Creatinine itself, being a breakdown product, no longer represents the slightest benefit for the body, and therefore is excreted from the body through the kidneys. In some diseases, the process of its elimination may be disrupted. Some physiological reasons also affect the level of creatinine in the blood.
Serum creatinine is always relatively stable because it is formed at the same rate. Normally, the level of creatinine is determined primarily by the volume of a person’s muscle mass: the better developed the muscles, the higher the level of this metabolite.
Indications for analysis
Most often, a creatinine test is prescribed to assess the filtration function of the kidneys. This research is also relevant for severe injuries and many diseases of various natures.
Indications:
- suspicion of the development of renal failure;
- any kidney diseases (pyelonephritis, polycystic disease, urolithiasis, glomerulonephritis);
- severe injuries or burns;
- any injury, atrophy or muscle breakdown;
- diseases of the endocrine system;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- acute inflammatory diseases;
- sepsis;
- postoperative period.
Creatinine levels are affected by muscle mass. The larger it is, the higher the indicator. Photo: drobotdean / freepik.com
Symptoms of low creatinine levels
Symptoms of low creatinine depend on the underlying condition, but may include:
- With low muscle mass
- weakness, difficulty performing physical exercises; - With liver disease
- weakness, pain in the upper right corner of the abdomen, nausea; - When dieting
- weakness or dizziness, weight loss.
In most cases, symptoms do not indicate low creatinine levels, but may indicate other health problems.
Preparing for analysis
The rules for preparing for a biochemical test to determine creatinine are not much different from the standards for preparing for any blood test. The study is carried out in the morning on an empty stomach (last meal no later than 8 pm). The day before the test you must:
- avoid nervous stress;
- limit physical activity;
- do not visit the sauna;
- do not drink alcohol;
- do not exceed the usual amount of meat dishes in the diet;
- avoid spicy, salty, fried foods;
- Stop smoking 1-2 hours before the test.
Of course, these rules complicate the patient’s life, but it is still necessary to adhere to them, otherwise the result of the study will be distorted, which may cause an incorrect diagnosis.
Normal blood creatinine level
Up to 15 years of age, gender does not affect the reference values - the norm of creatinine content in a biochemical blood test (S-Crea) during this period changes only depending on age.
With the onset of puberty, hormonal changes make their own adjustments, so after 15 years, the reference values for men and women change. For convenience, we provide a table. Table 1. Normal blood creatinine levels by age and gender.
| Age/gender | Normal indicator | |
| Newborn babies | 20 - 75 µmol/l | |
| Under 1 year | 15 – 37 µmol/l | |
| 1 – 3 years | 21 - 36 µmol/l | |
| 35 years | 26 - 41 µmol/l | |
| 5 – 7 years | 27 - 51 µmol/l | |
| 7 – 9 years | 34 - 52 µmol/l | |
| 9 – 11 years | 33 - 66 µmol/l | |
| 11 – 15 years | 45 - 75 µmol/l | |
| Over 15 years old | Men | 60 – 105 µmol/l |
| Women | 42 – 80 µmol/l | |
Causes of elevated creatinine
The reasons that cause an increased level of creatinine in the patient’s blood can be divided into physiological and pathological.
Physiological reasons:
- large amount of muscle mass;
- strength sports (powerlifting, bodybuilding, wrestling, etc.);
- eating a lot of meat dishes;
- the use of certain medications (tetracycline antibiotics, cephalosporins, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs).
Fasting affects creatinine levels
One of the common physiological causes of increased creatinine levels in the blood is prolonged fasting.
If the body does not receive the required set of amino acids and nutrients, it begins to use its own muscle tissue as a source of nutrition. As a result of the destruction of muscle fibers, an increase in creatinine levels occurs. Therefore, excessive enthusiasm for fasting is fraught with the development of muscular dystrophy. Fasting is one of the reasons for increased creatinine in the blood. Photo: freepik.com
Pathological reasons:
- acute and chronic kidney diseases;
- obstruction of the urinary tract;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system (the kidneys suffer due to impaired blood supply);
- excessive activity of the thyroid gland (from excessive synthesis of thyroid hormones, the process of breakdown in the muscles begins);
- radiation sickness;
- oncological neoplasms;
- ruptures, compression and other muscle injuries;
- septic shock;
- extensive burns;
- endocrine pathologies.
When is the analysis performed?
The referral is issued by a general practitioner, nephrologist, infectious disease specialist, gynecologist or endocrinologist. Indications for analysis:
- signs of disease of the urinary system: change in the color of urine, difficulty urinating, pain or cramping, persistently high blood pressure, pain in the lumbar region, swelling, insomnia, weakness and poor appetite;
- the need for hemodialysis and evaluation of its effectiveness;
- control over the effectiveness of treatment methods for kidney pathologies;
- identification of complications when taking nephrotoxic drugs;
- advanced diagnostics of skeletal muscle diseases;
- severe dehydration of the body;
- preparatory procedures before computed tomography.
Venous blood is collected for the study.
Consequences of deviation of creatinine from normal
First, you need to understand the reason for changes in serum creatinine levels. If deviations from the norm are due to physiological reasons, there is no particular reason to worry. However, even some physiological features should still be paid attention to.
For example, if eating large amounts of meat is not due to an increased need for protein in the body (a direct need exists for athletes, for whom protein is an important component of nutrition that ensures muscle growth), this can lead to gout, as well as deterioration of the kidneys and liver . Of particular concern in this regard are predisposing factors such as slow metabolism, as well as concomitant liver and kidney diseases.
If the deviation of the creatinine level from the norm is explained by any pathological reasons, comprehensive treatment should be started in a timely manner to prevent the disease from worsening.
Increased blood creatinine levels occur in children and adolescents as a result of active growth.
What is creatinine?
Creatine
is an amino acid produced naturally in the body and obtained in small quantities from food. Creatine has gained popularity as a dietary supplement following evidence that it can increase body weight, improve physical endurance and speed recovery. When creatine is broken down, it is used for energy and creatinine remains as waste products. Creatinine levels vary depending on factors such as height, age, or gender, so there is no standard value.
How to reduce creatinine in the blood
The first thing to remember is that self-treatment can do more harm than good. An increase in creatinine in a biochemical blood test very often indicates the presence of dangerous diseases, so you should completely trust your doctor when choosing medications.
In case of kidney damage or diseases of the cardiovascular system, the patient is offered hospitalization and treatment at a hospital. In addition to treating the underlying disease that has caused an increase in creatinine levels in the blood, the doctor prescribes medications to normalize protein metabolism. Extracorporeal detoxification is also used - this is a complex procedure for hardware blood purification. The most commonly used method is hemodialysis: the patient's venous blood is purified through a complex filter (dialyzer), and then returned back to the venous bed.
More vegetables and fruits in your diet! A proper diet helps normalize creatinine levels. Photo: sommail / freepik.com
An important aspect of normalizing creatinine levels is diet. You will have to give up many of your favorite dishes, but the results are worth it.
Foods to reduce creatinine levels:
- vegetables and fruits (preferably fresh or boiled);
- fermented milk products (kefir, fermented baked milk, yogurt);
- buckwheat;
- oatmeal;
- Brown rice;
- durum wheat pasta;
- rye and bran bread;
- nuts;
- honey.
To speed up the process of removing excess creatinine from the body, drink more purified water - preferably at least 1.5 liters per day. However, it should be remembered that if you have kidney disease, the amount of fluid per day should be limited.
Prohibited products:
- fatty meats, poultry and fish;
- whole milk;
- spicy seasonings;
- smoked meats;
- conservation;
- strong tea and coffee.
The consumption of meat and eggs should be kept to a minimum: 2-3 “meat” days per week are allowed. Moreover, even on such days, the amount of meat (as well as poultry and low-fat fish) should be moderate: no more than 150 grams of meat and 1 egg per day.
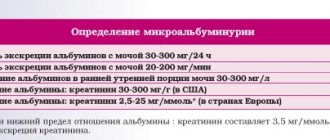
Urine collection instructions
The nurse will give you the necessary supplies:
- plastic container for collecting urine; manual urinal (issued to men);
- a cup for collecting urine (issued to women);
- if you are receiving hospital treatment, you may be given a bedpan;
Immediately before the start of daily urine collection
You must begin counting the urine collection period with an empty bladder. Immediately before the start of the daily collection, urinate in the toilet and flush. Then write down the date and time. This moment will be the beginning of the urine collection period. The collection will end in 24 hours.
Collection start date: ___________________ Collection start time: _________________
During the 24-hour urine collection period
- Collect all urine. Urinate only into a urine bag, urine collection cup, or bedpan. To use a urine collection cup, place it under the toilet seat and urinate into it.
- If you are in hospital, seek help if necessary.
How to increase creatinine in the blood
As with increased creatinine levels, you should start by eliminating the cause. Since a decrease in creatinine in the blood is most often explained by physiological reasons, you should analyze your own diet and lifestyle.
Adherents of therapeutic fasting must understand that a healthy balance is important in everything: you should not undermine your health by refusing the substances the body needs.
Low creatinine often occurs in athletes whose diet does not correspond to the level of physical activity. Many novice athletes, in an attempt to build muscle mass, act on the principle of “more is better”, exhausting themselves with unnecessarily hard training and at the same time completely forgetting about the importance of a balanced diet.
The body needs not so much creatinine itself, which is the end product of energy metabolism, but creatine phosphate, which provides the muscles with the necessary energy and strength. It is during the breakdown of creatine and creatine phosphate that creatinine is formed.
List of recommended products:
- meat and poultry;
- fish (herring, salmon, tuna are especially rich in creatine);
- pumpkin seeds;
- eggs;
- nuts;
- legumes
Treatment
Low creatinine levels can indicate a variety of medical conditions, so your doctor will use the test results to determine underlying problems. If low creatinine levels, along with other symptoms, indicate liver disease, treatment most likely begins with medications and lifestyle changes. These changes may include eating healthier and avoiding alcohol.
If a person has a muscle disorder, treatment may include exercise therapy, medications, or surgery.