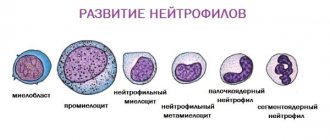
There are six types of neutrophils depending on the stage of their maturation. Immature types include myeloblasts, promyelocytes, myelocytes, metamyelocytes and band cells. The final stage of development is segmented neutrophils (mature cells with a formed nucleus, divided into several segments).
Even at the stages of their initial development, neutrophils are able to resist infection, although mature segmented cells cope with this task much more effectively.
In blood tests of people suffering from severe infectious diseases, immature forms of neutrophils can be detected. This is explained by the fact that in the fight against pathogenic microorganisms, segmented cells die too quickly, and therefore the body is forced to use cells that are not fully mature. But in the blood of a healthy person, predominantly mature neutrophils are found, since they cope well with their task with virtually no help from their young brothers.
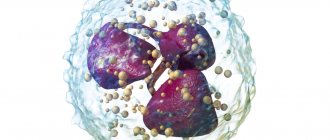
Figure 1. Phagocytosis. Image: mikrostoker/Depositphotos
Blood test for neutrophils
To determine the level of neutrophils, a complete blood count is used. To designate neutrophils on the analysis form, the Latin abbreviation NEUT is used, which can be expressed either in absolute (cell content per liter of blood, for example 0.04-0.3 × 109) or as a percentage. For general analysis, capillary blood is usually used. The biomaterial is collected from a finger after puncture with a scarifier. Sometimes blood is drawn from a vein - much depends on the methods the laboratory uses.
Leukocyte formula shift
In addition to increasing the number of neutrophil leukocytes, doctors also evaluate which forms of these cells caused the increase in their percentage. Diagnose:
- Shift of the formula to the left - band cells are increased, and juvenile forms are also present. This result is typical for severe intoxication, purulent infections, anemia (posthemorrhagic or hemolytic), leukemia, and burns. If the displacement is small, it may be caused by intense training or emotional stress.
- The formula shifts to the right - the number of “rods” is low, and the percentage of segmented cells is increased. This pattern is less common than a shift to the left. It occurs with anemia, polycythemia, leukemia and other pathologies.
Watch the episode of Dr. Komarovsky's program about clinical blood tests. In it you will hear answers to many of your questions:
Indications for analysis
A general blood test is the most common hematological test, so the range of indications for its use is wide. Neutrophils are a type of white blood cell whose main task is to destroy pathogenic microorganisms. Therefore, the main goal of the analysis for the content of neutrophils is to identify potentially dangerous conditions accompanied by infectious and inflammatory processes. In other words, a blood test for neutrophils can be informative both for colds and for kidney or liver diseases.
Causes of neutrophilia
It should be noted that the level of neutrophils directly depends on the cause - the stronger the impact on the child’s body, the higher these leukocytes will be.
A slight increase in the percentage of neutrophils occurs during physical or psychoemotional stress, as well as after eating. If the cause of a high neutrophil count is a disease, then the cell level is directly related to disease activity.

Pathological causes of neutrophilia include:
- Active inflammatory processes, for example, arthritis, pneumonia, dermatitis, inflammation of the pancreas, appendicitis and others.
- Bacterial infections, including purulent ones (abscess or cellulitis formation).
- Some viral infections.
- Infections caused by protozoa or fungi.
- Tumor processes.
- Extensive burns.
- Poisoning.
- Diabetes.
- Trophic ulcer.
- Use of certain medications, such as corticosteroids.
- Acute blood loss or hemolysis of red blood cells.
Neutrophils are also detected in increased numbers in the postoperative period.

Preparing for analysis
The study is carried out in the morning on an empty stomach, since food intake causes an increase in the number of neutrophils in the blood. Dinner on the eve of the test is allowed no later than eight o'clock in the evening. 2 days before the study, the patient should follow the following preparation rules:
- stop drinking alcohol;
- limit the consumption of spicy, fried and fatty foods;
- Avoid heavy physical activity and nervous stress.
The morning before the test you should not smoke. It is allowed to drink pure still water.
Figure 2. Preparation for donating blood for analysis.
Normal levels of neutrophils in the blood
The number of neutrophils in the blood is approximately 40-70% of the total leukocyte mass in both men and women.
When conducting research, experts primarily pay attention to the content of neutrophils at the middle and full stages of maturation, that is, band and segmented forms. Young cells are of interest if the development of the spread of inflammatory processes is suspected. The table shows the leukocyte formula, which reflects, among other things, the number of neutrophils. Table 1. Leukocyte formula with the number of neutrophils
| Index | × 10x9/l | Share as a percentage of the number of leukocytes | |
| Neutrophils | segmented | 2.0 – 5.5 | 40 — 70 |
| stab | 0.4 – 0.3 | 1 — 5 | |
| Basophils | Within 0.062 | Within 1.0 | |
| Eosinophils | 0.02 – 0.3 | 0.5 — 5 | |
| Lymphocytes | 1.0 – 3.2 | 17 — 38 | |
| Monocytes | 0.07 – 0.5 | 3 — 12 | |
In children of the first year of life, the number of band neutrophils can reach five, then the maximum value is limited to four, as in adults. The smallest number of segmented neutrophils is observed in children 4-5 years old (35-55%). In other age groups it varies between 40-70%.
What do elevated neutrophils mean?
The center of the neutrophil has a grain containing a complex of enzymes to destroy bacteria and deactivate their toxins. The tasks of neutrophils in the blood:
- infect foreign microbial cells;
- accompany the body's inflammatory reactions.
50-70% of the total number of leukocytes is considered normal. The normal absolute content of neutrophil elements for children of different ages is presented in the table.
| How old is the child | Absolute neutrophil count in 10⁹/l |
| Up to one year of age | 1,5-8,5 |
| 1-2 year olds | 1,5-8.5 |
| 2-4 year olds | 1,5-8.5 |
| 4-6 year olds | 1.5-8 |
| 6-8 year olds | 1,5-8 |
| 8-10 year olds | 1,8-8 |
| 10-16 year olds | 1.8-8 |
An increased level of neutrophils in the blood relative to the norm means the body is fighting an infectious agent - bacteria or fungi. Elevated neutrophils indicate that further examination is necessary to identify the cause of neutrophilia and isolate the causative agent of the disease.
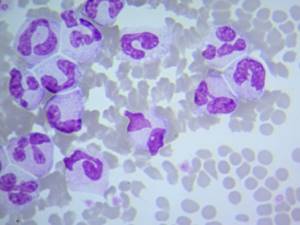
Segmented
There are simultaneously neutrophils of varying degrees of maturity in the blood. Segmented neutrophils are a mature form, ready to destroy bacteria and fungi. They show divisions between segments of the nucleus.
The indicators of segmented forms in the leukogram of healthy children are shown in the table.
| How old is the child | % segmented neutrophils from the total number of leukocytes |
| Up to one year of age | 10-44 |
| 1-2 year olds | 22-47 |
| 2-4 year olds | 26-54 |
| 4-6 year olds | 26-57 |
| 6-8 year olds | 32-59 |
| 8-10 year olds | 35-59 |
| 10-16 year olds | 37-59 |
Increased segmented neutrophils are considered a shift of the leukocyte formula to the right . If segmented neutrophils are elevated, this indicates a bacterial or fungal infection, a mild inflammatory process. When there is no infectious threat, the full life cycle of a neutrophil lasts about 14 days, and then it is destroyed in the spleen. When infected, one segmented neutrophil destroys 5-7 microbes and dies.
Increased mature cells with a nucleus having more than 5 segments suggest kidney and liver disease, radiation sickness, and recent blood transfusion. Increased segmented forms with increased granularity of the nucleus, vesicles (vacuoles) of the cytoplasm indicate inhibition of bone marrow function.
Increased mature neutrophil elements with a normal nucleus indicate the presence of microbial or fungal toxins in the body and a mild inflammatory reaction. Test data show the dynamics of the disease, the level of the immune response, and the effectiveness of treatment.
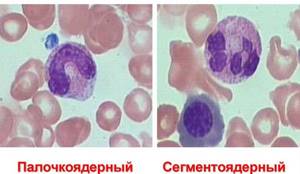
Neutrophils under a microscope
Rod
Neutrophil cells are born in the red bone marrow and go through successive stages of development:
- Myelocyte is the earliest form of maturation;
- Metamyelocyte or juvenile cell;
- Band neutrophil;
- Segmented neutrophil.
The nuclei of rod cells do not have fragmentary divisions. When viewed under a microscope, the nuclei of immature leukocytes look like rods. There are relatively few rod elements in the analysis of a healthy child. The normal percentage ratio of band neutrophils to the total number of leukocytes:
- newborn children – 3-12%;
- from 5 days and older – 1-5%.
An increased percentage of band forms in the blood is called a shift of the leukogram to the left. This means that the child has an acute bacterial or fungal infection.
When the level of band neutrophils in the analysis is increased, this indicates that it is difficult for the body to cope with the infectious-inflammatory process. The main cause of increased band cells is serious microbial infection. To help mature segmented cells, young band leukocytes are released from the reserve to fight the infectious agent.
Causes of increased neutrophils in the blood
Elevated neutrophil levels can indicate a wide range of illnesses and injuries. Very often, the cause of an increase in neutrophils in the blood is infectious processes of bacterial origin, which can be either focal or generalized (spread throughout the body).
Reasons for increasing the level of neutrophils in the blood:
- upper respiratory tract infections (laryngitis, pharyngitis, sore throat);
- pneumonia;
- kidney diseases;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- local purulent-inflammatory foci (abscesses, abscesses);
- viral diseases (measles, mumps, chickenpox, rubella, etc.);
- oncological diseases;
- taking hormonal medications;
- infections of bacterial origin (dysentery, tuberculosis, cholera, anthrax, etc.);
- poisoning with toxic substances;
- processes of tissue necrosis (gangrene, myocardial infarction, major burns);
- injuries of large organs;
- fractures;
- damage to the skin (cuts, abrasions, etc.);
- gout;
- sepsis (blood poisoning).
Eating canned foods can also cause an increase in neutrophils. This applies to those products in which there are no longer living bacteria left, but the toxic products of their vital activity have been preserved.
Causes of low levels of neutrophils in the blood
A decrease in the level of neutrophils in the blood is called neutropenia. The cause of this phenomenon can be diseases of various natures, as well as taking various medications.
Reasons for decreased neutrophil levels:
- infectious diseases (viral hepatitis, typhus, influenza, mononucleosis, etc.);
- autoimmune diseases (rheumatoid arthritis, systemic vasculitis, Crohn's disease, etc.);
- radiation sickness;
- blood diseases (leukemia, hemolytic and dyserythropoietic anemia).
Separate mention should be made of medications: taking them can also cause neutropenia. This is a very broad group of medications, which includes:
- NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: analgin, amidopyrine);
- antibacterial drugs (cephalosporins, penicillins);
- drugs to lower sugar (chlorpropamide);
- thyreostatic agents (propylthiouracil, Mercazolil);
- antimalarial drugs of synthetic origin (hydroxychloroquine);
- sulfonamides (sulfapyrazone; sulfasalazine);
- cytostatics (chlorambucil, methotrexate);
- antivirals (ganciclovir, zidovudine).
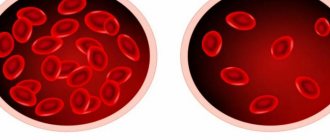
Figure 3. Blood cells in a healthy person and with neutropenia. Image: Sakurra/Depositphotos
Norm
In the blood of an adult and a child over 13 years of age, all types of leukocytes should be 4-10 * 10 to the 9th degree / l of blood, of which neutrophils - 48-80%. Of these, the initial form of neutrophils is 1-3%, band neutrophils 1-6%, segmented - 45-72%.
In children under 12 years of age, the immune system is developing, so their leukogram is somewhat different. Babies are born with an “adult” norm of segmented neutrophils , which continues to increase in the first day of the child’s life, and then sharply decreases.
At 5-7 years, the number of segmented neutrophils increases again, and during this period, pediatricians and parents note that the child begins to suffer from colds less often.
Age norms of segmented neutrophils in the blood of children:
- first day – 50-70%;
- 1-5 days – 35-55%;
- 5-15 days – 25-45%;
- 15-30 days – 15-30%;
- 1-12 months – 20-35%;
- 1-6 years – 35-55%;
- 7-10 years – 40-60%;
- 11-15 years 40-75%.
Consequences of deviation of neutrophils from the norm
A change in the level of neutrophils in the blood is a signal from the body about the presence of inflammatory diseases, injuries or poisoning. Therefore, it is necessary to accurately determine the cause of the increase or decrease in neutrophils in order to begin treatment in time or eliminate the provoking factor. If this is not done on time, the consequences can be severe (even death). The greatest danger among possible causes is infectious diseases of a bacterial nature, as well as processes of local suppuration and necrotization (death) of tissue.
What it is?
Segmented neutrophils are one of the types of neutrophils ; they make up the bulk of leukocytes. They are formed from rods - this is their immature form. Mature neutrophils stay in the blood longer than immature ones - about 2-8 hours, and only then penetrate through the vascular walls into the organs. This is due to the fact that there are always more segmented neutrophils in the blood than band neutrophils.
In band neutrophils, the nuclei are smooth, solid and similar to curved rods. In segmented ones, they are divided into segments of 2-5 pieces, which is why they are also called granular. This nuclear structure allows these cells to migrate through the walls of blood vessels into organs and tissues.
Reference! The cytoplasm of neutrophils is pink and the granulation is brown. If there is an inflammatory process in the body, the grain becomes larger and turns blue.
The main function of neutrophils is to fight various infectious pathogens that enter the human body from the outside (primarily fungal and bacterial), as well as maintaining the immune system at the proper level. Neutrophils are produced by the bone marrow and can quickly move and concentrate in areas of tissue damage or inflammation.
When pathogenic flora enters the human body, segmented neutrophils absorb and digest them, while the neutrophils themselves die - this is called phagocytosis or phagocytic activity.
Neutrophils are microphages; they are capable of absorbing only small foreign particles and cells. These structures contain myeloperoxidase, an enzyme that, after cell death, increases the effect of antibacterial agents in human blood. When these biological substances are released in large quantities, they begin to damage bacteria and activate the accumulation of immune cells in the affected area.
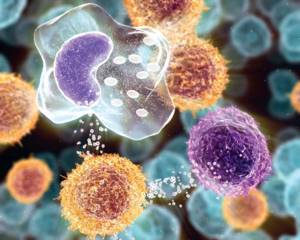
Dead neutrophils, cell mass destroyed by the inflammatory process, and pathogenic microorganisms form a mixture called pus. The pus is green because the enzyme myeloperoxidase has a green pigment.
As for viral infections, neutrophils play a much smaller role in the fight against them, and also practically do not participate in the fight against helminths and tumors.
How to reduce the number of neutrophils in the blood
To reduce the number of neutrophils in the blood, it is necessary to influence the cause of this phenomenon, since there are no separate ways to eliminate it. If the increase in neutrophil levels is caused by short-term stress or increased physical activity, then no specific correction is required.
For persistent neutrophilia, depending on the disease that caused it, the following treatment methods are used:
- antimicrobial therapy - antibiotics are used for infections (amoxicillin, cefixime);
- antiplatelet therapy - in case of heart attack and a tendency to blood clots, acetylsalicylic acid and alteplase are prescribed;
- anti-inflammatory therapy - glucocorticosteroids (prednisolone) are used to reduce inflammation that provokes neutrophilia;
- chemotherapy – aimed at combating malignant tumors (cytostatics, antimetabolites).
If there is a local focus of inflammation, surgical treatment can be used. For example, it is relevant for appendicitis or abscesses. The menu should limit the amount of meat products, canned and smoked. The diet should be rich in vegetables and fruits.
To normalize the level of neutrophils in the blood, it is recommended to eat more vegetables and fruits. Photo: sommail / freepik.com
How to increase the number of neutrophils in the blood
To correct neutropenia, it is necessary to identify its cause. If a decrease in neutrophil levels is caused by taking medications, you should first weigh the possible risks of a decrease in neutrophil levels with the importance of the therapeutic effect of the drugs used. In extreme cases, the drug can be replaced with an analogue that does not affect the level of neutrophils in the blood. The underlying diseases that cause neutropenia are treated with antibiotics, anti-inflammatory and antiviral drugs.
It is recommended to consume the following products:
- any meat dishes (it is important that they are all well thermally processed);
- hard boiled eggs;
- pasteurized milk;
- cheese (except for varieties with mold);
- potato;
- rice;
- pasta;
- fruits and vegetables;
- alcohol only in consultation with a doctor.
Careful heat treatment of meat and eggs is necessary in order to exclude the possibility of bacteria and microbes entering the body, which actively multiply in poorly fried or undercooked protein dishes.
Reduced values
A decreased neutrophil count is called neutropenia . There are:
- hereditary neutropenia;
- congenital;
- acquired.
Hereditary forms are passed on from generation to generation, and may have absolutely no effect on the child’s condition; they are considered an individual characteristic of the body.
Congenital pathologies of the immune system, as well as other disorders, contribute to the progress of neutropenia, and this naturally affects the functioning of the child’s entire body.
The mechanism for the decrease in segmented neutrophils may be as follows:
- Decreased production or disruption is the result of a malfunction of the bone marrow.
- Redistribution - segmented neutrophils cluster and move to the site of inflammation.
- Increased percentage of death and elimination - cells die or the body itself destroys low-quality pathological forms.
When the leukocyte formula shifts to the left, the number of segmented neutrophils decreases in favor of young forms - metamyelocytes, stabs and myelocytes.
Important! Changing the formula may be a natural response to exposure to a pathogenic factor; in all other cases, immediate medical intervention and identification of the causes are required.
In a newborn child, the norm of segmented neutrophils is the same as in an adult , and if the deviation occurs in the direction of decrease, parents should be wary of hereditary and congenital forms of pathology.

It could be:
- infantile agranulocytosis;
- cyclic congenital neutropenia;
- benign familial neutropenia.
Breastfed babies are well protected from infections , since a large number of immune cells enter their bodies with breast milk, which fight viruses and bacteria. Children who are bottle-fed are at risk for various pathologies.
When neutrophils are reduced to a year, neutropenia may be accompanied by the appearance of binuclear pathological segmented neutrophils.
You should be extremely careful when prescribing medications to children under 2 years of age, as in some cases this can cause agranulocytosis. This is especially true for drugs of the sulfonamide group and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.