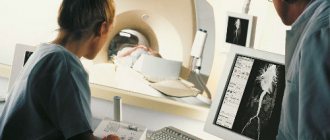
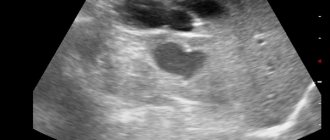
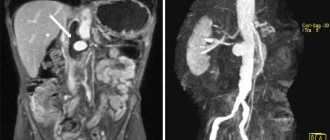
Contrast MRI of the abdominal cavity is a non-invasive, high-precision diagnostic method that allows you to visualize organs and anatomical structures using a phenomenon called nuclear magnetic resonance.
An important feature of the study is the absence of radiation exposure to the body, painlessness and safety, as well as the ability to obtain results immediately after the examination.
Contrast agents can be used in all types of diagnostic imaging: radiography, CT and MRI, in order to improve image quality and enable more detailed examination.
In some cases, pathologically changed and healthy tissues may be difficult to distinguish from each other in the resulting images due to their structure or location. In such cases, the use of coloring substances makes it possible to carry out diagnostics with high accuracy.
The first contrast agent in medicine was used for radiography of the digestive tract. It was barium sulfate, which was taken orally on an empty stomach. The next step was the creation of drugs for intravenous administration. Coloring drugs gave a high percentage of complications associated with the toxic effects of iodine in their composition on the body.
With the active introduction of magnetic resonance imaging into routine medical practice, a new class of contrast agents based on the rare earth metal gadolinium was developed. These drugs show high safety, practically do not cause complications and do not require preliminary blood donation for renal parameters. Adverse reactions to gadolinium contrast agents are approximately 10 times less common than to iodine-containing contrast agents.
Types of abdominal MRI
When referring for an MRI, the doctor determines what type of study will be chosen for diagnosis. The following MRI options are available:
- extensive overview;
- with or without the use of a contrast agent;
- angiography.
Most often, doctors prescribe an extensive examination of the abdominal cavity on a tomograph, as it allows one to assess the condition of the following group of organs:
- soft tissues;
- gastrointestinal tract;
- kidneys and adrenal glands;
- spleen;
- liver;
- lymph nodes;
- bile ducts;
- pancreas;
- veins and arteries located in the studied part of the body.
MRI diagnostics allows not only to assess the condition of the organs being examined, but also to see how negative the impact of the pathological process is on the organs and tissues located “in the neighborhood.”
In what cases do doctors refer for an MRI?
This procedure makes it possible to examine hard-to-reach areas located in the abdominal cavity. Clear 3D images show:
- Gastrointestinal organs - liver, pancreas;
- located retroperitoneally - kidneys, adrenal glands;
- spleen;
- stomach, small and large intestines;
- gallbladder and its ducts.
Patients with already diagnosed diseases and those who first consulted a doctor with complaints of sudden weight loss, bitterness in the mouth, yellowing of the skin, frequent abdominal pain, enlarged lymph nodes and other signs of dysfunction of internal organs are referred for abdominal tomography.
What diseases can be detected on an MRI of the abdominal organs?
The magnetic resonance imaging procedure consists of layer-by-layer scanning of a certain area of the body in order to identify pathological processes and anomalies. Based on three-dimensional images and a conclusion, the attending physician will make a diagnosis. MRI of the abdominal organs shows the following diseases and abnormalities:
- abnormal development of abdominal organs from birth;
- disturbances in the structure of nerve trunks;
- inflammatory processes;
- cystic formations;
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- the presence of malignant tumors;
- spread of metastases;
- formation of stones in the bile ducts;
- circulatory problems and vascular disorders (thrombosis or aneurysm).

In addition, using images, the doctor determines the structure and size of the organs being examined.
Which authorities check?
Magnetic resonance imaging allows you to determine pathologies of the structures of the digestive tract. The following internal organs are visualized:
- Pancreas.
- Spleen.
- Liver.
- Stomach.
- Gallbladder.
- Various parts of the intestine.
Despite its high information content, tomography allows one to evaluate only the structural features of the digestive tract. The study makes it possible to diagnose the disease or confirm the doctor’s suspicions. However, to obtain more information about the functional state of the gastrointestinal tract structures, additional diagnostics may be required. For example, scintigraphy, studying the functioning of organs after the administration of a radioisotope drug, etc. The choice of examination tactics is decided by the doctor after assessing the situation.
Reasons for referral for abdominal MRI
A referral for an MRI is issued by a doctor if a controversial situation arises, it is impossible to make an accurate diagnosis, or if it is necessary to urgently determine the source of the disease. Repeated tests may also be ordered to monitor the condition of the organ after surgery or a course of treatment (for example, chemotherapy). In this case, the MRI images will be compared with the previous study result to identify the dynamics of the disease.
The key reasons for referral for abdominal MRI are:
- suspicion of the presence of neoplasms to determine the type: malignant or benign;
- abdominal injury;
- confirmation of abnormal development of abdominal organs;
- search for the source of the inflammatory process;
- confirmation of the results of previous diagnostic procedures if the diagnosis has not been made definitively (ultrasound diagnostics, computed tomography, radiography);
- if internal bleeding is suspected;
- searching for spread or absence of metastases;
- gallbladder diseases (obstructive jaundice);
- inspection of the volume of fluid accumulation in the peritoneal area;
- determination of the stage of development of pancreatitis (acute or chronic);
- changes in the structure of organs or soft tissues of an ischemic nature;
- increased size of the spleen, gallbladder, lymph nodes or liver;
- to monitor the condition of the abdominal cavity after surgery;
- in order to confirm or reject the chosen treatment regimen.
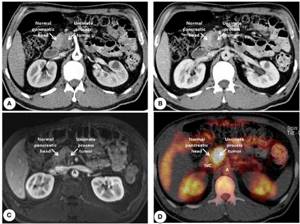
The magnetic resonance imaging procedure is also prescribed when it is impossible or it has been proven that other types of diagnostic testing are ineffective. For example, to identify stones in the bile ducts, it is better to do a computed tomography scan, since this type of procedure gives clearer pictures of bone structures. MRI is aimed at “transilluminating” soft tissues. Therefore, only a doctor can determine which diagnostic method should be used.
Indications for examination
The procedure is prescribed for:
- the need for detailed visualization of pathological changes and clarification of their location;
- receiving ambiguous results from X-ray, ultrasound and other studies;
- suspicion of cancer.
One of the main advantages of magnetic resonance imaging of the abdominal cavity is the possibility of early detection of malignant neoplasms. Some types of cancer do not manifest themselves for a long time, and late diagnosed pathologies are difficult to treat and not always effective. Scanning helps detect tumors at an early stage and saves patients from the severe consequences of late detection of cancer.
MRI examination is indispensable before planned operations and after surgical interventions. A preliminary scan shows changes in the tumor and the extent of its spread, and in the postoperative period, tomography data allows us to draw conclusions about the effectiveness of the treatment.
Get specialist advice or make an appointment
+7 (499) 400-47-33
Who should not undergo an MRI?
Despite the safety of examination using a magnetic resonance imaging scanner, there are restrictions or complete prohibitions on the procedure. A complete ban on undergoing MRI includes:
- the presence of implants containing metal compounds (cochlear implant, pacemaker, mechanical heart valve);
- the presence in the body of foreign objects with a metal base or inclusions (bullets, fragments);
- presence of tattoos using paint with metals;
- pregnancy period (1st trimester);
- the patient’s condition when artificial life support is required (resuscitation, coma);
- large body weight (more than 120 kg).
The reason for the prohibition of undergoing examination if a patient has permanent metal implants and tattoos on the body is due to the fact that these objects under the influence of the magnetic field of the tomograph can heat up, expand and even move slightly. This situation can bring not only pain, but also injury. Electronic items and metal implants may fail.
It is not a contraindication for magnetic resonance imaging if the patient has dentures or modern braces, as well as titanium implants.
Pregnant patients are prohibited from undergoing the procedure in the 1st trimester, because there is no collected information about the harm or safety of the examination for the correct formation of the fetus.
In some cases, undergoing a magnetic resonance examination is extremely important for the patient's life. According to the doctor's decision, if categorical reasons for refusing the procedure are not found, magnetic resonance imaging can be performed.
It is not advisable to undergo a tomography examination if the following circumstances exist:
- period of breastfeeding and pregnancy (if a contrast agent is used);
- allergy to gadolinium metals included in the contrast agent (extremely rare);
- diagnosed renal or liver failure;
- inability to keep the body still (in some cases, the doctor may suggest medication to induce sleep);
- the presence of mental disorders, acute fears and panic attacks associated with being in the “tunnel” of a tomograph (in this case, you can try to undergo research using open machines);
- severe pain that does not allow you to lie still on the medical table at the time of scanning (the doctor may suggest taking painkillers).
Who is contraindicated for MRI diagnostics?
An MRI examination of the abdominal organs does not harm health, but in some cases the use of this method is still impossible. Diagnosis is not carried out during the first trimester of pregnancy and in acute mental disorders. Another contraindication is the presence of metal objects in the body (implants, endoprostheses, clips, artificial heart valve, pacemaker, etc.). Contrast studies are not recommended in renal failure. With a body weight over 140 kg, the procedure is sometimes impossible for technical reasons (the patient cannot be placed in the tomograph chamber).
Rules for preparing for an MRI of the abdominal cavity
Magnetic resonance imaging is usually performed without prior preparation. However, when the procedure involves the abdominal region, the following preparatory measures should be observed:
- Avoid increased gas formation with a special diet. A few days before the study, it is necessary to exclude the following foods: brown bread, confectionery sweets, fresh vegetables and fruits, legumes, dairy products and alcoholic beverages.
- 2-3 days before an MRI of the abdominal cavity, you must stop taking medications that contribute to the formation of gases in the intestines (for example, Duphalac).
- If before the examination the patient feels that the accumulation of gases could not be avoided, it is necessary to take a carminative (for example, Espumisan).
- It is advisable to go on a low-carbohydrate diet to relieve the work of the liver, pancreas and spleen for several days.
- If you suspect you have an allergic reaction to gadolinium, you can take a challenge test before the test.
- If you complain of persistent constipation, you can take a laxative or do an enema to cleanse the intestines before the MRI.
- If magnetic resonance imaging using a contrast agent is planned, and the patient is a breastfeeding woman, breast milk should be expressed into special storage bags and placed in the freezer 2 days before the examination. After the contrast study, you should not breastfeed the baby for 2 days, and simply express the milk.
- If the patient has abnormalities associated with the inability to control body movements, it is necessary to warn the doctor about this. Perhaps the procedure will be carried out by putting the patient into medicated sleep.
- If you feel excessive anxiety, a panic attack or fear occurs, you can take sedatives. However, this information should be disclosed to the doctor.
- Before performing an MRI of the abdominal organs, you must stop eating 6 hours before the examination, and drink water 4 hours before the examination. You should not drink carbonated water, coffee or tea on the day of the test.
- An MRI should take the results of previous examinations, if any.
Preparation and contraindications
No special preparation is needed, but the day before the test you must stop taking foods that increase gas formation, for example, black bread. The examination is recommended to be carried out on an empty stomach or at least 6-8 hours after the last meal. The clinic employee separately considers the possibility of conducting an examination if the patient has prostheses and implants in the body (depending on their location, material), as well as during pregnancy. All metal objects must be removed during the study to prevent the influence of magnetic radiation on them. Diagnostic time is about 30 minutes, taking into account data processing. Information is displayed on the monitor in digital form; the information reaches the patient or doctor on any electronic medium.
Procedure for performing an MRI of the abdominal organs

MRI of the abdominal cavity is carried out in the following order:
- The patient must remove all parts containing metallic compounds before entering the X-ray room. They can be both on clothes and on the patient’s body. Electronic gadgets and bank cards should also be left outside the office, otherwise they may distort the tomography results.
- Before starting the procedure, the doctor will interview the patient, study the existing medical history and photographs. The patient is required to fill out a consent form for tomography.
- The patient lies down on the medical table, and the medical staff uses special straps to secure the body. The table is placed in the tomograph and the machine is started. The equipment makes a lot of noise during scanning. Before the examination begins, the patient may wear earplugs. If he feels any discomfort or severe anxiety, he can contact the doctor through a special microphone located inside the tomograph.
- The doctor, being in the next office, monitors the patient through glass and receives images of organs in a three-dimensional projection on a computer monitor. The images are processed by the program, and the doctor records images that show abnormalities. Magnetic resonance imaging of the abdomen lasts from 30 to 50 minutes.
- A few hours after the end of the study, the doctor issues a conclusion, which the patient must show to the attending doctor. After this, a final diagnosis will be made.
Magnetic resonance imaging procedure with contrast
Assessment of the condition of organs located in the abdominal cavity is most often carried out using magnetic resonance imaging using a contrast agent. In this way, the path of blood circulation, the condition of blood vessels, as well as the presence of malignant neoplasms and metastases can be seen as clearly as possible on the monitor screen.
The contrast agent contains gadolinium metals, which are practically hypoallergenic and do not cause an allergic reaction in the patient, unlike iodine during computed tomography.
How the research works
In an MRI of the abdomen with contrast, the patient is given a drug based on gadolinium salts before the scan. The use of a contrast agent gives a more complete picture of the condition of the organs.
Before the examination, the doctor must consult the patient about diet and drinking habits. For several days before the procedure, it is prohibited to consume legumes, raw vegetables and fruits, sweets and baked goods, carbonated and alcoholic drinks, as well as some other foods. You should not drink anything immediately before the examination. To obtain reliable research results, you must carefully follow all recommendations received.
The scanning takes place in a tomography machine. The patient is placed on a sliding table and placed in a cylindrical chamber for 20–40 minutes. You must remain still during the examination. Do not be alarmed if you hear noises and clicks: they accompany the normal operation of the tomograph. In case of emergency communication with medical staff, there is a call button in the cell. After the examination, the doctor interprets the results. The images are given to the patient along with the report in printed form or on digital media.
Is it safe to have an MRI?
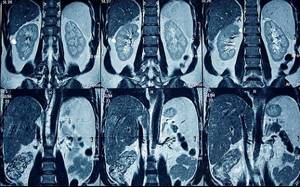
The magnetic resonance imaging procedure is recognized as the safest diagnostic method, given that the magnetic field induction is no more than 1.5 Tesla. The study does not use X-rays and the patient does not receive radiation exposure. Unlike computed tomography, MRI can be performed repeatedly, without restrictions and without maintaining certain intervals between procedures.
If we consider MRI using a contrast agent, then the level of safety here is also quite high. The contrast is based on gadolinium, which causes an allergic reaction in extremely rare cases. The substance does not harm the patient's health.
Advantages of the method
The MRI technique does not involve the use of ionizing radiation, which can cause the formation of free radicals in living tissues that damage cell membranes. Therefore, this diagnostic method can be used in examining patients as often as necessary in each specific case. This need arises, for example, during the treatment of patients with cancer, as it allows specialists to monitor the progress of treatment for this pathology.
Another important advantage of MRI is that modern tomographs make it possible to construct images of the organs under study in 3D, as well as obtain their sections in the projection required by the doctor. If you need an MRI of the abdominal organs in Moscow , then you can call our operators around the clock, they will sign you up for the procedure at one of the city clinics that is most convenient for you.
The cost of MRI is not the lowest compared to other studies, but performing this procedure allows you not only to establish a correct and accurate diagnosis, but also to avoid more traumatic research methods, for example, diagnostic laparoscopy.
Doctor diagnosing abdominal diseases

Doctors of different specialties can write out a referral for a magnetic resonance imaging procedure based on the indications and symptoms: general practitioner, oncologist, gastroenterologist, surgeon, urologist.
Timely examination of the abdominal cavity allows you to detect the disease in the early stages, when treatment will be most effective, and the pathological abnormality has not yet had time to cause serious damage to health.
You can find a suitable clinical diagnostic center on our website, where brief reviews of clinics performing magnetic resonance imaging procedures are presented. On your own or with the help of a specialist, you can sign up for a free MRI at a low price, and also receive a discount on your first appointment.
Benefits of abdominal tomography
The main advantage of abdominal tomography is the reflection of the area under study in three-dimensional format. The picture that is displayed on the screen is characterized by high accuracy, because it shows the development of even small pathologies. If necessary, the doctor can rotate the image to the desired angle.
Other benefits of MRI include:
- the equipment does not have a negative effect on the human body;
- High detail of the images makes it possible to identify pathologies even in the early stages;
- high degree of survey reliability.
The procedure is simple and does not require special preparation. It is carried out within 30-40 minutes. This is enough to make an accurate diagnosis.