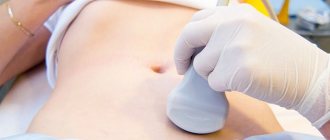
To take full advantage of your ultrasound machine's capabilities, you must have the right accessories. Thus, the main factor in the effectiveness of your ultrasound scanner is the correctly selected ultrasound sensors.
In this publication we will talk about the different types of ultrasonic sensors and what research each of them is intended for. Finally, we will share some useful tips to keep in mind when purchasing ultrasound sensors.
So, let's take it in order.
— What is an ultrasonic sensor and what is it for?
An ultrasound transducer is a device that generates ultrasonic waves. These waves are reflected from the tissues of the human body and are captured by the same sensor in the form of echo signals. The sensor transmits the received echo signals to a computer, which uses them to create an image called an echogram. The main element of each ultrasonic sensor is a piezoelectric crystal, which serves to generate and receive ultrasonic waves. Unfortunately, the medical imaging industry has been using the same piezoelectric material for over 40 years.
This was the case until recently, when a new type of material and a new technology of ultrasonic sensors - monocrystalline - appeared, which led to a significant improvement in image quality.
Ultrasound is a safe and effective diagnostic method
Modern medicine today does not question the fact that a professionally performed ultrasound examination does not pose the slightest risk to the patient.
At the same time, a certain volume of ultrasound can be dangerous for humans. This is a well-known fact, but ultrasound examinations are performed at very low volumes of ultrasonic waves. In addition, during ultrasound diagnostics, ionizing radiation is not used, which can provoke damage at the chromosomal level and cause cancer.
It cannot be said that ultrasonic influence passes completely without a trace on the body. It causes heating and changes in pressure in the tissues. However, this effect when using modern ultrasound scanners is so insignificant that there is no need to talk about any harm when diagnosing using ultrasound.
We offer a wide selection of expert-class ultrasound machines, including our exclusive representative in Russia. BK medical has been developing and producing premium ultrasound systems for over 30 years. The devices use modern imaging technologies to achieve high resolution. The devices are equipped with sensors for your specific tasks. In the BK medical catalog you will find: transrectal, transvaginal, neurosurgical, laparoscopic, abdominal and pediatric sensors from this manufacturer.
In order to get expert advice on the technical characteristics of the products we offer or to buy an ultrasound machine, call or fill out the feedback form on our website.
Types of ultrasonic sensors
Ultrasound sensors are currently available on the market in a variety of shapes, sizes and for a wide variety of applications. This is due to the fact that to obtain good image quality in different parts of the body, it is necessary to use sensors with appropriate characteristics. Ultrasound sensors can be external or cavity. External ones are located on the surface of the body or organ, and abdominal ones are inserted into a hollow organ or opening (for example, into the rectum or vagina).
Are there any other differences between them?
Certainly!
Ultrasonic sensors differ in their design depending on:
- Piezoelectric crystal arrangements
- Aperture size (pad size)
- Frequencies
Below we list the three most common types of ultrasonic sensors: linear, convex (standard or micro-convex) and sector phased. In addition, we included in the review some other sensors that are available on the market and in our warehouse.
Linear sensors
The piezoelectric crystals in these sensors are arranged linearly, and the scanning area is rectangular in shape. This sensor has good near-field resolution. The frequency and application of a linear transducer depends on whether it is intended for 2D or 3D/4D imaging.
The linear 2D sensor has a wide aperture and its center frequency is in the range of 2.5-12 MHz.
The linear sensor is used for the following purposes:
- Vascular examination
- Performing vascular catheterization under ultrasound control
- Performing regional anesthesia under ultrasound control
- Breast examination
- Thyroid examination
- Examination of muscles, tendons and joints
- Examination of other superficial organs
- Conducting intraoperative studies and laparoscopy
The linear 3D/4D sensor has a wide aperture and a center frequency in the range of 7.5-11 MHz.
Scope of application of this type of sensor:
- Breast examination
- Thyroid examination
- Study of blood vessels, in particular the carotid arteries
Convex sensors
A convex ultrasonic sensor is also called a convex sensor because the piezoelectric crystals in it are arranged in a curved manner. The shape of the scanning area is convex. This sensor visualizes deep structures well, even as image resolution decreases with increasing depth.
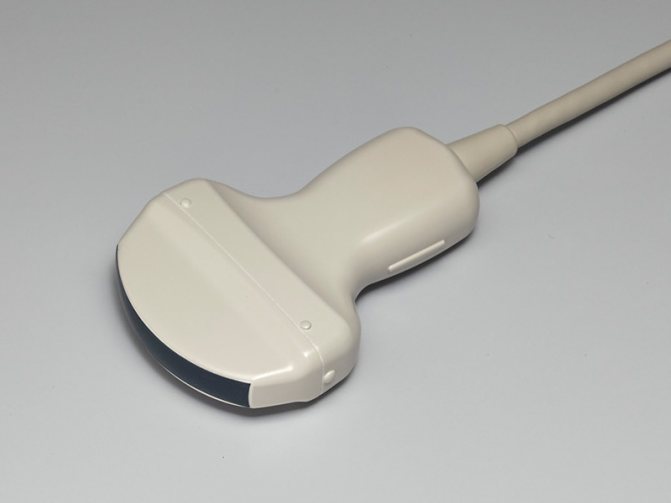

The scanning area, frequency and application of a convex probe depend on whether it is intended for 2D or 3D/4D imaging.
The 2D convex sensor has a wide aperture and its center frequency is 2.5-7.5 MHz.
The convex sensor is used for the following purposes:
- Examination of abdominal organs in adults and children
- Examination of the pelvic organs in adults and children
- Diagnosis of the fetus
The convex 3D/4D sensor has a wide aperture and its center frequency is 3.5-6.5 MHz. It is used to examine the abdominal organs, pelvic organs and diagnose the fetus.
There is a subtype of convex sensors called microconvex . It has a much smaller aperture. Doctors usually use it in neonatology and pediatrics.
Sector phased (cardiac) sensors
This sensor is named after a type of piezoelectric device called a phased array. The phased sensor has a small aperture and low frequency (center frequency is 2-7.5 MHz). The shape of the scanning area is almost triangular. These sensors have poor resolution in the near field but provide good visibility at depth. Allows observation of structures through a narrow intercostal gap.
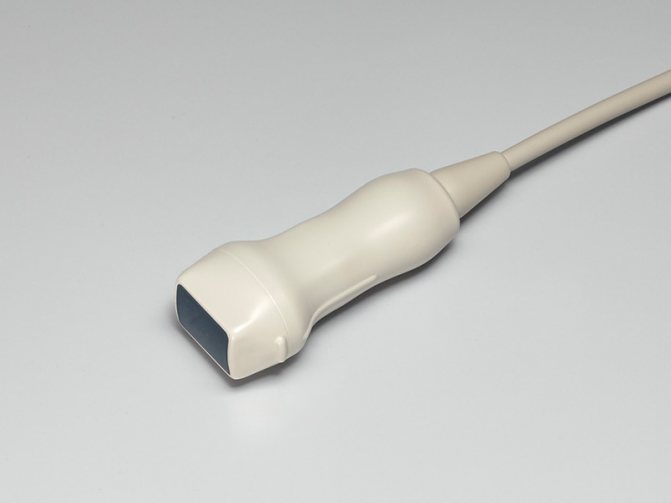

Scope of application of phased sensor:
- Cardiac testing, including transesophageal studies in adults and children
- Abdominal examinations in adults and children
- Brain studies in adults and children
To study children, high-frequency sensors (5 or 7.5 MHz) are used, which makes it possible to obtain a higher-quality image. This is possible due to the small size of the patients.
Other types of ultrasonic sensors
And that is not all. There are a large number of different types of ultrasonic sensors on the market. Here are some of them:
Pencil probes , also called CW probes, are used to measure blood flow. This sensor has a small aperture and uses a low frequency (typically 2-8 MHz). The next type of ultrasonic sensor is intracavitary . These sensors are designed to conduct research when inserted into certain hollow organs or openings. Intracavitary sensors include vaginal (gynecological), rectal and rectal-vaginal sensors . As a rule, they have a small scanning area, and their frequency ranges from 3.5-11.5 MHz. There is also a transesophageal (transesophageal) sensor . Like the previously mentioned sensors, it has a small aperture and is used in cardiology to obtain better images of the heart through the esophagus. These sensors operate at a medium frequency, in the range of 3-10 MHz. In addition, there are several sensors designed for surgical use, such as laparoscopic ones .
Modern ultrasound equipment
Modern ultrasound systems are far superior in their technical characteristics to obsolete equipment of the last century and can be used for early diagnosis of a wide variety of pathologies.
Ultrasound equipment can be classified into several categories according to its intended purpose and operating principle:
- Ultrasound scanners. Their purpose is to obtain a two-dimensional image of the research results in black and white. option.
- Ultrasound scanners with spectral Doppler. Among specialists they are also known as duplex devices. Compared to the previous type, they are more functional: they can be used to check the speed of blood flow.
- Ultrasound machines with color Doppler mapping. This type of equipment is equipped with the most complete range of options. In addition to all those modes that are provided for the ultrasound scanner of the class mentioned above, they provide color highlighting (on a gray 2D image of the area under study) of the two-dimensional distribution of blood circulation velocity.
- Specialized ultrasound equipment (ophthalmological, fetal monitors, echoencephaloscope, etc.). Each of these types of devices is designed for a specific type of diagnostics in a specific field of medicine. For example, fetal monitors are used to measure the heart rate of a baby in the womb. The echoencephaloscope is used for brain research, etc.
Tips to remember when purchasing an ultrasonic sensor
Now that you already know about the most common types of ultrasonic sensors, here are a few tips that you should remember when purchasing them:
- Make sure and double check that the sensor you are about to purchase is compatible with your machine - you can use the instruction manual for this or contact our sales department.
- Low frequency (2.5 to 7.5 MHz) provides better penetration depth, but has the disadvantage of lower image quality.
- The higher the frequency (above 7.5 MHz), the lower the penetration depth of the ultrasound, however you get higher quality images near the surface (7.5 MHz = 20 cm).
Attention!
- A black line on the monitor of an ultrasound machine will most likely mean that there is a crystal inside the sensor that has expired.
- A shadow on the ultrasound machine screen may indicate a weak crystal inside the transducer that is not producing the required vibration.
The history of the appearance of ultrasound in medicine
Ultrasound began to be used for medical purposes at the turn of the 20s and 30s. XX century In the 40s, it was used to alleviate the conditions of patients with arthritis, asthma, stomach ulcers, etc.
Ultrasound was first proposed to be used for diagnosis in 1940. However, German doctors who conducted experiments on detecting tumors and abscesses using ultrasound were never able to confirm the results of their research. Therefore, the pioneer of ultrasound as a diagnostic method is considered to be Karl Theodor Dussik, an Austrian psychiatrist and neurologist, who in 1947 invented the hyperphonography method.
In the 50s, research into the possibilities of ultrasound for diagnostic purposes began to be carried out in many countries - in Germany, Sweden, Japan, the USA, Australia, and also in the USSR.
Examination of women
What can be seen on a female ultrasound
Screenings for the fairer sex are prescribed for various conditions and to check the entire genitourinary system. Ultrasound of the pelvic organs in women is prescribed for the following reasons:
- signs of ectopic fetal development;
- pathologies of the uterus and ovaries;
- chronic inflammatory processes, the period of their exacerbation;
- the presence of neoplasms in the pelvic area;
- the presence of stone stones in the system;
- the use of ultrasound for obstruction of the fallopian canals;
- at the preliminary stage for installing an IUD (intrauterine device);
- to check the functionality of the IUD placement;
- primary and repeat ultrasound examinations for infertility;
- suspected fetal anomalies.
In addition to health problems that have already occurred, women are recommended to have a preventive visit to a gynecologist and check the reproductive system through an ultrasound. If you regularly (once a year) visit a doctor and undergo an ultrasound examination, you can avoid many serious disorders and cure them in early, harmless stages.
At what day of the cycle should an ultrasound be performed?
The optimal time for the procedure is determined by the doctor, since different pathologies require specific testing. At different stages of the female cycle, the reproductive system looks and “behaves” differently, which affects the information content of the examination. Unless otherwise prescribed by the doctor, the best time for an ultrasound is considered to be days 4-9 of the cycle. During this period, there is still no accumulation of the blood cushion in the uterine cavity, it is in a calm state, and an ultrasound examination shows the most realistic, accurate picture.
There are situations when ultrasound is performed on an emergency basis. In this case, it does not matter what day of the cycle the procedure falls on. The doctor urgently sends the patient for an ultrasound if she has extensive bleeding, her period does not end after a certain time, mechanical trauma to the abdominal area has occurred, or urgent monitoring of previously performed treatment is necessary. According to the indicated indications, ultrasound is also performed during menstruation.
Preparing for women's diagnostics
The examination must be scheduled for a specific day of the cycle and made an appointment in the morning. This is necessary so as not to suffer from prolonged fasting during the day. The main recommendation for transabdominal ultrasound is to arrive for the procedure on an empty stomach. It will be easier to wait for the session if you go to it after an overnight 8-hour sleep fast. If the ultrasound is scheduled for the afternoon, you can allow yourself a light breakfast or a small snack for lunch. Drinking water is not prohibited. Her last appointment should not take place 1-2 hours before screening. During a transabdominal ultrasound, the bladder needs to be filled, and during a transvaginal procedure, on the contrary, it must be emptied.
Any type of ultrasound screening requires a preliminary diet for 2-3 days before the ultrasound. Its requirements cannot be called strict, since heavy foods are replaced with easily digestible ones: cereals, lean meat and fish, eggs, broths. Unless your doctor prescribes otherwise, you can take publicly available medications that improve digestion for a few days before the ultrasound. On the eve of the scan, it is better to empty the intestines naturally or through auxiliary means.
Examination of men
What can be seen on an ultrasound
Examination of the male reproductive system differs slightly in results, since the anatomical structure of the area being studied is naturally different. Ultrasound of the pelvic organs in men helps to accurately examine and assess the condition:
- Endocrine glandular tissue - prostate. Due to age-related changes, a change in the volume of hormone production occurs in this area, causing the glandular tissue to change, become denser, and increase in size. Its functionality is lost, and therefore the protection of the genitourinary system from infections is reduced. For early warning of the described disorders, it is necessary to undergo regular ultrasound examinations.
- Seminal vesicles. Located in the internal pelvic region, they look like oblong cavities in which sperm production occurs. The tissue structure is also glandular, producing a number of hormones.
- Bladder.
- Adjacent objects and the inguinal region of the lymphatic network.
During a transabdominal ultrasound, a standard examination of the internal organs is performed and the general condition of the prostate is assessed. If compactions, an increase in size, or pathologies of neighboring lymph nodes are noticed, a repeat ultrasound scan is prescribed, but the procedure is performed transrectally. If the doctor considers the data received during the ultrasound to be insufficient, “second-tier” studies are prescribed, designed to confirm or refute the controversial ultrasound results. This may be a CT scan or MRI of the pelvis.
Indications for male ultrasound
You should go for an examination through ultrasound screening if you have the following complaints:
- discomfort during the next emptying of the bladder, pain and pain when urinating;
- pain in the lower abdomen or upon palpation by a doctor;
- foreign impurities in urine;
- erectile dysfunction at a young age;
- previously diagnosed infertility by a doctor;
- “poor” laboratory test results;
- systematic pain in the groin.
There is also an age period from the beginning of which a man is supposed to visit a specialized doctor and an ultrasound room at least once a year. The limit in this case is 40 years of age. In order for natural changes in the body to occur without complications, periodic monitoring and ultrasound checks are necessary. This will avoid the asymptomatic development of cancer, chronic cystitis, abnormalities of the testes and blood flow in the area of interest.
Features of preparation for ultrasound
Before an ultrasound scan, you need to find out from your doctor which way it will be carried out: through the abdominal wall or the rectum. In this regard, the preparation plan for the ultrasound will change. A conventional transabdominal examination requires only dietary preparation with the exclusion of fatty, difficult-to-digest foods and strong, alcoholic drinks. You need to change your diet a little 2-3 days before the session. The doctor may also prescribe Espumisan for this period.
If a transrectal ultrasound is planned, on the eve of screening it is necessary to carry out cleansing procedures: enemas or taking laxatives. After cleansing the intestines, you can only drink water. It is better to schedule an ultrasound in the morning and come to it on an empty stomach. The urine should be moderately full, so you need to drink a liter of clean water 1-2 hours before the start.