Full text of the article:
Chronic gastritis is an inflammation of the gastric mucosa, which leads to changes in its structure. According to some studies, more than half of the world's population suffers from chronic gastritis, but not all people know about their disease.
One of the most common causes of chronic gastritis is helicobacter pylori (HP) infection. The main danger of Helicobacter pylori gastritis is that it is difficult to diagnose due to the lack of symptoms. Often patients do not feel any discomfort: pain or nausea, so they do not consult a doctor. Meanwhile, prolonged development of gastritis without the necessary treatment can lead to stomach cancer.
Is it necessary to get tested?
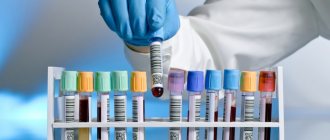
Timely tests make it possible to clarify the preliminary diagnosis and exclude the patient from other more serious diseases that may have similar symptoms. The following tests will be indicative for the doctor:
- general blood test (indicators of the number of leukocytes, hemoglobin and red blood cells will allow us to judge the presence of an inflammatory process in the body and possible internal bleeding);
- biochemical blood test (helps evaluate metabolic processes, serum iron is important to detect gastritis, and pancreatitis or hepatitis can be detected thanks to certain liver or pancreatic enzymes);
- A blood glucose test must be done by everyone who seeks medical help; it allows one to detect diabetes mellitus; if internal bleeding is detected, it is necessary to find out the patient’s blood type and Rh factor, since an emergency blood transfusion may be required;
- A general urine test can test kidney function, and a stool test for occult blood can test the theory of internal gastrointestinal bleeding.
What is research?
The fibrogastroduodenoscopy procedure, or as it is abbreviated as FGDS, is performed on an outpatient basis for the purpose of:
- visual assessment of the condition of the mucous membrane of the upper gastrointestinal tract (color, presence of erosions, ulcerations, neoplasms);
- obtaining information about the condition of blood vessels, assessing the risk of bleeding;
- studying the nature and relief of the mucous epithelium of the gastric wall;
- performing a targeted biopsy for histological analysis;
- determining the acidity of digestive juice and the presence of Helicobacter, which causes the development of peptic ulcers.
It also allows you to accurately identify or refute the presence of pathological changes and make an accurate diagnosis. When additional examination of the condition of the esophagus is required, EGDS may be prescribed - esophagogastroduodenoscopy, a similar method that greatly expands diagnostic capabilities.
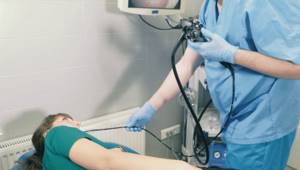
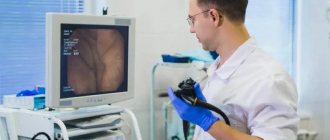
Manipulations are performed using an endoscope that penetrates the esophagus, stomach or duodenum. It is a thin fiber optic tube equipped with a microscopic camera at the end. As it moves through the digestive tract, it transmits an image to the monitor. If a more thorough examination is necessary, the doctor has the ability to rotate the probe, changing the internal position of the video device and the shooting angle. Due to its flexibility, it is able to penetrate into the most difficult to reach areas.
Why is an endoscopic examination of the stomach prescribed?
Endoscopy of the stomach makes it possible to obtain an image of its mucous membrane. In addition, during the endoscopic examination, the doctor takes samples of the mucous membrane, which helps to clarify the preliminary diagnosis. Research needs to be done on an empty stomach. The patient can eat food no later than 10-12 hours before the procedure, and for two hours he should refrain from drinking liquids, as well as from smoking. To sign up for gastric endoscopy, the patient must receive a referral from a general practitioner and also have a compulsory health insurance policy.
Kinds
FGDS is considered a procedure that does not pose a threat to the patient’s health, which, however, can hardly be called pleasant. Of course, this does not diminish its significance and effectiveness, because it is a highly accurate diagnosis and allows us to identify both minor disorders and serious gastrointestinal pathologies at an early stage. Ordinary people who have ever experienced this research method have formed the opinion that it is carried out only in one situation - exclusively to identify the disease and the severity of its course. The use of fiber-optic image transmission technology allows not only to monitor the internal surface of the gastrointestinal tract, but also to perform a number of other, no less important and significant manipulations.
Depending on the purpose of the appointment, today there are three types of FGDS.
Diagnostic
Since gastroscopy is considered one of the highly informative methods, it is primarily used as a tool for a thorough examination of the gastrointestinal tract to confirm the diagnosis if there are patient complaints. Indications can be considered:
- feeling of discomfort in the epigastric region;
- belching, burning, nausea ending in vomiting;
- deterioration in the passage of food during meals;
- rapid loss of body weight due to lack of appetite;
- food intolerance for no apparent reason;
- suspicion of internal bleeding due to a sharp decrease in hemoglobin.
Medical
For therapeutic purposes, it is recommended to do FGDS of the stomach if necessary:
- performing polypectomy (removal of small formations);
- stopping bleeding;
- local administration of drugs in the form of wall irrigation;
- carrying out therapy for peptic ulcer disease.
The decision on the need for the initial procedure and the timing of its implementation is made by the gastroenterologist. As a rule, it needs to be done again some time after the diagnosis has been clarified.
Preventative
Due to its absolute safety, doing FGS to monitor the internal state of the gastrointestinal tract is recommended for people with diseases of the digestive system during a period of stable remission. The optimal frequency is at least once every 10-12 months, but if there is a tendency to develop peptic ulcers, the study can be performed more often. What exactly and how many times a year is determined by a specialist.
For the purpose of prevention, diagnosis is performed in women when they are planning pregnancy. This need is due to the fact that during the gestation period, expectant mothers increase the likelihood of disruption of the digestive system. The availability of accurate diagnostic results expands the possibilities for choosing medications to alleviate early toxicosis or other pathologies.
After the prescribed examination, consult with your therapist.
If gastritis was detected during the research, it is necessary to additionally diagnose helicobacter pylori. This can be done using several tests: determination of antibodies in the blood (if the patient has not previously been treated for this infection); examination of biopsy samples of the gastric mucosa.
Some stomach diseases require adherence to a certain diet; your doctor will tell you about the required diet. The patient must strictly follow all prescriptions throughout the entire treatment period. The duration of treatment is also determined by the doctor, who also sets a date for re-examination. After completion of treatment, it is necessary to evaluate its effectiveness; this can be done only a month after stopping the medication.
Frequency
There is no clear answer to the question: how often can gastroscopy of the stomach be done. Prescribing the amount and frequency of intervention is within the competence of the gastroenterologist.
The frequency of endoscopic examination is directly dependent on the goals set for the specialist - diagnosis, treatment or prevention.
- At the initial visit, based on complaints, laboratory test results and medical history, the patient undergoes a gastroscopy. In the absence of pathologies, conservative therapy is carried out in relation to him and this is where medical intervention “in internal affairs” ends. In case of gastritis or cancer, the test is ordered again, but only after the course of treatment is completed or surgery is performed.
- Several times during the treatment course within a short time interval. The goal is to monitor the effectiveness of the chosen therapeutic technique, irrigation of the walls of the stomach and duodenum with drugs or other medical manipulations.
- No more than once a year in case of uncomplicated disease of the stomach or esophagus in order to promptly monitor possible deterioration of the patient’s condition.
- As a prophylactic agent in children over 6 years of age and pregnant women, including those suspected of developing a peptic ulcer or in case of surgery to remove a tumor in the gastrointestinal tract.
In the absence of contraindications, the study can be carried out several times a year, but not more than once a month.
It is within 30 days that the results of the previous procedure are considered valid.
Gastroscopy methods
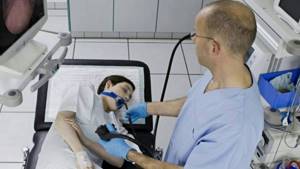
- Classic procedure with swallowing a probe. The advantages of this procedure are the ability to take tissue for biopsy or cauterize bleeding areas in the gastrointestinal tract. When using modern ultra-thin gastroscopes, pain is minimized. Before inserting the probe, the root of the tongue is treated with an anesthetic (local anesthesia is administered), the person is conscious, but the gag reflex goes away, which makes the procedure difficult and prevents relaxation. The probe can be inserted either through the mouth or transnasally (into the nose), while there is no gag reflex, and the essence of the study does not change.
- In cases where the patient cannot cope with his fear, or with an increased gag reflex, gastroscopy is performed in his sleep. The patient is put into a state of medicated sleep using a sleeping pill and the procedure is carried out. The drugs that doctors use are absolutely safe, and you can go home an hour or two after gastroscopy.
- Chromogastroscopy is an additional technique that is performed using a dye. It is sprayed onto the walls of the stomach and better visualizes the lesions.
- Capsule gastroscopy. A method that can be called unique. The patient swallows a special disposable capsule that looks like a regular tablet, but is a microchamber with sources of light and radio signals and a battery that ensures the device operates for eight hours. This capsule “travels” through the gastrointestinal tract, records and transmits information about the state of the organs to a special device. It is excreted naturally, without causing any discomfort to the subject. A huge advantage of this type of gastroscopy is that the entire gastrointestinal tract, including the intestines, can be examined.
- Endosonography is a study combining gastroscopy and ultrasound. It is performed using a special type of endoscope with an ultrasonic sensor at the end.
Contraindications
If a decision is made about the advisability of gastroduodenoscopy, the patient must first undergo a full examination to identify possible contraindications. If previously the procedure was carried out in outpatient medical institutions under the direction of a gastroenterologist, now it can be performed at any time in a private clinic for a fee.
If multiple interventions are necessary, doctors can still limit its frequency during periods of exacerbation of chronic diseases, such as gastritis. When planning an endoscopic examination for the first time (taking into account the above reasons), it would be useful to familiarize yourself with the list of contraindications for its implementation. They are considered conditionally absolute due to the need for consultation with other highly specialized specialists: a cardiologist, a psychotherapist. The list includes:
- problems with the heart and blood vessels - arrhythmias, heart attacks, strokes;
- mental disorders;
- hypertension, accompanied by frequent crises;
- blood diseases;
- esophageal stenosis;
- rehabilitation period.
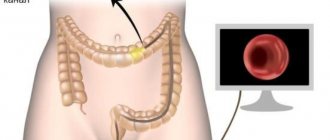
Colonoscopy
Colonoscopy is a technique for endoscopic examination of the colon using a video colonoscope. It has many advantages: the method makes it possible to examine the mucous membrane,, if necessary, take tissue samples (biopsy), and administer a drug. Modern devices allow the procedure to be performed without pain, and the patient can quickly return to normal life.
What is the purpose of a colonoscopy?
Using colonoscopy, you can diagnose many intestinal diseases: Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, diverticula, polyps, colon cancer.
The procedure is indicated for:
- Suspicion of colon tumors
- Inflammatory phenomena
- Pain, discharge of blood, mucus, pus from the anus
- Sensation of a foreign body in the rectum
- Stool disorders (constipation, diarrhea)
- Age after 40 years (once a year)
The doctor evaluates the color of the mucous membrane, the diameter of the intestinal lumen, vascular pattern, and inflammatory changes in the walls. Colonoscopy is the “gold standard” for diagnosing colon cancer pathologies.
Colonoscopy of the colon
On the eve of the procedure, the patient takes a relaxing drug (Fortrans or Moviprep). No need for enemas! Before starting the procedure in the clinic, the endoscopist collects an anamnesis (conducts a conversation), after which the patient lies on his left side, with his knees pulled up to his chest. The tube is inserted through the anus with moderate air supply and pushed forward. Sometimes the doctor may ask you to change position and roll over onto your back. There may be slight discomfort as you pass through the bends of the intestine. If during a colonoscopy, the doctor notices an abnormality, he takes tissue samples for analysis. Study time is up to 20-25 minutes.
Colonoscopy of the intestine
Colonoscopy is a rather complex procedure, its success depends on both the doctor’s experience and the patient’s attitude. The doctor assesses the condition of the colon mucosa. The intestinal loops are straightened by pumping air. The procedure is performed with a special endoscope, which allows detection of focal or segmental lesions. The doctor lubricates the anal area with anesthetic cream. After passing through the colon, a flexible tube can also be inserted into the small intestine; the illuminator operates on a xenon lamp: this eliminates burns to the mucous membrane. During manipulation, a small amount of air is pumped into the intestine. Using an endoscope, the doctor makes a visual assessment of the condition of the mucosa and, if necessary, performs a biopsy for histological examination.
Advantages of performing colonoscopy using endoscopic medical equipment
Our clinic strives to ensure that the colonoscopy procedure is as informative and safe as possible, therefore it uses only the best equipment made in Japan. Pentax endoscopes provide fast, accurate examination without the risk of complications.
Pentax is:
- Advanced imaging technologies in modern endoscopy
- Japanese quality and reliability
- Exceptionally high image resolution
- Special control of tube insertion: even softer, even safer
- Innovative computer programs for data processing
- Compliance with hygiene norms and standards
Expert-level equipment will allow you to identify possible pathology and begin treatment as soon as possible without the need for expensive additional studies.
Preparing for a colonoscopy
The purpose of preparing for the procedure is to allow the doctor to better examine the intestinal mucosa. There should be no feces in the lumen.
The patient needs:
- Follow a slag-free diet for 2-3 days per procedure: exclude foods rich in dietary fiber, do not eat brown bread, vegetables, fresh herbs, fruits, legumes, do not drink milk and carbonated drinks. All this causes bloating. You can eat lean fish, fresh meat, drink tea, and plain water. On the day of the examination you cannot have breakfast, you can drink water.
- To cleanse the intestines the day before - take a special drug: now there are means designed to prepare the patient for endoscopic examinations. They will help make the colonoscopy procedure more comfortable. The drug must be diluted in water and simply drunk. The intestines are cleansed gently and quickly. These are drugs such as Fortrans or Moviprep. There is no need to do enemas. For more detailed information about preparing for a colonoscopy, you can call the reception desk or visit the Diagnostic Medical Center website.
Colonoscopy “in a dream”, under anesthesia
Maximum comfort for the patient during endoscopic examinations is to perform a colonoscopy “in your sleep.” The clinic staff works using world achievements in the field of proctology and offers to conduct research without pain, discomfort and painful completion of the procedure.
Colonoscopy using non-toxic, safe drugs that put the patient to sleep is a guarantee of complete relief from pain and discomfort. Everything goes with comfort, awakening is easy, without nausea or dizziness. The high quality of medications used in our clinic minimizes the risk of complications that can occur during anesthesia (vomiting, heart rhythm disturbances, respiratory functions). Thus, sleep colonoscopy is the method of choice for patients with a high pain threshold or simply sensitive people .
How should you behave after a colonoscopy and colonoscopy “in your sleep”?
Medicinal sleep is stopped after the procedure. You may experience some feeling of fullness in your abdomen. You may need to spend some time in the clinic (the doctor will tell you about this); for this purpose, comfortable rooms are provided for the patient to rest. Then you can return to normal life. No food restrictions required. It is better not to drive a car on the day of the procedure. Qualified performance of all manipulations ensures safety for the patient and provides accurate information to the attending physician.
You can make an appointment for a consultation with our specialists by phone. 425-888 or via the feedback form.
What is gastroscopy?
This is a type of endoscopic examination in which the mucous membrane of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum are visually examined. The study is carried out using a gastroscope - a special instrument that is a flexible tube with an optical system. The gastroscope is inserted into the stomach through the mouth and esophagus and can be used both to visualize the condition of internal organs and to perform a biopsy.