X-ray diagnostic methods such as targeted dental imaging are an integral part of modern dentistry. Thanks to them, the dentist has the opportunity to look into those areas of the patient’s oral cavity that are inaccessible to his eyes due to the peculiarities of its anatomical structure. Diagnostics allows you to determine the condition of bone tissue, identify hidden carious lesions and the extent of their prevalence, and conduct a full assessment of the condition of tissues and structures under a crown or filling, as well as in the spaces between teeth.
In addition, a diagnostic study allows you to find out the state of the connective tissues that are located between the tooth root and the alveolar plate. Thus, the dentist can identify a number of disorders and diseases and develop individual tactics for their treatment.
X-ray of teeth (up to 2) - 400 rub.
1-2 minutes
(procedure duration)
Don't know where to take a targeted photograph of a tooth? Contact the multidisciplinary clinic CELT. We have our own diagnostic center, which has everything necessary to carry out various types of dental x-rays. Our diagnosticians have modern equipment in their arsenal, thanks to which the dose of X-ray radiation during the procedure is minimized.
Types of dental radiography
Depending on the purpose and method of implementation, there are different types of radiography. You can familiarize yourself with them and their features in our table below.
| Type of X-ray | Objectives |
| Sighting/intraoral | Provides an image of one or several (up to 4) teeth that are located nearby. Allows you to determine:
|
| Panoramic | Allows you to obtain accurate data on the condition of the jaw in general. Thanks to this diagnosis, it is possible to determine foci of infectious lesions, along with the condition of the maxillary sinuses and the ANS. It is indispensable when planning various types of dental operations, including implantation. |
| Digital | Allows you to obtain a model of the jaw in three-dimensional format and requires the use of a computed tomograph. Allows you to accurately and in detail determine the condition of the patient’s dental system, determine the scope of the upcoming surgical intervention and develop surgical tactics. |
Intraoral bite radiography.
Bitewing radiographs are performed in cases where it is impossible to take intraoral contact photographs (increased gag reflex, trismus, in children), if it is necessary to study large sections of the alveolar process (for 4 teeth or more) and the hard palate, to assess the condition of the buccal and lingual cortical plates of the lower jaw and floor of the mouth. A standard envelope with film is inserted into the oral cavity and held with closed teeth. Bitewing radiographs are used to examine all upper and lower anterior teeth. Also, occlusal radiography is used to obtain an image of the floor of the mouth in case of suspected stones of the submandibular and sublingual salivary glands, to obtain an image of the jaws in an axial projection. It allows you to clarify the course of the fracture line within the dentition, the location of bone fragments, the state of the outer and inner cortical plates in cysts and neoplasms, and identify the reaction of the periosteum
You can get acquainted with the prices of computer intraoral radiography and details by tel. 8, 8 (8442) 24-68-21.
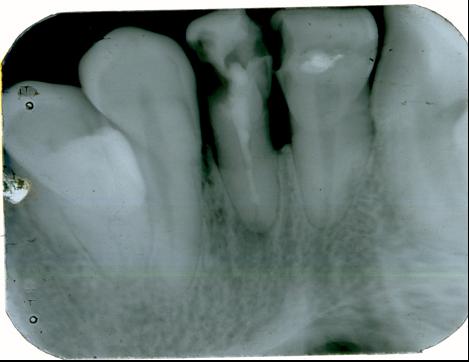
Indications and contraindications for targeted dental imaging
Indications
The dentist prescribes a targeted photograph to make a diagnosis and control the quality of dental canal filling for diseases such as caries, periodontitis or pulpitis. Indications for this procedure are:
- acute pain symptoms;
- gum disease;
- if you need to determine the parameters of wisdom teeth;
- to check the quality of dental canal cleaning during treatment of various diseases;
- in pathological conditions such as caries and pulpitis;
- after injuries to diagnose their consequences.
Contraindications
Contraindications to dental x-rays using targeted images are associated with the effect of x-ray radiation on the human body. It is so minimal that it is not capable of causing any harm - however, in a number of certain conditions it is used with caution. This happens if:
- the patient is pregnant or breastfeeding;
- the patient is in a difficult situation;
- the patient is under fifteen years of age;
- the patient has received a high dose of radiation in the past 12 months.
Indications for use
Dental radiography is used for two main purposes: to diagnose and evaluate the quality of treatment performed.
Allows you to detect the following diseases:
- hidden carious lesion;
- pulpitis (inflammation of the neurovascular bundle of the tooth);
- cyst at the roots of the teeth;
- periodontitis (purulent inflammation of the tissue between the root of the tooth and the hole in which it is located);
- gum disease, in which bone tissue atrophies (periodontitis, periodontal disease);
- neoplasm.
Intraoral radiography also helps evaluate the results of procedures such as:
- root canal filling;
- treatment of periodontal diseases.
How to take a targeted photograph of a tooth?
During the procedure using a modern X-ray machine, the patient is asked to take a sitting position. In order to prevent the body from being exposed to x-rays, the patient is wearing a special protective apron. The radiologist fixes the patient's head in a certain position, allowing to obtain the necessary image, and then directs the X-rays to the diagnosed area. The filming process lasts seconds, during which the patient must remain motionless. Almost immediately, the patient is given images on film or digital media.
X-ray of teeth
There are two main types of dental x-rays: intraoral x-rays, in which x-ray film is placed in the patient's mouth, and extraoral x-rays, in which the film is placed outside the mouth.
- Intraoral radiography is the most commonly used method in dentistry. Such images provide sufficiently detailed information, allowing the doctor to identify existing carious cavities, assess the general condition of the tooth and surrounding bone tissue, the stage of development of growing teeth, and also monitor the dynamics of the condition of the teeth and jawbone.
- Extraoral radiography also shows the condition of the teeth, but it is more aimed at examining the condition of the jaw and cranial structures. Such images do not provide as detailed a picture as intraoral x-rays, and therefore are not used in the diagnosis of caries or diseases of individual teeth. They are used to identify impacted teeth, dynamically monitor the growth and development of the jaws in relation to the teeth, as well as to identify potential disturbances in the relationship of teeth, jaws and the temporomandibular joint (see section “Temporomandibular joint dysfunction”) or other bones structures of the facial skeleton.
Types of intraoral radiography
There are several types of intraoral x-rays that show different aspects of the internal structure of a tooth:
- Interproximal (bite) radiography provides images of the upper and lower teeth in one area of the mouth. Each image shows the tooth from the crown to approximately the level of the bone that holds it. Bitewing images are used to detect interdental caries and changes in bone density due to gum disease. In addition, they are useful in checking the correct installation of a crown (or cast prosthesis) or the marginal integrity of a filling.
- Periapical radiography shows the entire tooth - from the crown to the root and further to the area of its attachment to the jaw bone. This image shows the tooth in full size (including all teeth within one area of the upper or lower jaw). Periapical images are used to identify abnormalities in the structure of the root and surrounding bone tissue.
- A survey radiograph covers a large area, giving complete information about the stage of development and location of the teeth. This image shows the complete dental arch of the upper or lower jaw.
Types of extraoral radiography
Your doctor may order one of the following types of extraoral x-rays:
- Panoramic radiography provides images of the entire oral cavity. Using this method, an image of all teeth (both upper and lower jaw) is obtained in one image. This type of study allows you to clarify the position of all erupted and cutting teeth, identify the presence of impacted teeth, and can also be used in the diagnosis of tumors.
- A tomographic image allows you to obtain an image of a certain layer (“slice”) of the oral cavity, while all other layers of tissue are blurred. This type of radiography is used to examine structures that are difficult to obtain a clear image of, for example, due to the close proximity of other structures that make it difficult to visualize the area under study.
- Cephalometric projections show the entire side of the head. This type of examination allows you to see the teeth in relation to the jaw and profile of the patient. Such images are used to develop an orthodontic treatment plan.
- Sialography (salivography) allows you to obtain an image of the salivary glands using a special dye (radiopaque substance) injected into the duct of the salivary gland, after which it becomes visible on an x-ray (the salivary gland is a soft tissue organ that is not visible on a regular x-ray). This type of test can be used in the diagnosis of salivary gland diseases, such as salivary gland blockage or Sjögren's syndrome.
- Computed tomography (CT) allows you to obtain a picture of the internal structures of the body in the form of a three-dimensional image. This type of examination (most often performed in a hospital setting) is used to diagnose changes in the bones of the facial skeleton, such as tumors or fractures.
Best Practices
In recent years, a new X-ray diagnostic method has been developed and may already be used or will soon be used in your dental practice. This is the so-called digital radiography. Instead of capturing the X-ray image on film, which must then be developed in a darkened room, the image from the X-ray machine is transferred directly to a computer, where it can be displayed, saved or printed. This technology has a number of great advantages:
- This type of examination uses significantly less radiation exposure. In addition, there is no need to wait for the photo to be developed - the finished image appears on the computer screen in a matter of seconds after taking it.
- The image taken (for example, a photograph of a tooth) on a computer screen can be made “better” and enlarged many times - this way it is much easier for the doctor to show the patient exactly where the violations are identified and what they are.
- If necessary, images can be sent by e-mail to another specialist (which speeds up obtaining a third-party consultation and making a decision about the need for the help of another specialist) or to another dentist (for example, when changing place of residence).
- Special software allows the use of digital methods to automatically compare subsequent images with previous ones (so-called subtraction radiography). Using this method, all matching elements of two images are "subtracted", leaving only a clear image of the non-matching elements. This allows the doctor to easily track even the smallest changes that might not be noticed by the naked eye.
Published under the editorship of specialists from the dental department of the Cleveland Clinic.
Advantages of targeted dental imaging in CELT
The price of a targeted dental photograph in our clinic is affordable for anyone, but contacting us has a number of advantages. You receive a guaranteed accurate image in which your attending physician will see everything he needs. We employ experienced radiologists with over fifteen years of experience. They have modern equipment at their disposal, which allows them to carry out the procedure as accurately and safely as possible.
You can familiarize yourself with our prices in the corresponding section of our website or find out by calling us at: +7 (495) 788-33-88.
Preparing for additional research
When it is necessary to get a complete picture of the severity of the disease or to see anatomical features, the doctor refers to radiography, CT, TRG and other types of studies. The basic rules for preparing for them are standard. Recommended:
- Remove metal jewelry during testing - alloys may distort the result.
- During the procedure, patient immobility is important. Stabilization is achieved by the presence of support on the armrests and headrests.
The doctor talks in detail about the detected pathology, offers options for eliminating it, and draws up a plan for the upcoming treatment. It is important for our clinic specialist to explain all the features of the upcoming treatment and warn about the consequences. The patient independently makes the final decision based on the information received.
If there is a violation, then you should not ignore it. You need to immediately begin treatment procedures or regularly see a dentist.
Our doctors
18 years of experience
Baghdasaryan
Armen Evgenievich
Chief physician, dentist-orthopedist-therapist
Graduated from VSMA named after. N.N. Burdenko. Internship on the basis of MGMSU named after. A.E. Evdokimov in “General Dentistry”.
Clinical residency at the Moscow State Medical University named after. A.E. Evdokimov in “Orthopedics”.
More about the doctor...
5 years experience
Sadina
Ekaterina Vladislavovna
Dental therapist, surgeon
Penza State University Medical Institute, specialty “Dentistry”.
In 2021, she underwent professional retraining in the specialty “Therapeutic Dentistry” at the Moscow State Medical and Dental University named after A.I. Evdokimov.
More about the doctor...
Why take an X-ray of your child's teeth?
To adequately diagnose oral diseases in children and adolescents, the doctor needs to have as much information as possible. An x-ray of a child’s baby teeth can provide this information. More than 50% of the tooth is hidden, and the dentist simply does not see some areas where pathological processes may occur. In these cases, x-rays come to the aid of the doctor. An image of a child’s baby teeth will show whether there is caries between the teeth, whether the roots of the teeth are changed, and how the rudiments of permanent teeth are located. This way, the dentist can predict the timing of the loss of baby teeth and identify the presence of impacted, or crooked, rudiments. Such early diagnosis makes it possible to recognize a possible malocclusion and prevent it. At this stage, it is much easier to correct the bite, and there is a chance of avoiding wearing braces in the future.
The Ministry of Health has developed the timing of the examination, as well as safety rules under which neither the patient nor the clinic staff will be exposed to unnecessary radiation. According to his recommendations, children should have an X-ray of their children's teeth once every two years, and after the eruption of permanent teeth - once every 1.5 - 3 years.