period when serious hormonal changes occur in the body, which cannot but affect a woman’s well-being. Now you are experiencing enormous psychological stress. Therefore, first of all, take care of yourself! And for all questions related to pregnancy, you can consult with the gynecologists of the Medical Women's Center.
Pregnancy management after IVF
Proper gestational support reduces the likelihood of spontaneous abortion and abnormal fetal development. To prevent complications, it is advisable to be observed by specialists at the clinic where the IVF procedure was performed within 6-8 weeks after conception.
During the first trimester of pregnancy, patients should undergo regular blood tests to determine the level of:
- human chorionic gonadotropin;
- estrogen;
- progesterone.
A low concentration of steroid hormones is the basis for corrective hormonal therapy. It should be understood that an ordinary obstetrician-gynecologist in the antenatal clinic does not have sufficient experience in managing patients who have undergone IVF. If the risk of miscarriage increases, the fertility specialist will recommend undergoing additional examination or hospitalization.
What a fetal ultrasound can and cannot reveal
1st trimester
: Ultrasound reveals the following pathologies:
- defects of the central nervous system (for example, anencephaly - absence of the brain);
- absence of the peritoneal wall (severe pathology - gastroschisis);
- spinal abnormalities - absence, hump, etc.;
- Down syndrome;
- umbilical hernia (diagnosis of omphalocele);
- absence of limbs.
2nd trimester
: all visible abnormalities can be identified, since all organs of the fetus are almost formed by this time.
3rd trimester
: defects previously identified by blood tests, chorionic villus biopsy and other methods are confirmed or refuted.
It is impossible to diagnose using ultrasound:
- blindness and deafness - ultrasound cannot show the quality of transmission of nerve impulses to visual and auditory receptors
- mental retardation, since these are properties of the brain, not its structure;
- minor disorders of organ development (for example, obstruction of the liver ducts or defects of the cardiac septum);
- some genetic diseases (for example, Duchenne myopathy, phenylketonuria, cystic fibrosis are not diagnosed);
- chromosomal abnormalities themselves (Edwards, Patau, Turner syndromes), the doctor can only observe the result of their development.
Having studied the list of problems that are not detected on fetal ultrasound, you should not worry - these pathologies will not go unnoticed. Many fetal malformations are detected by blood tests for fetal pathology and other special methods.