- Home /
- Center services /
- Ultrasound in early pregnancy
Is it worth getting an ultrasound in early pregnancy? Why might you need an ultrasound before 10 weeks of pregnancy? Is it harmful to perform an ultrasound of the fetus in the early stages? For what reasons is ultrasound in the early stages extremely necessary? Where can an ultrasound be performed in early pregnancy?
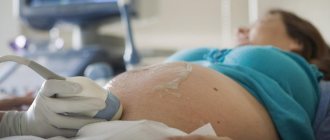
As you know, pregnant women routinely undergo 3 ultrasound diagnostic procedures during the entire period of bearing a child (in the 1st, 2nd and 3rd trimester) during a normal pregnancy. Ultrasound in the early stages of pregnancy is considered an unscheduled procedure and is prescribed by an obstetrician-gynecologist for certain indications. It is not recommended to do this procedure just like that, since during the period up to 10 weeks there is an active process of formation of the main organs and systems of the fetus. In addition, ultrasound in the early stages is very informative.
What are the indications for an unscheduled ultrasound during pregnancy?
An obstetrician-gynecologist should prescribe an ultrasound in the early stages only in a situation where he suspects any deviations from the normal process of pregnancy. It could be:
- Presence of chronic diseases in a pregnant woman (diabetes mellitus, hepatitis, oncology, etc.);
- The presence of congenital pathologies of the genitourinary system and pelvic organs in a pregnant woman;
- Unsuccessful pregnancies in the past: frozen pregnancy, ectopic pregnancy, miscarriages, premature birth, birth of a child with pathology;
- Presence of a pregnant woman complaining of pain in the lower abdomen, vaginal discharge;
- Other indications that cause the doctor to doubt the normal course of pregnancy.
Thus, with the help of an unscheduled ultrasound in the early stages, it is possible to accurately determine the fact of intrauterine pregnancy and clarify the timing of conception based on the size of the embryo. An ultrasound examination can be performed as early as the third week of pregnancy and visualize the fertilized egg in the uterine cavity.
At a period of 3-4 weeks, ultrasound is performed extremely rarely, only if the obstetrician-gynecologist is concerned about the diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy or in the case of an IVF procedure. It is carried out to confirm normal conception and set the exact date. Using ultrasound, you can see the developing legs and arms of the fetus and the umbilical cord.
At a period of 5-6 weeks, the ultrasound doctor will determine how many embryos are in the uterine cavity, and can already hear the fetal heartbeat. At this stage, the baby’s neural tube is formed, which will later turn into the brain and spinal cord. The formation of the lungs, intestines, liver and other organs occurs. The testes (sex glands) are formed, which begin to produce testosterone. If there is not enough hormone, the embryo will develop as a girl.
At 7-8 weeks, the fetus has almost formed all its organs, but it is still too small for a normal assessment of the anatomical structures. During this period, an ultrasound doctor can diagnose a frozen pregnancy or uterine hypertonicity, which can threaten miscarriage. It is also possible to evaluate the fetal heartbeat and calculate the PDR.
At 9-10 weeks, the fetus already looks like a small person with legs, arms and fingers, the movement of which can already be recorded. An ultrasound can identify possible pathologies in the uterus, placenta and umbilical cord and assess their threat to the life of the unborn child.
Signs of ectopic pregnancy on ultrasound
Characteristic ultrasound signs of ectopic pregnancy:
- absence of a fertilized egg in the uterine cavity, despite the presence of all symptoms of pregnancy;
- increase in size of the uterus;
- pathological increase in endometrial thickness;
- blood in the cavity of the fallopian tubes;
- intense blood flow at the site of embryo implantation;
- the presence of a false fetus in the uterus;
- foreign tumor in the ovary or fallopian tube;
- an accumulation of fluid is detected in the recess of the peritoneum.
Where can I get an ultrasound done during early pregnancy?
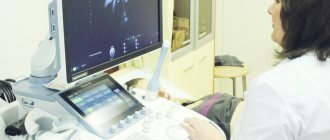
Medical specializes in providing a wide range of services related to ultrasound diagnostic examinations, including performing ultrasound in early pregnancy. In our center, the procedure is carried out using modern equipment, which gives the most accurate results during ultrasound in the first weeks of pregnancy.
An unscheduled ultrasound is performed in the most comfortable conditions for a pregnant woman in compliance with all norms and quality standards. Our patients do not stand in line and do not languish in long waits at the doctor’s office. Ultrasounds in the early stages of pregnancy in St. Petersburg are performed by experienced doctors - diagnosticians, the results are issued immediately after the end of the session.
Call us and receive a detailed consultation over the phone, specifying the cost of the procedure, the name and qualifications of the ultrasound doctor. Sign up for a consultation by calling ext. 1 +7 or using the form on the website.
Ultrasound of the kidneys during pregnancy
During pregnancy examinations, special attention is paid to ultrasound examination of the kidneys.
When you have kidney stones, various symptoms appear:
- renal colic;
- blood in urine;
- nausea and vomiting;
- chills and high temperature.
An ultrasound of the kidneys during pregnancy will allow you to identify the disease before alarming symptoms appear and treat it in time.
In addition to examining the kidneys during pregnancy, it is recommended to undergo examination of the genitourinary system, mammary glands, adrenal glands and thyroid gland. All this will show the general condition of the organs and, based on this information, will allow you to draw conclusions and prescribe the correct treatment.
As the fetus grows, the abdominal organs shift slightly in late pregnancy. This sometimes causes an incorrect diagnosis.
To prevent this from happening, the examination should be carried out by experienced diagnosticians using modern ultrasound scanners.
Medicenter clinics are equipped with modern Japanese diagnostic equipment, and doctors have been trained at the best medical universities in the country and have been working in the field of ultrasound diagnostics for many years.
Ultrasound at 18-21 weeks of pregnancy (second screening)
- Determination of the number of fetuses, their position and presentation.
- Measuring the main fetometric indicators (sizes) of the fetus and determining their correspondence to the gestational age.
- Study of the ultrasound anatomy of the fetus (detection of most developmental defects determined by echography), as well as the uterus and its appendages.
- Assessment of the amount of amniotic fluid, location, thickness and structure of the placenta.
At this stage of pregnancy, an ultrasound scan determines the sex of the child by 90-100%.
Indications for ultrasound before 10 weeks of pregnancy
- The presence of tumor formations of the uterus and/or ovaries and suspicion of their presence.
- Suspicion of ectopic pregnancy.
- Discrepancy between the size of the uterus, determined during a two-manual examination, and the gestational age determined by the first day of the last menstruation.
- The presence of an intrauterine contraceptive device and pregnancy.
- Trauma and intoxication in a pregnant woman.
- The need for a biopsy (obtaining tissue for research) of the chorion.
- A burdened obstetric and gynecological history (miscarriages and other complications in early pregnancy, abnormal development of the embryo in previous pregnancies, etc.).
Remember that only a doctor can prescribe the timing of an ultrasound scan during pregnancy . You should not sign up for this study on your own to satisfy your personal interest.
Ultrasound at 30-34 weeks of pregnancy (third screening)
- Assessment of the functional state of the fetus (diagnosis of intrauterine growth restriction, circulatory disorders in the mother-placenta-fetus system using Doppler ultrasound).
- Determination of the position and presentation of the fetus.
- Detection of developmental defects with late manifestation (echographic signs of which can be detected in late pregnancy).
- Determination of the amount of amniotic fluid, location and structure of the placenta.
Assessing the size of the fetus is an important stage in diagnosing its condition, obtained by measuring the size and comparing it with the average for a given period of pregnancy. These average sizes were obtained as a result of numerous studies and entered into the appropriate tables and memory of ultrasound scanners. Of course, each person is individual, so at the same stage of pregnancy, the biometric parameters of the fetus may differ. However, only a doctor can assess which deviations in the measured parameters are pathological and require additional examination and treatment. To clarify the condition of the fetus, the doctor may prescribe additional studies, such as Doppler ultrasound and cardiotocography.
Indications for Doppler examination
Doppler ultrasound during pregnancy is prescribed to many women. Indications for the study:
- Diseases of a pregnant woman: gestosis, pathological weight gain, increased blood pressure, the appearance of protein in the urine, hypertension, hypotension, kidney disease, systemic vascular diseases, diabetes.
- Disorders of the fetus (intrauterine growth restriction, discrepancy between the size of the fetus and the gestational age), oligohydramnios, premature ripening of the placenta.
- Multiple pregnancy.
- Aggravated obstetric and gynecological history (growth retardation, chronic hypoxia, gestosis, stillbirth, etc. in previous pregnancies).
- Post-term pregnancy.
A Doppler study makes it possible to objectively judge the state of the uteroplacental-fetal circulation, the normal parameters of which in most cases are the key to a successful pregnancy. Usually, Doppler ultrasound is prescribed in the second half of the second and third trimester , since ultrasound trimesters of pregnancy play an important role in obtaining reliable results. If a blood flow disorder is detected, after appropriate treatment, a control Doppler examination is prescribed to assess the effectiveness of the therapy.
Indications for cardiotocography
- Aggravated obstetric history: perinatal losses, intrauterine growth retardation, premature birth, etc.
- Diseases of a pregnant woman: hypertension, diabetes, kidney disease, systemic diseases of connective tissue and blood vessels.
- Complications of pregnancy: Rh immunization, gestosis.
- Multiple pregnancy.
- Post-term pregnancy.
- Decreased fetal activity noted by the pregnant woman.
- Intrauterine growth restriction.
- Low water.
- Premature maturation of the placenta.
- Congenital malformations of the fetus compatible with life.
- Dynamic study in case of unsatisfactory cardiotocogram results.
- Circulatory disorders in the mother-placenta-fetus system according to the results of Doppler measurements.
Cardiotocographic examination (CTG) during pregnancy is most often prescribed from 32 weeks (in some cases from 28 weeks). A special device is designed to record the fetal heart rate and its instantaneous changes, as well as the tone of the uterus and fetal movements. The purpose of the study is to identify signs of fetal hypoxia (oxygen starvation) and assess its severity.
During an ultrasound during pregnancy, you can also evaluate:
Condition of the cervix.
During pregnancy, the length of the cervix changes in proportion to its duration and is usually equal to 3 cm. Normally, the internal and external pharynx should be closed. Approaching the due date, the cervix smoothes out. If it smooths out prematurely, the question of isthmic-cervical insufficiency arises, which, as a rule, requires suturing the cervix.
Condition of the uterine myometrium.
Spasm of smooth muscles or hypertonicity of the uterus is manifested on ultrasound by thickening of the body of the uterus in one or another part of it. Increased hypertonicity on ultrasound examination is considered normal in the last trimester, since the uterus “trains” before childbirth, but if the stomach also tenses and this condition progresses, then they speak of a possible threat of termination of pregnancy.
Quantity and structure of water.
Oligohydramnios at the end of pregnancy may be due to post-term pregnancy. In the early stages, oligohydramnios can occur due to dysfunction of the placenta or an infectious process.
Polyhydramnios occurs both in physiological (normal pregnancy) and in pathological conditions, such as fetal development abnormalities, infections, and Rhesus conflicts. In addition, polyhydramnios occurs in multiple pregnancies, large fetuses, or, as already mentioned, is an individual feature.
Turbid waters or suspended matter do not always indicate an infectious process. After the 30th week, this may be due to the “molting” of your baby, the skin changes, and particles of old epithelium give the water a cloudy structure.
Calcification content.
Deposition of calcium salts (calcifications) may occur during the study in the later stages, which is a variant of the norm.
Presence of placental infarction.
Placental infarction is a term used when there are areas in the placenta with no blood circulation. It is a normal variant if it is detected approximately one week before birth. At earlier stages, a large area of infarction can lead to delayed fetal development due to fetoplacental insufficiency.