Ultrasound examination (ultrasound) of the female genital organs is one of the most informative types of diagnostics. Among its advantages are the complete absence of pain or discomfort for the patient, the absence of contraindications (safety), efficiency, instant receipt of data for prescribing treatment or detection of pathologies. Another definite plus is the minimum requirements for preparation for a gynecological ultrasound. A woman is not required to follow strict diets, preliminary manipulations, any training, etc. It is enough just to follow a number of simple rules.
How is a pelvic ultrasound performed in women?
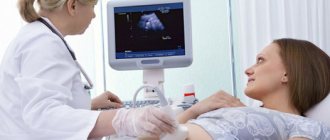
Transabdominal
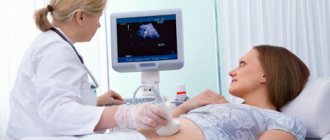
The doctor uses a probe to examine the organs through the outer wall of the abdominal cavity. If you have good digestion, preparation for a transabdominal pelvic ultrasound is practically not needed, but a couple of days before the procedure, eliminate foods that cause gas formation. An hour before the test, drink several glasses of water to fill your bladder.
Transrectally
The doctor inserts a probe into the rectum and examines the organs from the inside. This type of study is rarely prescribed to women if the data obtained by another method is not enough to make a diagnosis.
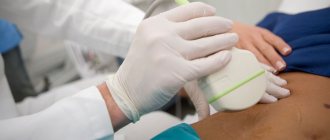
Transauginal
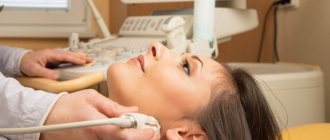
In this type of test, a probe is inserted into the vagina. Preparation for a transvaginal pelvic ultrasound is not required, but if you have frequent constipation and bloating. In this case, you will need to exclude gas-causing foods a few days before the procedure. Preparation also includes taking into account the day of the menstrual cycle. The doctor who issues the referral warns in advance on what day the ultrasound should be done. The bladder does not need to be filled.
When is it prescribed?
Ultrasound examination is actively used both for the diagnosis of various diseases and for preventive examinations. In the first case, an appointment for an ultrasound is issued if there are complaints:
- for pain in the lower abdomen and groin;
- prolonged tugging or other discomfort;
- frequent urge to urinate;
- disruptions of the menstrual cycle;
- spotting (not during menstruation);
- uncomfortable urination (accompanied by aching or acute paroxysmal pain);
- burning sensation in the urethra;
- too much (scanty) discharge during menstruation;
- the presence of blood or bloody mucus in the urine, etc.
Preventive ultrasound of the female organs is prescribed when planning pregnancy to monitor its course or progress of treatment (confirm recovery); before installing or removing an intrauterine device. An ultrasound examination is mandatory after operations on the organs of the woman’s reproductive system and during the recovery period. In addition, all women are strongly recommended to undergo preventive examinations to identify so-called female diseases at an early stage with a frequency of once every 1–2 years.
Preparation for pelvic ultrasound in women
Preparation for the pelvic ultrasound procedure includes general points that are characteristic of all types of examination, and specific ones:
- maintaining a certain diet for two days;
- to prevent bloating, take Espumisan 2-3 days before the test in the dosage prescribed by your doctor;
- drinking water immediately before the ultrasound (only for abdominal);
- quitting smoking and alcohol;
- bowel cleansing during transrectal examination.
What diseases are determined using ultrasound of the female organs?
The list of pathologies that an examination can confirm or refute is very large. A specialist can evaluate several indicators at once: position, size, structure of organs, and compare the obtained indicators with normal ones.
Based on the results of the ultrasound, the doctor can state:
- polycystic disease;
- oncology (indicated by various neoplasms, thickening of organ walls);
- ovarian cysts;
- fibroids;
- endometriosis and much more.
The research data is obtained immediately (no need to wait for processing), but it must be deciphered by a qualified doctor (urologist, oncologist, gynecologist, obstetrician). The patient’s area of responsibility is proper preparation for a gynecological ultrasound, on which the correct diagnosis largely depends.
What not to eat before a pelvic ultrasound
Meals before a pelvic ultrasound for 2-3 days the day before should consist of foods that are well digestible and do not cause heaviness or gas formation. This list includes:
| lean meat and fish |
| cereals |
| hard cheeses |
| boiled eggs |
| yeast baking |
| fresh vegetables and fruits |
| legumes |
| dairy products |
| carbonated and alcoholic drinks |
To prevent bloating, take Espumisan 2-3 days before the test, in the dosage prescribed by the doctor.
How is the procedure done?
The study is organized as follows:
- The patient should remove clothing from the lower part of the body (from the waist down)
- She sits on a special couch in the same way as during a regular gynecological examination.
- The doctor prepares the sensor: puts an individual condom on it, lubricates it with a special gel for the procedure
- The physician then inserts the device shallowly into the patient’s vagina.
- To get a complete picture of the state of the organs, he can move the sensor from side to side
- All data is recorded and processed by a doctor
The gel is necessary to facilitate the penetration of the sensor (and thereby reduce the likelihood of negative sensations) and enhance the ultrasonic effect by increasing conductivity.
This type of examination lasts no more than 10 minutes. It is painless and gives the most complete picture even in cases where an abdominal ultrasound shows nothing or cannot be performed.
On what day of the menstrual cycle should I do a pelvic ultrasound?
The day of the cycle depends on the purpose of the study:
- Days 5–7 of the cycle - routine ultrasound to assess the uterus and appendages, identify diseases;
- 3 times during the entire cycle - 8-10/15-16/23-24 days to monitor the dynamics of the development and maturation of follicles;
- 5–10 days, 16–20 — if fibroids are suspected; during pregnancy in the I, II, III trimester;
- from 25 to 28 days of the cycle, if the cycle is 28–30 days, respectively - for endometriosis.
If a cycle failure occurs, ultrasound can be done without taking into account a specific period. Any day is suitable for assessing the condition of organs after surgery or abortion.
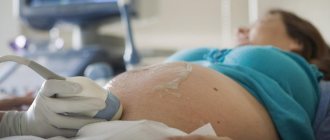
Ultrasound for expectant mothers
Pregnant women may undergo preventive or therapeutic ultrasounds up to 5–6 times. The mandatory minimum is a three-time study, which is prescribed at 11-14, 19-21 and 30-34 weeks. Ultrasound in the first trimester is the most effective and safe way to detect serious disorders/anomalies in fetal development (including Down syndrome).
In the second trimester, the normal development of vital organs and their systems in the fetus is monitored (sex is also determined here). The latter procedure is aimed at identifying late developmental abnormalities of target organs (heart, kidneys, gastrointestinal tract, central nervous system, etc.). During this study, the doctor can draw conclusions about whether the speed of fetal development is normal.
How to prepare for a pelvic ultrasound in a man
The pelvic organs in men are located close to each other, so the inflammatory process that begins in one organ quickly spreads to others. The examination is carried out abdominally or transrectally. Additionally, Doppler ultrasound examination of nearby vessels may be required.
As for the diet that should be followed for three days before the procedure, it involves abstaining from fatty foods and those that cause gas. You should not smoke or drink alcohol.
The examination is carried out on an empty stomach with a full bladder. If a transrectal examination is prescribed, the day before you need to take medications that cleanse the intestines, and do an enema 2-3 hours before.
Types of ultrasound in gynecology
Ultrasound in gynecology can be performed in three ways. The following types are distinguished:
- transrectal ultrasound (performed through the rectum in girls who are not sexually active);
- transvaginal ultrasound (carried out by inserting a sensor into the vagina for an accurate examination of diseases of the pelvic organs);
- transabdominal ( or simply abdominal) ultrasound , or simply abdominal ultrasound (performed through the abdominal wall when signs of inflammation of the pelvic organs are detected or in girls who are not sexually active).
1 Ultrasound in gynecology
2 Ultrasound scanner Voluson 10
3 Ultrasound in gynecology
For what indications is an ultrasound of the pelvic organs performed in women?
- identifying the causes of infertility;
- menstrual irregularities;
- assessment of pathology of the uterus and ovaries;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs: endometritis, parametritis, vulvovaginitis, salpingoopharitis;
- vaginal discharge;
- study of the nature of pelvic tumors (bladder cancer, fibroids, uterine cancer);
- inflammatory diseases of the urinary system (cystitis, pyelonephritis, urolithiasis);
- study of the condition of the ovaries and uterus during IVF;
- surgical manipulation of the bladder, uterus, fallopian tubes or ovaries;
- complications of pregnancy;
- monitoring the installed intrauterine device (see methods of contraception).
What diseases and conditions can ultrasound detect in gynecology?
- tumor processes in the pelvic area;
- torsion of ovarian cyst; ovarian cyst;
- complications after pregnancy and childbirth;
- pathology of the development of the uterus and appendages (duplication of the fallopian tubes, underdeveloped “infantile” uterus, bicornuate, saddle-shaped uterus);
- endometrial polyps;
- obstruction of the fallopian tubes (formation of adhesions and constrictions);
- the presence of fluid in the pelvic organs;
- uterine fibroids;
- pelvic inflammatory diseases, endometriosis;
- pregnancy (uterine and ectopic).

1 Ultrasound in gynecology

2 Ultrasound scanner Voluson 10

3 Ultrasound in gynecology
A female ultrasound will help determine the following indicators:
- ovarian size;
- the presence and type of ovarian cysts (follicular, luteal, endometrioid);
- size and shape of the uterus;
- thickness of the uterine mucosa (varies depending on the day of the cycle);
- the presence of tumors of the uterus and appendages, their location and the nature of the formation (benign or malignant).
Diagnosed diseases
Transvaginal ultrasound allows you to identify a number of diseases and problems in the reproductive system at an early stage. It allows you to detect:
- Fluid and pus in the uterus and fallopian tubes. The cause of their appearance may be infections, viruses, mechanical damage
- Endomentriosis is an excessive proliferation of cells in the inner layer of uterine tissue into other layers and organs. It can occur due to inflammatory processes, damage (surgery, abortion), the appearance of neoplasms, disruption of the endocrine system, too frequent use of certain medications and substances
- Myoma is a benign neoplasm in the tissues of the uterus or its cervix. May occur due to chronic diseases, frequent abortions, hormonal imbalances, constant stress, pathologies, excess weight, or with hereditary predisposition
- Cysts and polycystic ovaries are tumors filled with fluid. Occurs with endocrine disorders, chronic diseases of the genitourinary system
- Various polyps on the walls of the uterus are benign formations in the endometrium of the organ. They can reach several centimeters in diameter. Their appearance may be associated with polycystic disease, chronic diseases, mastopathy, fibroma
- Inflammation and enlargement of organs can occur due to both infection and injury.
- Hydatidiform mole - appears instead of a full-fledged embryo during the process of conception, filled with fluid. Occurs due to duplication of male chromosomes with the loss of female chromosomes, sometimes due to fertilization of an egg that does not contain a nucleus. This disease is rare
- Fetal development disorders during pregnancy
- Defects and pathologies in the development of the fallopian tubes: obstruction, spiral-shaped or too long tubes, blind passages, duplication of organs
- Ectopic pregnancy occurs when an egg implants outside the uterine tissue after fertilization. Occurs due to blockage of the fallopian tubes, congenital anomalies in them, as well as after an inflammatory process, abortion
- Cancer is a malignant tumor in various organs:
- Uterus
- Ovarian
- Cervix