Article for the “bio/mol/text” competition: When a misfortune occurs in the body, and out of 100 trillion normal cells at least one degenerates into cancer and is not destroyed, a trigger is triggered and tumor growth begins. Gradually it adapts the surrounding cells to itself, and also has a significant effect on the entire body. As the disease progresses, some cancer cells leave the tumor and form metastases—secondary foci of tumor growth. Often, timely removal of the primary tumor and postoperative therapy are not able to induce remission. It turns out that the primary tumor is capable of “educating” the microenvironment in the foci for the development of future metastases already in the early stages of its growth. In addition, metastatic cancer cells reprogram the expression of their genes so that they can better take root in their new habitat. Knowing how to prevent these processes, not just the growth of the primary tumor, could save up to 90% of people who die from major cancers.
What are metastases?
Cancer metastases are secondary lesions that appear at a certain distance from the primary tumor. For each type of cancer, there are “favorite” organs for metastasis. In most cases, the liver, lungs, peritoneum, bones, and adrenal glands are affected.
Modern concepts of the development of metastases are based on the fact that metastases develop almost immediately as soon as the malignant tumor itself appears. Individual cells detached from it first penetrate the lumen of the blood (hematogenous dissemination path) or lymphatic (lymphogenous dissemination path) vessel, and then are transported with the blood or lymph flow, stop at a new place, leave the vessel and grow, forming metastases. At first, this process is slow and imperceptible, since cancer cells from the maternal lesion suppress the activity of secondary lesions.
From the moment when secondary foci appear, the cancer is called metastatic. The process of cancer cells spreading is called metastasis.
The ability to metastasize is one of the key features of malignant tumors, which distinguishes them from benign neoplasms.
Diagnosis of kidney cancer
Patent for invention. A method for determining the optimal installation sites for manipulation trocars during laparoscopic operations on organs of the retroperitoneal space “Hand suture in endoscopic surgery”, K. V. Puchkov, D. S. Rodichenko
The latent course of the disease makes early diagnosis of a kidney tumor difficult, but as experience shows, even a late diagnosis allows one to count on a favorable outcome. I can guarantee to help you diagnose a kidney tumor and develop an optimal surgical treatment program.
Why is cancer suspected?
Diagnosis of kidney cancer is possible in different ways, they are used in combination. Radiological diagnosis of kidney cancer is preceded by a detailed examination with palpation, general and biochemical blood tests, cytological examination, and urinalysis. Increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate, enzyme disruptions, anemia, and increased levels of certain hormones, such as insulin and hCG, may be signs of kidney cancer. Based on the results of the examination, medical history and blood tests, the doctor decides on the next steps.
Methods for diagnosing kidney tumors:
- Ultrasound
- CT
- MRI
- X-ray
- Intravenous excretory pyelography
The first stage is an ultrasound examination of the kidneys and abdominal organs; it shows the outline of the kidney and allows preliminary conclusions to be drawn about what is happening to the tissue: is there necrosis, etc. In the differential diagnosis of kidney cancer or cyst, renal angiography is necessary. CT and MRI with contrast will show a detailed picture: the exact size of the tumor, where and how much it has grown, whether there are metastases in the lymph nodes or not, the level of damage to the veins, etc.
What causes metastases?
Will individual cells break away from the mother tumor and form metastases? Tumor cells are coming off and will always come off. Local factors of the immune system protect the body from the rapid growth of tumor cells for a very long time. The only question is the likelihood of metastases, and it depends on the type of tumor, its growth rate, the degree of cell differentiation (how different they are from normal), the stage at which the cancer was diagnosed, and other factors.
Having spread, tumor cells can remain inactive for a long time, over a number of years, or grow very slowly. The exact mechanisms that trigger the rapid growth of metastases in the body have not been studied.
Another fact is important: as the number of cells in the metastasis increases, they begin to secrete special substances - growth factors. These growth factors stimulate the formation of a capillary network, which provides cancer cells with all the nutrients to the detriment of other body tissues.
There are several stages in the spread of cancer throughout the body:
- Penetration of tumor cells into the nearest blood or lymphatic vessel;
- Distribution through blood or lymph flow to various parts of the body;
- Then the cancer cell stops in one of the small vessels and penetrates through its wall into the tissue;
- For some time it is inactive or reproduces, but very slowly;
- Rapid growth, expansion of the capillary network.
Many tumor cells die at one of these stages. Those that manage to survive give rise to metastases.
Causes of metastasis to lymph nodes
The mechanisms of metastases are not completely clear. It is known that in this process the activation of the ability of malignant cells to migrate and the structural restructuring of the blood and lymphatic vessels that feed and surround the tumor play a role - they lack a basement membrane and pericytes. Some capillaries are even formed directly by tumor cells. Thus, malignant cells enter the lymphatic vessels and reach the nearest lymph nodes through them.
The ability of cancer to metastasize is determined by several factors:
- The degree of malignancy of the cancer. The less differentiated the tumor cells, the more aggressive it is and the earlier it begins to metastasize.
- Histological type of tumor. Most often, carcinomas, malignant neoplasms originating from epithelial tissue, metastasize through the lymphogenous route.
- Patient's age. In young people, metastases from the same tumors appear, on average, earlier than in older people. This is associated with the characteristics of blood circulation and the activity of the immune system.
The process of metastasis can be accelerated by thermal procedures and physiotherapy on the area where the tumor is localized, as well as non-compliance with the rules of ablastics when removing the tumor. The last point is very important in the surgical treatment of cancer, therefore oncological operations should be performed in specialized hospitals, which have certain conditions for carrying out such interventions and qualified personnel.
What determines the rate of spread of metastases throughout the body?
The time required for the clinical manifestation of the first metastases is largely determined by the type of tumor and the degree of differentiation of its tissues.
- Highly differentiated tumors, as a rule, metastasize much less frequently and later than poorly differentiated tumors.
- In poorly differentiated tumors, cells practically lose the features of normal tissue. This cancer behaves more aggressively.
Sometimes metastases appear very quickly, following the appearance of the primary tumor node. In many patients, metastases are detected after 1–2 years. Sometimes latent or “dormant metastases” are discovered many years after surgical removal of the tumor.
The likelihood of metastasis can be reduced using various treatment methods:
- Chemotherapy. For example, adjuvant chemotherapy is given after surgery and helps destroy any cancer cells that may remain in the body.
- Radiation therapy.
Can metastases occur because the doctor “damaged” the tumor during surgery or biopsy?
There is a misconception that metastases occur due to the procedure performed. However, removing part of the tumor or biopsy (taking tumor tissue for examination) does not increase the incidence of metastases.
Could a mistake happen?
Oncological tumors are always determined by ultrasound. An error may occur if the doctor has not prescribed additional procedures to help confirm the presence of pathology.
Ultrasound helps to distinguish benign from malignant tumors, so the probability of error tends to zero.
If a person is obese, it is better to use other diagnostic methods. Due to the thick fat layer, ultrasound sensors are not always able to detect and distinguish cancerous tumors. In such cases, diagnosis is made using MRI.
How do different types of cancer metastasize?
Most often, metastases are found in the lymph nodes, liver, lungs, and much less often in the heart muscle, skeletal muscles, skin, spleen, and pancreas. The central nervous system, skeletal system, kidneys, and adrenal glands occupy an intermediate place in the frequency of detection of metastases in various types of cancer.
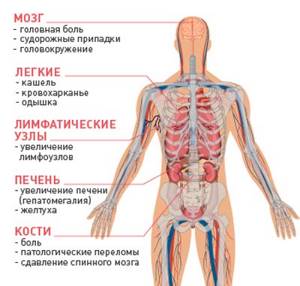
Some tumors have favorite sites for metastasis. Such metastases have their own “names” - special terms:
- Krukenberg metastasis - to the ovaries;
- Metastasis of Sister Mary Joseph - to the navel;
- Virchow's metastasis - to the lymph nodes above the left collarbone.
Common types of cancer and typical sites for metastases
- Breast cancer: lungs, liver, bones.
- Ovarian cancer: peritoneum, liver, lungs.
- Stomach cancer: liver, peritoneum, lungs.
- Intestinal (colon) cancer: liver, peritoneum, lungs.
- Rectal cancer: liver, lungs, adrenal glands.
- Prostate cancer: bones, lungs, liver.
- Uterine cancer: liver, lungs, peritoneum.
- Kidney cancer: lungs, liver, bones.
- Lung cancer: adrenal glands, liver, second lung.
- Melanoma: lungs, skin/muscle tissue, liver.
- Pancreatic cancer: liver, lungs, peritoneum.
- Thyroid cancer: lungs, liver, bones.
Metastases are always named after the primary tumor. For example, if lung cancer has spread to the adrenal glands, the tumor in the adrenal glands is called “metastatic lung cancer.” However, at the molecular genetic level, metastases may differ from the maternal tumor. This phenomenon is called heterogeneity.
Get cost and treatment plan
Why are metastases dangerous?
Metastasis, as a rule, occurs in cases when the body's reserves in the fight against the tumor are exhausted. Metastases significantly disrupt the functioning of all vital organs and systems. The vast majority of deaths in cancer patients are caused by metastases.
In addition, metastases significantly worsen the general condition, often accompanied by unbearable pain requiring constant pain relief.
Complications of metastatic liver cancer
The most common complication of secondary tumor foci in the liver tissue is the growth of the tumor into the gallbladder and biliary tract, which manifests itself:
- pain in the upper and right parts of the abdomen, which is dull and constant;
- increased formation of gases in the intestines;
- a slight increase in body temperature, which stubbornly remains at the same level;
- appetite disturbances and weight loss;
- nausea and sometimes vomiting that does not bring relief;
- icteric coloration of the skin and whites of the eyes;
- increased sweating, especially at night.
How do metastases appear?
The clinical picture of metastatic cancer is determined by the location of the metastases:
- Damage to the peritoneum (peritoneal carcinomatosis) leads to ascites, which requires laparocentesis;
- Damage to the pleura (pleural carcinomatosis) causes the development of exudative pleurisy, which requires thoracentesis;
- Damage to the bones and spine leads to pain in different parts of the body, fractures;
- Lung damage manifests itself as shortness of breath;
- Brain metastases lead to headaches, dizziness, convulsions, and impaired consciousness;
- Liver damage leads to obstructive jaundice.
In addition, toxins released during the constant death of tumor cells cause cancer intoxication of the body.
New treatments
Radiofrequency ablation
Modern surgery allows this method to be used for metastatic liver disease. A source (electrode) of high-frequency radiation is brought through the skin and muscles to the tumor node. The accuracy of the electrode location is controlled by electroanatomical mapping. Radiation directly affects the metastasis and destroys tumor cells. At the same time, the impact on surrounding tissues and the risk of bleeding are minimal. The procedure can also be performed under local anesthesia.
Chemoembolization of tumor
Used when ablation is contraindicated. Having provided access to the vessels feeding the tumor, a chemotherapy drug is injected into them through a needle. This substance “solders” the walls of the arteries, blood stops flowing through the vessels into the metastasis, and without nutrition the tumor node dies. Aseptic necrosis and death occurs.
Targeted therapy with biologics
Specific drugs obtained as a result of high-tech synthesis (Sorafenib, in particular) selectively act specifically on cancer cells. Substances toxic to tumor cells accumulate in them and prevent further growth of cancerous foci. The method is used in complex therapy, as an addition to other treatment methods, in the presence of contraindications to radical treatment.
How are metastases diagnosed?
Plain radiography, ultrasound, radioisotope research, computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, positron emission tomography - all these techniques are essential in recognizing metastases. These techniques make it possible to clarify the size, prevalence and growth pattern of metastases, their disintegration, suppuration, and germination into neighboring organs and tissues. In addition, these same diagnostic techniques make it possible to monitor the effectiveness of treatment based on the degree of regression of metastases.
Conventionally, two stages of diagnosing metastases can be distinguished:
- Primary examination, when the main tumor is only diagnosed;
- Follow-up with an oncologist after treatment. If no metastases were initially detected, and the treatment was successful, you will still have to undergo periodic examinations in the future - there is a risk of relapse.
The main ways of growth of metastases
- Through blood vessels (hematogenous route)
- Through lymphatic vessels (lymphogenous pathway)
The most vulnerable are the liver, lungs, brain, bone marrow, and bones of the axial skeleton. The main target organs are the pelvic and retroperitoneal lymph nodes, iliac lymph nodes, and less commonly the central nervous system organs.
Is it possible to cure metastases, and what does it give?
The main goal of active chemotherapy and radiation therapy is to prevent the occurrence of cancer metastases at the earliest possible stage. Treatment is based on the general principles of tumor treatment, including chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and surgical treatment (for single metastases).

Treatment of cancer metastases has certain difficulties. Therefore, in some cases, we treat metastases in order to relieve symptoms and prolong life. We use systemic therapy (chemotherapy, hormone therapy, targeted therapy), and local treatments (surgery, radiotherapy). Treatment inhibits tumor growth, reduces its size, and slows down the process of metastasis. This helps give the patient extra months, and sometimes years.
At the same time, maintenance therapy is carried out to help cope with the symptoms and side effects of chemotherapy. For pain, strong painkillers are prescribed.
Abroad, percutaneous transhepatic radiofrequency ablation is often used for metastatic foci in the liver. This technique is available to patients of the Euroonco clinic in Moscow.
As mentioned above, treatment in such cases is a means of alleviating the patient’s condition. The likelihood of achieving remission is very low.
At Euroonco in Moscow, we also use a technique such as embolization of arteries that feed large metastases in various organs.
Learn about modern methods of treating cancer metastases in the liver, which are used by Euroonco doctors, as well as about the results of treatment - patient stories.
When is it necessary to do a liver biopsy for cancer?
A puncture biopsy allows for histological examination of cells from a suspicious area. Determine the type of cancer tumor and the degree of its differentiation. The results can directly affect the volume of subsequent surgery and treatment tactics.
Biopsy in many cases is a necessary diagnostic method. Through a puncture of the skin and muscles, under instrumental visual control, a sample of the metastatic tumor is obtained. The sample is a column of tissue caught in a puncture needle with a diameter of up to 6 mm. The biopsy is sent to the laboratory for examination.
This mini-operation (biopsy) is the final (BUT NOT ALWAYS MANDATORY) stage in the examination of a patient with a suspected oncological process in the liver.
For which patients with metastasis of malignant cells is a liver biopsy indicated?
- if there is a nodular formation in the organ, and other diagnostic methods cannot confirm/refute the oncological diagnosis;
- with a small node (up to 2 cm in diameter), but with cancer-specific blood flow in the tumor;
- with a large formation (more than 2 cm) without obvious signs of malignant vascularization (blood supply);
- if there are inconsistencies in previous tests and MRI (for example, a patient has a normal level of alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) in the blood but there is a tumor on contrast-enhanced MRI images);
- for any neoplasm (tumor) in the liver without concomitant cirrhosis.
Photo: liver metastases on T2-weighted axial MRI.
Where is it better to treat cancer with metastases - in Russia, Israel or Germany?
In order to receive the most modern and effective treatment for cancer with metastases, a Russian patient does not have to go abroad. Euroonco clinics use the same drugs and technologies as the leading cancer centers in the world.
Even if the likelihood of remission is low, treatment should be continued. Our doctors know how to alleviate the patient’s suffering and prolong life. To do this, we use the most modern techniques and drugs. If you are undergoing treatment at another clinic, you can always get a second medical opinion from us: sometimes the approaches of different doctors to the treatment of metastatic cancer differ greatly.
| More information about treatment at Euroonco: | |
| Oncologist consultation | from 5100 rub. |
| Emergency oncology care | from 11000 rub. |
| Chemotherapy appointment | 6900 rub. |
| Palliative care in Moscow | from 40200 per day |
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78
Prognosis for kidney cancer
There is no exact prognosis for survival; it highly depends on concomitant factors: other diseases, the environment, the size and shape of the tumor, and the psychological state of the patient. The most important thing is timely, qualified medical care, which you can receive at our medical center.
What are the numbers?
90% of kidney cancers detected at the first stage are curable. Survival of a patient with stage 4 cancer with metastases is usually less than 1 year.
The chance of surviving 5 years after diagnosis in the first and second stages is 76% and 54%, respectively, in the third stage it is already 42%, in the fourth stage it is about 10%.
What happens if you don't have surgery?
If you do not undergo surgery for early stages of kidney cancer, the survival prognosis will be disappointing. This aggressive form of cancer is removed surgically. Other treatment methods are used to maintain the condition of an already doomed patient and alleviate his symptoms.
What is the most important thing if you are suspected of having kidney cancer?
Medicine does not stand still; new ways to combat kidney cancer at different stages are emerging. Our breast-conserving laparoscopic techniques are among the most advanced in this field. How long you will live after kidney cancer depends on your body and how wisely you choose your doctor. Contact our clinic and we will help you survive this disease.
Assessing the risk of lymph node metastasis
| Risk group | PC stage | PSA, ng/ml | Sum of Gleason scores | Probability of metastasis to lymph nodes | Relapse-free survival for 10 years |
| Short. All factors | T1–T2a | < 10 | 2 — 6 | < 5 % | 70 – 90 % |
| Intermediate. one of the factors | T2b–T2c | 10 — 20 | 7 | 5 – 15 % | 60 – 75 % |
| High one of the factors | T3a | > 20 | 8 — 10 | 16 – 49 % | 43 – 60 % |
Treatment of advanced prostate cancer
Most patients choose radical treatment methods in situations where the cancer is potentially curable, and surgery offers hope of maintaining the usual quality of life. If we are talking about a tumor that has already extended beyond the prostate capsule, radical prostatectomy can be performed as one of the stages of complex (multimodal) treatment. Surgeons at the European Prostate Center in Gronau adhere to this tactic in all cases where the patient’s health condition allows for surgery and prolongation of life expectancy.
Radical prostatectomy + lymphadenectomy In the presence of an oncological process that has spread to the organs surrounding the prostate, patients at high risk (stage ≥T3a, Gleason score 8-10, PSA >20 ng/ml) may be offered robot-assisted radical prostatectomy prostatectomy (RP) combined with lymphadenectomy (removal of affected lymph nodes). At the European Prostate Center in Gronau, both operations are performed simultaneously using the da Vinci robotic system.
Features of the operation at stage T3a:
- Refusal of nerve-saving techniques, removal of neurovascular bundles (preserving potency at this stage is not a priority goal when performing the operation);
- Extensive removal of tissue outside the gland capsule that is affected by the tumor;
- Removal of lymph nodes - external, obturator, internal and common iliac.
Even with an increased volume of intervention, the precision of Da Vinci robot-assisted prostatectomy allows minimizing injuries to the proximal urethral sphincter, as well as the bladder neck. For the patient, this means that the rehabilitation process will be easier, and the natural function of urinary continence will be restored faster.
Radiation therapy Indications for radiation therapy after RP surgery are:
- Positive surgical margin;
- Disease stage T3a -T3b;
- Gleason score 8 – 10 points.
As an alternative, at stage T3a - T4N0M0 patients with a life expectancy of more than 10 years may be recommended conformal radiation therapy with dose escalation using the IMRT technique (effective dose ≥70 Gy).
Like radical prostatectomy, radiation therapy is used as one component of combination treatment. The option of combining radiation and hormonal therapy is considered more effective than each of them separately. Combined treatment significantly improves the quality and life expectancy of the third and fourth stages of the prostate in the presence of metastases.
Symptoms that should cause concern
- Urinary tract obstruction and difficulty urinating indicate compression of the bladder neck due to a large volume or tumor growth;
- Blood in the urine and episodes of urinary incontinence occur when a tumor grows into the neck of the bladder;
- Erectile dysfunction may indicate that the tumor has affected the neurovascular bundles;
- Discomfort when sitting and pain in the perineum are felt when the pelvic floor muscles are affected;
- Swelling of the legs or groin area, lymphostasis are signs of damage to the pelvic lymph nodes.
If you notice one or more of these symptoms, you should immediately consult a doctor. Prostate cancer with metastases in nearby organs (locally advanced) responds quite well to complex treatment. The first choice methods are radical robot-assisted prostatectomy with removal of the seminal vesicles and pelvic lymph nodes (lymphadenectomy) or external beam radiation therapy. Surgery reduces the risk of tumor recurrence and metastases in the future. To enhance the effect, patients who are at intermediate and high risk are additionally prescribed a course of radiation therapy or hormonal treatment.