The probability of becoming pregnant with twins, according to statistics, is approximately 2%. Moreover, before the widespread introduction of ART methods into medical practice, this happened even less often, only in 1 out of 90 cases.
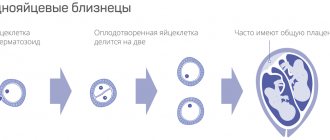
If both children developed from the same fertilized egg (that is, they are monozygotic), then they necessarily have the same sex and genotype. Twins are difficult to tell apart because they are very similar in appearance.
If embryos are formed due to the fertilization of two eggs by two sperm, then they can have different sexes and genotypes.
Predisposing factors
The chances of having twins increase if:
- there is a hereditary predisposition;
- the age of the expectant mother is more than 35 years;
- before starting to plan a pregnancy, the woman took COCs (in this case, the so-called rebound effect occurs);
- more than one embryo was transferred in the IVF program;
- The woman already has several children. According to statistics, in approximately 30% of cases the fourth pregnancy is multiple.
Signs
In many ways, the signs of singleton and multiple pregnancies are the same. In both cases, in the early stages, expectant mothers can quickly get tired and experience mood swings. Severe toxicosis is also not a specific symptom.
When carrying several fetuses, the abdomen increases in size faster, the first movements are noted earlier, and body weight increases more noticeably. However, as a rule, at these times the woman already knows that she is expecting twins, since an ultrasound scan reveals several fetuses in the uterus at once.
What is multiple pregnancy, how do twins differ from twins?
A multiple pregnancy is a pregnancy in which a woman carries two or more fetuses. If there are 2 of them, this is a pregnancy with twins, if 3 - with triplets. Each of the babies being carried is called a twin. There is an opinion that twins are children who have the same appearance, but if babies born from the same pregnancy do not look alike, they are twins or triplets. In fact, all children born to the same mother from the same pregnancy are called twins.

Multiple pregnancy develops if:
- fertilization of two or more mature eggs at the same time;
- atypical fragmentation of a fertilized egg.
In the first case, the twins are fraternal, or heterozygous. They can be of different sexes and look like any brothers and sisters. They may have the same blood type or different ones.
In the second case, identical or homozygous twins are born. They come in only one gender - both boys or only girls, have almost the same appearance, the same blood type and Rh factor.
Features of pregnancy
Since carrying twins is a serious burden on the female body, qualified doctors with experience in managing complicated pregnancies should monitor the condition of the expectant mother and babies until birth.
An ultrasound can establish the fact of a multiple pregnancy at about 6 weeks.
The scope of the examination as a whole is no different, however, some tests (for example, a coagulogram) need to be done more often in order to identify possible violations at the initial stage and promptly correct them.
Ultrasound examinations are performed monthly. If we are talking about monozygotic twins, then ZI in the second trimester (in the interval from 16 to 28 weeks) is carried out twice a month so as not to miss the development of such a complication as feto-fetal transfusion.
Ultrasound during multiple pregnancy
A multiple pregnancy is considered a high-risk pregnancy for various complications for the mother and fetus, since a woman’s body is more designed to carry one fetus. Therefore, during multiple pregnancies, it is necessary to conduct ultrasound more often and monitor the growth and development of the fetus. There are several types of twins, depending on the number of placentas and membranes.
Dichorionic diamniotic twins are the most favorable type of twins. Each fetus has its own placenta and its own amniotic space, separated from the other by the amniotic septum. The fruits can be of the same or different sex. The probability of delayed development of one of the fetuses is 20% (4 times higher than in a singleton pregnancy), premature birth is 5% (1% in a singleton pregnancy). In order to promptly identify these complications, it is necessary to conduct an ultrasound at 11-13 weeks, 18-22 weeks (as in a singleton pregnancy) and then every 4 weeks until birth (in a singleton pregnancy - at 32-34 weeks). If any complications are detected, the number of ultrasound scans may increase.
Monochorionic diamniotic twins - occurs when a fertilized egg splits into two parts. In this case, the fetuses have one common placenta and their own amniotic space. The fruits are always the same sex and completely genetically identical. The presence of a single placenta can lead to the development of specific complications associated with the fact that the vessels in this placenta can connect the circulatory systems of both fetuses. In this case, one fetus receives some blood from another fetus, and they both suffer from this: one has excess blood, which leads to increased stress on its heart; the second does not receive enough blood, oxygen and nutrients, and begins to grow more slowly, as a result of which it develops intrauterine growth retardation. This complication is called feto-fetal transfusion syndrome, and without timely treatment can lead to the death of one or both fetuses. In order not to miss this complication, it is necessary to do an ultrasound at 11-13 weeks (as in a singleton pregnancy), at 16, 18, 20, 22, 24, 26, 28 weeks of pregnancy. If signs of feto-fetal syndrome are detected, ultrasound should be performed even more often - once a week. If there are no signs of this syndrome before 28 weeks of pregnancy, then its development in the future is extremely unlikely, and ultrasound can be performed once every 4 weeks - as with dichorionic twins.
Monochorionic monoamniotic twins - occurs when a fertilized egg is divided into two parts, while the fetuses have a common placenta and a common amniotic space. The fruits are always the same sex and completely genetically identical. This is an extremely rare type of twins, and is accompanied by the greatest risk of complications, developmental delay and intrauterine death. In addition to the complications associated with a single placenta (see description above), the fetuses are located in a common amniotic space and are not separated by the amniotic membrane. This can lead to torsion and compression of their umbilical cords, stopping the flow of blood to one of them and, accordingly, its death. The risk of this complication is very high, so an ultrasound is performed every week of pregnancy, and if signs of umbilical cord torsion are detected, hospitalization and daily monitoring of the fetus are recommended; If the condition of one of the fetuses becomes critical, immediate delivery by cesarean section is required. Management of multiple pregnancies requires a highly qualified doctor and should be carried out in an expert center.
Childbirth during pregnancy with twins
Most often, twins are born at 34-36 weeks of pregnancy. Much less often, childbirth occurs at 38-40 weeks.
The doctor chooses the optimal method of delivery based on factors such as the condition of the mother, presentation of the fetus, the volume of amniotic fluid, and the risk of hypoxia (oxygen starvation). According to statistics, a caesarean section is performed in 2 out of 3 cases.
If a woman is expecting twins, she is hospitalized in the antenatal department 2 weeks before the expected date of birth.
If babies are born long before their due date, resuscitation and skilled care may be required.
Complications
When carrying twins, the risk of anemia, threat of miscarriage, premature birth, preeclampsia, isthmic-cervical and fetoplacental insufficiency increases.
In addition, it is possible:
- anembryony of one fertilized egg;
- intrauterine fetal death;
- feto-fetal transfusion (impairment of placental blood flow, due to which nutrients flow unevenly to the fetus), which is typical for twins who share a placenta and amniotic sac;
- fusion of two organisms, which is possible during a monozygotic pregnancy if the division of the egg occurs at a late stage. In this case, Siamese twins are born.

Twins
There is data on the frequency of twins with anomalies in the development of the uterus, characterized by its bifurcation (bicornuate uterus, having a septum in the cavity, etc.). The cause of polyembryony may be the separation of blastomeres (in the early stages of fragmentation), resulting from hypoxia, cooling, disturbances in the acidity and ionic composition of the environment, exposure to toxic and other factors. Multiple pregnancy can occur: as a result of fertilization of two or more simultaneously matured eggs, as well as the development of two or more embryos from one fertilized egg.
Twins formed from two (three, etc.) eggs are called fraternal (multi-ovular), those formed from one - identical. Origin of fraternal twins (multi-zygotic twins): it is possible for two or more follicles to mature (and ovulate) simultaneously in one ovary. There may be maturation of two or more follicles and ovulation in both ovaries.
A third way of origin of fraternal (multi-zygotic) twins is possible - fertilization of two or more eggs matured in one follicle. Origin of identical twins: most often the occurrence of identical twins is associated with fertilization of an egg that has two or more nuclei. a single embryonic rudiment at the cleavage stage is divided into two parts; from each part an embryo (fruit) is formed. Fraternal twins. Fertilized eggs develop independently. After penetration into the mucous membrane, each embryo develops its own aqueous and villous membranes; Subsequently, each twin develops its own placenta with an independent network of blood vessels; each fertilized egg, except for the chorion and amnion, has an independent capsular membrane (decidua capsularis). In some cases, anastomoses are formed between the vessels of independent placentas. Fraternal twins can be same-sex (both boys or both girls) or opposite-sex (a boy and a girl). Their blood type may be the same or different. Identical twins. Identical twins share a common capsular and villous membrane and a common placenta; The vessels (both arterial and venous) of both twins in the placenta communicate through numerous anastomoses. Each twin has a separate aqueous membrane; the septum between the fetal sacs consists of two aqueous membranes (biamniotic twins).
Identical twins always belong to the same sex (both boys or both girls), look alike, and have the same blood type.
In case of dizygotic twins, the membranes in the septum are located as follows: amnion - chorion, chorion - amnion; with monozygotic amnion—amnion. Important signs for the diagnosis are: blood type (and other blood factors), eye color, hair color, skin texture of the fingertips, shape and location of the teeth. In identical twins, these characteristics are completely the same. Fraternal twins share characteristics of similarity to the same extent as ordinary brothers and sisters.
COURSE OF MULTIPLE PREGNANCY
During a multiple pregnancy, increased demands are placed on a woman’s body: the cardiovascular system, lungs, liver, kidneys and other organs function under great strain. In this regard, multiple pregnancy is more difficult than singleton pregnancy.
- Pregnant women often complain of fatigue and shortness of breath, which worsens towards the end of pregnancy. The cause of shortness of breath is difficulty in the activity of the heart due to a significant displacement of the diaphragm by the fundus of the uterus, the size of which in a multiple pregnancy is larger than in a singleton pregnancy.
- Dilatation of the veins of the lower extremities often occurs. Towards the end of pregnancy, there is often an increase in the urge to urinate due to the pressure of the large fetal sac on the bladder.
- Pregnant women often complain of heartburn and constipation.
- In multiple pregnancies, toxicoses occur more often than in singleton pregnancies: vomiting, drooling, edema, nephropathy, eclampsia.
- In case of twins, polyhydramnios of one of the fetuses often occurs, which leads to a sharp enlargement and overstretching of the uterus, shortness of breath, tachycardia and other disorders. Polyhydramnios is more common in one of the identical twins. In some cases, polyhydramnios in one twin is accompanied by oligohydramnios in the other twin.
- Premature termination of multiple pregnancies often occurs.
- With twins, premature birth occurs in at least 25% of women.
- With triplets, premature termination of pregnancy occurs more often than with twins. The greater the number of fetuses gestated, the more often premature births are observed.
- The development of twins born at term is normal in most cases. However, their body weight is usually less than that of single fruits. There is often a difference in the body weight of twins by 200-300 g, and sometimes more.
- Uneven development of twins is associated with unequal supply of nutrients from the single placental circulation.
- There is often a difference not only in weight, but also in the body length of twins. In this regard, the theory of supergeneration (superfoetatio) was put forward. Proponents of this hypothesis believe that it is possible to fertilize eggs of different ovulation periods, i.e., the onset of a new pregnancy in the presence of an existing, previously occurring pregnancy.
- Due to uneven delivery of nutrients and oxygen, significant developmental disruption and even death of one of the twins can occur. This is more common in identical twins. The dead fetus is compressed by the second, well-growing fetus, amniotic fluid is absorbed, and the placenta undergoes regression. The compressed mummified fetus ("paper fetus") is released from the uterus along with the placenta after the birth of a live twin. Polyhydramnios in one fetus, which occurs during multiple pregnancies, often also interferes with the proper development of the other twin. With severe polyhydramnios, certain anomalies in the development of the fetus are often observed, growing with an excess of amniotic fluid. Occasionally, fused twins are born (fusion can occur in the head, chest, abdomen, pelvis) and twins with other developmental defects.
- The position of the fetus in the uterine cavity in most cases (about 90%) is normal. In the longitudinal position, different presentation options are observed: both fetuses are presented with the head, both with the pelvic end, one with the head, and the other with the pelvic end. With a longitudinal presentation, one fetus may be behind the other, making diagnosis difficult. Less commonly observed is the longitudinal position of one fetus and the transverse position of the other. The most rare occurrence is the transverse position of both twins.
- Position of twins in the uterus: both fetuses are presented with the head, one fetus is presented with the head, the second - with the pelvic end, both fetuses are in a transverse position
- During multiple pregnancies, women are specially registered and closely monitored. When the earliest signs of complications appear, the pregnant woman is sent to the pregnancy pathology department of the maternity hospital. Considering the frequent occurrence of premature birth, it is recommended that a pregnant woman with twins be sent to the maternity hospital 2 - 3 weeks before birth, even in the absence of complications.
RECOGNITION OF MULTIPLE PREGNANCY
Diagnosis of multiple pregnancy often presents significant difficulties, especially in the first half. In the second half, towards the end of pregnancy, recognition of twins (triplets) becomes easier. However, diagnostic errors occur during examinations at the end of pregnancy and even during childbirth.
When recognizing a multiple pregnancy, the following signs are taken into account:
- The enlargement of the uterus during multiple pregnancy occurs faster than during pregnancy with one fetus, so the size of the uterus does not correspond to the duration of pregnancy. The fundus of the uterus is usually high, especially at the end of pregnancy; the abdominal circumference during this period reaches 100-110 cm or more.
- The following signs are inconsistent and not sufficiently reliable: a) deepening of the fundus of the uterus (saddle uterus), the formation of which is associated with protrusion of the corners of the uterus by large parts of the fetus; b) the presence of a longitudinal depression on the anterior wall of the uterus, formed as a result of the adjoining of fetuses located in a longitudinal position to each other; c) the presence of a horizontal groove on the anterior wall of the uterus with the transverse position of the fetus.
- The small size of the presenting head with a significant volume of the pregnant uterus and a high position of its fundus also allows one to suspect a multiple pregnancy. The presence of this sign is explained by the fact that during the study, the head of one and the pelvic end (in the fundus of the uterus) of another fetus, lying slightly higher, are determined.
- Feeling the fetus move in different places and feeling parts of the fetus in different parts of the abdomen (both right and left) also indicate multiple pregnancy.
Fruit development by week
| 4-6 weeks | The formation of internal organs and the brain occurs. |
| 7-8 weeks | An ultrasound can examine the baby's heads and limbs. The height of each of them at this stage is about 4 centimeters. |
| 9-10 week | The internal organs are already formed. The kids move their arms. |
| 11-13 weeks | Babies master the basic reflexes: sucking, grasping and swallowing. At this stage, identical twins can already hug each other. |
| 14-15 weeks | Babies develop unique fingerprints that are different even between identical twins. |
| 16-18 weeks | The genitals are already fully formed. Multiparous women may feel the first movements. |
| 19-20 weeks | Babies begin to respond to sounds coming from outside. Women who will give birth for the first time also feel the movements. |
| 21-24 weeks | Children actively move and react not only to sounds, but also to light. |
| 25-28 weeks | Babies begin to accumulate subcutaneous fat. The lungs and immune system develop. |
| 29-32 weeks | Each child develops its own sleep-wake cycle. Usually at this stage they occupy a position in the uterus that will remain unchanged until childbirth. |
| 33-36 weeks | During this period, babies can already be born. |
| 37-40 weeks | If childbirth has not yet occurred, children gain more weight, but in any case they are smaller than their “singleton” peers. |
At what stage is twins or twins visible on ultrasound, how is the study carried out?
When an ultrasound examination is performed using high-quality modern equipment by a highly qualified specialist, a multiple pregnancy can be diagnosed as early as the 5th week. The monitor will show 2 or more echo-negative formations if fraternal twins develop.
During pregnancy with identical twins, diagnosis is difficult. Such a pregnancy can be detected at approximately 7–8 weeks, when the embryos are clearly visualized. However, even in this case an error is possible.
Ultrasound in the early stages is performed transvaginally. The woman lies on the couch on her back, bends her knees and spreads her legs apart, the diagnostician puts a condom on the vaginal sensor and inserts it deep into the vagina.
During the study, the sonologist determines the size of the uterus, fertilized egg and embryo, the number of embryos (or fetuses, if the study is carried out after the 8th week of pregnancy), their location in the uterus and the location of the chorion or placenta (after the 12th week). The development of children is also assessed, the presence or absence of pathologies or markers of chromosomal abnormalities.
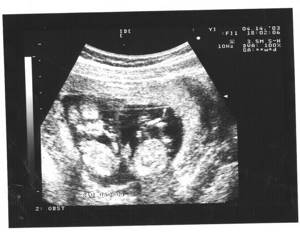
Ultrasound photo of twins at 20 weeks of pregnancy
Recommendations
Since pregnancy with twins entails an increased risk of various complications, expectant mothers need to be regularly monitored by a doctor and strictly follow all his recommendations.
If your pregnancy is progressing normally, try to lead a moderately active lifestyle and take walks in the fresh air more often. At the same time, you should not go far from home, especially in the later stages.
Don't lift heavy objects.
Normalize your sleep and wakefulness patterns. During the daytime, you can lie down several times to rest.
A visit to the pool will be beneficial, but it is better to avoid a bath or sauna for now.