Ultrasound, MRI and CT in the diagnosis of gallbladder diseases
“Pearl necklace” and “porcelain bubble” in clinical practice, not in a museum
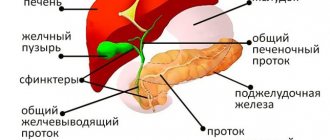
If you dig deeply into the problem of diagnosing gallbladder diseases, you can understand that serious people were engaged in the issue of improving it, because the terminology describing the pathology of this organ includes both a “pearl necklace” and a “porcelain” bladder.
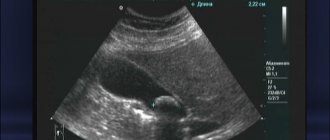
Will an ultrasound show cholecystitis?
People knew a lot about valuable things and identified them with an equally valuable organ - a reservoir of bile, which can be used urgently, or can be saved “in reserve.” The organ, on the one hand, is small, but on the other, very responsible. Ideally, it should work as a shock absorber. A lot of liquid - it expands, a little - it contracts. Accordingly, the walls must be very elastic and mobile. And if the wall thickens, then we write in conclusion - chronic cholecystitis. More often - if the patient came for an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, however, during CT and MRI they can write the same.
How to correctly diagnose cholecystitis?
In fact, it is still necessary to study the reservoir (storage) and evacuation functions (the ability to reduce and release a portion of bile during a food load). Therefore, you should not “throw away” this diagnosis, and if you really “want” to make it, then you need to perform contrast enhancement - in the delayed phase, the connective tissue will accumulate a contrast agent and the wall will be contrasted evenly along the entire perimeter.
Signs of cholecystitis on ultrasound, CT and MRI
The uniformity of wall thickness is the most important sign on which almost all diagnosis of gallbladder diseases is based. The second sign is a change in the structure of bile and the reflection of these changes during ultrasound diagnostics, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging.
Often during ultrasound they talk about “sand” (but who likes that there is sand in it?). The mysterious foreign term “sludge” sounds more humane. This is a kind of violation of the structure of the solution, when there are both liquid and denser fractions, and even microcrystals (the same “sand”). This is already a harbinger. If it is stable and often visible, this is a sure path to stone formation.
What are the dangers of gallstones?
Small stones have little effect on the wall of the bladder, but under pressure they can slip into the cystic duct (causing occlusion of the neck); if their diameter is larger, then we see the symptoms of Mirizzi syndrome, and if they are very small stones, then they fly into the common bile duct. If it is passable for a stone of this diameter, then it can slip through or be pinched in the ampulla of the nipple of Vater, and if it is larger, then it can block the common bile duct. And as a result, either occlusion of the bile ducts and obstructive jaundice, and if the block is lower and the main pancreatic duct is involved, then this can become a trigger for the development of acute pancreatitis against the background of a suddenly developed occlusive syndrome.
Ultrasound, CT and MRI will help clarify the diagnosis
In all cases, ultrasound diagnostics, computed tomography and MRI will help - the dilated duct and its break at a certain level will be visible. But the reason (that is, the stone itself) is not always visible - with ultrasound a dense stone will give an acoustic track, on CT it will be visible if it is calcium-bilirubin, well, with MRI we can only judge the contour of the obstacle that caused outflow disturbances bile or pancreatic juice.
Gallstones: is surgery necessary?
Let's return to the gallbladder. A large stone will not go away, but it is believed that long-term stone carriage is a path to gallbladder cancer due to the constant impact of the stone on the wall when it is fixed in a deformed bladder in chronic cholecystitis.
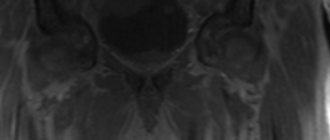
What does a “pearl necklace” look like on an MRI?
Thanks to MRI, it is possible to find that very “necklace” when, like diverticula in the colon, the lining of the bladder protrudes outward, beyond the muscle layer. These dilated Aschoff-Rokitansky sinuses, lined up in a row, with a pinched neck, really resemble a necklace.
As for the rest, the capabilities of the methods are similar - everyone can see necrosis of the wall and the formation of paravesical accumulations, only with contrast-enhanced tomography there is no doubt, which means there are no question marks in the conclusion either.
Gallbladder cancer can be located anywhere. If in the area of the body or fundus, the tumor can grow for a long time until it manifests itself as a symptom of peritoneal irritation - germination of the liver capsule. And cervical cancers grow in the area of the common hepatic duct. The patient turns yellow and only then they begin to examine him.
Those who read carefully did not find anything about... porcelain.
Porcelain gallbladder. What it is?
It happens when the wall of the bladder becomes calcified due to chronic inflammation and really resembles an eggshell (almost like a Faberge egg). But there is one pseudotumor condition that closely resembles a tumor in appearance, but in essence is chronic inflammation. This is xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis. It looks scary, but is not deadly. And here the archival base is important. With such external manifestations, or gradually increasing signs, patients live for years. By comparing the data with the results of a previous study, one can understand its morphology. But more often this pathology is diagnosed after cholecystectomy, according to the results of a morphological study.
Author: Karmazanovsky Grigory Grigorievich
Advantages of computed tomography:
CT examinations have a number of undeniable advantages compared to other methods of radiation diagnostics, such as X-ray, MRI, and ultrasound.
- Painless, non-invasive procedure
- The examination time is less than that of MRI
- Clearer images taken
- Volumetric, layer-by-layer image, the ability to evaluate changes in more detail
- The ability to simultaneously obtain images of bones, tissues, vessels, organs
- Low radiation dose compared to x-rays
- Ability to diagnose internal bleeding
- The ability to accurately determine the localization and extent of the pathological process
- Possibility to evaluate the results of treatment
Preparing for an abdominal CT scan
CT scan of the peritoneal organs is one of the few types of examination that requires careful preparation. It will depend on it how well all organs will be visualized in the pictures.
Before the procedure, it is advisable to undergo additional examinations, such as ultrasound of the peritoneum, x-ray or colonoscopy. It is worth consulting with an allergist and anesthesiologist about the possible risks from the introduction of X-ray contrast. If the urinary system is to be examined, laboratory tests must be done for the presence of creatine, urea, AST and ALT enzymes.
Since the main problem that reduces the information content of the examination may be intestinal bloating and fullness, it is necessary to normalize the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract in advance. To do this, three days before the tomography, you need to switch to a gentle diet: exclude not only heavy and fatty foods, but also those foods that cause increased gas formation. These include: cabbage, legumes, beets, celery, fresh and dried fruits, cereals, dairy products, fresh baked goods, confectionery products. It is also undesirable to consume kvass, carbonated water, strong coffee and tea, and alcoholic beverages. It is allowed to eat lean steamed fish, omelettes, light non-rich broths, boiled chicken, and oatmeal with water.
The test is done on an empty stomach, which is why a CT scan of the abdominal cavity is usually scheduled for the first half of the day. The day before, they give a cleansing enema, take a mild laxative, or administer a suppository with glycerin. In addition, 18 hours before you can drink enteric sorbents: activated carbon or smecta.
Two hours before the scan, you should stop drinking any drinks; this may increase intestinal motility.
It is worth noting that the introduction of X-ray contrast without appropriate preparation can provoke vomiting, nausea, and in some cases, intestinal volvulus. If the patient had a CT scan of the abdominal cavity with contrast, then after it it is advisable to drink a liter of clean drinking water. This promotes rapid removal of the dye.
Disturbance in the functioning of the bile ducts
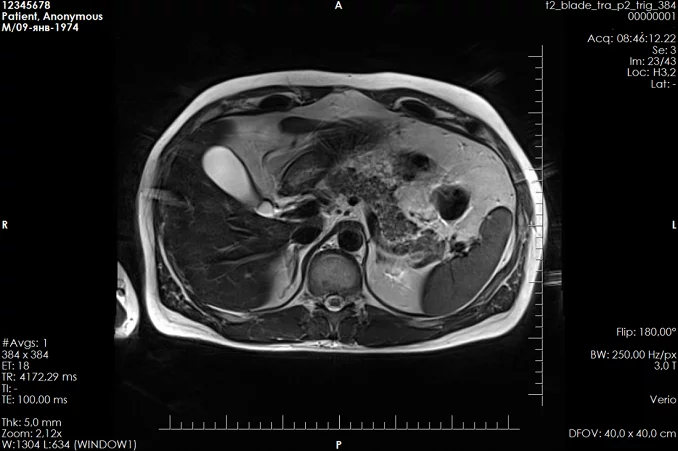
A CT scan is prescribed if there is no other way to investigate the problem, establish the cause of the pathology, and a way to combat it. This could happen if:
- the organ being examined is located too high, which does not allow ultrasound to be performed due to the ribs;
- There are other pathologies that interfere with normal diagnosis.
How much does an abdominal CT scan cost?
The price range for this type of diagnostics is quite large. It is influenced by a lot of factors: the model of the tomograph, the qualifications of the diagnostician, the location of the clinic. It is worth considering that an abdominal CT scan with contrast will cost 20-30 percent higher. To save money, it is advisable to study the cost of the procedure at various medical centers, as well as find out about the promotions and discounts available there. This is easy to do using our service. Also here you can immediately make an appointment at any diagnostic center at a time convenient for you.
Peculiarities
A gallbladder CT scan differs from an MRI scan in that it involves minimal exposure to radiation to the human body. Tomography allows you to obtain high-quality images, without interference and shadows, which is impossible to achieve with other methods of studying the human body. A tomograph can detect even small differences in the structure of tissues. If you additionally use contrast, you can identify even those diseases that are difficult to detect in the early stages of development.
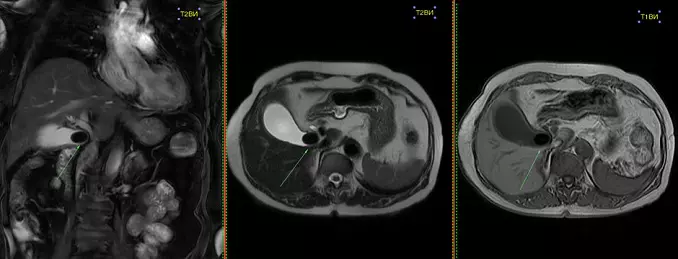
Positive and negative sides
Gallbladder tomography is chosen for many reasons.
- Non-invasive. No surgical or laparoscopic intervention is required.
- High level of image accuracy.
- High resolution of the technique.
- Efficiency.
- Minimal absence of contraindications.
- Information content.
- Affordable price.
There are also disadvantages.
- It is not always possible to find a clinic with a high-quality tomograph the first time.
- In rare cases, CT cannot provide reliable data when diagnosing certain diseases. Either contrast or other technology for examining the gallbladder may be required.
Indications for computed tomography:
- Diagnosis of chest organs
- Diagnostics of the central nervous system
- Diagnostics of the cardiovascular system
- Diagnostics of the spine and musculoskeletal system
- Diagnosis of back pain
- Diagnosis of severe injuries and fractures
- Diagnosis of pain in joints
- Detection of internal bleeding
- Detection of inflammatory processes
- Search for malignant and benign formations
How is an abdominal CT scan performed?
The examination may take from a few minutes to an hour. The patient will have to undress, remove all jewelry, glasses and other wardrobe items containing metal, and lie down on the retractable table of the device. After this, the patient is placed in the tomograph tunnel and the study begins. It is worth noting that the device operates with a characteristic noise that can cause anxiety in the patient. If a person suffers from claustrophobia, panic attacks and anxiety disorder, it is worth discussing this issue with a diagnostician in advance. Perhaps in this case, the use of sedatives will be indicated to prevent an attack.
In a CT scan of the abdomen with contrast, dye injection can be done in different ways depending on the affected area. To clarify the condition of hollow organs and vessels, intravenous administration of the drug is used. If it is necessary to examine the liver, kidneys or pancreas, a person takes a solution of an iodine-containing substance orally in small sips. To detect pathologies of the large intestine, the dye is administered rectally. In particularly difficult cases, the diagnostician may suggest a bolus administration of radiocontrast, that is, it will be introduced into the body by drip using an automatic injector.
After the scan is completed, the diagnostician prepares a transcript of the results. Based on the images obtained, he enters into the research protocol information about the size, shape and relative position of organs, notes congenital anomalies and detected disorders. The conclusion and photographs are transferred to the attending physician or handed over to the patient. Many medical centers are also willing to record the results on a computer disk or flash card, or send them by email. It is worth considering that the final diagnosis is made by a doctor of the appropriate profile based on the images and the research protocol.
Contraindications
It is worth remembering that any procedure, even the most non-invasive, safe and not requiring surgical intervention, may have contraindications, which should be reviewed during a preliminary consultation. These include:
- Pregnancy period.
- Age up to 14 years. It is permissible to remove the restriction, but only with the permission of a specialist.
- Carrying out the procedure for problems with the heart, kidneys, liver, diabetes, as well as diseases affecting the thyroid gland, can only be done with a doctor’s prescription. You should not undergo a CT scan on your own, as this can cause a number of serious consequences.
- If a woman is breastfeeding, then the process is stopped for a couple of days and the baby is transferred to artificial feeding, especially if contrast is used in the tomography.
To obtain high-quality results, you should entrust the diagnosis of your body only to a trusted specialist and a clinic equipped with the latest technology.