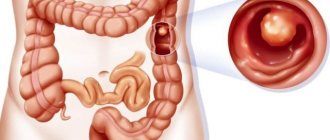
- Brief description of methods
- Possible restrictions
- Cost of examinations
Intestinal examination can be carried out using different methods.
Colonoscopy, which is performed using a special probe, and computed tomography of the intestine are also applicable for this. Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages, which should be taken into account when referring a patient for diagnostics. Usually, to decide which is better, a CT scan of the intestines or a colonoscopy, patients rely on well-known facts like “X-rays can cause cancer” or “injecting air into the intestines is a hellish pain that cannot be tolerated.” As a result, the choice may fall on the research method that causes the least amount of concern, and not on the one that will provide more useful information to the attending physician and contribute to making the correct diagnosis.
This article presents the main arguments for and against this or that method of examination, taking into account the pathology for which the diagnosis is carried out, contraindications and limitations of computed tomography and colonoscopy.
What is the difference between a colon CT scan and a colonoscopy?
CT bowel
or colonoscopy
:
which is better? Before answering this question, you should understand what the difference is between these procedures.
A CT scan allows the doctor to carefully examine every centimeter of the intestine along its entire length absolutely painlessly. The tomograph transmits the image to the monitor in 3D format, which allows the doctor to see not only pathological changes, but also all the features of the blood supply to the mucous membrane, the composition of the muscle fibers that form the intestinal wall. With the help of CT, you can see the patient’s organ as a whole and compare its different points at the same time.
Colonoscopy is a fairly invasive and quite painful procedure. However, unlike the virtual method, it is more reliable. It gives the doctor more information, because the probe is equipped with special optics, and this makes it possible to detect all pathological changes in the smallest detail.
Only a doctor can determine which is better, a CT scan of the intestine or a colonoscopy.
Brief description of both methods
Colonoscopy involves the use of a special flexible fiber optic probe for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes, which is inserted into the intestine and moves along the rectum, sigmoid and colon. To facilitate the advancement of the probe through the intestine and straighten the intestinal loops, air is pumped through the anus. The injection of gas may cause pain.
Colonoscopy allows:
- visual examination of the intestinal mucosa to identify areas of ulceration, bleeding, space-occupying formations, intussusception of the intestinal wall and other pathological changes;
- tissue sampling for biopsy;
- a number of therapeutic manipulations, such as cauterization of a bleeding vessel, straightening the intestinal walls in the area of intussusception, etc.
Computed tomography of the intestine involves taking a series of images, which are thin layer-by-layer sections of tissue of the examined area. The information content of the method is so high that it is sometimes called “virtual colonoscopy.”
To improve the clarity and detail of images, special iodine-based contrast agents are used, which can be injected into the blood or orally.
Virtual colonoscopy allows you to see:
- the intestine itself throughout, including the small intestine;
- stomach;
- bones of the lumbar spine, sacrum and coccyx;
- vessels, lymph nodes;
- retroperitoneal organs (kidneys, adrenal glands, ureters);
- pelvic organs.
As can be seen from the description of both methods, computed tomography of the intestine allows you to obtain information about all organs and tissues of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space, but does not give the doctor the opportunity to carry out diagnostic and therapeutic manipulations during the examination procedure. This means that if there are indications for taking a biopsy, stopping bleeding or other manipulations after a computed tomography scan, a regular colonoscopy will have to be performed.
What is a CT scan of the intestine?
This is an examination technique that involves presenting images of the large intestine and rectum from the inside onto a computer screen. Does not cause discomfort. During diagnostics, the patient can only receive small doses of radiation in the tomograph tunnel (in a supine position). The whole process takes about 15 minutes.
Advantages and disadvantages
Experts still cannot decide which procedure is more reliable, CT or colonoscopy, and all because both procedures have both pros and cons.
Pros :
- non-invasive;
- indicated for people with pulmonary insufficiency and those with poor blood clotting;
- it is possible to examine nearby organs;
- The entire research process lasts up to 15 minutes.
Minuses:
- a person receives a dose of radiation;
- a woman is strictly prohibited from undergoing a CT scan if she is pregnant;
- Overweight people are difficult to examine and the machine can only support a certain amount of weight.
Contraindications to CT
CT has two types of contraindications: absolute and relative. The following can be considered absolute:
- pregnancy;
- claustrophobia;
- general extremely serious condition of the patient: shock or coma;
- overweight - tomographs have their own limit, often about 150 kg.
Relative:
- hyperkinesis;
- diverticulitis;
- exacerbation of Crohn's disease.
What a virtual colonoscopy can show
Virtual colonoscopy is the same as computed tomography, but with a certain method of performing it, when the computer recreates an image of the colon in the form of a three-dimensional picture, similar to the image obtained with a colonoscope inserted inside. This procedure is non-invasive and is well tolerated by patients, who are more willing to undergo it than a classic colonoscopy.
Virtual colonoscopy allows a specialist to see on a computer monitor intestinal neoplasms with a diameter of more than 1 mm, erosions, inflammation and other changes, but with this method it is impossible to assess the color of the mucous membrane or take biopsy material. Therefore, virtual colonoscopy is indicated for patients with an already established diagnosis to determine the dynamics or rehabilitation control after surgery.
What is a colonoscopy?
A proctologist prescribes a colonoscopy in case of complaints about the gastrointestinal tract. This procedure plays an important role in determining the real cause of complaints, because the symptoms of many intestinal diseases are very similar.
Advantages and disadvantages
Pros of colonoscopy:
- the gastrointestinal tract can be examined more accurately, some inflammatory processes cannot be seen on CT;
- You can immediately remove polyps and cauterize ulcers.
Minuses:
- risk of bleeding;
- blood pressure may drop;
- Diarrhea may occur.
Contraindications
Colonoscopy is contraindicated if:
- acute gastrointestinal diseases, as well as colds;
- peritonitis;
- pulmonary and heart failure;
- ulcerative colitis;
- poor blood clotting;
- general poor condition of the patient.
CT and colonoscopy of the intestine have no general contraindications.
Possible limitations for the use of a particular diagnostic method
Colonoscopy is not performed in the following cases:
- peritonitis;
- intestinal perforation;
- massive intestinal bleeding;
- abdominal hernia;
- previous surgery on the pelvic organs and abdominal organs;
- heart and pulmonary failure.
In all these cases, a CT scan of the intestine can be performed, except in cases where the patient is in serious condition.
Computed tomography of the intestine is not performed:
- during pregnancy and while breastfeeding a child;
- in the presence of renal and liver failure;
- in patients with diabetes mellitus;
- with intolerance to iodine-based contrast agents;
- in the presence of severe obesity.
Almost all of these diseases and conditions, with the exception of pregnancy, are not contraindications for colonoscopy.
Thus, if there are contraindications for one examination method, you can always find an alternative diagnostic method.
Computed tomography has a number of limitations that relate to the volume and frequency of examination. The optimal interval between two procedures should be 12 months. If there are serious indications, the examination can be repeated no earlier than after 6 months. There are no such serious restrictions for performing a colonoscopy.
Indications and contraindications for virtual colonoscopy
This type of diagnostic examination has its own absolute indications:
- in case of intestinal bleeding to determine its location;
- to determine bulk intestinal tumors;
- to confirm the presence of an inflammatory process in the colon.
Virtual colonoscopy has become widespread as a screening (first, screening) study for patients over 50 years of age and those at risk for the possible development of colon cancer. This risk group includes the following categories of patients:
- regularly detecting blood in their own stool;
- close relatives suffering from colon polyps or malignant tumors in any part of the intestine.
It is recommended that such patients undergo a virtual colonoscopy once every 5 years.
Despite its apparent simplicity, this method of virtual research also has its contraindications, of which, in principle, there are not so many:
- pregnancy and lactation;
- obesity;
- history of perforation of any part of the large intestine.
Preparing for a virtual colonoscopy
Preparation for a virtual colonoscopy is identical to preparation for an examination of the large intestine according to the standard procedure.
- 3 days before the examination, you will need to adjust your diet by removing all foods that contain toxins, as well as those that provoke increased gas formation and an increase in the volume of feces.
- The day before the procedure, you can only eat liquid food, and the evening before and in the morning you should cleanse the intestines with enemas or using laxatives, for example, Fortrans.
- It is not recommended to take conventional laxatives, and 3 days before a virtual colonoscopy you should completely avoid drinking alcohol.
Which examination method to choose for certain diseases
Both procedures have important diagnostic value in medicine. Doctors often use them not as interchangeable procedures, but at different stages of the same disease or in the presence of different pathologies. The purpose of any of the studies depends on the suspected or specified disease.
CT is performed if:
- features of the intestine that do not allow colonoscopy (multiple adhesions, narrowings, large tumors);
- the need for a thorough study of the intestinal wall using contrast agents;
- suspicion of intestinal or abdominal tumors or the presence of metastases.
Colonoscopy is performed if there is:
- the need for a biopsy;
- inflammation of the colon;
- erosive or ulcerative colitis;
- polyps or intestinal tumor.
Patients' attitude
A negative attitude towards colonoscopy is most often associated with the presence of pain and various unpleasant sensations. Often patients categorically refuse the necessary manipulation due to fear of these sensations occurring. They occur due to intestinal features that prevent the free and painless passage of the colonoscope through the intestines (strictures, adhesions).
CT scan is painless. Unpleasant sensations may be present for some time. Therefore, it makes no sense to perform anesthesia during CT scanning. It is performed only on mentally ill people and pediatric patients, because they cannot remain motionless for a long time, which during the study can interfere with diagnosis.
During colonoscopy, sedation and anesthesia are performed quite often.
Which method is more reliable in making a diagnosis?
Colonoscopy is a method of examining the intestines using a special device (endoscope).
Colonoscopy allows you to visually assess the characteristics of the human intestinal mucosa, the presence of foci of inflammation or lesions, nodes and microcracks.
In addition to diagnostic criteria, there is another one that allows colonoscopy to be the most preferred method for various types of pathologies - the possibility of carrying out therapeutic manipulations directly during the procedure. The doctor may decide to remove the polyp, which will save the patient from future surgery. Using the coagulating properties of the endoscope, bleeding can be stopped. In this case, thermal coagulation is performed directly during the examination procedure.
In these cases, colonoscopy is the most productive diagnostic method. In some diseases, it is necessary to carry out high-quality diagnostic manipulations to evaluate the mucous membrane, because Without this, it is often not possible to make a correct diagnosis and prescribe adequate treatment. In such cases, colonoscopy is preferred.
The disadvantage of colonoscopy is that it is a rather unpleasant procedure and causes a number of painful and unpleasant sensations. Various methods of anesthesia and sedation may be used during this procedure, but doctors believe that the use of anesthesia may complicate the diagnostic process.
CT diagnostics cannot be called less informative, but in some respects it is inferior to colonoscopy. This lies in the fact that during CT diagnostics there is no direct contact with the intestinal mucosa. However, CT is the most informative method for suspected intestinal tumors.
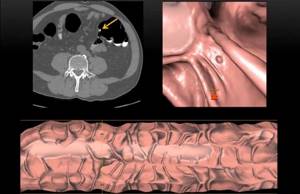
In addition, there are a number of advantages when using CT:
- good visualization of the tumor;
- intestinal stenosis is not an obstacle to the study;
- the ability to check the sections adjacent to the intestines;
- painlessness;
- can be carried out in cases where it is difficult or impossible to conduct a colonoscopic examination (weakened condition of the patient).
How is a CT scan performed?
Before the procedure, the patient will be asked to remove all metal objects and lie down on the CT scanner table. For CT colonography, the colon is filled with air. To do this, a thin tube is inserted into the anus through which air is supplied. This approach may cause discomfort, but air injection is necessary in order to straighten the intestinal walls and allow inspection of hard-to-reach areas. After this, the table smoothly moves into the scanner and the procedure is carried out. If the injection of air into the intestines leads to pain, you must inform the specialist who is performing the procedure.
Advantages and disadvantages of virtual colonoscopy
Virtual colonoscopy allows you to examine the condition of the colon over a length of one and a half meters with a minimum of radiation exposure to the body. This method has the following advantages:
- accurate assessment of the shape and location of all parts of the colon, the thickness of its walls and the condition of nearby tissues and lymph nodes;
- the ability to view the inner lining of the digestive tube;
- the process does not require serious manipulation in the internal structure of the body;
- examination of intestinal areas difficult to reach for standard colonoscopy is available;
- painlessness and excellent tolerability by patients of all age groups.
Like any other diagnostic method, virtual colonoscopy also has its disadvantages, namely:
- it is not possible to detect intestinal tumors that are less than 5 mm;
- Diagnosis of squamous cell intestinal cancer is difficult;
- impossibility of taking biopsy material or excision of benign neoplasms discovered during the study;
- not suitable for examining patients in whom the development of an oncological process is suspected.
The presence of these disadvantages does not allow virtual colonoscopy to completely replace the standard invasive endoscopic procedure!