The norm of leukocytes in the blood of children: causes of increase and possible diseases
A decrease or increase in the level of leukocytes indicates the development of disorders in the human body.
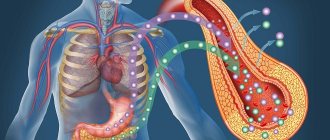
Leukocytes are otherwise called white blood cells, which are produced by the bone marrow. Their function is to restore damaged tissue and maintain immunity at the proper level. Leukocytes live for 20 years or more, although some types of cells live for only a few hours. Memory cells are distinguished by their long life, which, if necessary, are ready at any moment to remember the health offender and rush to destroy him. In the event of a quantitative violation, suspicion immediately arises of the penetration of an infection or virus.
In any case, the level of leukocytes changes frequently, this is influenced by stressful situations, physical activity, changes in the body’s condition, but the indicators fluctuate within the normal range. However, blood sampling for testing is carried out early in the morning on an empty stomach, then the indicators give an accurate result.
Causes of pathological leukocytosis
Pathological leukocytosis is caused by:
- infectious diseases caused by bacteria and viruses;
- rheumatic diseases that are systemic in nature;
- allergies;
- blood diseases;
- parasite infection;
- inflammatory diseases that are accompanied by suppuration;
- ulcerative colitis;
- extensive tissue burns;
- endocrine pathologies;
- eczema, other dermatological diseases;
- malignant tumors;
- radioactive radiation, lead poisoning;
- heart attack, stroke;
- consequences of surgery to remove the spleen.
It is impossible to treat pathological leukocytosis. It is necessary to eliminate the reason that caused it so that the content of blood cells returns to normal. Medicinal and surgical methods can be used for this.
Treatment of neonatal sepsis
The following are used as treatment:
- antibiotics;
- symptomatic (supportive) therapy.
Sepsis is dangerous for a child’s life, as it quickly destroys his body, so treatment with antibacterial drugs should be started as quickly as possible, followed by adjustments in accordance with the sensitivity of microorganisms to them. It happens that the cause of the infection remains unclear, the child is apparently healthy, but tests show negative bacterial culture results. In such cases, antibiotics are administered according to established schedules for 48 hours, after which treatment can be stopped. If the child's body weight is low, the duration of treatment should be 72 hours.
Typically, initial therapy for the treatment of sepsis begins with an aminoglycoside and ampicillin, used together. Sometimes it is advisable to add cefotaxime or completely replace it with aminoglycosides in cases of suspected meningitis caused by gram-negative microorganisms. Replacement of antibiotics, if necessary, is carried out after accurate identification of the causative agent of infection.
Healthy children from the group of newborns where the sick child was also prescribed antibiotics in the form of a combination of gentamicin with ampicillin or ampicillin with cefotaxime. If we are talking about the late version of nosocomial sepsis, children are prescribed vancomycin as part of initial therapy.
If the child has previously undergone a course of treatment with aminoglycosides from 7 days to 2 weeks and needs re-therapy, other antibacterial drugs related to aminoglycosides or third-generation cephalosporins should be considered.
When using indwelling venous catheters, there is a risk of infection with coagulase-negative staphylococcus. In this situation, initial therapy for sepsis should begin with vancomycin, but if sensitivity of the microorganism to nafcillin is detected, the drug is replaced with nafcillin or cefazolin. Of course, the catheter must be removed. It should also be taken into account that when taking a culture test, fungal structures manifest themselves within two to three days. It is necessary to quickly begin empirical treatment with amphotericin B even before the test result is received, since this is what can save the life of the newborn.
Physiological leukocytosis
In some cases, leukocytosis is not a pathology, since it is caused by natural causes. There are three types of this condition:
- myogenic (physical activity);
- nutritional (food intake);
- gestational (pregnancy);
For physiological reasons, an increase in the number of white cells in the blood is normal and does not harm health. Similar processes occur in the body of healthy people.
How is the analysis performed?
When testing blood for a general or, as it is also called, clinical analysis, the child should, if possible, be hungry, i.e., the procedure is done on an empty stomach. Typically, blood collection rooms in clinics are open from 8.00. until 9.30. At this time, blood levels in the body are the most optimal.
Blood must be donated on an empty stomach, because after eating, the stomach begins to work actively and the number of leukocytes may increase, and this, in turn, may give the doctor incorrect information about the child’s health status. Also, before taking the test, you should not undergo any procedures, such as x-rays, FGDS and various physiotherapeutic procedures, this can also lead to an increase in leukocytes in the blood.
Types of leukocytosis
Leukocytes are a group of cells that differ in structure, function, and content in the blood. For pathological causes of leukocytosis, the doctor determines which cells have exceeded the norm. According to this criterion, five types of leukocytosis are distinguished:
- basophilic;
- monocytic;
- eosinophilic;
- neutrophilic;
- lymphocytic.
Each type has its own reasons. Allergic reactions and ulcerative colitis lead to an increase in basophils. Excess is considered to be the content of such cells above 1%.
With granulomas, septic endocarditis, protozoal infections, the monocyte content exceeds 10%. If a blood test reveals a neutrophil content above 75%, this may be a sign of a bacterial infection or purulent process.
The norms of lymphocyte content differ depending on the age of the patient. In newborns and children under 7 years of age, the norm is within 55%. If this value is higher, we are talking about lymphocytic leukocytosis. In patients older than 7 years, the norm of lymphocytes is within 38%, that is, a value above this figure will be a pathology. The cause of lymphocytosis is viral diseases, malignant blood diseases.
Exceeding the norm of eosinophils (above 5%) occurs when infected with worms or allergies.
Due to the difference in the body's reactions to the pathogen according to the type of leukocytosis, it is possible to establish a preliminary diagnosis and determine the nature of the pathology.
What are leukocytes and what are they for?
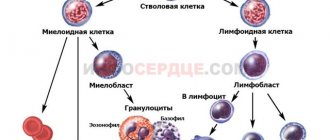
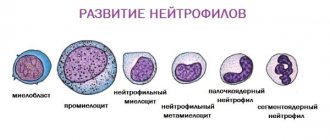
White blood cells are produced by the bone marrow and move throughout the body, penetrating even into its most secluded areas. If inflammation is detected in any organ or tissue, the number of cells begins to increase in this particular focus, and the bone marrow begins to produce them with renewed vigor. Leukocytes themselves are divided into several types. Cells with a granular component are usually called granulocytes, and those without grains are called agranulocytes.
The first category includes band and segmented, basophils and eosinophils. Agranulocytes are divided into lymphocytes and monocytes. They all have different structures and perform different functions in the process of hematopoiesis. The total number of white blood cells is called the body's leukocyte formula. White blood cells protect the child from various diseases that develop due to the penetration of viruses and infections into the body.
It is worth noting that they are the main assistant in the restoration of tissues after injury and inflammation, and also contribute to the manifestation of the body’s reactions to allergens, unusual stress, and fluctuations in ambient temperature.
Leukocyosis due to bacterial infections
When pathogenic bacteria enter the body, the patient is found to have increased neutrophils and monocytes. Sore throat, other respiratory diseases, and kidney inflammation cause a moderate increase in white blood cells. With purulent processes, such as phlegmon or abscess, as well as blood poisoning, the level of leukocytes can exceed 15,000 units. With generalized infectious processes, hyperleukocytosis develops, that is, a leukemoid reaction.
As a rule, during an exacerbation of the disease, the level of leukocytes increases rapidly, then gradually decreases to normal. In chronic diseases, a person has a slight excess of leukocytes, or their level is at the upper limit of normal.
Prevention
In order to prevent an increase in the level of leukocytes in the blood of a child, it is necessary to adhere to the following preventive measures:
- Avoid hypothermia;
- Monitor the child’s health;
- Enrich your baby’s diet with vitamins and macroelements (as a last resort, consult a doctor about the possibility of taking multivitamin preparations);
It is also worth remembering that the pathology can be asymptomatic. That is why it is important to regularly visit the doctor and have the little patient’s blood tested.
Hematological diseases
Extremely high levels of white blood cells, which can reach 100,000 units, indicate malignant blood diseases. These include leukemia and lymphoma. They lead to pathological changes in bone marrow cells, from which leukocytes subsequently develop.
Lymphoma causes a high degree of lymphocytosis. In leukemia, the content of monocytes, neutrophils or eosinophils increases significantly. During an exacerbation of leukemia, a large number of immature white cells can be found in the blood. Due to pathological processes, intermediate forms of leukocytes are not produced. Acute leukemia is also accompanied by an increase in the number of eosinophils and basophils.
To reduce the level of leukocytes, a patient with blood diseases is prescribed chemotherapy.
Physiological causes of increased white blood cells
An increased level of leukocytes in the blood for a child may be a sign of physiological conditions that are caused by reasons such as:
- Taking a bath, both hot and cold, before performing medical procedures.
- Physical activity. Therefore, before the analysis, it is better to refrain from active games with the child, which can increase the amount of formed elements in the blood.
- Recent feeding. This is due to the fact that food entering the stomach increases the number of white blood cells. The highest rate is observed after eating. In addition, their number may fluctuate throughout the day. That is why there are certain preparation requirements before donating blood.
- Carrying out physiological procedures: x-rays, fibrogastroduodenoscopy.
- Fear. Before visiting the laboratory, it is necessary to distract the child from sad thoughts and not focus on the procedure. A large number of white blood cells can even be associated with the child’s crying before the test.
Diagnostic methods
As a rule, the patient does not suspect that his white blood cells are elevated, since this condition does not cause any special symptoms. Only a disease that has led to a change in the leukocyte formula manifests itself. A person may be bothered by fever, pain, fatigue and other symptoms.
If an excess of white cells is detected in the blood, an additional examination is prescribed.
First of all, bacterial seeding of the biomaterial is carried out: a laboratory examination of blood, urine, and sputum is performed. Thanks to it, the causative agent of the disease can be identified. The main diagnostic method is an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, which detects antibodies to viruses and bacteria.
If there are signs of an allergic reaction, an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay is used, which helps determine the content of immunoglobulin E, the main marker of allergies. Basophil tests are also performed, and the patient is prescribed various allergy tests to determine the type of allergen.
Radiography is a universal method that is used for pulmonary diseases, rheumatoid arthritis, and bone diseases. The same applies to the ultrasound method. It is used to identify possible changes in tissues due to inflammation of the kidneys and other organs.
The ECG method is used to assess the condition of the myocardium and heart valves.
If leukemia is suspected, histological studies are carried out, the material for which is obtained by puncture.
Symptoms of neonatal sepsis
The first symptoms of sepsis are almost the same and do not depend on what type of pathogen causes them:
- the baby sucks poorly;
- eats poorly;
- his heart rate is reduced;
- breathing problems up to stopping;
- Body temperature can fluctuate from hypothermia to high numbers.
The occurrence of a febrile state is observed in 10-15% of clinical cases. If the fever persists for a long time (an hour or more), infection is most likely obvious. Other early manifestations of sepsis that should prompt doctors to take emergency measures include convulsions, jaundice of the skin, vomiting, and intestinal disorders.
Early sepsis caused by B-streptococcus often manifests itself in newborns as a transient form of pneumonia. With late onset of sepsis (the period can be up to 12 weeks), the incidence of meningitis is very high.
Interpretation of blood tests in children
On the Internet you can find a lot of tables that show the norm of blood counts by age, but this is not the case where independence and fortune telling on coffee grounds are appropriate. Currently, there are several hundred (!) parameters by which blood can be examined, and all of them are important not on their own, but in comparison with each other. Deciphering a blood test requires serious professional training. Our center's pediatricians are always in touch with patients during business hours, and if you purchase our comprehensive health care program, you can call your personal doctor around the clock. You will receive comprehensive and qualified answers to all your questions.
What happens to the baby in the treatment room?
A calm, positive atmosphere reigns in the treatment room of our center. Moms and dads have the opportunity to come in with the baby and, during blood sampling, hold him on their lap, hug, kiss, and blow in his ear. The child's attention will be distracted by funny pictures on the walls and bright toys. We do everything to make sure that the children have a pleasant and pain-free experience. For example, instead of conventional scarifying needles to take blood from a finger, we use an expensive new product - lancets . These funny devices, similar to a fountain pen, with a button and a spring, are very popular with little patients. The needles in the lancets have a special sharpening: they pierce the skin almost painlessly and so that the blood flows quickly and you don’t have to press on the finger for a long time. At the end of the procedure, the doctor seals the wound with a plaster with funny faces or animals.
Many mothers are wary of taking blood from a vein. And in vain! Our center employs an experienced procedural doctor who will perform all the necessary manipulations quickly and comfortably for the baby. In winter, for example, this method is preferable: blood will flow from a vein faster than from a cold finger, which means that the baby will have fewer reasons for dissatisfaction.