Indications for X-ray examination of the gastrointestinal tract
An X-ray examination of the upper digestive tract is prescribed if the patient has the following symptoms:
- a feeling of heaviness in the abdomen and/or aching pain , which intensifies after a spicy meal or on an empty stomach;
- frequent nausea after eating;
- sharp decrease in appetite;
- the appearance of a bitter or sour taste in the mouth;
- tendency to constipation or diarrhea ;
- pain in the upper abdomen, which intensifies when pressed;
- sensation in the chest or heartburn (occurs mainly after eating);
- the appearance of white plaque on the mucous membranes of the mouth and tongue;
- increased gas formation in the stomach ;
- reducing body weight with unchanged diet and level of physical activity;
- suspicion of a violation of the integrity of the stomach wall.
Help In emergency situations, an X-ray examination of the stomach is performed if it is not possible to do an ultrasound, CT or MRI as soon as possible. This opportunity is used especially often in the surgical department and intensive care unit.
How to get rid of unpleasant odor and discomfort
The presence of a small amount of plaque (especially after sleep) is a normal natural reaction of the body. Tooth enamel is covered with a thin layer that is responsible for interaction with saliva and oral microbiota. The bacteria living here secrete special enzymes that ensure their fixation. In addition, leukocytes, food debris, protein substances and salts present in saliva are attached to it. As a result, the thickness of this layer increases. In the presence of concomitant dental diseases (presence of an infectious or inflammatory focus, wound surface), the rate of plaque formation may change. This is why some people do not feel discomfort in their mouth in the morning and may not brush their teeth. However, most are faced with the presence of an unpleasant odor that causes severe discomfort.
Despite the fact that using toothpaste (as well as mouth rinses or deodorants) before gastroscopy is not recommended, you can use simplified oral hygiene. To do this, you can wet your toothbrush well with water to remove any remaining toothpaste and brush it over all your teeth. After this, you can simply rinse your mouth with running water. It is also worth noting that the use of chewing gum to freshen breath is strictly prohibited. In response to their consumption, gastric juice is also produced.
How is radiography performed?
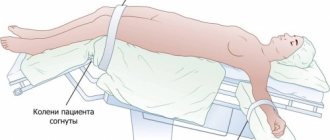
The patient arrives at the agreed time, after which he takes off his clothes in such a way as to completely expose the abdominal area. Diagnostics can be carried out both in a horizontal and vertical position of the patient (depending on the decision of the attending physician).
If the study is carried out in a horizontal position, the patient lies on his back on a special couch; if in a vertical position, he stands close to the screen. After establishing the correct position, the doctor and accompanying persons go to a special room, which is protected from x-ray radiation. The duration of the procedure does not exceed 5-7 minutes.
Help If
contrast enhancement , then the patient is given a dissolved preparation of Barium sulfate , after which a series of photographs are taken at certain intervals.
Carrying out the procedure
To properly prepare for a stomach x-ray, you need to understand what it is and how the examination is carried out. Depending on the purpose of the procedure, the technique may vary. Therefore, preparing a patient for an X-ray of the stomach, in addition to general requirements, may include specific steps that the doctor warns about.
In most cases, the specialist prescribes an x-ray of the stomach without contrast. In this case, the patient takes a horizontal position on the couch, after which a series of photographs is taken.
If the examination is carried out with contrast, preparation for an x-ray of the stomach includes the use of a barium-based drug. The substance does not cause harm to health and is eliminated naturally. X-ray data of the stomach with contrast are more complete than with a conventional examination.
In cases where a detailed examination of the walls of the stomach is required, their natural folds must be straightened. Then the specialist prescribes a fluoroscopy of the stomach with double contrast.
After taking the contrast agent, air is pumped into the stomach through a tube. Under slight pressure, the folds of the walls are straightened, which allows you to obtain more detailed images of the surface.
How to prepare for the examination?
General rules
Preparing the patient for radiography of the esophagus is aimed at increasing the diagnostic information content. Why is it important? The presence of food or air in the digestive tract affects the quality of the images that the doctor receives.
24 hours before the X-ray examination, the consumption of alcoholic beverages is prohibited. They can irritate the mucous membrane, provoke the development of new ulcers, and also stimulate the production of gastric juice.
The patient is also advised to refrain from smoking on the day of the diagnosis. Substances contained in smoke are factors of aggression and also lead to vasospasm of the mucous membrane. also not recommended chewing gum , since chewing reflexively activates the production of gastric juice, and to brush your teeth immediately before the procedure.
Important The doctor must explain to the patient that numerous
folk tips that are aimed at reducing radiation exposure to the body are ineffective and can only reduce the quality of the image .
Preparation can be neglected only in emergency situations, when delaying time can lead to serious consequences for the health and life of the patient.
Features of the DIET

Additionally, it is important to prescribe a diet 2-3 days in advance , to exclude foods from the diet that can contribute to increased gas formation. This is especially important for older patients who have chronic digestive problems. Therefore, they are prohibited from the following products:
- alcoholic and carbonated drinks;
- legumes;
- fresh bakery products;
- cuts, whole grain wheat;
- fermented milk products (kefir, yogurt, fermented baked milk);
- juices from apples, pears;
- grapes, raisins;
- fatty meats and fish;
- most types of cabbage (fresh, pickled and sour), Jerusalem artichoke;
- onions, turnips, radishes, Chinese salad;
- ice cream;
- products containing chocolate;
- barley;
- pasta.

Additionally, unload your diet by increasing the frequency of meals up to 5-6 times a day in smaller portions . This will allow the digestive tract to more quickly digest and break down food products, which will reduce the time they spend in the stomach cavity and the severity of gas formation.
At the same time, the diet should remain as balanced . The patient should consume sufficient amounts of nutrients and vitamins with food.
An example of a diet for 2 days before an x-ray of the stomach is given in the following table:
| 1 DAY | |
| First breakfast (8-9 am) | 2 soft-boiled eggs, buckwheat porridge with butter, a glass of warm still mineral water |
| Second breakfast (10-11 am) | Lightly warmed cottage cheese with sugar and weak green tea |
| Lunch (14-15 pm) | Vegetable soup (can be with thoroughly cooked meat), mashed potatoes with a steamed cutlet and a cup of weak tea |
| Afternoon snack (17-18 pm) | A few fresh bananas, a glass of compote |
| Dinner (20 pm) | Oatmeal (cooked in water), lean fish fillet and a glass of still water |
| Before bed (10 pm) | Dry cookies with a mug of weak herbal tea |
| DAY 2 | |
| First breakfast (8-9 am) | Boiled rice porridge with vegetable salad (cucumbers, tomatoes, carrots), a glass of still mineral water |
| Second breakfast (10-11 am) | Baked apple, a cup of weak green tea |
| Lunch (14-15 pm) | Vegetable soup with buckwheat and poultry (for example, chicken), buckwheat porridge with chicken Kiev, carrot and beet salad, a glass of compote |
| Afternoon snack (17-18 pm) | Scrambled eggs and a glass of still water |
| Dinner (20 pm) | 3-4 cheesecakes with sour cream and a cup of weak herbal tea |
Taking medications
Often, before an X-ray examination, the doctor additionally prescribes certain groups of medications:
- Adsorbents (activated carbon, Smecta). This group of drugs is capable of absorbing toxic substances, gases and food particles in the lumen of the digestive tract. They are usually given 2-3 hours before the expected start of the diagnosis.
- Antispasmodics (platifilin, drotaverine) reduce the tone of the smooth muscle muscles of the digestive tract. This is especially important if the patient has pain, or if a study using contrast agents is planned. They are given to the patient or administered 60-90 minutes before an x-ray of the stomach.
- Drugs that reduce the production of gases in the digestive tract (simethicone, espumizan). They prevent their accumulation in the lumen of the stomach. The medication is taken 6-8 hours before the test.
Please note: When scheduling an x-ray, be sure to tell your doctor what other medications you are taking. This is important, since the use of certain drugs (antacids, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) can reduce the diagnostic information.
X-ray with contrast
Sometimes a cleansing enema is also required on the day of diagnosis . It is necessary to discontinue medications prematurely that can slow down the motility of the digestive tract (muscle relaxants, narcotic analgesics).
Fluoroscopy analysis of the stomach
The results of fluoroscopy of the stomach are analyzed by a radiologist, gastroenterologist.
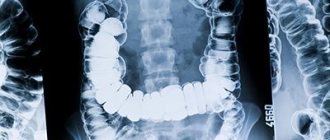
During the study, data is obtained on the speed of movement of the barium suspension through the esophagus, stomach, and the time of its entry into the duodenum and colon. These signs indicate the presence of motility disorders, difficulty in moving food from the esophagus or stomach. Also, by the uniformity of barium distribution, the presence or absence of changes in the mucosa is determined.
X-ray shows:
- location of organs (normal or displaced), their size and shape;
- structure and elasticity of walls;
- folding of the mucous layer;
- level of intestinal motor-evacuation function;
- the presence of changes (narrowing/expansion) of the lumen of the esophagus, stomach and intestines.
The results of fluoroscopy of the stomach are not the only basis for diagnosis. Information is assessed taking into account patient complaints, laboratory tests, and other instrumental diagnostic methods. The study is not prescribed by the patient independently, because Excessive radiation exposure can negatively affect health. If you detect symptoms of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, you should first consult a doctor (general practitioner, gastroenterologist, surgeon), who will prescribe a study if necessary.
In children
Some difficulties may arise when it is necessary to conduct radiography in young children (up to 5-6 years).

It is important to explain to them in advance that the procedure is absolutely painless. If the child remains anxious, you can show how an x-ray is done to another patient in order to calm him down.
also important for parents to remain calm themselves , since their emotional state is easily transmitted to their children. Also, medical personnel should be understanding of the child’s fear and remain friendly. Cases where a doctor scares or yells at a child are completely unacceptable.
An important aspect of the examination is the presence of parents nearby during the x-ray. This will significantly calm the child and follow all the necessary instructions from the doctor. To protect against X-ray radiation, parents or accompanying persons are given special gowns with lead plates , which protect the most important parts of the body.
Help You can also take your child’s favorite toys with you. This will create a more comfortable environment in the X-ray room.
The time for complete refusal of food in children is shorter than in adults and depends on their age.
| Child's age | How long should you refrain from eating? |
| Up to a year | 2-3 hours |
| 1-2 years | 3-4 hours |
| 3 years | 4 hours |
| 4-6 years | 4-5 hours |
| 7-8 years | 5 o'clock |
| 9-10 years | 6 hours |
| 11-12 years old | 7 o'clock |
| 13 years and older | 8 ocloc'k |
Important At the same time, if a one-year-old child is very hungry , then instead of milk or formula, he can be given a small amount of water to drink, which will reduce the feeling of hunger for a certain time.
What to take with you?

This will allow diagnostics to be carried out free of charge in a significant number of medical institutions. If radiography is carried out for a fee in a private clinic, then a referral from a doctor and a document that identifies the patient’s identity is sufficient.
Help Data from previous examinations (X-ray, ultrasound, CT, MRI) are of great importance, since they can facilitate the interpretation of diagnostic results. Therefore, it is always recommended to take them with you.
It is also advisable to bring food with you (for example, several sandwiches, bananas or croissants) so that you can have a snack immediately after completing the examination . When conducting radiography with contrast , it is recommended to buy 1.5 liters of still mineral water , which should be drunk after the diagnosis. This will help remove the Barium drug from the patient’s body more quickly after fluoroscopy.
How is contrast fluoroscopy of the stomach performed?
The first is a survey radiography of the chest and abdominal cavity to identify possible gross pathological changes.
After this, the patient is asked to drink a contrast agent. This is barium sulfate. This is a white powder that is safe for the patient. The suspension dissolved in water is white and tastes like chalk.
The first photo is taken after two sips. The doctor looks at the relief of the walls of the esophagus. Next, the patient drinks the remaining volume of the glass. Subsequent images are taken on an x-ray table. During the procedure, the patient periodically changes position at the request of the doctor.
The average duration of a fluoroscopy is about 40 minutes.
As a result of the passage of barium sulfate through the gastrointestinal tract, the organs being examined become distinctive from neighboring tissues, which allows them to be viewed on a screen, and subsequently on film. If it is intended to examine the lower intestines, then the images are repeated at certain intervals throughout the day.
Please note that after the study, the patient may experience constipation for the next 2-4 days. The stool may be white or gray for some time - this is normal. After completing the study, it is recommended to drink 1.5-2 liters of clean water to speed up the removal of barium.