What are amylase enzymes used for, what function do they perform in a child’s body, what is the amylase level in children?
Many biochemical reactions in the human body require the participation of enzymes, or substances that are not themselves consumed in these reactions, but accelerate the speed of their flow hundreds and thousands of times. One of these enzymes is amylase (alpha amylase). In the body of a person of any age, including a child, there are several types of these enzymes, of which two subtypes are of clinical importance. These are alpha-amylase, which is produced by the pancreas (pancreatic amylase) and an enzyme that is produced in the salivary glands (diastase).
What is amylase and what types does it exist?
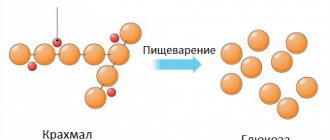
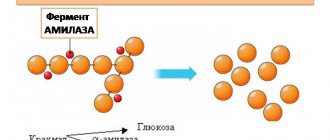
Amylase, wherever it is produced, takes an active part in the metabolism of polysaccharides, or carbohydrates. The job of this enzyme is to cut long chains of plant and animal starch, called glycogen, into small components. Amylase is an enzyme that works in the cavities of the gastrointestinal tract.
At the very beginning of the food path, the enzyme, which is produced in the salivary glands, enters the oral cavity, because it is there that the primary digestion of carbohydrates begins, and the resulting sugars begin to be absorbed in the mouth. This is how diastase, or salivary gland amylase, works.
The pancreas secretes its digestive secretion into the duodenum, which contains another form of the enzyme, pancreatic alpha-amylase. In order to assess the function of the corresponding glands and the state of carbohydrate metabolism in children and adults, a biochemical method is used, such as studying the concentration of these enzymes in the blood.
Pancreatic amylase
Pancreatic amylase is one of the types of amylase that is produced by the pancreas.
Synonyms Russian
P-amylase isoenzyme, pancreatic alpha-amylase, P-amylase, P-type amylase.
English synonyms
Pancreatic alpha-amylase, pancreatic AML, P-type amylase, P-type alpha-amylase, amylase isoenzymes, amylase isoforms.
Research method
Enzymatic colorimetric method.
Units
U/L (unit per liter).
What biomaterial can be used for research?
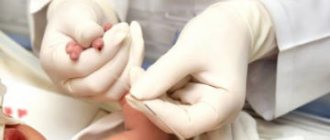
Venous blood.
How to properly prepare for research?
- Do not eat for 12 hours before the test.
- Avoid physical and emotional stress and do not smoke for 30 minutes before the test.
General information about the study
Amylase is a digestive enzyme that can break down carbohydrates.
The largest amount of amylase is found in the salivary and pancreas glands.
Amylase, which is produced in the pancreas, is pancreatic amylase (P-type) and is part of pancreatic juice. From the pancreas, pancreatic juice containing lipase passes through the pancreatic duct into the duodenum, where it helps digest food.
Amylase of the salivary glands - salivary amylase (S-type) - digests food starch in the oral cavity.
Normally, a small amount of amylase circulates in the blood. In this case, about 60% is salivary amylase (S-type), and the remaining 40% is pancreatic amylase.
When damage to the pancreas occurs, as in pancreatitis, or if the pancreatic duct is blocked by a stone or tumor, pancreatic amylase (P-type) begins to leak into the bloodstream in large quantities. There is no increase in salivary amylase activity.
Small amounts of amylase are also produced in the ovaries, intestines and skeletal muscles.
What is the research used for?
- An increase in the activity of pancreatic amylase in the blood without a change in the activity of salivary amylase confirms the pathology of the pancreas. For example, in acute pancreatitis, its activity in the blood can increase to 90% of the total amylase activity.
- For the diagnosis of pancreatitis in the postoperative period, when the activity of total amylase is increased.
- If pathology of the salivary glands, ovaries or bronchi is suspected.
When is the study scheduled?
- When the diagnosis of “acute” or “chronic pancreatitis” is confirmed.
- If you suspect a disease of the salivary glands and ovaries.
What do the results mean?
Reference values
| Age | Reference values |
| < 1 year | < 8 U/l |
| 1 – 10 years | < 31 U/l |
| 10 – 18 years | < 39 U/l |
| > 18 years old | < 53 U/l |
Interpretation of the results of the analysis for pancreatic amylase is carried out taking into account the assessment of the total amylase activity in the blood or urine. If the total amylase activity is increased and the activity of pancreatic amylase is decreased, then damage to the pancreas is unlikely and pathology of the ovaries, intestines, bronchi or other organs must be excluded.
Reasons for increased pancreatic amylase activity
- Acute pancreatitis. In this disease, the activity of pancreatic amylase can be significantly higher than normal and constitute a larger percentage of the activity of total amylase. However, in some patients with acute pancreatitis, amylase may increase slightly or even remain normal. In general, amylase activity does not reflect the severity of pancreatic damage in pancreatitis. For example, with massive pancreatitis, sometimes the death of most of the cells that produce this enzyme occurs, so its activity may not be changed.
- Chronic pancreatitis. With it, amylase activity is initially moderately increased, but then may decrease and return to normal as damage to the pancreas worsens.
- Decompensation of diabetes mellitus is diabetic ketoacidosis, both due to high sugar levels and due to the concomitant involvement of the pancreas in the pathological process.
- Trauma to the pancreas.
- Pancreas cancer.
- Blockage (stone, scar) of the pancreatic duct.
- Acute appendicitis, peritonitis.
- Perforation (perforation) of a stomach ulcer.
- Acute cholecystitis is inflammation of the gallbladder.
- Intestinal obstruction.
- Ruptured aortic aneurysm.
- Macroamylasemia is a condition where amylase binds to large proteins in the serum and therefore cannot pass through the glomeruli, accumulating in the blood.
Reasons for decreased pancreatic amylase activity
- Decreased pancreatic function.
- Cystic fibrosis (cystic fibrosis) of the pancreas is a severe hereditary disease associated with damage to the exocrine glands (lungs, gastrointestinal tract).
- Removal of the pancreas.
What can influence the result?
- Captopril, corticosteroids, oral contraceptives, furosemide, ibuprofen, and narcotic analgesics can increase amylase activity.
- Chronic renal failure sometimes leads to increased activity of pancreatic amylase.
- Elevated cholesterol can cause decreased activity of pancreatic amylase.
Important Notes
- In acute pancreatitis, an increase in pancreatic amylase activity is usually accompanied by an increase in lipase activity. The latter may be somewhat delayed, but lipase activity remains elevated longer.
- Amylase activity in children in the first two months of life is low; it rises to adult levels by the end of the first year.
Also recommended
- Total amylase in daily urine
- Serum total amylase
- Lipase
Who orders the study?
General practitioner, therapist, gastroenterologist, surgeon.
Indications for analysis, or why test amylase?
Since these enzymes perform the same function in the body of an adult and a child, the indications for studying amylase levels in children and adults are the same. The pancreatic variety is examined for suspected acute and chronic pathology of the pancreas, as well as for acute and girdle pain in the upper abdomen, which may indicate acute pancreatitis.
In early childhood, there is a dangerous, severe hereditary pathology associated with impaired carbohydrate metabolism, which is called cystic fibrosis. If cystic fibrosis is suspected, one of the first tests performed is to determine the concentration of both types of amylase.
In early childhood, there is such a well-known infectious viral disease as mumps, or mumps. The virus causes inflammation of the salivary glands (and the pancreas too) and a sharp change in the concentration of the corresponding enzymes.
The role of amylase in the blood
This is a digestive enzyme that is involved in the breakdown of carbohydrates, starch and glycogen. It is formed in the pancreas and salivary glands. If there are failures in carbohydrate metabolism, its value deviates from acceptable norms.
Functions
By breaking down carbohydrates, this enzyme becomes involved in the digestion process. Its main function is the hydrolysis of starch. Its breakdown occurs in the mouth under the action of saliva. During this period, salivary amylase is active.
Its activity decreases if food is not chewed properly.
Hydrolysis of starch continues in the intestine under the action of alpha-amylase produced by the pancreas.
The digestive enzyme is activated at night when you eat. Therefore, late snacking and poor chewing are harmful to the body. An enzyme excluded from the digestive process provokes the development of pancreatitis and other diseases.
Normal blood amylase level in children
It is somewhat more complicated with the pancreatic fraction. Its age-related indicators largely depend on age and the development of the pancreas. That's why:
- in babies under 6 months of age, the normal value ranges from 1 to 12 U/l;
- at the age of up to one year - this value increases to 23 U/l;
- in children older than one year, gender should be taken into account: in boys under 2 years of age this concentration does not change (1-23 U), and in girls the figure is slightly higher: from 3 to 38 U/l;
- finally, from the age of two until the age of puberty (19 years), the concentration of the pancreatic form in boys and girls is again comparable and ranges from 4 to 31 units per liter.
As for the enzyme that is produced by the salivary glands, everything is simpler here:
- the norm of amylase in the blood of children under one year of age is 5 – 65 U/l;
- starting from the age of one, and throughout life, up to the age of 70 years, the norm is from 25 to 125 units per liter.
In order to pass the test without errors and without retaking, to determine this enzyme, you must take blood on an empty stomach in the morning. You can drink water, and, as a last resort, you can feed the baby, but no later than 4 hours before taking blood. This applies, first of all, to infants who are fed “by the hour.”
Causes of increased or decreased amylase. What do deviations in results indicate?
Most often, enzyme levels are elevated. In the case of the pancreatic variety, we can talk about acute inflammation of the pancreas, which is very rare in a child, since the main cause of pancreatitis is prolonged alcohol intake and poor diet. Most often, an increase in value occurs with mumps. You should not think that mumps affects only the salivary glands, although they are the ones that change the face of a small patient when mumps develops. This virus is tropic to all glandular tissue, and therefore, with mumps, the pancreatic fraction may also increase.
As for diastasis of the salivary glands, its increase can also occur not only with mumps, but also with:
- pancreatitis;
- with acute inflammation of the peritoneum, or with peritonitis;
- with the first type of diabetes mellitus in children, and in the stage of complications with ketoacidosis;
- for abdominal injuries, if the pancreas was affected.
Of great clinical interest is a decrease in the level of diastase, when the value is either not determined at all or close to zero. This almost always in children indicates a high risk of a congenital genetic abnormality - cystic fibrosis, which affects glandular tissues and the bronchopulmonary system. This may also indicate severe pancreatic insufficiency, and in adults such a “zero value” of diastase often indicates extensive pancreatic necrosis, or severe chronic hepatitis.