| Ultrasound diagnostics in Moscow clinics. Ultrasound at home. | Reception is strictly by appointment, make an appointment by phone: +7 | Prices for services | Reviews about the clinic |
Ultrasound examinations are recommended annually. This is a highly informative examination method that allows you to examine in detail the condition of each internal organ.
The modern equipment of our center makes it possible to obtain high-quality images of organs in action and identify pathologies at an early stage.
Sign up for an ultrasound diagnostic by phone or by filling out the online form
| Select a clinic | All types of analyzes | Ultrasound at home | Calling a doctor to your home |
The most popular types of ultrasound examination
Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity (pancreas, liver, spleen and gall bladder).
This examination is carried out to monitor the size and structure of the abdominal organs. Using ultrasound, you can identify congenital anomalies and pathologies of the liver, pancreas or spleen. Also, through research, you can consider in detail:
- condition of the walls of the gallbladder (timely detect the presence of inflammatory processes, changes that have arisen due to metabolic disorders, the formation of malignant tumors);
- study of the gallbladder cavities;
- condition of the biliary tract and blood vessels in the abdominal cavity.
In addition, ultrasound will help to timely identify the initial stages of intestinal or stomach disease.
Preparing for the study
1. Limit food intake and fluid intake; 2. Eliminate alcohol and nicotine; 3. Stop chewing gum 5-7 hours before the procedure. Reliable results will be obtained if the study is performed in the morning and on an empty stomach. Ultrasound of the urinary system The examination will help identify congenital malformations of the urinary system and will help to correctly assess:
- sizes of examined organs;
- structure of organs and renal parenchyma;
- the condition of the pyelocaliceal cavity, where urine accumulates;
- the presence of pathologies of kidney development (focal or diffuse);
- presence of stones in hummocks;
Preparing for the study
1. 60 minutes before the test, you must drink at least 700 milliliters of liquid (plain water without gas); 2. Do not relieve minor needs; 3. Eating before an ultrasound is allowed.
Ultrasound of female genital organs
Using this ultrasound, the gynecologist will find out:
- parameters and structure of the uterus, fallopian tubes and ovaries.
- the presence of congenital pathologies of the development of the genital organs.
- the presence of diseases in the early stages.
- the presence of pregnancy in the earliest stages and the condition of the fetus.
The examination can be carried out in different ways - vaginal or abdominal. The choice will depend on the situation and the task facing the diagnostician. Preparation for the study depends on the method of conducting the study.
Ultrasound of the pelvic organs in men
An ultrasound examination is necessary for a correct assessment of the condition of the organs of the reproductive system; it will help:
- identify various diseases at early stages;
- determine the presence of inflammatory processes;
- exclude or confirm the presence of malignant tumors.
The examination is carried out abdominally and rectally.
Preparing for the study
1. If the examination is carried out abdominally, then you need to drink 500-700 ml of water in advance to fill the bladder before the examination. 2. If the ultrasound is performed rectally, first cleanse the body with enemas. The first is performed in the evening, the second - early in the morning. Eating is allowed before the procedure; fluid intake is not required.
Ultrasound of the fetus during pregnancy
Ultrasound examination of the expectant mother is carried out in stages:
- The first study is at 9-14 weeks.
- The second is at 20-24 weeks.
- The third is at 30-34 weeks.
The examination is necessary to monitor fetal development and timely detection of congenital pathologies or developmental anomalies. No preparation for the study is required.
Ultrasound of the endocrine system
Ultrasound examination of the thyroid gland helps to obtain information about the structure and size of the organ, as well as to detect developmental pathologies in time. Does not require special training.
Ultrasound of the mammary glands
The study helps diagnose breast diseases at an early stage and identify the presence of cysts and other formations.
The examination sometimes includes examination of the axillary lymph nodes. Does not require preliminary preparation. What other ultrasound examinations are performed? Along with the above, there are also rarely prescribed specific ultrasounds. These, for example, include studies of the salivary glands, lymph nodes, postoperative scars, and joints.
Ultrasound in gynecology and endocrinology
1. Ultrasound of the thyroid gland.
Ultrasound examination of the thyroid gland is the basis of endocrinology. It allows you to detect the presence of nodes or cysts, determine changes in the size of the thyroid gland or its structure. It is with the help of ultrasound that malignant neoplasms can be detected in time, which will allow the doctor to prescribe the necessary treatment and avoid serious consequences.
2. Ultrasound for pregnant women.
Ultrasound examination of pregnant women is carried out not only to determine gender, but also to monitor the development of the fetus. The harmonious development of the limbs, the absence of any pathologies - all this would be impossible to determine without ultrasound.
3. Ultrasound of the pelvic organs.
There are two types:
- Abdominal - i.e. without introducing an examination device into the body;
- Transvaginal - with the insertion of a sensor inside and a more detailed study of the internal organs of the small pelvis.
The decision to prescribe one type of ultrasound or another is made by the doctor. Examinations without insertion of a sensor are usually prescribed for children, whose anxiety may affect the results. At the same time, ultrasound with the introduction of a sensor is not prescribed to all adults, being limited only to special cases: for example, in the presence of pain in the lower abdomen or bleeding not associated with menstruation.
4. Ultrasound of the mammary glands.
Breast cancer is the most common cancer among women. And the cancer is getting younger. Today, women under 40 are beginning to encounter it more and more often.
The most reliable way to avoid serious consequences is to visit a gynecologist and mammologist annually and undergo an ultrasound examination. This is especially true for those women who have been diagnosed with mastopathy, a dishormonal disease that occurs in more than half of the female population.
5. Ultrasound of the pancreas.
Diabetes is a serious disease associated with improper or insufficient production of insulin in the pancreas. Ultrasound of the pancreas helps to diagnose malfunctions in its functioning in the early stages and prevent the development of dangerous diseases, including cancer.
6. Ultrasound of the adrenal glands.
The most common reason for prescribing an ultrasound examination of the adrenal glands is a suspicion of hormonal changes, which can manifest themselves in the form of the following symptoms:
- Sudden weight gain and problems losing it
- Sexual dysfunction, potency
- Sudden changes in the menstrual cycle
- Hair problems: excessive or insufficient
- Muscle weakness
Using the ultrasound results, the doctor will be able to determine the presence of pathologies: cysts, tumors, inflammation or enlargement of the adrenal glands, which will ultimately help to create an objective picture of the state of health and prescribe hormonal therapy or another type of treatment.
Difference between MRI and ultrasound
Before we look at how MRI of joints differs from ultrasound, it is necessary to give clear definitions of each procedure.
Ultrasound examination is a diagnostic technique; scanning is carried out using ultrasonic waves. As a result, the doctor examines the condition of soft tissues and organs. The procedure is harmless. In this case, the doctor reads information about the condition of the meniscus, periarticular soft tissues, and cruciate ligament, but is not able to scan the bones and lungs. MRI is used to study bone tissue.
An MRI is a large magnet that produces magnetic waves within a specific magnetic field. During an MRI scan, the doctor examines all tissues and organs. The procedure can be used repeatedly and allows one to study the dynamics or consequences of an injury or disease. The question of which is better: MRI or ultrasound is not relevant. The difference is in information content, reliability and price.
Virtual colonoscopy
The method is the construction of a model of the gastrointestinal tract with the ability to study the relief of the walls of the tract, neoplasms, defects of the mucous membrane, and developmental anomalies. The image is obtained as a result of a computed tomography scan of the abdominal cavity with preliminary expansion of the gastrointestinal tract cavity with air.
Indications and preparation for the procedure are similar to other instrumental examination methods. The advantage of virtual colonoscopy is that it is non-invasive, painless for the patient, and the ability to build a detailed three-dimensional model of the gastrointestinal tract. The method is used when an oncological process in the gastrointestinal tract and adjacent tumors of the abdominal cavity and pelvis is suspected, as well as to monitor postoperative changes in the large intestine. The examination is prescribed when an intestinal ultrasound or colonoscopy cannot be performed due to contraindications.
The disadvantage of this method is the inability to perform surgery or take material for research. Due to the use of ionizing radiation, the method has limited use in pregnant women and children.
How does ultrasound work?
Ultrasound travels freely through empty spaces and liquids, but is reflected from solids. The denser the structure of an organ, the stronger it reflects ultrasonic waves.
During the examination, the doctor uses a special sensor that emits ultrasonic waves and records those that return to him, reflected from the internal organs. The received signal is transmitted to the device and converted into an image on the monitor. The more waves an organ reflects, the lighter it appears on the screen.
During an ultrasound, the doctor can not only obtain an image, but also observe the functioning of the organ in real time.
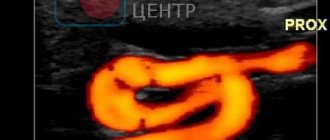
When ultrasonic waves are reflected from a moving object, their frequency changes. This phenomenon is called the Doppler effect. Thanks to it, you can study the direction and speed of blood flow in large vessels. This study is called Doppler sonography.
How is the examination carried out?
Often, an ultrasound examination is performed with the patient lying on his back on a couch. If you need to turn on your side, the doctor talks about it.
The procedure is carried out as follows:
- the patient takes off his clothes and provides for examination that part of the body that is necessary for this diagnosis;
- The doctor lubricates the surface of the skin with a special gel to ensure good sliding of the sensor and its maximum contact with the skin;
- The duration of the examination depends on the type of diagnosis and can range from 15 to 40 minutes.
At the end of the study, the doctor writes a conclusion, assessing all indicators. He compares the results with the norm and assesses possible pathological processes. Each organ has its own digital indicators.
Some methods for diagnosing diseases in our clinics:
- Calling a doctor to your home
- Diagnosis of urological diseases
- Diagnosis of gynecological diseases
- Tests in the clinic and home visits
- Diagnosis of skin diseases
- Diagnosis of cardiac diseases
- Diagnosis of surgical diseases
- Diagnosis of ENT diseases
- Gastroscopy for adults and children
- Removal of skin tumors
- Diagnosis of sexually transmitted infections
This article is posted for educational purposes only and does not constitute scientific material or professional medical advice.
Author:
Kasabov Alexander Vladimirovich Urologist, Candidate of Medical Sciences, Ultrasound Doctor
Back to section
Advantages of performing ultrasound at Euroonco
In Euroonko clinics you can undergo ultrasound examination of the mammary glands, abdominal organs, and pelvis. We perform endosonography of the esophagus, stomach, large and small intestine, and chest using an Olympus expert-class device. We provide our patients:
- Research of any degree of complexity, including endoscopic ultrasound, using expert-class devices.
- Comprehensive examination, the opportunity to get advice from an oncologist, oncologist, gynecologist, oncologist, chemotherapist and other specialists.
- Expert opinion, drawing up a program for further examination and treatment based on ultrasound results.
- The clinic's convenient location is easy to reach by metro and private transport.
What is examined on an ultrasound
Using ultrasound waves, you can see any human organ online. Ultrasound examines:
- Abdominal organs (liver, gall bladder, bile ducts, spleen, pancreas, large and small intestines, stomach).
- Organs of the urinary system (kidneys, adrenal glands, bladder).
- Pelvic organs (ovaries, uterus, early pregnancy detection).
- Heart (determination of arrhythmia, lack of blood supply, necrotic changes, myocardial inflammation, pericarditis, etc.).
- Thyroid gland (enlargement of the organ, inflammation, tumors, cysts).
An ultrasound examination allows you to assess the condition of the organ being examined. Its shape and size, wall thickness, structure, echogenicity (ultrasound conductivity), identify neoplasms, stones (kidneys, gall bladder).
Answers to frequently asked questions about ultrasound diagnostics:
- Is ultrasound harmful?
- Where can I get an ultrasound done?
- How to properly prepare for an ultrasound?
- What organs are examined by ultrasound?
- What diseases are ultrasound used to diagnose?
- Is it possible to do an ultrasound at home?
- What symptoms require an ultrasound?
- How often should an ultrasound be done?
- Do they do ultrasounds for children in your clinic?
- Can I get the transcript and ultrasound images in hand?
- What organs are examined during an abdominal ultrasound?
- What organs are examined during a pelvic ultrasound?
- Ultrasound in Moscow
- Paid ultrasound
- What other diagnostic methods are used in your clinic?
- How to sign up for an ultrasound?
How is this research carried out?
Usually, no special preparation is required before an ultrasound. If an ultrasound examination of the liver and gallbladder is to be performed, the patient is asked not to eat anything for several hours. Some time before scanning the genitourinary system, the patient is given several glasses of water to drink and asked not to urinate. A full bladder pushes back the bowel loops and provides a better view.
An ultrasound can last from 15 to 45 minutes. The doctor places the patient on the couch in a position that will provide the best visualization of the organ being examined. A special gel is applied to the skin area and an ultrasound sensor is placed. During the examination, the doctor can move the sensor, rotate it at different angles, apply slight pressure, ask the patient to change position, or turn over to the other side. There is no pain or any discomfort.
Sometimes, in order to better examine the organ of interest, the doctor inserts a special thin sensor into the vagina or rectum. This may cause some discomfort; you will have to be patient.
After the examination, the ultrasound diagnostic doctor will issue the result on a special form.