Very often, patients complain to a doctor, but clinical symptoms do not define the disease. The tests give satisfactory results, but the patient’s state of health is much better. Then medical specialists resort to functional diagnostic methods that help assess the functioning of individual organs and systems.
The Doctor Nearby clinic has a functional diagnostics room. Here patients can undergo instrumental studies to assess the functioning of the cardiovascular system. An experienced doctor has modern equipment and a new room at his disposal to ensure high accuracy of the examination and comfort of each patient.
What is functional diagnostics
Functional diagnostics is a branch of medicine that evaluates, detects abnormalities, and establishes the degree of disturbances in the functioning of various organs and systems by objectively measuring their performance using instrumental studies.
The specific purpose of functional diagnostics depends on the clinical task. So in some cases it is necessary to identify deviations in a specific organ function. For example, analyze the secretion of hydrochloric acid by the stomach. In other cases, it is necessary to evaluate the functioning of several important organs that constitute a physiological system. For example, evaluate blood pressure indicators over time. Studies are also carried out to assess the functioning of the system - blood circulation, breathing.
Functional diagnostic methods
Functional diagnostics is based on the use of modern precision equipment with high sensitivity. There are various methods for diagnosing diseases of the heart, cerebral vessels, central nervous system, pulmonary system, muscular system, etc. All of them have one feature - they do not provide an unambiguous interpretation of the results in all cases. Each person’s body is unique and the norms for the functioning of its organs and systems are different. Therefore, in functional diagnostics, a comprehensive comparative study takes place under different loads, which makes it possible to evaluate the functioning of an organ or system in dynamics.
Echocardiography with color Doppler mapping (EchoCG with color doppler)
Description
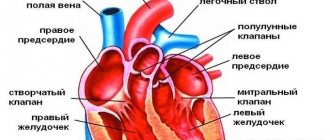
Echocardiography with color Doppler mapping (EchoCG with color Doppler mapping) is a method for studying morphological and functional changes in the heart and its valvular apparatus using ultrasound. Echocardiography with Doppler mapping allows one to evaluate not only the anatomical features of the organ, but also the main characteristics of the blood flow in it and nearby vessels, which gives doctors maximum information. EchoCG with CD is one of the most informative and simple diagnostic methods. The procedure is not accompanied by discomfort for the patient and the doctor, and there is no radioactive radiation, which allows the examination to be carried out an unlimited number of times. To conduct the study, the patient needs to undress in the office from top to waist and lie down on the couch on his left side. The examination, depending on the complexity of the case, can take up to 30 minutes. The echocardiographic research method allows: • Quantitatively and qualitatively assessing the functional ventricles of the heart • Assessing regional contractility of the left ventricle (for example, in patients with coronary artery disease). • Assess left ventricular mass and identify ultrasound signs of symmetric and asymmetric hypertrophy and dilatation of the ventricles and atria. • Assess the condition of the valve apparatus (stenosis, insufficiency, valve prolapse, presence of vegetations on the valve leaflets, etc.). • Assess pulmonary artery pressure levels and identify signs of pulmonary hypertension. • Identify morphological changes in the pericardium and the presence of fluid in the pericardial cavity. • Identify intracardiac formations (thrombi, tumors, additional chords, etc.) • Assess morphological and functional changes in the main and peripheral arteries and veins.
Indications for the study:
• presence of high blood pressure; • previous myocardial infarction; • suspicion of congenital or acquired heart disease; • angina pectoris clinic (pain in the heart area); • signs of chronic heart failure; • detected noises during auscultation; • pathological changes during electrocardiography; • chronic diseases of other organs (liver, kidneys); • condition after an ischemic stroke; • Presence of a feeling of palpitations, shortness of breath during physical exertion; • febrile conditions of unknown cause; • regular sports training; • suspicion of a heart tumor; • when preparing an elderly patient for planned surgery; • chronic lung diseases; • diabetes.
Contraindications for the study:
No.
Preparing for the study:
Not required.
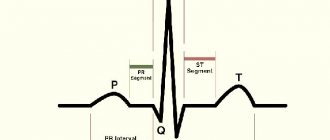
ECG
This is the main and most relevant research method in cardiology for diagnosing heart function, the main method for diagnosing myocardial infarction. Allows you to determine most cardiac anomalies, including enlargement of the heart muscle, death of the heart muscle, insufficiency of blood flow and in which artery it is impaired, changes in heart rhythm and electrical conductivity.
Indications:
- chest pain, shortness of breath, dizziness, loss of consciousness;
- suspicions of ischemia, stroke, myocardial infarction, arrhythmia, hypertension and other diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- endocrine disorders, thyroid function, metabolic problems;
- Diabetes;
- Chronic diseases of internal organs;
- Chronic diseases of the respiratory system;
- Preparation for surgery;
- Prevention for people after 40-45 years of age, for professions with a high level of health risk.
Possible types of procedure
In cardiology, there are several types of echocardiography depending on the technique used:
- Transthoracic. This is the most standard type of study, in which a hardware sensor is located on the surface of the skin within the chest. It is used most often due to its safety and availability. However, in rare situations this technique is not informative, for example, if the patient has too much fat or the chest is deformed. Then the standard technique will not allow you to obtain a clear image.
- Transesophageal. The difference between this type is that the sensor is inserted into the body through the esophagus. Studying the structure of the heart in this way provides more information than with the standard method. After all, the esophagus is located near the heart, and this allows the use of high-frequency sensors and obtain images of its segments with high resolution. Examination through the esophagus is prescribed to diagnose pathological changes in natural and prosthetic valves, diseases of the aorta, atrial septal defects, pathological condition of the pericardium, thrombosis and atherosclerosis, infections in the myocardium. The disadvantages of this type of examination include the patient’s discomfort when the sensor moves along the esophagus: increased gag reflex. Unpleasant sensations are relieved by taking specially selected sedatives and analgesics for the pharynx. If necessary, general anesthesia is given.
- Stress echocardiography. The method is an ultrasound examination of the heart with a simultaneous stress test. In other words, the patient receives a certain load, and the doctor monitors the heart’s reaction on the screen of the device. Running on a treadmill, simulating cycling on a simulator, electrical stimulation through the esophagus, and medications are used as test loads. The load is selected individually for each patient. The main purpose of such an echocardiography is to find out whether the coronary vessels are narrowing before and after exercise or stimulation, and to assess the condition of the myocardium. This method will also confirm or deny the presence of ischemia or angina.
Echocardiography is also classified according to the format of the resulting image:
- One-dimensional echocardiography (or M-mode). It will show a top view of the heart on the device screen.
- Two-dimensional. The sensor transmits two-plane visualization to the monitor.
- Doppler. An improved method that allows you to additionally see the direction and speed of blood flow in the vessels. Doppler sonography is of great diagnostic importance in cardiology, as it reveals hidden heart defects and the filling of the left ventricle. Doppler is usually combined with two-dimensional echocardiography.
- Contrasting. It involves the introduction of an echo contrast agent into the patient’s circulatory system, as in a CT scan (computed tomography). This allows you to clearly visualize the inner surface of the heart and see abnormalities.
Echocardiography with Doppler analysis
Ultrasound examination of the chest area to assess the condition of the blood vessels and heart. Allows you to obtain a two-dimensional or three-dimensional image to make an accurate diagnosis and etiology of the disease. A common, safe and convenient method for quickly assessing the condition of the heart. EchoCG helps to assess the diameter of the heart, the condition of the structures of the heart, atrium, and myocardium.
Indications:
- Chest pain, weakness, drowsiness, bluish lips, skin;
- abnormal readings on the ECG;
- heart murmurs, arrhythmia;
- symptoms of heart failure;
- chronic diseases of internal organs;
- hypertension;
- after myocardial infarction;
- Congenital heart defect.
Daily blood pressure monitoring (ABPM)
Measuring the patient’s blood pressure throughout the day to assess the indicators over time. Used to diagnose hypotension or hypertension, to prescribe therapy or to evaluate the effectiveness of treatment. The method is also informative for analyzing the functioning of the cardiovascular system. A portable recorder is used, which automatically measures the patient's blood pressure. As a rule, blood pressure is measured every 30 minutes during the day, and every 60 minutes at night.
Indications: m
- “borderline values” of blood pressure, when they are not high enough for diagnosis, but cause concern;
- increased blood pressure at the time of its measurement - “white coat syndrome”;
- frequent fainting;
- hypertension, cardiac ischemia, vascular pathologies of the brain;
- assessment of the effectiveness of drug therapy.
Heart and vascular studies
What does it show?
Echocardiography shows the heart's function in real time, so there is virtually no chance of erroneous results.
- analyze the condition of chambers and valves;
- clarify the boundaries of the heart cavities;
- measure the thickness of the myocardium;
- determine how fast blood moves in the heart;
- assess myocardial activity;
- learn about the condition of the aorta;
- see the position of the great vessels.
The doctor, using this diagnostic method, can detect congenital and acquired defects, degenerative changes in the valves, blood clots directly in the heart and its vessels, excess fluid in the pericardium, analyzes the structure and density of the aortic walls, and its compliance with standards.
The technique helps to discern pathology at its initial stage and take measures to eliminate it. Repeated studies make it possible to track changes in the heart over time and analyze the results of therapy.
Holter monitoring
24-hour ECG monitoring or dynamic electrocardiogram, which allows you to evaluate the work of the heart, its rhythms, over 24-72 hours in a state of daily activity. It is used to diagnose cardiac arrhythmias, coronary heart disease, to assess the effectiveness of drug treatment, and the presence of indications for installing a pacemaker.
Indications:
- dizziness, loss of consciousness, rapid heartbeat, sudden shortness of breath;
- chest pain of unknown origin;
- heart rhythm disturbances, myocardial infarction;
- assessment of pacemaker performance;
- suspected long QT syndrome;
- significant bradycardia, etc.
How is it made?
The research algorithm is simple. The subject's actions vary depending on what type of echocardiography the doctor prescribed to him.
During transthoracic echocardiography, the patient is naked to the waist and lies on the couch with his back or left side. The doctor applies the gel to the breast and moves the sensor along it. As a result, the heart segments are visualized on the electrocardiograph monitor. Next, the doctor, using the buttons on the device, takes measurements of the departments and calculates cardiac activity indicators. The duration of the procedure is approximately 15-20 minutes.
Transesophageal echocardiography will require insertion of a transducer into the patient's esophagus. To avoid discomfort as much as possible, the throat is treated with an anesthetic spray. The doctor smears the ultrasound sensor with gel and moves it along the esophagus. To obtain the necessary information, the sensor must be in the esophagus for about 15 minutes.
Stress echocardiography takes place in two stages. Initially, the patient undergoes a standard resting echocardiogram. The doctor records the indicators, and then artificially creates a stressful state of the heart in the subject: either by administering certain pharmaceutical drugs (oral pills, intramuscular or intravenous injections) or through physical exercise. If physical activity is chosen as the load, then the patient moves on a treadmill, pedals on an exercise bike (sitting or lying down) or simply performs the exercises indicated by the doctor.
The doctor continues an ultrasound examination of the heart at the time of drug loading and bicycle ergometry in a supine position. If walking on a treadmill or bicycle ergometry in a sitting position is chosen for the load, then an ultrasound scan is performed immediately after the cessation of activity.
This research method involves increased work of the heart, so there is a risk of worsening the patient’s condition. In this regard, medical specialists are present during the stress test to monitor the patient’s well-being and provide assistance in a dangerous situation.
If echocardiography has detected heart disease, it is recommended to repeat the examination every six months in order to monitor the disease over time.
In cardiology, the validity period of cardiac ultrasound results is stipulated: shelf life is 6 months. But if the patient is hospitalized, for example, in the cardiovascular surgery department, the validity period is reduced to 1 month.