Imagine that you are sitting at the office of the Carnelian Medical Center in Novosibirsk, where ultrasound scans in the field of gynecology are performed. At the same time, you worry about the future result, since a visit to any doctor is associated with anxiety. At the same time, you think: was it necessary to drink water, was the right time chosen for the procedure, and were all the rules for preparing for this examination followed? What are the features of preparatory procedures for gynecological ultrasound examination?
An ultrasound examination of the pelvic area is performed to visually determine whether a woman has any disorder or to detect pregnancy. The test can be performed through the abdomen (abdominal probe) or through the vagina (vaginal probe). The attending physician himself determines the method of performing an ultrasound, since the vagina, fallopian tubes, uterus, bladder and ovaries can be examined in the pelvis.
Preparatory activities before the study
Basically, the accuracy of ultrasound results will depend on the correctness of the preparatory procedures. If women are not pregnant, for a simple gynecological ultrasound, you should fill your bladder or follow your doctor’s recommendations.
In order to obtain more reliable and accurate results of examination of the pelvic organs, the patient must strictly follow the following rules of preparatory measures:
- with transvaginal examination (through the vagina), no special preparation for ultrasound examination is required; ultrasound is performed with an empty bladder;
- during a transabdominal gynecological examination (through the abdomen), you need to prepare the bladder by drinking 1-1.5 liters of non-carbonated liquid an hour before the procedure and not emptying it;
- during obstetric ultrasound during pregnancy, the bladder is moderately filled when the patient drinks 2 glasses of water an hour before the examination.
For an ultrasound examination to be successful, the intestines must be empty and free of gases. Therefore, you should begin preparatory procedures in advance: 2-3 days before the ultrasound, follow a diet with a small amount of foods that cause gas and constipation. Such products include black bread, milk, confectionery products, raw vegetables and fruits.
It is advisable to take enzyme agents (enzistal, panzinorm, creon, festal, etc.). Doctors also recommend taking espumisan, activated carbon, and dill water. For constipation, it is advisable to take laxatives, which is required before analysis using a rectal sensor.
General description of ultrasound
The essence of the ultrasound diagnostic procedure is to study the information that is received from internal organs that have already absorbed/reflected the waves of the ultrasound machine. On the equipment screen, the specialist sees an image of the structures being examined and interprets the result.
Since the liver is a parenchymal organ with a dense structure, ultrasound is reflected and electrical impulses are converted into a corresponding image on a computer monitor. The quality of the ultrasound result directly depends on the patient’s preparation for the examination and the doctor’s qualifications.
Indications for liver ultrasound:
- characteristic complaints of deteriorating health - change in skin color, pain in the right hypochondrium, bitter belching;
- suspicion of a tumor;
- diagnosis of acute/chronic inflammatory process;
- control of the treatment;
- clarification of the results of other diagnostic procedures;
- examination before and after surgery.
When prescribing an ultrasound of liver structures, the doctor must stipulate all the rules for preparing for the examination, so as not to waste the time of specialists and the patient himself.
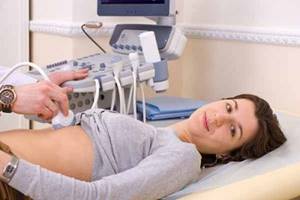
Can I drink the water?
An important point in proper preparation for an ultrasound is maintaining a drinking regime. The human body cannot do without clean water. Therefore, every day a person should drink at least 1.5–2 liters of liquid - tea, juice, compote.
However, immediately before the diagnostic procedure, certain rules should be followed:
- drink only clean drinking water - in small sips, little by little;
- the volume of fluid consumed should not exceed one and a half liters per day;
- the optimal time for drinking water is 30–40 minutes before the main course, or 40–60 minutes after a meal;
- immediately before visiting the diagnostic room, refrain from water for 1.5–2 hours;
- sparkling water is prohibited.
If a person has special reasons for drinking frequently, such as diabetes, it is necessary to discuss them with a doctor in advance. The ultrasound specialist will take such information into account so that the results of the diagnostic procedure are not distorted.
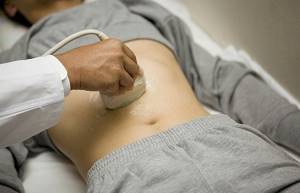
Ultrasound of the prostate gland - Preparation
This study, or TRUS as it is also called, is performed through the rectum. Therefore, it will need to be cleaned. This is done as follows. A couple of hours before the start of the study, the patient is given a microenema. Its volume is 200 ml. To do this, take plain water and use a special bulb to inject it into the rectum. The patient empties within a few minutes. It is necessary to fill the bladder by taking liquid an hour before the procedure. If the patient is unable to tolerate it, you can go to the toilet. But then you will need to drink some liquid again.
Ultrasound cost
| Duplex study of the arteries of the upper or lower extremities | 3000 | rub |
| Duplex examination of the veins of the upper or lower extremities | 3000 | rub |
| Duplex examination of veins and arteries of the lower extremities | 4900 | rub |
| Duplex examination of veins and arteries of the upper extremities | 4900 | rub |
| Duplex examination of the portal system | 3500 | rub |
| Duplex scanning of brachiocephalic and transcranial vessels | 5200 | rub |
| Duplex scanning of brachiocephalic vessels | 3000 | rub |
| Duplex scanning of hemorrhoids | 1900 | rub |
| Duplex scanning of the renal arteries | 3100 | rub |
| Comprehensive examination of the gastrointestinal tract (ultrasound) | 5200 | rub |
| Neurosonography | 3100 | rub |
| Stress echocardiography | 4200 | rub |
| Transcranial duplex scanning of blood vessels | 3100 | rub |
| TRUS of the prostate gland + bladder + scrotum (without CD) | 3400 | rub |
| TRUS of the prostate gland + bladder + scrotum (with color circulation) | 3600 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity (to exclude free fluid) | 1600 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the abdominal aorta | 3000 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the maxillary sinuses | 1900 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the eyeball and paraorbital space with color circulation | 1900 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the stomach | 1650 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the gallbladder | 1600 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the retroperitoneum | 2200 | rub |
| Ultrasound examination of the salivary glands | 1800 | rub |
| Ultrasound examination of gallbladder function (before food load and after 30-40 minutes) | 1800 | rub |
| Ultrasound of complex MPS in women TA, without CDK (kidneys, ureters, bladder) | 2800 | rub |
| Ultrasound of complex MPS in women with TA with CD (kidneys, ureters, bladder) | 2900 | rub |
| Ultrasound of complex MPS in men TA without CDK (kidneys, ureters, bladder, residual urine, prostate gland) | 3500 | rub |
| Ultrasound of complex MPS in men TA and TRUS without color circulation (kidneys, ureters, bladder, residual urine, prostate gland) | 3800 | rub |
| Ultrasound of complex MPS in men TA and TRUS with color circulation (kidneys, ureters, bladder, residual urine, prostate gland) | 4000 | rub |
| Ultrasound of complex MPS in men TA with CDK (kidneys, ureters, bladder, residual urine, prostate gland) | 3800 | rub |
| Comprehensive ultrasound in men of the TA (bladder, prostate gland, residual urine) with color circulation | 2500 | rub |
| Comprehensive ultrasound in men TA (bladder, prostate gland, residual urine) without color circulation | 2100 | rub |
| Ultrasound of large joints (1 joint) | 2000 | rub |
| Ultrasound of large joints (2 joints of the same name) | 2900 | rub |
| Ultrasound of lymph nodes (group 1) | 1900 | rub |
| Ultrasound of any part of the large or small intestine | 1450 | rub |
| Ultrasound of small joints (up to 2 joints) | 1800 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the mammary glands with regional lymph nodes (without colorectal circulation) | 2200 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the mammary glands with regional lymph nodes (with color circulation) | 2400 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the bladder (without colorectal dosage) | 1700 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the bladder (with color circulation) | 1900 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the bladder + prostate gland TA (with color circulation) | 2400 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the bladder + prostate gland TA (in men) without color circulation | 2200 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the scrotum (without color circulation) | 1600 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the scrotum (with color circulation) | 1900 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the scrotum and spermatic cord (without color circulation) | 2000 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the scrotum and spermatic cord with color circulation | 2000 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the adrenal glands (without color circulation) | 1700 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the adrenal glands (with color circulation) | 1900 | rub |
| Ultrasound OBP + Kidneys | 2900 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the abdominal organs (liver, gall bladder, pancreas, spleen) (without colorectal dosage) | 2300 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the abdominal organs (liver, gall bladder, pancreas, spleen) with colorectal dosage | 2500 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the liver | 1600 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the liver with colorectal dosage | 1800 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the liver + gallbladder without color circulation | 2050 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the liver + gallbladder with color circulation | 2250 | rub |
| Ultrasound of pleural cavities | 1800 | rub |
| Ultrasound of superficial structures (soft tissues) without color circulation | 1800 | rub |
| Ultrasound of superficial structures (soft tissues) with color circulation | 2000 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the pancreas | 1500 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the pancreas with color circulation | 1600 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the spine (1st section) without color circulation | 2200 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the spine (1st section) with color circulation | 2400 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the penis (without color circulation) | 2200 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the penis (with color flow) | 2400 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the kidneys (without colorectal dosage) | 1800 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the kidneys (with color flow) | 1900 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder (without colorectal dosage) | 2400 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder (with colorectal dosage) | 2600 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the kidneys and ureters | 2100 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the kidneys and adrenal glands | 2200 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the prostate gland (PA) with a full bladder (without CDB) | 1400 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the prostate gland (PA) with a full bladder (with color circulation) | 1500 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the prostate gland (TRUS) (without colorectal dosage) | 1900 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the prostate gland (TRUS) (with color doppler) | 2300 | rub |
| Comprehensive ultrasound of the prostate gland (TA and TRUS) without CD | 2400 | rub |
| Comprehensive ultrasound of the prostate gland (TA and TRUS) with color circulation | 2450 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the spleen | 1500 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the spleen with color circulation | 1500 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the heart without Dopplerography | 2700 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the heart with color circulation (Echocardiography) | 3100 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the hip joints (children) | 2200 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the thyroid gland with regional lymph nodes (without CDK) | 2100 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the thyroid gland with regional lymph nodes (with color circulation) | 2300 | rub |
| Ultrasound guidance (1 organ, 1 area) | 1700 | rub |
| Ultrasound mark (marker) 1 study | 1500 | rub |
| Echohydrosalpingoscopy (with consumables) | 9300 | rub |
| Ultrasonic densitometry | 2000 | rub |
| Ultrasound elastography of parenchymal organs (1 organ) | 3500 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the stomach with water-siphon test | 2500 | rub |
| Ultrasound in gynecology | ||
| Volumetric 3D/4D ultrasound during pregnancy 2-3 trimester with recording on a flash drive/disc | 3800 | rub |
| Volumetric 3D/4D ultrasound during pregnancy 2-3 trimester (with recording on a flash drive) with calculations | 4800 | rub |
| Volumetric 3D/4D ultrasound during pregnancy 2-3 trimester | 3300 | rub |
| Volumetric 3D/4D ultrasound for twins in any trimester (optional) | 1300 | rub |
| Dopplerography (assessment of uteroplacental blood flow) | 2100 | rub |
| Dopplerography in gynecology | 1600 | rub |
| Dopplerography (assessment of uteroplacental blood flow) (twins) | 2900 | rub |
| Dopplerography (assessment of uteroplacental blood flow) according to the program | 0,00 | rub |
| Ultrasound monitoring of the luteal phase, category 1 | 2800 | rub |
| Ultrasound monitoring of the luteal phase, category 2 | 3500 | rub |
| Ultrasound monitoring of the luteal phase, category 3 | 4500 | rub |
| Ultrasound monitoring of follicle and/or endometrial growth without stimulation of superovulation, category 1 | 1600 | rub |
| Ultrasound monitoring of follicle and/or endometrial growth without stimulation of superovulation, category 2 | 1800 | rub |
| Ultrasound monitoring of follicle and/or endometrial growth without stimulation of superovulation, category 3 | 2100 | rub |
| Ultrasound in the first trimester of pregnancy transabdominal (without CD) | 2100 | rub |
| Ultrasound in the first trimester of pregnancy transabdominal (without CDK) according to the program | 0,00 | rub |
| Ultrasound in the first trimester of pregnancy transabdominal (with color doppler) | 2500 | rub |
| Ultrasound in the first trimester of pregnancy transabdominal (twins) (without colorectal doppler) | 2900 | rub |
| Ultrasound in the first trimester of pregnancy transabdominal (twins) (with color doppler) | 3600 | rub |
| Ultrasound in the second and third trimesters of pregnancy (twins) transabdominal (without CD) | 3900 | rub |
| Ultrasound in the second and third trimesters of pregnancy (twins) transabdominally (with color dispersion) | 4800 | rub |
| Ultrasound in the second and third trimesters of pregnancy transabdominally (calculation of fetal size) (without color circulation) | 2800 | rub |
| Ultrasound in the second and third trimesters of pregnancy transabdominal (calculation of fetal size) (without color circulation) according to the program | 0,00 | rub |
| Transabdominal ultrasound in the second and third trimesters of pregnancy (calculation of fetal size) (with color doppler) | 4100 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the symphysis pubis | 1900 | rub |
| Ultrasound determination of fetal sex (without calculations) | 1800 | rub |
| Comprehensive ultrasound of the pelvic organs (TA and TVUS) | 2900 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the pelvic organs (PA) without color circulation | 1900 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the pelvic organs (PA) with color doppler | 2050 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the pelvic organs (TVUS) (with color doppler) | 2300 | rub |
| Ultrasound of the pelvic organs (TVUS) without color circulation | 2100 | rub |
| CDC in the second and third trimesters of pregnancy | 1900 | rub |
| Cervicometry | 2200 | rub |
Why is liquid needed?
Often doctors, when referring a patient for an ultrasound, warn that they need to drink 1 liter of water before the procedure. But not everyone explains why this is necessary.
Water is necessary for the bladder to enlarge. This makes the surrounding organs clear on the screen. And the research turns out to be more reliable.
Water is especially needed before diagnosing the condition of the urinary tract. With its help, the presence of stones, tumors, pathological changes in the mucous membrane is better visible, and the condition of the genitourinary organs can be accurately determined.
It is also recommended to drink liquid before examining the uterus and ovaries. As the bladder grows larger, it shifts these organs, making them easier to see on the screen.
During pregnancy, such preparation is necessary in the initial stages for the same reason.
Information content of ultrasound research methods
The informative value of ultrasound is beyond doubt. Among the many advantages of the procedure, the safety and painlessness of the diagnosis deserve special attention.
The absence of radiation exposure to the body, the ability to scan and visualize various organs and structures of the body, technical simplicity and accessibility, the absence of contraindications (with rare exceptions) - all this is typical for ultrasound in Krasnoyarsk, and you will get all this by contacting the Center for Andrology and Diagnostics " Andromeda!
Indications
The functional load of the kidneys is extensive - they take part in many processes within the human body. All liquids and waste pass through them. Therefore, diseases in the renal glomeruli appear frequently.
Experts recommend ultrasound in the following cases:
- frequent pain in the lower back in the area of the lower ribs;
- fluctuations in blood pressure, especially with an increase in its lower parameters;
- lower back injuries suffered by a person;
- excessive swelling of tissues, for example, in the facial area;
- discomfort that appears when urinating;
- suspicion of tumor formation;
- assessment of organ activity in pregnant women;
- pathological changes in urine tests.
The popularity of kidney ultrasound is understandable. After all, the procedure does not cause pain in people, it is highly informative, it can be repeated many times without negative consequences for the person, and the patient receives the result right there, in the doctor’s office.
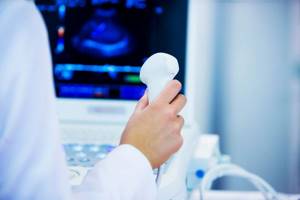
How is an abdominal ultrasound performed?
Ultrasound diagnostics allows you to visualize internal organs and tissues on the screen. To do this, the patient lies down on the couch. A hypoallergenic gel, safe for health, is applied to his stomach, which ensures a stable connection between the ultrasound sensor and the human body, prevents the penetration of air and allows the device to move unhindered over the skin. The doctor moves the sensor across the abdomen and records the data in an electronic protocol. The procedure takes from 20 minutes to an hour.
The main difficulty that specialists face when conducting ultrasound diagnostics of the abdominal cavity is gas bubbles that prevent the penetration of ultrasonic waves to the examined organ. Reducing gas formation allows you to obtain reliable data about the organs and tissues of the abdominal cavity.
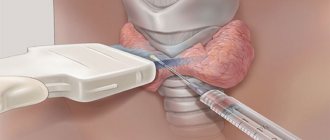
About pelvic ultrasound

An ultrasound examination of the pelvis is performed through the surface of the anterior abdominal wall (transabdominal) or through the vagina (transvaginal). In the latter case, the diagnostic value of the method is increased due to more accurate visualization.
The need for an ultrasound of the pelvic organs may arise in the following cases:
- For men, this is pain in the lower abdomen, diseases of the pelvic organs, the appearance of pathological impurities in seminal fluid or urine, as well as a history of trauma or suspicion of infertility.
- Women require an ultrasound of the pelvic organs if they have difficulties conceiving a child, when using intrauterine contraceptives, or if they suspect diseases of the pelvic organs.
At the Andromed Medical Center for Andrology and Diagnostics in Krasnoyarsk, ultrasound is performed using modern European-level devices. If there are specific requirements for preparing for the study, specialists will definitely inform you about them, telling you what cannot be done before the ultrasound or, on the contrary, what needs to be done.
Why are drinks prohibited before an ultrasound?
In the rules for preparing for a diagnostic examination of the liver, water is indicated as a factor that affects the reliability of the information. Doctors explain that when drinking even pure drinking liquid, the intestines mistake it for food and begin to actively work. Seething appears and gases are formed. The image on the ultrasound machine screen will be unclear.
You will have to demonstrate willpower for no more than 1–1.5 hours. It is for this period that the intestines should remain calm. If thirst still torments a person, you should blot your lips with a damp cloth.
The optimal time for studying internal organs using ultrasound methods is in the morning, when the body has already rested and the digestive system has had time to absorb the food consumed the day before. In cases where the study of the condition and functional activity of the liver is scheduled for the afternoon, a light breakfast and weak drinks, for example, green tea, pure water without gas, are allowed.
High-quality preparation is the key to the success of ultrasound examination of the liver. You can drink water, but follow the rules.
Colon cleansing before the procedure
Before the ultrasound procedure, you will need to cleanse the intestines. This is done on the eve of the study, but no later than 18 pm. Instead of an enema, you can use alternative methods, which include taking laxatives or using microenemas. Currently, pharmacies sell very easy-to-use microenemas “Microvax” or “Norgalax”.
These drugs will help cleanse your stomach without unnecessary hassle.
Drinking regime
Preparatory instructions rarely mention whether you should drink water before a kidney ultrasound? In general, the drinking regime at the preparatory stage should be plentiful and correspond to the age and state of health of the person.
It is allowed to drink green tea and fruit drinks, natural vegetable and fruit juices, preferably freshly prepared. Drink water abundantly and regularly, but avoid gases. Because sweet carbonated drinks, as well as kvass, enhance fermentation processes in the intestinal loops.

Avoid alcoholic beverages. Even low-alcohol drinks – white wine, beer – increase kidney activity, which will distort ultrasound information. If there is a feast coming up, during which it will not be possible to stop drinking alcohol, it is better to postpone the examination procedures to another day.
In cases where, in addition to the kidneys, it is necessary to evaluate the condition of the adrenal glands, as well as the bladder, an indispensable condition is to take 2-3 glasses of clean water. Transabdominal examination will be more informative. It would be a good idea to take 0.5 liters of juice with you and take it 15–20 minutes before visiting the ultrasound room.