MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) is a diagnostic method with high accuracy. As a result of the examination, the doctor receives images that show numerous sections of the organ being examined, directed in planes. After completing the procedure using special equipment, all obtained images appear on the computer. Can MRI make mistakes in diagnosis? This depends on a number of factors. Everything, from preparation for the procedure to the doctor’s conclusion, is directly related to an accurate diagnosis.
How often do errors occur?
The accuracy of the results of MRI studies depends on the tomographs: on the strength of the magnetic field and the power of the gradients. The higher they are, the better the quality of the examination. Old tomographs produce fewer images and are of poor quality.
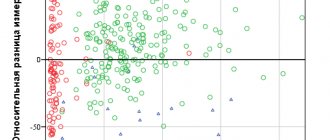
The accuracy of MRI is 98%. Errors at the diagnostic stage account for 34% of all primary diagnoses (that is, every third diagnosis is incorrect).
Statistics show that MRI is an accurate method. After scanning the required organ, the doctor receives complete information about the condition of muscle tissue, blood vessels, bones, and lymph nodes. The MRI machine does not make any conclusions about the patient’s condition, does not analyze images, and does not determine organ disease. A tomograph is a tool for transmitting images to a doctor’s computer. After the examination, the specialist makes a diagnosis for the patient.
Second, conducting research on devices with low power
It is imperative to specify the number of slices for the CT machine. “To conduct modern research, the number of CT slices must be at least 64, the power of the MRI machine must be at least 1.5 Tesla. If the clinic staff rolls their eyes or refuses to name the parameters of the device, it is better to look for another place for diagnostics. Unfortunately, situations are still common when CT is performed on devices with a number of slices of 16.32. Using software and firmware, it is possible to obtain a number of slices close to 64, but the image quality will be quite low. The maximum quality is provided by a 128-slice device. It is mainly used for diagnostics with contrast and provides the best sharpness, but if the study is standard, you can get by with a 64-slice device,” advises Serebryansky.
Article on the topic
Lung damage in percentage. How to correctly interpret a CT scan?
MRI also has its own rules: “For MRI, one of the important parameters is power. It should be from 1.5 Tesla. Some institutions do not even disdain devices that are not intended for medical purposes. For example, they use an old, decommissioned device with a power of 0.35 Tesla, which was previously used in some zoo in Europe and miraculously then ended up in Russia. Special software allows you to increase the power, but it will still be insufficient to diagnose a person, no more than 1 Tesla.”
Reasons for misdiagnosis
If the patient does not fit into the machine correctly, there may be erroneous images. Before the procedure, the doctor is obliged to check the person’s position and select the correct area for tomography. For example, displacement of the headrest due to incorrect positioning of the patient leads to errors in the interpretation of the brain tomogram. Correct positioning of the patient is possible under the control of three optical centralizers, and not just one side one.
The appearance of artifacts in images is an additional problem. Artifacts are errors that the doctor makes during the examination process; they can deteriorate the quality of the images. Most artifacts do not lead to errors in reading the results. However, sometimes they can copy pathological conditions. Such artifacts include:
- motion artifacts;
- magnetic susceptibility;
- truncation;
- chemical shift;
- overlays
Incorrect choice of examination methodology
To diagnose serious diseases, MRI cannot be performed without contrast. A procedure for diagnosing cancer without contrast will not be able to indicate the location of metastases, the size and structure of a small tumor. MRI with contrast will allow you to see the smallest metastases, which are not noticeable during conventional diagnostics, and make a more accurate diagnosis.
Violations during the preparation and conduct of the study by the patient
If an MRI of the intestines and peritoneal organs is planned, the patient should refuse solid food several hours before. An important condition during the procedure is complete immobility of the person. After all, the slightest movement blurs the image, it will no longer be reliable. Since the study can take quite a long time (from 20 to 60 minutes), it is best to empty the intestines and bladder first. Young children need to take sedatives.
For clothing, natural fabrics are desirable. You need to remove foreign objects from yourself - watches, chains. The radiologist will definitely find out about the presence of metal dentures, implants containing metal, pacemakers, and intrauterine devices. You cannot undergo the procedure during pregnancy (the first trimester is a direct contraindication). If you have tattoos, your body may burn. For patients weighing more than 110 kg, diagnosis is not carried out.
Low qualification of a radiologist
A significant portion of the error rate occurs during the reading of MRI results. This is a question of the competence and qualifications of radiologists. To conduct an examination and correctly interpret the results, it is important to know information about diseases and diagnoses.
The doctor is required to know:
- Anatomy and pathology. After all, on a cross-section, one can simply mistake a structural feature of an organ for pathology.
- Rules for obtaining radiation signs of the disease. How organ processes affect MRI.
- Symptoms of radiation diseases. What signs are used to identify the disease on MRI?
- Clinical diagnosis.
It happens that a patient underwent a study using the latest equipment, but the doctor was unable to correctly and efficiently interpret the images. Common mistakes made by an MRI reader include:
- Incorrectly diagnose a disease by confusing conditions;
- It is incorrect to determine the specific stage of the disease;
- Miss the disease without noticing pathological changes in the sections;
- Confuse normality with pathology by diagnosing a disease that does not exist.
Can an MRI make a mistake?
During magnetic resonance imaging, monochrome images (grayscale images of areas of interest) are obtained. The alternation of light and dark areas corresponds to the contours of the anatomical structures located in the study area. Pictures may vary depending on scanning mode. Pathological changes appear as foci of abnormal MR signal (hypo- or hyperintense). The listed phenomena can be seen with sufficient clarity and high resolution of the images. Even an experienced specialist will not be able to interpret blurry scans.
To obtain accurate images, the following conditions are necessary:
- Sufficient equipment power. Low-field open devices provide less detailed sections than tunnel-type tomographs.
- Contrasting. Foci of inflammatory changes, tumors and blood vessels are better visible after injection of an amplifier into a vein.
- Correct scanning mode. Before starting the study, the radiologist adjusts the equipment to perform sections in certain projections; if the settings are made incorrectly, organs and tissues may be poorly visualized.
- Taking into account the natural contrast of structures. Dense tissues that contain little water are difficult to see on MRI.
- Risk of artifacts resulting from physiological movements of the body or organ. It is not advisable to use magnetic resonance imaging to study hollow and contracting structures, since changes in position provoke the appearance of blurred areas on the scans.
When these factors are taken into account, the study produces clear and accurate images, and the risk of difficulties during interpretation is reduced.
What to do if you doubt the result
After an MRI examination, patients seek advice from radiologists or other specialized specialists whose specialty was the procedure. At this stage, the doctor will be able to delve into the problem in detail, taking into account information about the patient: the results of the MRI study, the necessary tests, conclusions from the study of the anamnesis. Only this will allow us to determine the cause of pathological changes.
For patients who have doubts, the research results can be sent to another specialist for interpretation. A second opinion is necessary for patients if there are doubts about the correctness of the existing description or it has been completely lost. A second opinion is a kind of independent examination from another radiation therapy doctor.
The first is the lack of accurate information about the brand of equipment and the year of its manufacture
“There are devices made in China and Europe. Naturally, the latter are more expensive; in most cases, they are designed for more complex tasks. In principle, Chinese technology also has a right to exist, but if you have a really serious problem, you have already done more than one study in different places and you need to either confirm or refute the diagnosis, it is better to choose European devices,” says Oleg Serebryansky.
The second important factor is the service life of the equipment. Needless to say, if you are offered to undergo diagnostics on a device that was released back in the nineties of the last century, has already undergone the third or fourth renovation, then, most likely, the study will be inaccurate, if only because technology has changed since then. have stepped far forward, the expert notes.
Also, you should not try to save money on the procedure, the specialist notes. “Some clinics offer examinations at a surprisingly low price, citing various promotions and discounts; in fact, there cannot be discounts for diagnostics using good equipment, because the cost and maintenance are expensive. Therefore, you should not undergo CT and MRI for promotions, coupons, etc. Most likely, what you will be offered at half price is a formal examination on decommissioned equipment that was restored,” explains Serebryansky.
CT, MRI, ultrasound, x-ray: what types of studies are there and why they are needed Read more
Can MRI make mistakes in diagnosis?
In particular, one of the most important studies is MRI of the brain? American neuroscientists asked themselves this question and decided to conduct an experiment. They inserted electrodes into the brains of experimental monkeys to determine the strength of electrical signals in brain neurons and measure circulatory activity. When the animals watched an “interesting video” on the screen, the intensity of the signals increased and blood circulation increased. But when the same animals, in a state of nervous tension, looked at the screen turned off, the blood flow in their organs remained no less active. At the same time, electrical signals indicating brain function were no longer recorded by sensors.
Scientists have concluded that the brain has the ability to predict upcoming workloads and provide oxygen to exactly those cells that need it most. This means that in such a situation, the tomograph can record incorrect results, showing brain activity even while the person is sleeping.
Therefore, when using MRI, it is necessary to take into account the brain’s ability to premonition, otherwise the results will be incorrect. (At this point you can say a big hello to the specialists who are trying to determine with the help of a tomograph whether a person is in love or not). Time will tell how correct the hypothesis of US scientists turns out to be.
Third, the timing of the study.
Another important parameter is the time of the study. A CT scan can be performed within 10-15 minutes, for an MRI it is 45 minutes - 1 hour. A quick MRI is also possible; it lasts about 15 minutes, but does not give a complete picture. “Thus, it is possible to identify only the presence of gross pathologies: yes, yes, no, no. It is impossible to view the zone in more detail in such a short time. Therefore, after undergoing a short examination and receiving a positive conclusion, do not rush to rejoice. You may not be as healthy as you think, especially if you have symptoms of an illness or feel unwell. Now rapid diagnosis is used for seriously ill patients on mechanical ventilation to determine how bad the situation is,” notes Oleg Serebryansky.
Fifth - poor quality transcription
“How can a person find out whether he was given a quality conclusion or not? Very simple. If you were given an A4 piece of paper with a few lines, which are summarized by the conclusion “no pathologies were identified,” you spent your money in vain. The employee performing CT and MRI is not a doctor, he is a medical specialist who may or may not see certain problems, nothing more. He is obliged to describe them in detail for the doctor who will evaluate the results,” notes the doctor.
For example, if an examination of the abdominal cavity is carried out, then there may be many formations, some of them are normal, some should not be there. And the specialist conducting the research must indicate them all and describe them in detail, otherwise the procedure makes no sense, explains Serebryansky. “The correct description has quite a lot of columns and fields. There is also a reason to be wary if you are given results too quickly. If you received them less than half an hour after the study, this means that no one was involved in you,” says the doctor.
Question answer
What is the difference between CT, MRI, X-ray and fluorography?
It is also worth paying attention to the medium on which the information is given to you. “If these are only a few pictures, then you can assume that you haven’t actually done any research. Due to the fact that the number of sections on modern devices is quite large, many do not print pictures at all; everything is recorded on a disk or flash drive if the amount of information is too large,” emphasizes Oleg Serebryansky.
Sixth - use contrast when not required
“You can often hear the following phrase: “Let’s do a study with contrast, it’s more reliable.” Actually this is not true. Contrast in CT and MRI is a very difficult thing, especially if we are dealing with a patient whose kidney or liver function is impaired. Just in case, contrast cannot be used; in this case, the doctor deliberately exposes the patient to danger. In approximately 10% of cases, patients develop an allergy to contrast during CT, and about 3% of cases develop a fatal allergy to contrast during MRI,” notes Oleg Serebryansky.
Tomography with contrast is a very serious medical procedure. An excellent solution is to locate the diagnostic room next to the intensive care unit, so that emergency measures can be taken if something goes wrong.
What do cancer cells look like on a CT scan?
In the image obtained on a computed tomograph, tumors and metastases usually appear as formations of reduced density. But sometimes identifying cancer cells in images can be difficult for a number of reasons:
- Closely located hemorrhages;
- Accumulations of tissues of certain organs nearby;
- Calcification of metastases.
In such difficult situations, for a clearer image before the procedure, the patient is injected with contrast - a special substance that details the picture of the disease. At the same time, on computed tomography images, the formations show an increase in contrast, since their X-ray density decreases.
Error due to technical equipment malfunction
If the device on which the examination is performed has problems or incorrectly installed software or settings, the information received may contain errors. They are expressed in the appearance of noise (artifacts), blurred areas and other inaccuracies in the images. The quality of the images can also be affected by the characteristics of the device itself - its power and modernity. Step-by-step or 2-4 slice scanners are outdated equipment, which makes it difficult to see minor pathologies.
Errors of this kind can be prevented by undergoing diagnostics on a working tomograph in a trusted medical center with a good reputation.
Diagnosis after MRI: the influence of the human factor
With the active growth in the popularity of MRI diagnostics, almost all clinics in our country have purchased MRI equipment. In this regard, the problem of an acute shortage of highly qualified specialists to carry out the procedure and interpret images has arisen. The complexity of the technique and its specificity do not allow even doctors with extensive experience working with ultrasound, CT, and X-ray machines to work with tomographs, and a special training course is quite an expensive and lengthy undertaking.
This problem is partially solved through the information provided by large medical portals on the Internet. In controversial and severe cases, the attending physician can post images online - MRI results of his patients, which will be assessed by experienced specialists from leading clinics in our country, Israel, Germany, etc.