Ultrasound examination is based on the physical properties of high-frequency sound to penetrate and reflect from organs and tissues with variable changes in amplitude due to their different densities. Therefore, in healthy lung tissue, ultrasound is attenuated and ultrasound allows only the pleura to be visualized. However, when the lungs are damaged or injured, their airiness decreases. Due to the difference in acoustic impedance, sonography makes it possible to accurately identify a number of pathologies and determine in real time the sliding of the lung in the chest. The method is absolutely safe, which makes it possible to perform ultrasound examination of the pleural cavity in patients with various diagnoses, which is especially important in cases of severe damage to the respiratory system. The technical features of ultrasound make it possible to quickly integrate its results into the clinical decision-making process.
The need for ultrasound of the pleural cavities
Indications for prescribing ultrasound of the pleural cavities:
-pain behind the sternum;
- shortness of breath, difficulty breathing;
- injuries, damage to the chest.
Ultrasound is prescribed for both relatively healthy patients and those who are in serious condition. In addition, people who are employed in hazardous industries (chemical, metallurgical, mining) need to undergo regular chest examinations.
The examination is safe, so it can be prescribed to pregnant women. Ultrasound is not performed only if the patient has injuries in the chest area (fractures, burns), since diagnosis involves direct contact of the device’s sensor with the skin
Ultrasound of the pleural cavity will show:
-inflammatory changes in tissues, such as pneumonia, pleurisy, abscess;
- malignant neoplasms and metastases;
- benign tumors (fibromas);
- exudative pleurisy - accumulation of fluid due to inflammation;
-the nature of the fluid in the pleural cavity (serous, fibrinous, purulent, etc.);
- pneumothorax - accumulation of air or gases in the pleural cavity;
- adhesion processes, etc.
Structure of the pleural cavity
The pleura is a thin membrane whose main task is to protect the lungs and ensure normal breathing.
The pleura is divided into two parts:
- visceral, or internal - it covers the lung itself and its components (vessels, nerves and bronchi), covers it on all sides and separates the lobes from each other. At the root of the lung it continues in the parietal pleura;
- parietal, or external, - this membrane lines the chest cavity (its walls).
What is in the middle of these two components is called the pleural cavity. It contains a liquid whose main task is lubrication. Thanks to it and the elastic pleura, the lungs increase and decrease in volume. It also helps reduce friction between the chest cavity and the lungs.
Sign up for ultrasound diagnostics
In the medical center, ultrasound examinations are performed using expert-class equipment.
The appointment is conducted by doctors:
– GONTAREV ALEXANDER GENNADIEVICH,
– ZHEVED ELENA SERGEEVNA,
– MAKOVEEVA IRINA SHAUKATOVNA
professional diagnosticians with extensive practical experience.
Ultrasound examinations in the clinic are carried out by appointment.
Phone number for registration.
Address: Sevastopol, Heroes of Stalingrad Avenue, 63
(stop b. Omega)
Opening hours: Mon. - Fri: 07:30 - 17:00, Sat. — Sun: 08:00 — 16:00
The patient should check with the administrators about the need for additional preparation for diagnosis.
The cost of ultrasound of the pleural cavities (with determination of fluid volume) is 650 rubles.
Indications for ultrasound examination
Unlike many other ultrasounds, this type is not prescribed simply for prevention, since it is not at all informative. It is carried out only when there are certain indications or complaints from the patient. The reasons may be:
- difficulty or painful breathing, as well as shortness of breath;
- the presence of blood clots when coughing and sputum coming out;
- accumulation of fluid inside the cavity;
- prolonged dry cough, large amounts of sputum.
In addition, during the study, the doctor looks at the space between the parts of the pleura (they are also called leaves), in such cases:
- injury to the chest or lung itself;
- pleurisy, inflammation of lung tissue or suspected tuberculosis;
- bronchitis and other inflammatory diseases;
- suspicion of a tumor or other neoplasms.
Ultrasound is also performed for additional control during biopsy.
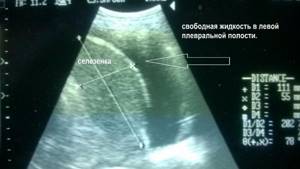
When should an ultrasound be done?
If you have been experiencing chest pain for several days, this is a reason to consult a therapist or immediately sign up for an ultrasound examination. Also among the indications for examination are:
- shortness of breath;
- various chest injuries;
- prolonged cough, difficulty breathing;
- biopsy control;
- work that is potentially harmful to the respiratory system.
Ultrasound detects pleural effusion with high accuracy. With the help of research you can confirm:
- pleurisy;
- tumor foci;
- pneumonia.
Recovery period
After pleurectomy, the patient is periodically invited to the clinic for dressings and control photographs. The following recommendations must be followed:
- Keep the drainage tube insertion site clean.
- Do not rub this area or touch it with dirty hands.
- Do not apply ointments or lotions to this area.
- Until complete healing, you should not take baths or swim in pools or ponds.
- Do not take ibuprofen or other NSAID pain relievers without your doctor's approval. All these medications act as anti-inflammatory drugs, because of them, inflammation in the pleura is reduced, and they stick together worse.
- Do not lift loads heavier than 4.5 kg.
- Avoid high physical activity, do not hold your breath.
For some time, a small amount of ichor may be released from the place where the drainage tube is installed; this is normal.
We will call you back, leave your phone number
Message sent!
expect a call, we will contact you shortly
Decoding the results
An ultrasound of the lungs allows you to see the changes that occur in them. The image is so clear that even the slightest deviations from the norm can be seen. Usually there are several possible options for the condition of the pleura:
- the leaves may be thickened, which is easily visible using an ultrasound machine;
- accumulation of fluid (blood, pus) inside the cavity, this is called pleural effusion;
- fusion of its two parts, which causes the inability to breathe normally;
- tumors (benign and malignant).
Based on the image on the device screen, the ultrasound specialist determines the condition of the cavity, which helps the attending physician prescribe further treatment. Usually, if fluid is detected, the patient is recommended to undergo a puncture or biopsy.

In order for treatment to be effective, good and timely diagnosis is necessary. Ultrasound of the pleural cavity plays a major role in identifying diseases of the human respiratory system, as well as in assessing its condition. Its undoubted advantage is its relative safety for the patient.
What does an ultrasound show?
Ultrasound has a high diagnostic value in the assessment of pulmonary diseases. Today, when conducting an ultrasound examination of the pleural cavity, the pulmonary pulse, the presence and thickness of the pleural cavity, and the presence of air in it are identified. Also defined:
- the structure of the lung tissue and the degree of its hepatization;
- the presence of small, extended and extensive consolidations;
- degree of patency of the proximal airways;
- the presence or absence of free fluid in the pleural cavities.
Ultrasound fully visualizes the condition of the parenchyma and pleura. Echography allows you to identify hidden bleeding, malignant pleurisy, small effusions and determine the need to wash the pleural cavity.
Benefits of Ultrasonography
Ultrasound waves are not capable of causing any harm to the human body; thanks to this quality, they are actively used for examining expectant mothers. During the examination of the pleural cavity, the doctor receives a reliable result and can correctly diagnose the disease. There is no need for special preparation for the diagnostic procedure - it can be performed on both practically healthy people and patients in serious condition. The high resolution of the method, which is considered the most informative alternative to radiography, allows the doctor to detect the accumulation of even a small volume of fluid and accurately determine its nature (inflammatory or tumor). Due to its easy availability and low price range, ultrasound is widely used in medical practice. Its additional advantages are:
- no age restrictions;
- automatic quality optimization;
- speed of obtaining final data;
- repeated diagnostics;
- saving the final data in the computer memory;
- the ability to use not only stationary but also portable equipment.
Using ultrasound, anomalies in the structure of the pleural layers are detected, which can be clearly seen on the monitor screen - it is possible to enlarge the image many times.
Highly qualified specialists of the Clinical Medical Center, who have extensive practical experience (they have thousands of studies under their belt), perform ultrasonography of the pleural cavity using modern expert-class equipment. Depending on the sonologist’s workload, the planned time of the ultrasound procedure may shift slightly. The medical staff of our clinic tries to do everything necessary to make the patient’s visit comfortable and take a minimum of time.
The essence and objectives of the procedure
This manipulation is carried out without preparation, takes up to 20 minutes, and does not cause discomfort.
It can be performed in the 1st position or with changing poses for a clearer understanding of the picture displayed on the ultrasound image. Purposes of ultrasound examination of the pleural space:
- assessment of the size of the pleural cavity;
- measuring tissue thickness (pleura);
- search for possible violations of the integrity of pleural tissue;
- detection of neoplasms between the layers/on the pleural tissue itself;
- detection of accumulated moisture in the cavity.
When is ultrasound recommended?
Ultrasound of this area is prescribed if there is a fairly wide range of indications. The most common reasons for examining the pleural zone are:
- severe long-term pain in the sternum for no clear reason;
- for representatives of certain professions associated with high risks for OD, ultrasound of the pleural cavity is recommended on an ongoing basis for prevention;
- severe shortness of breath (especially before 30–35 years);
- previous sternum injury;
- suspicion of cancer.
Ultrasound is mandatory as a control measure when taking a biopsy from the pleural cavity. It can be carried out an unlimited number of times, has no age restrictions, but requires serious qualifications of a specialist who works with ultrasound equipment. This is due, among other things, to a wide range of lesions in the pleural zone, pleura, lung cavity and their structural elements, which can be detected by hardware diagnostics.
Treatment methods in Medscan
As a symptomatic treatment, oncologists remove fluid from the pleural cavity. For these purposes, thoracentesis is prescribed. The procedure does not solve the problem, but only facilitates the patient’s general well-being.
At the Medscan clinic, specialists provide oncological care for various forms of cancer, using expert-level equipment:
- Surgical intervention. Indicated for oncological processes that provoke the development of hydrothorax (lung, uterine, ovarian cancer).
- Chemotherapy. The use of effective chemotherapy drugs helps to eliminate pleurisy caused by cancer.
- Pleurodesis and immunotherapy. As hydrothorax progresses, medications are injected into the pleural cavity with a thin needle, causing the sheets to stick together. As a result, a small gap disappears where exudate could accumulate. The modern approach involves the introduction of chemotherapy and immunotherapy drugs, which allows not only to get rid of the symptom, but also to destroy atypical cells. With the help of pleurodesis, it is possible to solve the problem of hydrothorax in 90% of cases.
- Cytological examination of pleural fluid reveals tumor cells. The procedure is carried out three times to evaluate the treatment over time.
What abnormalities are detected by ultrasound?
Among the main points of attention during the procedure (deviations that the image can show), it is necessary to highlight:
- pleurisy (inflammatory process in the pleural tissue itself, accompanied by characteristic manifestations in the interleaf cavity);
- tumor-like inclusions in the pleural zone (verified by size, this is one of the fastest ways to distinguish a malignant neoplasm from a benign one, the latter occupies no more than 1 cm of the cavity);
- pneumonia and early stages of development of inflammatory processes in the lungs.
One of the most valuable visualized abnormalities that can be detected by ultrasound is the presence of fluid accumulated in the cavity - the so-called effusion. It may contain admixtures of purulent/bloody inclusions and have a different character (trans-/exudal). The last factor allows us to judge the likelihood of developing cancer in the pleural cavity or other elements of the OD structure.
Ultrasound provides information about the condition of the accumulations and their volume. With regular examination of pleural tissue, it allows one to judge the activity of its formation. All this forms the basis not only for recognizing pathology, but is also used to build therapeutic tactics.