Optical coherence tomography of the eye has become widespread in clinical ophthalmology over the past 15 years. The popularity of this innovative technology is easily explained by the ability to visualize intravital structures of the eyeball in high quality and resolution. Of course, during the existence of this research method, technology has made significant strides forward. The article is an overview of the principles of operation of modern equipment for optical coherence tomography, as well as the most significant clinical aspects of this examination technique, indications for its implementation and the cost of optical coherence tomography on the Moscow medical services market.
What is optical coherence tomography (OCT)?
The principles of optical coherence tomography were first explored at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology in the early 1990s. Carl Zeiss (Germany) created the first commercial version of a coherence tomograph in 1996. Currently, optical coherence tomography is an advanced innovative technology for visualizing the structures of the eyeball, without which no center of ophthalmology and eye microsurgery can do today. OCT of the eye is an easy-to-use, highly accurate non-invasive and non-contact technology that allows you to identify and monitor morphological changes in the tissues of the eyeball.
The method allows you to visualize cross-sectional images of the structures of the eyeball. You can study in detail the condition of the retina, the structure and features of all its layers, evaluate vitreoretinal relationships, and study the condition of the optic nerve and nerve fibers. High-frequency optical coherence tomography of the eye with an axial resolution of 3 μm allows intravital “optical biopsy” of intraocular structures of the eye. This resolution is tens of times more accurate than data obtained using ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging.
Operating principle of optical coherence tomography
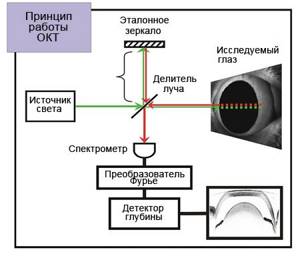
The essence of the tomograph is to measure the time during which a beam of light reflected from a particular optical section (A-scan) returns to the device. A series of A-scans performed on all structures of the area under study allows for reconstruction of both the anterior and posterior segments of the eye in the cross-sectional plane. Images of such cross-sections are called B-scans.
Due to the fact that the speed of light is very high, and the distance between the layers of the eyeball is very small (measured in microns), it is not possible to directly measure the transit time of light rays. For this purpose, the optical coherence tomograph uses low-coherence interferometry technology. During operation of the device, the emitted light beam is divided into two parts - the first beam of light is sent to the eyeball, and the second is a control beam and is directed to a special mirror surface. After reflection, both beams are captured by a special detector, after which the resulting data is analyzed and an image is formed. Using coherence analysis, the tomograph allows you to study even weakly reflective layers of the retina.
|
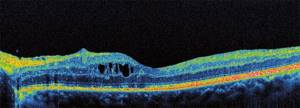
After the examination is completed, the computer generates an image that is available for analysis and interpretation by the attending physician. Depending on the ability to reflect light rays, all structures of the eyeball are painted in different colors on the resulting optical tomogram. For example, the vitreous body is black because it is a transparent, non-reflective medium. The anatomical structures of the eye, which have a high degree of reflection, give a red color or its shades on the tomogram. Weakly reflective structures are painted in cooler shades.
|
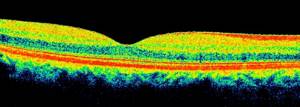
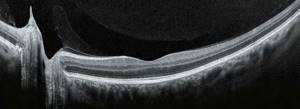
| Optical coherence tomography of the retina is normal |
Indications for optical coherence tomography of the eye
Ocular OCT provides the clinician with the ability to perform both qualitative (morphological features and reflectance) and quantitative (thickness, mapping and volume) analyzes of ocular structures in-situ in real time. Coherence tomography of the eye is indicated in the following clinical situations:
- verification of macular holes and pseudo-holes;
- diagnosis of epiretinal membranes;
- determination of the state of the vitreomacular interface: vitreoretinal relationships, vitreomacular adhesion, vitreoretinal traction syndrome;
- epiretinal fibrosis;
- retinal detachment, retinoschisis, maculoschisis;
- diabetic retinopathy and diabetic macular edema;
- senile macular degeneration and choroidal neovascularization;
- assessment of optic disc parameters;
- early diagnosis of glaucoma and glaucomatous damage to the optic nerve;
- assessment and analysis of the structures of the anterior chamber of the eye, including the volume and thickness of the cornea.
However, despite the apparent universality of this method, assessment of the state of the organ of vision and diagnosis must be carried out based on the results of several examinations, including taking into account the clinical picture of the disease. Indications for each specific patient are determined by the attending physician based on individual clinical characteristics.
Optical coherence tomography of the retina
OCT of the eye is an extremely accurate intravital method for measuring the thickness of the retinal layers. The ability of different structures to reflect light rays differently makes it possible to clearly differentiate the layer of optic nerve fibers, nuclear and plexiform layers in the resulting image, as well as assess the condition of the retinal pigment epithelium, external limiting membrane, photoceceptors and choriocapillaries.
OCT of the retina is used to diagnose a large number of vitreoretinal pathologies. The technology allows for clear visualization of vitreoretinal adhesions, which play a key role in the formation of lamellar and through macular holes and macular edema.
|
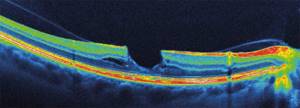
| OCT of the retina with vitreomacular traction syndrome, lamellar tear |
The development of macular holes has been studied in detail thanks to the advent of coherence tomography. Such studies play a key role in working with the patient, especially when deciding on the need for surgical treatment. The fact is that surgical tactics depend on the extent of the tears, which can most accurately be assessed using retinal tomography. Postoperative management of macular holes using OCT diagnostics is especially important, especially in the presence of recurrent pathology.
|
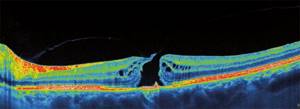
| OCT of the retina for a through macular hole |
Macular edema is a common complication of diabetic retinopathy. Fluorescein angiography plays an important role in the diagnosis of wet macular edema. However, the only way to identify cystoid macular edema and monitor macular thickness, which correlates with central vision impairment, is optical coherence tomography.
|
| OCT of eyes with diabetic macular edema |
Measuring the thickness of the retinal nerve fiber layer using OCT gives specialists a clear picture of glaucomatous retinal damage. This diagnostic method allows you to identify point defects even with the initial manifestations of glaucomatous damage. OCT of the retina allows specialists to make a correct judgment about the condition of this sensitive area, which ensures timely and adequate treatment.
Optical coherence tomography of the optic disc
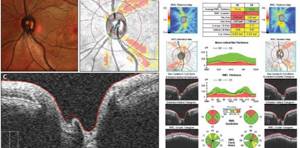
The main purpose of visualizing the optic nerve is to determine its contours and excavation parameters. Determining these parameters is important for diagnosing glaucoma, as well as various neuropathies. For example, the study has proven itself excellent in diagnosing multiple sclerosis. Tomography allows you to study the following parameters: the width of the neuroretinal ring on all meridians, as well as the size of the disc itself and the excavation.
Coherence tomography of the optic disc is especially important in glaucoma. In cases of long-term persistent increase in intraocular pressure, for example, an increase in the thickness of the neuroretinal ring in the vertical plane is observed. The results obtained allow specialists to verify the stage of the disease, the degree of damage to the optic nerve and dynamically assess the effectiveness of the treatment.
|
| Early diagnosis of glaucoma using OCT of the optic nerve |
Optical coherence tomography of the anterior segment of the eye
In modern ophthalmological practice, OCT is used not only to study the structures of the posterior part of the eye. This study is also very effective in diagnosing diseases of the anterior segment of the eyeball. OCT is widely used to assess the condition of the visual organ after antiglaucomatous surgery. In the postoperative period, situations often arise associated with impaired fluid outflow and increased intraocular pressure. Diagnostic procedures previously used in such situations did not provide a clear idea of the level of blockade, unlike OCT. The undeniable advantage of this method is its non-contact nature, which is important for the prevention of infectious complications in the postoperative period.
|
| Anterior segment OCT: visualizes the cornea, iris, AP, anterior lens capsule |
OCT also allows you to study the iris in detail and clearly differentiate all its layers, including the stroma and pigment epithelium. Changes in the iris are an early diagnostic criterion for many diseases, including pigment dispersion syndrome and rare types of glaucoma.
OCT of the cornea is widely used to determine its thickness, shape and stromal condition after surgical interventions. OCT allows you to study the transition between your own cornea and the graft during keratoplasty, and this method also helps in visualizing damage in various diseases and injuries of the cornea.
How the research is carried out
It was already mentioned above that OCT of the eye is a non-contact and absolutely painless diagnostic procedure. OCT is performed on an outpatient basis and takes only a few minutes.
The patient is asked to sit down, his head is fixed and he is told to focus his gaze on the flashing dot. In situations where visual acuity is greatly reduced, it is enough to simply not move, fix your gaze on one point and not blink. The patient does not experience any discomfort or pain during OCT.
After the examination, the computer analyzes the data obtained and displays the corresponding images on the monitor. The specialist carefully studies them and gives his conclusion based on the data obtained during the research process.
|
| Conducting OCT of the retina to verify the diagnosis |
How is it carried out?
The procedure is similar to an ultrasound examination, but instead of an ultrasonic sensor, infrared optical radiation is used, the wavelength of which is about 1 micrometer. The main quantitative characteristics of tomographs for OCT are axial and transverse resolution, as well as the number of scans per second.
During scanning, the radiation of a beam of infrared rays is concentrated on the eye tissue: they are reflected from it, which is recorded by an interferometric modulator, which further processes the collected data. Two planes are captured: horizontal and vertical, and a cross-section of the area under study can be obtained. Upon completion of the operation of the device, the specialist clears the images of noise obtained during the study, interprets them and makes a diagnosis.
During OCT, the subject must remain absolutely still, especially the eyeball, otherwise the result will be distorted. To capture your gaze at the time of scanning, there is a video camera with a flashing object on it. A certain distance is set between the eye and the camera, which is 9 mm. If the patient is unable, for some reason, to fix his gaze on one point, then the study is not carried out, since the data will be uninformative. The procedure itself is carried out quickly and is not accompanied by any pain or discomfort.
No preparatory measures are required; ophthalmologists can only resort to dilating the pupil with medications: this is necessary in order to have the most accurate information about the anatomy of the posterior part of the visual organ. The subject must be warned that for several hours after using medications to dilate the pupil, he will have blurred vision, especially close up. Therefore, it is imperative to exclude driving and any activity that requires high concentration.
The cost of retinal OCT, despite its complexity, is affordable for almost every person. Therefore, this examination is increasingly recommended for a person to undergo in order to obtain a reliable and quick idea of the state of the organ of vision.
Cost of optical coherence tomography in Moscow
Currently, almost all large ophthalmological clinics and ophthalmic surgical centers in Moscow are equipped with modern models of tomographs. This examination is mandatory for adequate diagnosis and treatment of many pathological conditions of the eyeball. The cost of optical coherence tomography in Moscow ranges from 4,000 to 6,000 rubles per eye. Indications for the study are determined by the doctor after examination and face-to-face consultation. Often, a comprehensive diagnosis of a particular disease requires several diagnostic tests. The price of coherence tomography of the retina and optic nerve in our clinic is 3,000 rubles for both eyes, which is one of the most budget options for Moscow. The examination is carried out using advanced equipment from Topcon, Japan. At the end of the study, the specialist will prepare a conclusion on the diagnostic results and propose a treatment plan.
Optical coherence tomography is an example of how modern technologies are breaking into our lives. Even 20 years ago, this method was at the stage of scientific research, and today it is difficult to imagine modern ophthalmology without this diagnostic device. OCT of the eye is a fast and comfortable way for the patient to obtain an intravital biopsy of the eyeball, see the state of the intraocular structures of the eyeball on a computer monitor, and, together with the attending physician, evaluate the effectiveness of the treatment.
Dear patients, you can sign up for OCT diagnostics of the retina and optic nerve or a consultation with an ophthalmologist at the clinic reception by phone: +7,. You can also make an appointment through the on-line registration form. To do this you just need to follow the link below.
Examination at the Miracle Doctor clinic
The medical center uses a modern coherence tomograph OPTOVUE RTVue100, manufactured in the USA, which performs eye scanning at high speed and with maximum resolution. The technical data of medical equipment ensures diagnostic accuracy for a wide variety of eye diseases.
The clinic employs professional ophthalmologists with extensive experience. They make smart decisions in any situation and provide timely assistance. Specialists work with all ophthalmological problems and find a way out of a seemingly hopeless situation.