Bacteriological culture of urine for flora
- Microbiological (cultural) study for yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida (Candida) and others with determination of sensitivity to antifungal drugs
- Microbiological (cultural) study of aerobic and facultative anaerobic flora with determination of sensitivity to the main spectrum of antimicrobial drugs and bacteriophages
- Microbiological (cultural) study of aerobic and facultative anaerobic flora with determination of sensitivity to an expanded range of antimicrobial drugs
Bacteriological culture of urine (bacteriological culture of urine) is a type of bacteriological study in which microorganisms present in the urine are detected and identified, and their concentration is determined.
For this purpose, biological material (urine) is placed in a nutrient medium (agar, sugar broth) favorable for the growth and development of microbes. If there is no growth of microorganisms, the result is negative. If the growth of bacteria or, for example, fungi is still detected in a concentration at which infection may develop, then the result of urine culture is considered positive. The concentration of microorganisms (the number of microorganisms per unit volume of biomaterial) during bacterial culture of urine is determined in colony-forming units (CFU). Colony-forming unit (CFU) is a single living microbial cell (or group of cells) from which a visible colony of microorganisms grows.
If the urine culture results are positive, that is, the causative agent of the infection is identified, it is necessary to select an effective antibacterial drug to combat it. To do this, the sensitivity to antibiotics of isolated cultures of microorganisms is determined (antibioticogram). Determining antibiotic sensitivity is extremely important in order to prescribe effective treatment.
Bacteriological urine culture is a fairly common test with high sensitivity and specificity. This test is widely used during pregnancy. Urine culture is also indicated to determine the effectiveness of treatment for urinary tract infections.
The disadvantages of the method are the relative duration of the study (4-7 calendar days) and high requirements for collecting material. However, urine culture can provide information that other research methods cannot provide.
Indications for urine culture:
- urinary system infections,
- control of the treatment performed,
- clarification of the diagnosis in case of an atypical picture of the disease,
- relapsing course of the disease,
- pregnancy,
- diabetes,
- immunodeficiency,
- suspicion of resistant (resistant to antibacterial therapy) flora.
For urine culture, an average morning urine sample of 3-5 ml is taken, collected in a sterile plastic disposable container. A container for collecting urine for bacteriological culture should be obtained in advance from the CMD laboratory reception. Urine collection for urine culture testing is carried out after thorough toileting of the external genitalia without the use of antiseptics.
Biomaterial for urine testing is taken before the start of antibacterial therapy or in the intervals between courses of treatment, but not earlier than two weeks after its completion.
The collected urine must be delivered to the Laboratory as quickly as possible: at room temperature (+18+20°C) – within 1-2 hours; at +4+8°C (refrigerator) - 5-6 hours.
Reasons and purposes of analysis
Collecting urine for this type of test may be recommended in certain situations:
- the initial sampling produced poor results;
- urination becomes more frequent and severe pain is felt;
- signs of pain appeared in the lumbar region;
- there was a suspicion of a disease of the urinary and reproductive systems;
- the treatment course for inflammatory pathology has ended;
- children aged two to four months undergo routine examination;
- there is a need to identify the responsiveness of microorganisms to certain drugs;
- for the male half, this type of test is prescribed to detect hidden diseases that occur without pronounced symptoms;
- Pregnant women receive biological fluid for testing at the time of registration.
Indications for bacteriological examination
In a healthy person, urine is sterile. Bacteria enter it directly from the urinary tract or from the outside due to errors in collecting material for research. Typically, the manifest forms of urinary infections are easily identified by a general urine test. But sometimes it is necessary to donate urine for bacterial culture:
- Suspicion of an infection of the bladder, kidneys, urinary tract (cystitis, pyelonephritis or unspecified localization), the symptoms of which are: fever, painful and frequent urination, pain in the lower back or abdomen, chills, vomiting, diarrhea, discoloration and turbidity of urine.
- A large number of bacteria or leukocytes in a general urine test.
- Monitoring the treatment of urinary tract infection (7th day of antibiotic therapy).
- To detect relapse after acute pyelonephritis (convalescence period).
- To detect exacerbation of chronic pyelonephritis.
- Preventive examination in pregnant women upon registration in the first trimester and shortly before birth (at 36 weeks).
- Preventive examination in infants 3 months.
A referral for a urine test for sterility is issued by a general practitioner, pediatrician, family doctor, nephrologist, urologist, obstetrician-gynecologist.
When is the procedure scheduled?
Indications for the study can be divided into two main parts - symptoms of urinary tract infection (UTI) and monitoring of therapy for these diseases. In addition, bacterial culture can be prescribed to catering staff and personnel whose activities are aimed at direct contact with people (medical workers), especially specialized institutions. The latter include infectious diseases hospitals, tuberculosis dispensaries, etc.
Signs that may lead a doctor to suspect the presence of a UTI include the following:
- frequent urination, accompanied by pain;
- changes in the color and amount of urine excreted, its turbidity;
- fever, chills, weakness, drowsiness;
- nagging, dull pain in the lower abdomen and lower back.
If you have such symptoms, you should definitely have your urine culture tested for sterility if the person has recently had a cold or viral disease. It should be taken into account that some infectious diseases of the male reproductive system may not manifest themselves for a long time. And since the reproductive and urinary systems are in close proximity and interaction, the pathogen often spreads.
In addition, culture for sterility performs preventive functions - it is necessary during pregnancy, both in the early and late stages. The ability to identify pathogenic microorganisms in pregnant women in the initial stages makes it possible to prevent the development of various diseases that can lead to complications during pregnancy and even miscarriage.
As delivery approaches, a similar check is also needed - since during the passage of the birth canal the child may become infected with an infection, which will subsequently cause serious illness. The procedure must be carried out routinely for all newborns.

Reasons for false results
One of the most significant reasons for the appearance of false results of bacteriological analysis of urine is non-compliance with standardized research technology, in particular:
- 1Increase the seed dose of the test material;
- 2 Failure to comply with the duration of the preanalytical period of urine storage;
- 3 Violation of urine collection standards;
- 4 Lack of hygiene of the external genitalia before collecting urine;
- 5Collecting urine in inappropriate containers;
- 6 Violation of temperature conditions for storage and transportation;
- 7Conducting research during antibiotic therapy or during menstruation in women;
- 8 Non-compliance with the holding time of the material in the thermostat.
Video Photo Tables
How to get tested during pregnancy?
When collecting urine, a pregnant woman should cover the vaginal opening with a clean napkin during the procedure. In some cases, a sterile disposable catheter is used. This usually happens if the gestation period is significant.
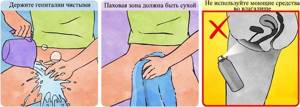
It must be remembered that when preparing for the test, everyday hygiene procedures will not be enough. Additional measures have been developed:
- It is not recommended to use public toilets when taking the test.
- After each visit to the toilet, you must wash yourself using regular soap for children.
- Underwear or sanitary pads should be changed frequently.
- It will be better if the linen is made from natural materials. It is not recommended to use synthetics.
- Washed linen must be carefully ironed with a hot iron.
How to determine the norm in children?
Collecting urine from a child is considered a difficult task. It all depends on the age category of the child.
Features of sampling
It is difficult to collect urine from a baby. To do this, you should use urinals, which can be purchased at pharmacy kiosks. For boys, this device is attached to the penis; for girls, it is fixed above the pubis with the upper edge, and on the anus with the lower edge. In the case of boys, it is possible to wear a diaper, but girls have to be held in their arms until the biological fluid is released.
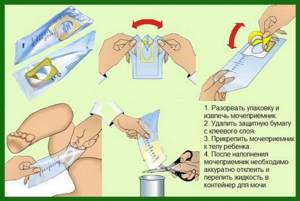
Indicators and standards
Normal urine values are:
- its absolute transparency, straw tint;
- no proteins, no glucose, no bacteria with salt accumulation should be detected;
- mucus is either absent or present in small quantities. This means that the baby’s genitals were poorly washed;
- epithelium – no higher than 2 units;
- white blood cells – up to six;
- acidity – weak, from 4.5 to 8.0;
- number of cylinders – at least one.
The specific gravity will depend on the age category of the patient:
- up to two years – 1,002 – 1,004 g/l;
- up to five years of age – 1,012 – 1,020 g/l;
- up to twelve years – 1,011 – 1,025 g/l.
A low value of urine density is allowed in case of kidney pathologies, elevated body temperature, during vomiting or diarrhea.
The presence of an alkaline reaction confirms the abundance of vegetables in the diet or the development of inflammation. Glucose is considered a sign of diabetes, casts indicate urethritis or cystitis. Harmful microorganisms or fungi are considered signs of an infectious disease of the baby’s genitourinary system.
What the result shows
The purpose of the study is to identify the causative agent of the inflammatory process and whether the permissible limit for the number of bacteria is exceeded. Are there any among them that can cause serious harm to health? The concentration of various microorganisms (fungus, protozoa, bacteria) is taken into account, and a general assessment of the condition of the urinary system is made.
On average, results are prepared within 10 days. All this time, the bacteria grow and are studied. If no process occurs, the test will be negative - the person is healthy. Active proliferation of microorganisms indicates a positive test result. The type of bacteria affecting the genitourinary system is identified using a microscope and chemical testing. The conclusion indicates which drugs these microorganisms are sensitive to.