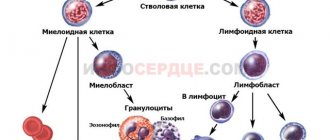
What are neutrophils?
Before moving on to the question of what neutrophils are and why their level is elevated, we note that blood consists of red and white blood cells. White cells - leukocytes - are responsible for fighting infection. Experts divide them into several groups, which are differentiated by the color obtained after treatment with a special coloring composition. Neutrophils are white blood cells that react to any type of dye reagent.
Among white cells, the content of neutrophils is approximately 50%, although this figure varies depending on the age of the patient. These bodies perform the task of capturing the emerging infection and destroying it. Band nuclei in the total number of neutrophils are only from 1 to 6%.
Stages of neutrophil development
Neutrophils are produced in the bone marrow. These bodies are divided according to their age:
- myelocytes – newly emerged neutrophils;
- metamyelocytes are also early leukocytes, slightly older than the previous type;
- band neutrophils – the next oldest neutrophils;
- segmented.
There should be no young myelocytes and metamyelocytes in human blood. They are required to undergo the procedure of full maturation and only after that enter the vessels and arteries. But it doesn't always work out that way. Mature neutrophils self-destruct when fighting infection.
If the disease is not defeated, the rod cells have to enter the fight. As a result, their levels become elevated. And behind them, metamyelocytes and myelocytes may appear in the blood. The norm of leukocytes in the blood of a woman, man and child.
Neutrophils stay in the body for only 2 weeks. The period of formation of these leukocytes in the bone marrow takes 6 days. Then they move into the blood, where they travel for no more than 10 hours. In the next period of life, the corpuscles are found in tissues and organs, where for a week they perform the main function of counteracting infection.
Another feature of neutrophils is the presence of enzyme granules in their plasma. As part of these leukocytes, the granules are assigned the most important functions. They contain 2 dozen active substances that do the job of destroying the infection.
In addition to destroying pathogenic microorganisms, neutrophils secrete cytokines that notify the cells of the human body about the presence of infection.
Description of band neutrophils and signs of their increase
Band neutrophils are neutrophils whose main function is to absorb small foreign particles, bacteria and microbes
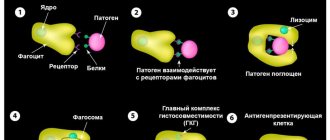
Neutrophils make up the majority of all leukocytes. Their main task is to protect the body from foreign cells by absorbing and digesting them. This process is called phagocytosis. After engulfing and breaking down a foreign cell, neutrophils destroy themselves.
Neutrophils are able to penetrate through the walls of blood vessels and tissues to the affected area. They have several stages of development. The youngest and immature neutrophils are called band neutrophils. This is due to the fact that their core has not yet split; it looks like an elongated stick. These cells are not yet able to penetrate tissue or absorb foreign cells because they do not have enough enzymes. Their main function is to mature in order to become a full-fledged cell capable of phagocytosis.
The bone marrow, spleen, and liver are responsible for the production of neutrophils.
Bands are increased when an inflammatory process begins in the body. The body begins to actively produce young neutrophils to fight infection. Neutrophils are localized at the site of inflammation, actively engulf pathogenic cells, and then die off themselves. The breakdown products of neutrophils soften tissues, causing them to suppurate. Therefore, the main sign of increased and active work of neutrophils is a purulent process. It can manifest itself in the form of sinusitis, otitis, purulent wounds, purulent plaque on the tonsils, etc.
An increased content of neutrophils is called neutrophilosis. Because band neutrophils are produced early in the disease and take time to mature, neutrophilia may begin asymptomatically.
When neutrophils mature and begin to act, typical signs of the inflammatory process appear: swelling and redness of the skin or mucous membranes, increased body temperature, purulent discharge, soreness of the affected areas, fatigue and poor health, headache.
What does an increase in blood mean?
The table of the norm for the presence of band neutrophils as a percentage of all leukocytes of this type in an adult and a minor child, depending on age, looks like this:
| Age | Blood content in % |
| Baby's first days of life | Up to 15 |
| From 3 months to six months | Up to 8 |
| 1 year | Up to 7 |
| Up to 14 years old | Until 6 |
| Mature man | Up to 1 |
What does an increased rate in an adult indicate:
- condition following surgery;
- treatment with certain medications;
- stressful situation.
These are the so-called non-pathological reasons for the increase in the indicator, which, as the name suggests, are not associated with internal diseases.
Pathological causes of an increase in the number of band neutrophils include:
- infectious diseases of the nose, ear and throat;
- damage to the upper respiratory tract and lungs;
- diabetes mellitus, complicated by metabolic disorders and pathological changes in the functioning of organs;
- bacterial rheumatism;
- initial stages of heart attack;
- tumor pathologies;
- injuries accompanied by severe bleeding;
- various skin lesions;
- beginning of pregnancy.
Since there are many reasons for the increase in band neutrophils in the blood, the doctor usually prescribes additional examination to make a diagnosis. Diagnosis can be aided by examining the patient's medical history.
The main reasons for the increase in stab
An increase in the level of stabs in the blood is a sign of the development of an inflammatory process
There are typical and atypical reasons for the increase in band neutrophils in the blood. Typical causes are associated with infection, inflammatory diseases, and atypical causes are associated with other diseases that are not always accompanied by neutrophilia.
Main reasons:
- Otitis. Inflammation of the middle ear is often accompanied by purulent processes, pain in the ear area, headaches, and fever. The number of neutrophils in the blood increases significantly. Otitis media can occur as an independent disease or as a complication of influenza or ARVI.
- Pneumonia. Pneumonia is inflammation of the lungs, which has many forms and degrees of severity. Pneumonia can even be fatal. Pneumonia is usually caused by a streptococcal infection, which causes the body to respond and the number of white blood cells in the blood increases significantly. Pneumonia is accompanied by fever, chest pain, cough with sputum and sometimes pus.
- Rheumatism. Rheumatism is usually associated with joints, but this disease primarily affects the heart. Rheumatism affects connective tissue and significantly impairs the functioning of the musculoskeletal system. One theory for the occurrence of rheumatism is associated with a bacterial infection.
- Diabetes. Diabetes mellitus can be considered an atypical cause of an increase in band neutrophils in the blood. Diabetes mellitus disrupts all metabolic processes in the body, which affects the functioning of internal organs. In some cases, diabetes mellitus occurs due to a viral infection.
- Tumors. Benign and malignant tumors also trigger the body's immune response. The body tries to fight tumor cells, so the number of white blood cells in the blood increases.
- Heart attack. This reason for the increase in neutrophils is also atypical. An incipient heart attack is most often detected by other indicators. However, at the initial stages, the number of band neutrophils can increase several times.
Diagnostics and treatment methods
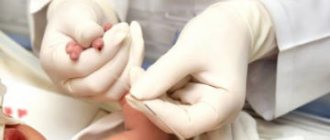
To diagnose the level of stabs in the blood, it is necessary to take a blood test in the morning on an empty stomach.
Neutrophilia is determined exclusively using a general blood test. The procedure is standard, quick and virtually painless. The patient needs to donate blood from a vein on an empty stomach, and then laboratory assistants use a microscope to study the resulting material and count the number of bodies and cells.
In some cases, the number of neutrophils increases for physiological reasons, so it is recommended to undergo simple preparation. A couple of days before the test, you need to give up fatty foods, heavy physical activity, alcohol, and stop taking medications.
The treatment method depends on the specific disease.
As a rule, if a patient has an increased number of band neutrophils in the blood, further testing is prescribed after a blood test to determine the source of the inflammation. Additional tests include ultrasound, bacterial culture, urine and stool analysis, tonsil mucus analysis, gynecological smear, etc.
Once the diagnosis is made, treatment is prescribed:
- Antibiotics. For infectious diseases, antibacterial drugs are often prescribed. Purulent processes accompanying neutrophilia, as a rule, indicate a bacterial infection. Antibiotics are often prescribed for pneumonia and otitis media. Antibacterial drugs help the body cope with infection by acting on pathogenic bacteria and destroying them.
- Immunostimulants. Similar drugs include Immunal, Timalin. They are prescribed for recurrent bacterial and viral infections. Immunostimulants help activate the body's protective functions. In some cases, drugs combine antiviral and immunostimulating properties.
- Corticosteroids. These are hormonal drugs that have a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect. Such drugs include Prednisolone, Kenalog. Corticosteroids eliminate inflammation and have an analgesic effect. They are available in the form of tablets, injection solutions, and ointments.
Increased levels during pregnancy
During pregnancy, the level of neutrophil leukocytes sometimes increases to 12x10⁹/l.
The reason is that the genetic material of the embryo is essentially an antigen and the body produces neutrophils to fight unidentified proteins. If the indicator remains markedly and persistently elevated, then the following pathologies in pregnant women are possible:
- damage to the lymphatic system;
- bacterial infection;
- food poisoning or intoxication in a pregnant woman with waste products of the fetus;
- cancer;
- blood poisoning.
Also, an increased level of band neutrophil leukocytes is observed when there is little of their segmented variety in the body. This happens with reduced immunity during pregnancy.
In a pregnant woman, the growth of band neutrophils can be observed as a reaction to changing climatic conditions. Nervous stress, physical work, a reaction to certain medications, and large blood loss can cause an increase in the rate.
Physiological causes of neutrophilia:
For the first time, a person experiences an increase in neutrophils at an age he does not remember. During infancy, all people experience neutrophil-lymphocytic crossover. Neutrophils and lymphocytes either increase or decrease relative to each other. In some periods, neutrophils are increased in a child to 80% or more, although the generally accepted norm is a lower value.
Other physiological reasons for the increase in these cells are equally characteristic of children and adults. In particular, these reasons include intense physical activity: a person who has moved a lot has a high level of neutrophils in the blood for several hours afterward.
Also, upward fluctuations in the indicator are typical for the time after eating. This is one of the reasons why it is recommended to come for a general blood test on an empty stomach. Otherwise, doctors may mistakenly explain a falsely elevated neutrophil count by the presence of some disease in the patient.
Infections:
Every person has experienced purulent-inflammatory processes at least once in their life. Most often, we observed them in the most harmless form - in the form of pimples and pustules on the skin, but this can also be another, more serious and difficult process.
Did you know that pus is dead white blood cells? And not just leukocytes, but those that have the ability to phagocytose: destroy, “devour” harmful particles. In the fight against the aggressor, they die and cell by cell form a focus of inflammation. One drop of pus contains millions of leukocytes, and these are mainly neutrophils. And there are diseases when up to several tens of milliliters, up to a liter of pus and even more accumulate in the body of patients! Can you imagine the loss of neutrophils the body suffers?
But immunity will not allow itself to be offended. In response to the attack of microbes, it will reproduce and release new white blood cells into the blood, so that in general their number may even increase above normal, despite the fact that the body is continuously producing pus. So neutrophilia is a sign of almost any infectious disease caused by bacteria and fungi. Pneumonia, tonsillitis, soft tissue abscesses, sinusitis... The list can be very long, and in all such cases, neutrophils in the blood are elevated in any patient.
If neutrophils are elevated in a child or adult, and the reason for this is an infectious process, then their different types increase unequally. Blood tests evaluate two main types of neutrophils: band and segmented. In bacterial and fungal diseases, mainly band neutrophils increase. These are young forms of cells, and an increase in their number allows us to draw obvious conclusions that the bone marrow is actively working and producing them intensively.
By how much a person's neutrophils are elevated, one can judge the severity of the disease. If the increase does not exceed twofold, this usually indicates the presence of an obvious infection. But sometimes it happens that due to neutrophils, the total number of leukocytes increases by 5-10 times. This could be a sign of a very serious condition - blood poisoning, or sepsis.