General blood tests
08/07/201801/25/2019 Yulia Martynovich (Peshkova) 3235 Views hemoglobin, general tests
This time we will analyze low hemoglobin, all the reasons and consequences of such an analysis result. Without a sufficient amount of hemoglobin, a complete supply of oxygen to the tissues in a woman’s body is impossible. Monitoring its level is important for timely detection of the development of various anemias, chronic bleeding (ulcerative, hemorrhoidal, etc.), helminthic infestations, etc.
It is important to understand what the hemoglobin norm is in different age categories of women, what its deviation indicates, and how to deal with it.
- 1 What does hemoglobin show in the blood?
- 2 What is the name of the hemoglobin test?
- 3 Signs of low hemoglobin in women
- 4 What is the norm for women?
- 5 Low hemoglobin - causes and consequences in women 5.1 Blood anemia
- 5.2 Synthesis of mutant forms of Hb
- 5.3 Other reasons
What does hemoglobin show in the blood?
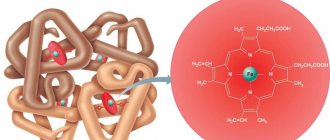
Hemoglobin (Hb) is a two-component protein found in red blood cells. It consists of a peptide part and an iron-containing heme. The molecular weight of the protein reaches 66.5 kDa. English biochemist M.F. Perutz was awarded the Nobel Prize in 1962 for his contributions to the study of the structure and functional features of Hb.
The protein is able to bind with oxygen, delivering it from the lungs to all cellular and organ structures. Transport algorithm: excess molecular oxygen in the small capillaries of the alveoli binds to hemoglobin. Together with the systemic bloodstream, the complex is carried to organs and tissues with oxygen deficiency. Upon reaching them, oxygen is split off from the complex and enters into biochemical oxidation reactions.
Protein is also known to form a complex with carbon monoxide. Unlike the connection with molecular oxygen, the connection with it is 250 times stronger. The resulting stable complex is called carboxyhemoglobin. However, this reaction is not completely irreversible. A small amount of carbon monoxide is displaced from the complex by the increased partial pressure of molecular oxygen in the lung tissues. In parallel with this, oxygen transport in the human body is blocked.
As a result, severe oxygen starvation develops in organs and tissues. If timely assistance is not provided, carbon monoxide poisoning can be fatal.
Read further: What is hemoglobin in the blood, its types, about analysis, alcohol and much more
What is the hemoglobin test called?
Determining the level of hemoglobin is necessary for the primary diagnosis of a person’s health status, primarily the hematopoietic system. The study is carried out as part of a routine laboratory blood test. A decrease in hemoglobin indicates the development of pathological reactions in the body and requires extensive diagnostics.
The analysis is carried out using the sodium lauryl sulfate method in combination with the capillary photometry method. Venous blood serum is used as a biomaterial. The waiting time for receiving results ranges from several hours to 1 day, depending on the workload of the laboratory department.
A glycated hemoglobin test is mandatory for women with a history of diabetes. The peculiarity of the analysis is that it reflects the glucose level 2 or 3 months before blood collection. Therefore, the technique is used to track the level of simple carbohydrates over time, and not at the time of blood collection. The analysis plays an important role in monitoring the effectiveness of diabetes treatment.
If a patient has low hemoglobin in a routine blood test, she is additionally prescribed a test for haptohemoglobin levels. It is important to exclude the fact of intravascular hemolysis (decomposition of red blood cells), and if it is detected, determine the severity and select appropriate treatment. In addition, it is advisable to carry out the study to diagnose liver pathologies, anemia and oncological diseases of the hematopoietic organs.
In order to implement laboratory analysis, the immunoturbidimetry method is used, the execution time is no more than 1 day.
Additionally, determination of the level of ferritin, serum iron and folic acid in the blood may be indicated.
Treatment of low hemoglobin with traditional recipes
- You need to take 200 g of walnuts, 200 g of buckwheat, chop and mix with dark honey (1 tablespoon). The finished mixture is drunk on an empty stomach, after 30 minutes you are allowed to have breakfast.
- Chop dried apricots, raisins and walnuts into 1 tbsp. Add a spoonful of the resulting mixture to the same amount of honey and eat before each meal.
- Grind prunes, raisins, dried apricots and walnuts and mix in equal proportions to ultimately form a glass. Using a blender or food processor, grind the whole lemon with zest and add the dried fruit mixture. At the end add 3 tbsp. spoons of honey. You need to use the product three times a day, one teaspoon.
- Mix 100 ml of carrot and beet juice, drink on an empty stomach every morning.
- Mix freshly squeezed apple or cranberry juice with 50 ml of beet juice. Use daily.
- Mix 100 ml of boiled milk and 100 ml of carrot juice and drink until the hemoglobin level returns to normal.
- 3 tbsp. Pour 100 ml of boiling water over spoons of dried rowan and rosehip fruits and let it brew for about 15 minutes. The infusion should be consumed every day on an empty stomach.
- Grind the buckwheat in a food processor or coffee grinder, pour in 200 ml of kefir and leave to brew overnight. The result is swollen porridge, which must be consumed instead of breakfast.
- Make an infusion of dried red clover. Pour boiling water over the mixture and let it brew (about 50 minutes). You need to drink 2 tbsp of medicine. spoons before breakfast, lunch and dinner.
- Pour boiling water over a mixture of dried nettle leaves, yarrow flowers, and dandelion root and leave for several hours. You need to drink the product four times a day, 15 minutes before meals. The course of treatment is about 2 months.
- Pour 300 g of garlic into a liter of alcohol and leave for 30 days, shaking occasionally. Take the resulting hot tincture 1 teaspoon three times a day with a glass of milk.
We recommend
“How to prevent stroke using folk and medical means” Read more
Signs of low hemoglobin in women
Signs of low hemoglobin levels in women are as follows:
- decreased performance, general weakness;
- rapid fatigue;
- increased desire to sleep and dizziness;
- frequent headaches;
- tachyarrhythmias;
- pale and yellow skin;
- desire to eat chalk, earth, etc.;
- changes in blood pressure;
- heart rhythm disturbance;
- fainting conditions;
- muscle pain;
- impaired sense of smell;
- hair loss.
With low hemoglobin and a deficiency of iron ions in a woman’s body, dry skin, cracks in the corners of the lips, and increased brittleness of hair and nails may be observed.
If a woman notices the above symptoms of hemoglobin deficiency, she should consult a doctor.
Any specialist can send you for a blood test to check your hemoglobin level.
Why do hemoglobin levels decrease in older people?
Anemia or low hemoglobin (less than 110 g/l) in older people, especially those over 60, is diagnosed in 50% of cases. Previously, it was believed that this was due to inevitable age-related changes in the body, but today this hypothesis is a thing of the past. Doctors were able to find out that even in old age, blood does not lose its properties and continues to work, as in youth. That is why, with low hemoglobin in elderly women and men, the causes should be identified and treatment prescribed individually.
What could cause this situation? It is noteworthy that anemia most often occurs in men. But the occurrence of low hemoglobin is not associated with gender. The source of the problem lies in the presence of various concomitant or chronic diseases. The causes of anemia can be heart disease, chronic infections, tumors, malfunctions of the endocrine or autoimmune system. Among other things, it happens that long-term illnesses become the culprits of low levels of complex iron-containing proteins, and this, in turn, provokes the worsening of a particular illness.

An insufficient amount of iron entering the body or its loss can cause the development of anemia due to a deficiency of this element. The main provoking factors for this failure, as a rule, are poor nutrition and chronic diseases, accompanied by regular bleeding. These include Crohn's disease, intestinal diverticulitis, ulcerative colitis, gastric and duodenal ulcers, and various tumors.
Also, low hemoglobin levels in older people can develop due to a deficiency of folic acid and vitamin B12. In the case of anemia, this is determined by the following signs:
- Paleness of the skin.
- Rapid breathing and pulse.
- Fast fatiguability.
- Frequent headaches.
- Regular dizziness.
- Noise in ears.
- Spots, floaters in the eyes.
- Muscle weakness.
- Absent-mindedness, decreased concentration.
- Irritability.
- Lethargy.
- Slight increase in temperature.
It happens that low levels of iron are already present in the body, but this is not yet reflected in the test results. In this case, you need to pay attention to the following symptoms:
- Dry skin appears.
- Strange gastronomic preferences arise.
- Painful cracks form in the corners of the mouth.
- Nails become brittle, pale with longitudinal grooves.
- Hair breaks and thins, possibly even baldness.
- A burning sensation begins, pain in the tongue and its smoothing.
The lower the hemoglobin levels in older people, the more pronounced the symptoms described above. If the deficiency of this blood component approaches critical levels, a person may experience neurological disorders: consciousness becomes confused, fainting occurs, mucous membranes and skin become very pale.
If there is a slight decrease in hemoglobin levels, then symptoms may not appear at all. The usual accompanying symptoms - lethargy and dizziness - are attributed to other diseases. But you can’t trigger anemia. At the slightest suspicion, all blood tests must be taken. Based on their results, the doctor will determine the degree of progression of anemia and its type. When making a diagnosis, the doctor must take into account the chronic diseases of the elderly person. Only after obtaining a complete history can treatment begin.
If diagnosis and therapy are timely, it will not be difficult to cope with anemia with the help of medications. Low hemoglobin in older people will begin to rise very quickly, and their health will begin to improve.
In case of advanced anemia, the patient is at risk of developing chronic iron deficiency, the main symptoms of which are fainting, confusion, lethargy and dizziness. The skin of an elderly person begins to dry out and crack, turn pale and peel. The complex of these symptoms is medically called typical anemic syndrome.
There are several stages of anemia, the most severe of which is the third. Very low hemoglobin in older people provokes tremors, muscle atony, sudden changes in pressure, bradycardia, tachycardia and regular fainting. Advanced low hemoglobin in an elderly person can cause oxygen starvation of the brain, which threatens the development of Alzheimer's disease.
The causes and consequences of low hemoglobin differ little in both older people and young people or representatives of the middle age category. The problem is that pensioners suffer more severely from this disease, and anemia very quickly turns into chronic anemia. And if the patient’s age is above 65 years, then the chances of developing this pathology are even higher.
In addition, in older women with low hemoglobin levels, the risk of tumors of the reproductive system increases several times. In older men, iron deficiency can cause early dementia (dementia).
As already mentioned, low hemoglobin is more common in older men (especially those over 65). They are recommended to get tested at least once every three months, even in the absence of obvious signs.
We recommend
“Pneumonia in old age: diagnosis and treatment methods” Read more
What is the norm for women?
Normal hemoglobin values should be determined taking into account the woman’s age, as well as the stage of the menstrual cycle or pregnancy.
For girls in adolescence (from 12 to 15 years), permissible Hb values are in the range of 110 – 155 g/l.
After puberty (from 15 to 19 years), the normal values increase: 119 – 157 g/l.
Then, at the age of adolescence and before maturity (from 19 to 45 years), normal values for women have equal values: 117 – 159 g/l.
During the period of preparation of a woman’s body for menopause and after it (from 45 to 65 years), the range of normal hemoglobin values is 120 – 165 g/l.
The normal hemoglobin level in elderly women (after 65 years) is considered to be 119 – 165 g/l.
It should be emphasized that the value of the indicator under consideration decreases slightly during menstruation. At the same time, normally, the hemoglobin level does not fall below the lower limit of normal.
If you have prolonged and excessively heavy menstruation, as well as inter-cycle bleeding, you should consult a gynecologist.
During pregnancy, hormonal and biochemical changes are aimed at providing the baby developing in the womb with nutrients and oxygen. During this period, a woman’s blood volume increases, but the number of red blood cells remains the same. Therefore, low hemoglobin in women during pregnancy is a variant of the physiological norm. The rate can be reduced to 110 g/l.
To prevent hemoglobin deficiency, experts recommend taking iron-containing medications when planning pregnancy. Also iron supplements, folic acid, etc. (as part of multivitamin complexes) are prescribed during pregnancy.
Normal hemoglobin levels in the elderly
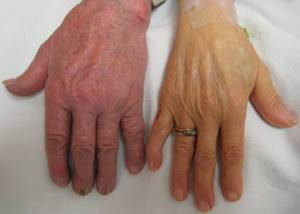
The blood composition of a healthy person must comply with established medical standards. This also applies to the content of complex iron-containing proteins (hemoglobin). In one liter of a man’s blood, the level of these complex proteins should be about 130–160 g. For women, the norm is 20–30 units less. If this figure drops to 110 g/liter of blood, the development of anemia is possible.
What does low hemoglobin in the blood indicate in elderly patients? Just like that, without the influence of external factors, the hemoglobin level does not drop. This usually happens for two reasons: either the body does not produce enough of it, or it uses too much.
Hemoglobin synthesis occurs due to foods rich in vitamin B, iron, and amino acids. If the body does not receive enough of the necessary microelements and vitamins due to a monotonous and unhealthy diet, a person begins to have problems with blood formation.
Another reason for low hemoglobin levels in older people is a malfunction of the producing organs. Insufficient iron reserves in the body can be caused by frequent or heavy internal bleeding. For example, gynecological bleeding is one of the reasons why there is low hemoglobin in older women.
The composition of hemoglobin in pensioners, adults, children, fetuses and embryos has significant differences. In modern medicine, there are two concepts of hemoglobin level: normal and pathological. Both of these types have differences, both in composition and in functions.
It is not enough to simply detect and diagnose low hemoglobin levels in the blood; it is important to find the reason for its decrease. Without testing, you can improve your performance on your own, for example, by taking additional medications, but this will only give a temporary result. There are some situations where hemoglobin levels may become low. For example:
- Regular blood loss occurs, for example, in donors or with frequent bleeding.
- A person eats poorly or monotonously.
- For severe infections or enteritis in the chronic stage.
- With a fairly strict vegetarian diet.
- With regular consumption of alcoholic beverages in large doses.
- An elderly patient has been on a drip for a long time.
If hemoglobin is low, older people must be provided with good nutrition. Convinced vegetarians, if their health deteriorates in such a situation, should reconsider their gastronomic principles. Plant foods have a low iron content - only 5%, but fish and meat products contain six times more iron.
If an elderly person exhibits external signs of low hemoglobin for no apparent reason, he should urgently seek advice from his doctor and undergo an examination.

Recommended articles on this topic:
- Boarding home for the elderly: features and rules of choice
- Low blood pressure in older people: causes, symptoms and treatment
- Health of the elderly: old age is not a problem
Low hemoglobin – causes and consequences in women
There are 2 main reasons for low hemoglobin in women:
- direct reduction of iron-containing protein in the blood;
- decreased ability of Hb to form a complex with molecular oxygen.
Let's take a closer look at each of them.
Blood anemia
Blood anemia is the reason why hemoglobin concentration decreases. As a rule, it is accompanied by a combined decrease in the number of red blood cells and a violation of their chemical structure.
It should be emphasized that anemia is not an independent pathology, but a symptom or consequence of a disease. There is a decrease in the woman’s respiratory activity, and in the extreme form, oxygen starvation develops.
Anemia develops as a result of:
- failure in the process of formation and differentiation of blood cells, in particular red blood cells. As a rule, this occurs with a deficiency of iron, folic acid or B vitamins, as well as with bone marrow cancer;
- excessive loss of blood, and with it red blood cells. The condition is typical for chronic bleeding, heavy menstruation, injury, fractures or surgery;
- disturbances in the absorption of nutrients in the intestines;
- gastric resection;
- chronic gastrointestinal pathologies; infectious pathologies;
- helminthic and parasitic infestations;
- abnormal increase in the process of destruction of red blood cells. In the blood of a healthy woman, red blood cells live and function for up to 4 months. For genetic abnormalities, infectious pathologies, intoxications, etc. the lifespan of blood cells decreases.
The prognosis of outcome largely depends on the cause of anemia and the severity of the disease. With successful compensation of the iron deficiency state, the patient’s complete recovery without the development of complications is noted. In other forms, the prognosis is less favorable.
Synthesis of mutant forms of Hb
The second reason why hemoglobin cannot fully bind to molecular oxygen is due to the synthesis of mutant forms of Hb. For example, hemoglobin C and S.
Despite the fact that hemoglobin C is a mutant form, it can increase human survival when infected with malaria. The distribution of this form is typical for Ghana, central Africa, India and southern China.
Hemoglobin S is produced in people with the hereditary disease sickle cell anemia. Its peculiarity is the altered morphology of red blood cells, due to which people are immune to malaria. Mutant hemoglobin does not dissolve in the cytoplasm, but crystallizes. It breaks down faster than regular Hb and is less capable of transporting molecular oxygen. The lifespan of red blood cells in people with sickle cell anemia is shorter than in those without.
Other reasons
If the above two reasons are excluded, the patient should be checked for the presence of the following pathologies:
- chronic bleeding of internal organs (gastric and duodenal ulcers, hemorrhoidal bleeding);
- diseases of the hematopoietic organs;
- renal failure.
In addition, the low value of the laboratory indicator in question is typical for people with nutritional deficiency and undergoing chemotherapy.
Read further: About the norm and deviations of hemoglobin in pregnant women by trimester
How to normalize low hemoglobin in older people
There are several types of the disease:
1. IDA - iron deficiency anemia.
This type of disease occurs most often in older people. If IDA develops in the body, then the following is observed in the blood test:
- Her "blanching".
- Hypochromia and microcytosis of erythrocytes.
- Reduced serum iron concentration.
- An increase in the iron-binding capacity of blood serum (iron deficiency level) and a decrease in the level of ferritin in the blood.
The easiest way to determine IDA in older people against the background of low hemoglobin is to look at the color indicators of the blood. The optimal value is from 0.85 to 1.1. To calculate the data, it is necessary to divide the amount of hemoglobin by the number of red blood cells. In the case of IDA in an elderly person, the result will be approximately 0.7. You can find out the hemoglobin content in a red blood cell using special blood tests. The normal value should be 27–35 picograms. Moreover, a blood test will also show the ratio of microcytes to the total number of blood cells.
If the doctor sees hypochromia in the tests, then most likely the elderly person has IDA. To accurately diagnose anemia, it is necessary to determine the amount of iron in the blood serum. It is important to identify these results before starting supplemental iron supplementation. For anemia caused by a lack of vitamin B12 and folic acid, differential diagnosis is carried out.
As in other situations, it is not the symptoms that appear that need to be treated, but their cause. It is worth paying attention to the factors that cause low hemoglobin and high ESR, and to look for the reasons for its development in older people. Iron supplements can be prescribed only as an auxiliary measure. But often this therapy replaces basic care, due to the fact that not all old people can undergo surgery.
There are strict parameters that medications prescribed to older people must meet:
- High content of ferrous iron.
- Application and dosage should be comfortable for an elderly patient.
- Medicines must contain substances to improve the absorption of iron ions.
- Affordable price.
After taking 150–300 mg of preparations with ferrous iron or ferrous sulfate, hemoglobin levels increase. You need to take such medications twice a day (preferably with meals, so they are easier to digest).
But we cannot rule out the occurrence of unpleasant side effects after using these medications, especially in older people. Stomach problems, nausea, vomiting or constipation may occur. Sometimes there is an inflammatory process in the walls of blood vessels, pain in the posterior region of the sternum, hypotension or allergic manifestations.

We recommend
“Disposable diapers for adults: how to make the life of a loved one more comfortable” Read more
You can also increase your iron levels with the help of a special diet. Adding meat products to your diet helps especially well.
2. Anemia with B12 or folic acid deficiency.
DNA synthesis in red blood cells can be impaired due to a lack of vitamin B12 or folic acid in the body. With this option, red blood cells look like macrocytes - abnormally large cells.
Signs of such anemia:
- Increased blood color index.
- Remnants of nuclei in erythrocytes are observed.
- Magalocytosis.
- Leukopenia.
- Increased serum iron levels.
- Reticulocytopenia or thrombocytopenia.
- Megaloblastic hematopoiesis in the bone marrow.
- Neurological and mental disorders.
The reason for low hemoglobin levels and the development of this type of anemia in older people may be the following:
- Development of a cancerous tumor of the gastric fundus or atrophic gastritis.
- Inflammatory processes in the intestines, surgical interventions on the stomach.
- Pancreatitis or diverculosis.
- Chronic hepatitis or dysbacteriosis.
- Deficiency of nutrients.
- Incorrect use of medications.
A bone marrow test will help make an accurate diagnosis of anemia due to a lack of vitamin B12 or folic acid. Sometimes this diagnosis is impossible (for various reasons). In such a situation, only experimental treatment can save you. The patient is prescribed special courses of medications with vitamin B12. For an older person, just one or two injections may be enough to improve blood counts and overall health.
When a doctor diagnoses very low hemoglobin in an elderly person, he prescribes vitamin therapy, which usually takes a very long time. At first, injections must be given every day, continuing until the hemoglobin level reaches normal. After the patient’s condition has returned to normal, injections are given 1–2 times a month. With irregular treatment and chaotic use of medications, the disease can recur. But courses of folic acid for such anemia are not prescribed to older people: there is a risk of neurological symptoms.
Anemia caused by low folic acid levels has signs and symptoms similar to anemia caused by B12 deficiency. But it happens less often and is provoked by other factors. A similar illness occurs:
- Due to frequent alcohol intoxication of the body.
- In the presence of exfoliative dermatitis of Ritter, oncological tumors, destruction of red blood cells.
- For nutritional deficiency, enteritis with malabsorption.
- From the adverse effects of anticonvulsants, barbiturates, triamterene, methotrexate on the body.
In advanced forms of the disease and very low hemoglobin levels in older people, the doctor prescribes folic acid injections. In other cases, the patient takes drugs with this substance in the form of tablets (5 mg per day). If the cause of anemia is a tumor or hemolysis (and they cannot be eliminated), taking medications takes a very long time. For epilepsy, such therapy for low hemoglobin is prescribed very carefully so as not to increase neurological symptoms.
We recommend
“How to care for a bedridden elderly person” Read more
What is dangerous about a lack of hemoglobin?
Important: neglecting the symptoms of low hemoglobin in women is dangerous to health.
Low hemoglobin levels can cause decreased immunity, disruption of the cardiovascular system, etc.
The consequences of low hemoglobin levels in women also include insufficient oxygen supply to the cells and tissues of organs throughout the body. The central and peripheral nervous system suffers to a greater extent.
It should be emphasized that a decrease in hemoglobin during pregnancy is a normal physiological phenomenon. However, its critical decrease can cause uterine hypotension, fetal hypoxia, intrauterine growth retardation, spontaneous abortion, etc.
Signs of oxygen starvation in the fetus are considered to be low weight of the newborn baby, pathologies of the respiratory or nervous system, decreased expression of reflexes, underdevelopment of internal organs, further developmental delays, etc.
Obviously, low hemoglobin is a dangerous condition for the patient’s health, so it is extremely important to undergo an annual preventive examination on time and promptly contact specialists at the first symptoms of the disease.
Attention to hemoglobin
Low hemoglobin is a phenomenon that is not always given due attention. Few doctors make the diagnosis “anemia” a separate line. We generally believe that there is nothing terrible here, “all my life I’ve had this hemoglobin - and it’s okay, it’s alive.” At the same time, due to a decrease in hemoglobin, all organs, systems, and tissues of the body regularly experience a lack of oxygen and receive less nutrition.
What hemoglobin is considered low? Here it is worth turning to the average WHO data, which are also used for laboratory testing. So, the standards look like this:
Men - below 130 g/l;
Women - below 120 g/l.
It is important to remember that anemia is not an independent disease, but a manifestation and/or complication of another serious disease. It cannot be ignored, and in any case the life prognosis is unfavorable. I'm not exaggerating. When a person has a heart attack or stroke (and these diseases are not uncommon in our country), anemia significantly aggravates the course of the disease, causes additional difficulties in treatment and worsens the prognosis. After all, how to save a person whose blood does not carry oxygen to his organs?

Become an "iron man". Low hemoglobin is a sign of ulcers and even cancer Read more
What to do with low hemoglobin in women?
Initially, it is necessary to accurately determine the cause of the Hb deviation. The importance of the rule is determined by the fact that each of them requires a different approach to treatment.
If a deficiency of iron or B vitamins is detected, the patient is given a course of drug treatment with iron-containing drugs and vitamin complexes. In parallel with this, an optimal menu rich in missing substances is being developed.
In critical situations, when the hemoglobin concentration drops below 55 g/l, the patient is hospitalized and given a blood transfusion. Such therapeutic measures are aimed at quickly replenishing protein in the blood, while restoring performance and normal well-being. However, transfusions cannot be used as a permanent treatment.
Anemia therapy is selected by the doctor individually for each patient, taking into account the severity of the condition and its underlying cause. The main points of therapy should be highlighted:
- the patient is placed under 24-hour medical supervision in a hospital;
- exclusion of proteins and iron-containing foods from the diet is unacceptable;
- if the condition is caused by large blood losses, then the blood loss is first stopped, and then iron-containing drugs are selected (blood transfusions are performed if necessary);
- in case of acute shortage of iron ions, their parenteral administration is acceptable;
- in case of aplastic anemia, when the bone marrow completely loses the ability to synthesize blood cells, the only treatment method is its transplantation and the simultaneous use of hormonal drugs (in order to reduce the risk of transplant rejection).
It should be emphasized that treatment for hemoglobin deficiency should be selected exclusively by the attending physician. Because delay or choosing the wrong therapeutic methods poses a serious threat to the life and health of a woman.