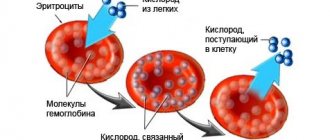
Hemoglobin (Hb or HGB) is a special protein that is part of red blood cells and is responsible for the transport of oxygen and carbon dioxide. The indicator is important in diagnosing diseases and assessing human health. An insufficient amount of the substance in the blood is called anemia. This condition can accompany various diseases and manifest itself with serious symptoms.
Signs and causes of low hemoglobin
The normal hemoglobin level in women is 120-140 g/l, in men – 130-160 g/l. The appearance of the following symptoms gives the right to suspect its decline:
- Chronic fatigue syndrome. With poor oxygen supply to the muscles and nerves, a person feels weak and passive, concentration decreases, and memory deteriorates.
- Difficulty falling asleep and restless sleep.
- Paleness of the skin and mucous membranes. Due to low hemoglobin, the blood is not oxygenated in sufficient quantities, so there is no bright color. When there is a lack of oxygen, blood flow is redistributed in favor of vital organs, but there is not enough of it in the capillaries.
- Muscle weakness and dizziness. Due to insufficient oxygen supply to the brain, dizziness occurs. Physical activity is difficult to bear.
- Heart problems and shortness of breath. Manifests itself in shallow breathing and rapid heartbeat. Indicates severe anemia and hospitalization is indicated.
- Poor tolerance to cold. Ears, fingertips and toes get cold due to slow blood circulation.
Thus, against the background of a reduced level of hemoglobin, the body tissues are insufficiently supplied with oxygen. The severity of symptoms depends on the severity of the anemia.
A decrease in HGB levels may be caused by:
- Loss of blood, which causes a decrease in the concentration of a substance in the blood.
- Insufficient intake/absorption of folic acid and vitamin B12.
- Destruction of red blood cells. This prevents hemoglobin from performing its oxygen-carrying function.
- Violation of the synthesis of porphyrins or globins. Caused by a lack of protein or congenital pathologies.
- Violation of heme formation. Caused by insufficient iron intake.
- Failure in hematopoiesis.
A reduced level is observed with a deficiency of certain substances and diseases: bone marrow tumors, kidney pathologies, chronic infections, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
You can increase your hemoglobin level only after identifying the exact cause of anemia.
Why do you need to monitor your hemoglobin level?
The body needs hemoglobin to transport oxygen to all organs and tissues. Accordingly, its low level provokes oxygen starvation, against the background of which the oxidation of nerve cells accelerates, many metabolic processes slow down (the same carbohydrates and fats, for example, are absorbed using oxygen and nitrogen), and regeneration processes are inhibited.
Often, against the background of low hemoglobin, heart failure also develops, since the vessels in this case lose their elasticity and their patency is impaired.
Low hemoglobin is often accompanied by the following symptoms:
- increased fatigue;
- dyspnea;
- sleep disturbance (even long sleep does not help to get the proper burst of energy);
- neuralgic disorders (decreased resistance to stress, susceptibility to depression, neuroses);
- delayed reaction (as after taking somatic medications).
The body's reaction to low hemoglobin in each individual case is purely individual. For some, this is not accompanied by any painful symptoms at all, but at the same time the body is constantly in a state of stress (which will subsequently certainly affect the functioning of the brain and cardiovascular system).
To normalize hemoglobin levels, it is imperative to follow a balanced diet to provide the body with vitamins and other micronutrients. To absorb the same iron, vitamin C, A, E, PP, B-groups are needed.
The main ways to increase HGB in the blood
For anemia therapy to be effective, it is important to establish an accurate diagnosis. Different types of anemia are treated differently. The urgency and radicality of treatment are determined by the patient’s condition.
- If hemoglobin is low due to lack of iron, then a special diet will help. Eat liver, buckwheat, beef, greens, sesame, seeds, legumes, bran. When HGB is less than 100 g/l, special medications are prescribed: Sorbifer, Actiferrin, Hemohelper, Ferlatum.
- If hemoglobin is low due to a lack of vitamin B12, then increase the amount of foods containing it in your diet: liver, meat, fish, cheese. If the diet is ineffective and severe anemia, drug therapy is prescribed - cyanocobalamin injections or courses of vitamin B12 injections.
- If hemoglobin is low due to folic acid deficiency, then pay attention to your diet. Include vegetables and herbs, tangerines, nuts, liver and meat, and legumes in your menu. If ineffective or severe anemia occurs, folic acid is taken in tablets, powder, or by injection.
- If hemoglobin is low due to a deficiency of protein and amino acids, then a special diet containing a variety of protein-rich foods is indicated. Consume meat and fish, seafood, eggs, dairy products, legumes and nuts, or dietary supplements with amino acids.
In severe anemia and critical hemoglobin levels due to severe bleeding, a blood transfusion is prescribed. This is an emergency method, as it is contraindicated for:
- Blood clotting disorders.
- Cardiac, renal or respiratory failure.
- Bronchial asthma.
- Atherosclerosis.
The donor's blood is perceived as foreign, and there is a risk of adverse reactions and blood clots.
Nutrition rules
To increase the level of hemoglobin in the blood, an adult needs to change his diet. The largest number of substances necessary for the synthesis of hemoglobin is contained in the following products:
- beef;
- veal;
- mutton;
- pork liver;
- rabbit meat;
- turkey meat;
- chicken eggs;
- mussels;
- shrimps;
- mushrooms;
- beans;
- lentils.
The cooking process should be as fast as possible. It is better to do this either steamed or over high heat. Prolonged cooking should be avoided.
To normalize processes in the red bone marrow, you also need products with the maximum possible amount of vitamins (B6, B9, B12, C, E):
- legumes;
- fish;
- pomegranate;
- chicken's meat;
- Brewer's yeast;
- cheeses;
- citrus;
- horseradish;
- spinach;
- Bell pepper;
- dried apricots.
Expert commentary
Kardash Anton Borisovich
Therapist, cardiologist. Doctor of the highest category.
Before using traditional methods, you should consult a specialist. In most cases, home treatment is not enough to correct the pathological condition caused by a decrease in hemoglobin concentration in the blood. This is especially true for pregnant women and the elderly.
Folk remedies to increase hemoglobin
If HGB is reduced slightly (not lower than 100 g/l), there are no severe symptoms, then anemia can be treated with folk remedies.
At home, you can prepare decoctions, infusions from plants containing folic acid, iron, vitamin B12, as well as dietary dishes.
Basic recipes:
- Nettle decoction. Prepared from the tops of young shoots. Add one glass of herbs to 1 liter of boiling water, cook for about 5 minutes and filter. Drink 1-2 glasses daily.
- Potato juice. The drink stimulates hematopoiesis. Drink 100 ml before meals 2-3 times a day for 2-3 weeks.
- Rowan infusion. Pour two teaspoons of ripe berries into one glass of boiling water and leave for at least 1.5 hours. Take 100 ml 2-3 times.
- Infusion of rosehip berries. A handful of dried fruits are poured into 500 ml of boiling water, left in a thermos overnight and drunk 100 ml before meals several times a day.
- Carrot and sour cream salad. For breakfast, eat 100-150 g of carrots, this stimulates the production of red blood cells and hemoglobin.
For low HGB, freshly squeezed juices from pomegranate, carrots, beets, as well as grapefruits, oranges, kiwis, blueberries, black currants, raspberries, and persimmons are useful.
The disadvantages of traditional methods are the duration of treatment, side effects such as diarrhea, flatulence, and exacerbation of gastritis.
If your hemoglobin level continues to decrease during treatment, malabsorption or bone marrow disease may be suspected. Additional examination is required.
Is traditional medicine effective?
Almost all herbal folk remedies are insufficiently effective.
As we have already found out, in 90% of cases, anemia is caused by a lack of iron, folic acid or vitamin B12. In turn, 100 g of any plant material contains a maximum of 9-11 mg of iron or 0.05 mcg of vitamin B12 or 90-100 mcg of folic acid. And, for example, to treat iron deficiency anemia you need about 150-300 mg of iron per day.
It turns out that you need to completely switch to a different diet, limit yourself to other essential vitamins and microelements, but even this will be insufficient due to the different bioavailability of each plant, which is also influenced by the anatomical and functional state of the gastrointestinal tract.
Expert commentary
Kardash Anton Borisovich
Therapist, cardiologist. Doctor of the highest category.
We can conclude that folk remedies can only be used as an auxiliary method of therapy or for prophylactic purposes.
How to increase hemoglobin during pregnancy
During the period of bearing a child, the indicator is of particular importance: as the fetus grows, it needs more nutrients and oxygen, and the woman’s body lacks the necessary substances. Complications during pregnancy and bleeding can also cause a decrease in hemoglobin. For these reasons, the expectant mother is prescribed folic acid, vitamin B12, iron supplements and is advised to adhere to a diet. Be sure to consume red meat, liver, spinach, freshly squeezed juices, nuts, and cereals.
If hemoglobin still decreases, then special drugs are prescribed: Sorbifer, Maltofer, Ferroplex. Complex medications containing vitamin C, B12, B9, and fructose are indicated.
What reduces its level?
In addition to including foods that increase serum iron in your diet, it is also important to exclude foods that reduce it.
These include, first of all, the following:
- fast food and junk food - fatty, very salty foods fried in copious amounts of oil;
- snacks and appetizers with added preservatives - chips, crackers lead to depletion of nutrients in the body;
- soda (sweet) – leads to leaching of useful substances, contains phosphates;
- containing calcium in large quantities (milk and milk-based products);
- containing phytates (primarily bread and a variety of beans);
- soy and milk protein;
- tannin-containing (tea, coffee, persimmon).
Top 7 healthiest juices
Almost all juices from red fruits and vegetables help raise hemoglobin. The most “effective” among them is pomegranate, but you should not abuse it, especially with chronic hypertension.
Apple
Among the fruits common in the Russian Federation, apples are the richest in iron. But to increase hemoglobin, applesauce without pasteurization (without heat treatment) is better suited.
The recommended daily intake is 250 - 300 milliliters.
Pomegranate
Contains iron, vitamins E, A, B-groups. Pomegranate increases hemoglobin concentration and also increases blood pressure, which will be extremely useful for hypotension (low blood pressure).
Doctors also say that drinking pomegranate juice is an excellent prevention of migraine attacks.
You should not drink concentrated pomegranate juice - the ascorbic acid content in it is so high that it irritates the mucous membrane of the stomach and esophagus.
A more preferable option is to consume this juice in diluted form (with a ratio of 1 to 2). And children under 12 years old should not be given it at all - it is better to eat fresh pomegranate seeds.
Beetroot
Beetroot juice is rich in iron, iodine, cobalt, manganese - all these elements are used by the body in the production of hemoglobin (as well as other formed elements of blood).
One of the features of beet juice is that it does not lose its beneficial properties during pasteurization or heat treatment. Therefore, even beet kvass will be beneficial for the circulatory system in the same way as freshly squeezed juice.
Carrot
There is no iron in carrot juice, but it is one of the best sources of vitamins A and E.
Carrots also contain thiamine, riboflavin (B1 and B2), and niacin. All this indirectly accelerates the production of hemoglobin (in the absence of iron deficiency).
Tomato
It contains iron, zinc, manganese, cobalt, iodine, chromium, fluorine, boron - this mixture allows you to comprehensively normalize the biochemical composition of the blood.
Tomato juice also contains a fairly large amount of organic acids that help break down triglycerides in the blood plasma - their excess often leads to a decrease in hemoglobin and the formation of blood clots in the feeding vessels.
Tomato juice is one of the most beneficial juices for the cardiovascular system (but at the same time it is quite aggressive to the gastric mucosa - this nuance must be taken into account).
Grape
Grape juice is rich in iron, cobalt and provitamin A.
And at the same time, its use reduces blood sugar levels - this reduces the load on blood vessels and reduces the likelihood of side symptoms of low hemoglobin.
Strawberry
The iron content in this juice is not the highest among fruits, but it also contains copper, fluorine, boron, nickel and iodine, which help the body produce red blood cells. Strawberry juice should be consumed fresh, without diluting with water or adding sugar.
By the way, “late” strawberries, the last ones picked, are more useful.
Strawberries are no less useful. True, the juice from it is quite expensive.