A woman’s age is one of the important factors influencing the effectiveness of ART methods, since this parameter is directly related to the quality of the eggs located in the ovaries. This parameter is not absolute, since a 45-year-old woman could have good quality eggs and still be fertile at this point - although this particular situation is more unusual than usual.
On the other hand, in some cases there are women who even at the age of 25 have “low-quality” eggs and even need donor eggs.
These extreme examples, however, quite existing, led to the need for some way to assess the quantity and quality of eggs in women of different age groups. It was for this purpose that the concept of “ovarian reserve” was introduced, since it became necessary to evaluate a woman’s reproductive age, not as the absolute number of years from the date of her birth, but as her real existing ability to become pregnant.
Ovarian reserve is the number of eggs in women at a given time that can be used for fertilization.
But how to count them, they are located in the ovaries? For this purpose, a number of functional tests have been proposed, which you can learn a little about in this section.
In what cases is transvaginal examination prescribed?
This method of ultrasound examination has significantly expanded the possibilities of diagnosing diseases of the female genital organs, including the uterus.
It may be prescribed by a gynecologist or surgeon for the following indications:
- The girl has spotting, but she is sure that it is not menstruation.
- A woman has been sexually active for six months, but cannot become pregnant.
- She feels pain in the lower abdomen, but not on the days when she has her period.
- If menstruation is too long or short, it normally lasts from 3 to 7 days.
- Under certain conditions, transvaginal ultrasound is prescribed as part of an annual preventive examination.
The only contraindication to this procedure can only be the virginity of the girl. In such cases, a conventional abdominal ultrasound is used or an examination through the rectum is performed. Also, do not forget that transvaginal ultrasound is prohibited in the second and third trimesters of pregnancy.
Counting the number of antral follicles
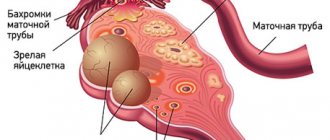
Antral follicles are small follicles (2-8 mm in diameter) that we can see, measure and count using ultrasound. Transvaginal ultrasound is the optimal method for counting these small structures.
The fact is that the number of antral follicles has a direct relationship with the number of primordial follicles, visible only during microscopic examination, located in the ovaries. Each primordial follicle contains a precursor to an egg, which may become one in the future.
Thus, counting antral follicles visible on ultrasound replaces microscopic examination of the ovaries for accurate assessment of the number of oocyte precursors.
Counting antral follicles using ultrasound is a simple and accessible method for assessing ovarian reserve.
Figure 1 on the left shows an ovary (outlined in blue) in which antral follicles were counted at the beginning of the menstrual cycle (outlined in red). In this projection of the ovary, 16 such follicles are visible.
What is the “good” number of antral follicles?
Based on a number of studies by foreign authors, the following pattern has been revealed:
| Number of antral follicles | Expected response to ovulation stimulation and the effectiveness of ART techniques |
| Less than 4 | Very low quantity. Poor or no response to stimulation. Enrollment in an IVF program should be seriously considered. Very low chance of pregnancy. |
| 4-7 | Low quantity. There may be a slight response to stimulation. It is preferable to use very high doses of FSH for stimulation. Unsuccessful attempts. |
| 8-10 | Slightly reduced quantity. A large number of unsuccessful attempts. |
| 11-14 | Normal (but average) amount. The response to stimulation is reduced, but, as a rule, sufficient. Group with a favorable prognosis for pregnancy. |
| 15-26 | Normal good quantity. Excellent response to ovulation stimulation. It is preferable to use low doses of FSH. Best efficiency. |
| More than 26 | A high amount characteristic of polycystic ovary syndrome. The use of low doses is necessary due to the risk of hyperstimulation syndrome. In some cases, the eggs are of low quality, which reduces the chance of pregnancy. |
What diseases can this procedure diagnose?
This ultrasound scanning method will help the doctor determine exactly how healthy the female reproductive system, uterus, ovaries and fallopian tubes are. It is also often used to diagnose pregnancy pathologies.
Using such a scan, you can detect the following diseases and developmental features:
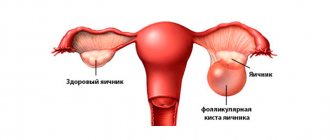
- Ovarian cyst.
- Endometriosis.
- Uterine and ectopic pregnancy.
- Inflammatory processes.
- The presence of pathological fluids - blood or pus in the fallopian tubes.
- Uterine fibroids.
- Endometrial polyposis.
- Partial or complete hydatidiform mole.
- Different types of tumors: benign and malignant.
- Chorionepithelioma.
- Rupture of ovarian cysts or ovarian cancer.
- Fluid in a woman's pelvis.
An ultrasound performed in this way will also help a woman find out when she is ready to conceive; for this, it is enough to monitor the development of the ovaries.
If during the procedure a special contrast agent is injected into the fallopian tubes, you can easily see whether they are passable. This method is indispensable in the treatment of infertility. Also, only he is able to detect the heartbeat of a child from 5 weeks of pregnancy.
Features of the transvaginal ultrasound diagnostic method This method of examining the pelvic organs is much more accurate and informative than conventional ultrasound through the abdominal cavity. More detailed results can be obtained due to the fact that the ultrasound sensor is separated from the objects under study only by the vaginal wall, which has a small thickness. Such a gynecological examination of the uterus and other pelvic organs greatly simplifies the diagnosis; it is done very often, if necessary, repeatedly. The sensor looks like a plastic rod about 12 cm long, its diameter is 3 cm, the handle is usually beveled, and at the end there is a special channel with a needle for performing a biopsy.
Normal ovaries
Rice. 2. Normal ovary with follicular apparatus. There is no dominant follicle, since the study was carried out on the 3rd day of the menstrual cycle.
When assessing the condition of the ovaries using ultrasound, it is determined:
- Position of the ovaries. Normally located on the sides of the uterus, most often asymmetrically, at a short distance from the corners of the uterus. The shape of the ovaries is usually oval, while the right and left ovaries are not at all identical to each other.
- Dimensions of the ovaries (longitudinal, anteroposterior and transverse). The average size of normal ovaries in length is from 2.4 to 4.0 cm, anterior-posterior from 1.5 to 2.5 mm.
- Structure of the ovaries. Normally, the ovaries consist of a capsule and follicles of varying degrees of maturity (in the first phase of the cycle). In the second phase of the cycle, as a rule, the corpus luteum is visualized - a sign of ovulation. The number of follicles may be different on the left and right. The maturing follicle is detected already in the first phase of the cycle and reaches its maximum size by ovulation, on average about 20 mm. The contents of the dominant follicle are homogeneous because it contains follicular fluid and the capsule is thin. After ovulation, at the site of the dominant follicle, a corpus luteum is formed, which, as a rule, has a mesh echostructure (it contains adipose tissue) and also a thin capsule - 1-2 mm. Most often, the shape of this formation is oval or irregularly shaped. In postmenopause, the ovaries are normally either not visualized or are located in the form of fibrous cords.
How is transvaginal ultrasound performed?
You take off all your clothes below the waist, lie down on the couch, bend your knees and spread them apart. Any gynecological examination or examination is performed in the same position. The doctor puts a condom on the sensor and lubricates it with a special gel, which performs two functions: it eliminates the air space between the sensor and the organs, and serves as a lubricant for better penetration.
The vaginal sensor, or transducer as it is also called, is carefully and slowly inserted into the vagina. Due to the absence of sudden movements and the shallow depth of penetration, the procedure should not cause unpleasant or painful sensations in the woman. The organs being examined are displayed on the screen, and the doctor records the necessary data. The procedure lasts no more than 5 minutes.
Possible complications
The main negative consequences of the disease include:
- premature aging of the body;
- inability to conceive and bear a child on your own;
- decreased bone density, pathological fractures;
- increased likelihood of developing coronary heart disease, myocardial infarction;
- decreased performance;
- deterioration in the quality of intimate life.
In addition, depressive disorder may result from exhausted ovarian syndrome. Women feel inferior, some find themselves having suicidal thoughts. Such patients need qualified psychiatric and psychotherapeutic assistance.
How to prepare for a transvaginal examination?
Such an ultrasound is performed only as prescribed by a doctor, most often a gynecologist. Almost no preparation is required; this gynecological examination of the pelvic organs, including the uterus, can be performed any day.
If before a regular ultrasound it is necessary to fill the bladder through the abdominal cavity, then a transvaginal ultrasound is performed on an empty bladder. You should not drink an hour before the procedure; if necessary, the doctor may ask you to go to the toilet. A little preparation is needed only if a woman suffers from increased gas production.
To reduce flatulence, you need to drink Espumisan or Smecta about an hour before the ultrasound.
Diagnosis and treatment of ovarian cysts at ON CLINIC
If you have an ovarian cyst or are suspected of having one, seek advice from specialists at the ON CLINIC International Medical Center. Experienced gynecologists will conduct a full cycle of examination and make an accurate diagnosis, on the basis of which they will select the most effective treatment method.
Do not delay visiting a doctor, make an appointment, because a timely diagnosis will allow you to avoid the development of possible complications and restore the normal functioning of the reproductive system. Our clinic’s modern diagnostic equipment and our own laboratory, which has an international quality control certificate, allow our specialists to conduct any research in the shortest possible time.
According to statistics, 90% of cysts are functional, that is, they do not require treatment, but we should not forget about the remaining 10%. These are dangerous formations that require radical intervention. In order for the disease to be diagnosed at the very initial stage of development (and this allows it to be successfully and quickly treated), it is necessary to undergo a gynecological examination regularly - at least once a year.
The professional team of doctors at ON CLINIC are gynecologists with extensive practical experience. Our specialists can eliminate any problem and restore the health of the female reproductive system. Contact us!
- Ovarian cyst: sizes and norms
What days of the menstrual cycle are suitable for the procedure?
Preparation for this study also involves choosing the appropriate day of the cycle. How accurate the sensor readings will depend on how long ago the woman last ovulated.
It usually occurs from 12 to 14 days after menstruation, and after its completion the condition of the pelvic organs changes significantly. Thus, the girl’s body prepares for possible conception. Transvaginal ultrasound in the area of the uterus and pelvis is mainly performed in the first days of the cycle, immediately after the end of menstruation.
That is, it is recommended to choose days 5 to 8 of the cycle if we are talking about a routine scan. If the doctor suspects that a woman has uterine endometriosis, the procedure is postponed to the second part of the cycle.
If there are inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs, or you need to monitor the dynamics of follicle development, then the procedure is carried out several times in one cycle. If a girl starts bleeding, which is definitely not menstruation, then an ultrasound is done urgently any day.
Short term intrauterine pregnancy
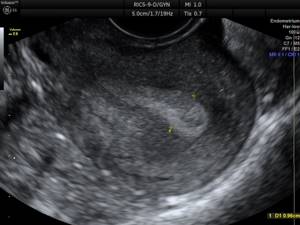
Rice. 3. Uterine pregnancy 7-8 weeks. The size of the fertilized egg and embryo corresponds to the period of delayed menstruation.
During pregnancy, only the fertilized egg is visualized in the uterine cavity in the early stages; later, an embryo appears. The size of the fertilized egg and embryo must correspond to the period of pregnancy according to menstruation.
It is also mandatory to evaluate the fetal heartbeat, which, as a rule, appears after 10-14 days of delayed menstruation.
M-echo thickness, normal. 2D.
Ultrasound of a normal uterus. 2D.
Ultrasound of a normal uterus. 2D.
During pregnancy, the corpus luteum of pregnancy should be visualized in one of the ovaries, which controls the development of this pregnancy and ensures the vital activity of the fetus in the early stages (before the formation of the placenta).
IVF for low ovarian reserve
Standard IVF programs, including hormonal stimulation, in our case are associated with great risk. When only a few cells are left in reserve, ovarian stimulation can deplete the already tiny reserve at once, and no one can guarantee that this particular attempt will be successful. That is why such patients usually undergo IVF in a natural cycle, without additional hormonal stimulation. This leaves the woman with more attempts and the overall chances of success of the procedure increase.
Read more about IVF in a natural cycle in this material - note. altravita-ivf.ru.
If these attempts do not yield results, there is always the possibility of using donor cells.
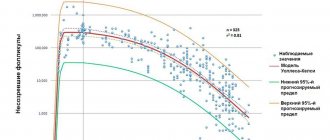
How does follicle size affect egg quality and fertilization?
A very interesting study was conducted by McCulloh et al. (2020), carefully measuring each follicle before aspiration and separating the resulting eggs from each other. These oocytes were then fertilized and the development of the embryos was monitored.
It is believed that larger follicles are more likely to provide good quality mature oocytes compared to smaller follicles.
Here is a summary of the results of this study regarding the relationship between follicle size and oocyte maturity:
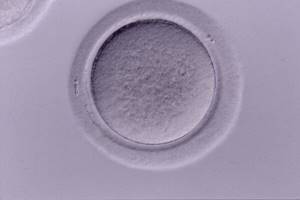
Oocyte MI
317 eggs were obtained from 22 oocyte donors aged 24.5 years ± 3.5 with follicle diameter:
- 255 were mature (MII) (80.4%);
- 31 were grossly immature (GV) (9.8%);
- 29 were immature (MI) (9.1%).
There are two stages of immaturity before the completion of oocyte maturation (GV - germinal vesicle and MI).
MII are mature oocytes.
These 255 mature oocytes were fertilized using the ICSI method:
228 (89.4%) were fertilized.
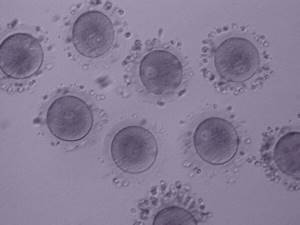
GV oocytes
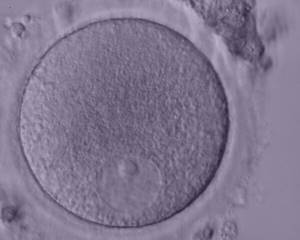
Oocyte GV
The size of the follicles corresponded to different eggs. Each fertilized egg was cultured individually so that they could be monitored during embryo culture.
Norm of ovarian reserve
Adequate AMH parameters for a favorable prognosis.
As for any accurate assessment, there are norm values for this factor:
- For ultrasound. During an ultrasound examination, the doctor determines the number of follicles less than 10 mm in size. A woman of reproductive age should have at least 5-6 such cells in one section of each ovary. If these indicators are lower, then the prognosis for pregnancy may be unfavorable even if ART methods are used.
- For FSH, the critical parameters are 10-12 IU/l. An increase in the concentration of this hormone above these values indicates a decrease.
- For AMH, a value of less than 1.2 ng/l is considered low. AMH analysis is the most accurate prognostic factor for assessing reproductive function and therefore the highest requirements are usually placed on the quality and accuracy of this analysis.
What causes a decrease in the number of eggs?
As mentioned above, the number of eggs naturally decreases with age. But if the decrease does not occur in accordance with the norm, or reproductive specialists are faced with the task of achieving pregnancy at a low level, this becomes a problem. Even ART methods can fail in this case, because with age, not only their quantity, but also their quality decreases.
Reasons beyond age-related changes may include:
- consequences of surgical operations;
- inflammatory processes in the ovaries;
- genetic predisposition to early wasting of the appendages;
- environmental factors, work with toxic substances and radiation;
- Lifestyle;
- bad habits, especially alcohol and smoking.
Natural pregnancy with a reduced ovarian reserve, although possible, is unlikely, but even the use of IVF has some peculiarities in this case.
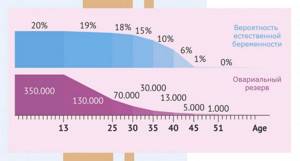
Effect of age
A woman’s reproductive function declines with age, and this process is also reflected in the size of the ovaries. With age, they decrease, and when postmenopause occurs, the ovaries become the same size. During this period, the following are considered normal indicators:
- Volume 1.5-4 cubic meters. cm.
- Length 20-25 mm.
- Width 12-15 mm.
- Thickness 9-12 mm.
When post-menopause occurs, the ovaries still continue to produce single follicles throughout the early years. Because of this, millimeter fluctuations in the size of paired organs are possible.
Reasons for deviations from the norm
When the ovaries begin to work during puberty, they may undergo a number of changes. During pregnancy, they increase in size as blood flow to the genitals increases. This is necessary so that the fetus receives nutrients. If the uterus with the fetus, which is continuously growing, gradually increases, then it is capable of displacing the pelvic organs upward. At the same time, the size of the ovaries increases by a couple of cm.
It is also important to note that during pregnancy, the ovaries do not produce eggs and are not able to produce estrogen. But instead, the paired organs produce progesterone. This hormone is necessary for pregnancy and childbirth. After the birth of a child, the ovaries gradually decrease in size. As a rule, within 2 months the synthesis of estrogen is completely resumed and the woman’s body improves reproductive function. But if a woman is breastfeeding, then the restoration of the size of the paired organs slows down and their normal functioning begins only after breastfeeding is completed.
The ovaries are located at the so-called ribs of the uterus. The distance from them to the uterus may vary, although gynecological ultrasound does not indicate such indicators. The normal functioning of paired organs excludes the presence of any neoplasms filled with fluid. The presence of other tumor-like growths is also considered a deviation from the norm.
What is ultrasound examination
Ultrasound examination (Ultrasound) is an instrumental examination method widely used in medicine. In the diagnosis of sexually transmitted infections, it is an auxiliary method that allows identifying complications of the genitourinary organs. The method is based on the use of ultrasonic waves, which are reflected passing through the boundaries of various organs and are then captured by special sensors. A distinction is made between ultrasound or scanning itself and Dopplerography, which can be used to determine the state of blood flow and the patency of blood vessels.