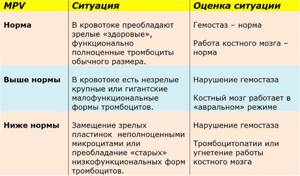
MPV (short for mean platelet volume) is the designation of the platelet index, which characterizes the degree of platelet maturity in peripheral blood. The measurement is based on the fact that the size of young cells is larger than that of mature and aged cells. There is a connection between the size of platelets and their functional activity, so the index characterizes the state of the blood coagulation system, which platelets represent.
Determination of MPV in a general blood test is carried out within two hours after collecting the material, since with a later study the result may be distorted.
General blood analysis
A complete blood count (CBC, clinical blood test) is one of the most important and frequently prescribed laboratory tests. This analysis makes it possible to assess the condition of the body as a whole, confirm or exclude the suspected diagnosis, and monitor the progress of treatment.
Platelets are blood cells that stop bleeding if a blood vessel is damaged.
The first general blood test is performed for children in the maternity hospital. As the child grows up, it is recommended to carry it out regularly during routine medical examinations, which will make it possible to promptly identify abnormalities (for example, the development of iron deficiency anemia) and take the necessary measures in a timely manner. For preventive purposes, it is recommended to conduct a general blood test for adults once, and for children twice a year.
A general blood test includes determination of hemoglobin concentration, number of red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets, hematocrit level, as well as erythrocyte and platelet indices and erythrocyte sedimentation rate. A detailed blood test also includes a leukocyte count, which consists of determining the percentage of different types of leukocytes in the peripheral blood.
Counting the number of platelets and determining MPV is mandatory for women during pregnancy, as well as for patients with autoimmune diseases, varicose veins, liver pathologies, etc.
Drugs for low mean platelet volume
Derinat

Derinat solution for intramuscular administration
When treating poor vascular condition, patients are prescribed the drug in the form of injections for intramuscular use. The classic adult dosage is 75 mg of the active substance. The patient can receive from 3 to 15 injections of Derinat; the exact number of procedures is selected individually for each patient.
Etamzilat

Drug Etamzilat
This drug is taken in situations where bleeding has begun due to the development of the disease. When problems arise, the patient may be advised to take 125-250 mg of the active ingredient up to four times a day. Therapy continues for an individually selected time, usually no more than 5 days.
Dicynone tablets

Dicynone tablets
The medication is available in the form of tablets, which must be taken taking into account the patient’s body weight. Typically, 10 mg of the active substance is prescribed for every kilogram of body. Take Dicinon up to four times a day. Typically, the drug is prescribed when there is bleeding or severe weakness of the blood vessels.
Platelets, their types and functions
Platelets (PLT, platelets) are blood cells with a diameter of 2-4 microns that provide blood clotting. The functions of platelets include angiotrophic (the ability to maintain the structure and functions of the walls of microvessels), adhesive-aggregation (formation of a primary platelet plug in damaged blood vessels), platelets are also involved in fibrinolysis, maintaining vasospasm, and blood clot retraction. These blood cells have the ability to transport circulating immune complexes on the membrane.
An increase in MPV may indicate the presence of thrombocytopenia, myeloproliferative diseases, posthemorrhagic anemia, hyperthyroidism, and diabetes mellitus.
There are five forms of platelets: young, mature, old, irritable and degenerative.
Platelets, like other blood cells, are produced in the bone marrow. Approximately two-thirds of the total number of platelets is in the bloodstream, and one-third is in the spleen. The precursors of platelets are megakaryocytes - giant cells with a large nucleus, from which platelets are released. Platelets are fragments of the cytoplasm of megakaryocytes surrounded by a membrane. They do not have a nucleus and their lifespan is approximately ten days. Platelet granules contain clotting factors, serotonin, calcium ions, adenosine diphosphate, peroxidase, platelet growth factor, von Willebrand factor, etc.
Platelets are round or oval in shape. When a blood vessel is damaged, they are activated, the cells flatten, form pseudopodia (long outgrowths) and acquire the ability to stick to other platelets (aggregation) and the walls of the damaged vessel (adhesion). A blood clot forms, which blocks the damaged area and thereby stops bleeding. Stimulators of platelet aggregation include serotonin, thrombin, collagen, and adrenaline. In a normal (inactive) state, the platelet membrane does not support coagulation reactions. There is a connection between the size of platelets and their functional activity, the content of biologically active substances in their granules, and their tendency to adhere.
Normally, the number of platelets in the blood is 180-320×109/l, varying depending on the time of year and time of day (daily fluctuations can reach 10%). A physiological increase in the number of platelets in the blood occurs when rising to altitude, in winter, after injury or exhausting physical activity. A physiological decrease in the number of platelets is observed before and during menstruation (up to 25-50%), as well as during pregnancy.
A significant decrease in MPV in the blood of a pregnant woman indicates a threat of miscarriage.
When the balance between the formation and destruction of platelets is disturbed, a tendency to thrombosis or increased bleeding occurs. With an increase in the number of platelets and the development of thrombosis, there is a risk of pulmonary embolism, stroke, myocardial infarction, and blockage of blood vessels in other organs by clots. A decrease in the number of platelets leads to hemorrhages and bleeding, which can also cause the development of life-threatening conditions.
The counting of platelets in the blood is carried out using an automatic hematological analyzer; in some cases, there is a need to determine the number of platelets and their sizes in stained blood smears under a microscope when calculating the leukocyte formula.
Platelet indices of a general blood test include:
- mean platelet volume (MPV);
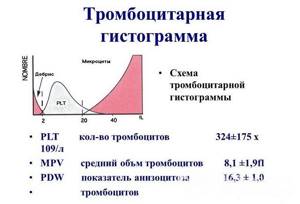
- platelet distribution width by volume (PDW) - an indicator of platelet anisocytosis (depending on the predominance of young or old forms in the blood);
- thrombocrit (PCT) - indicates the proportion of blood volume occupied by platelets (depending on the total number of platelets and the MPV index).
Platelet indices allow you to assess the state of the blood coagulation system
Reasons for the increase in MPV
High levels of MPV can be caused by both physiological reasons (described below) and pathological ones.
The latter include:
- systemic diseases (systemic lupus erythematosus);
- blood pathologies;
- endocrine disorders;
- infectious diseases;
- inflammatory processes;
- burns, injuries;
- some hereditary diseases.
Endocrine diseases
The average platelet volume is increased in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus. This indicator is used as a prognostic indicator to determine the level of risk of microvascular complications in patients of this group.
In diabetes mellitus, platelet activation occurs, and the incidence of atherosclerosis is 2-4 times higher compared to healthy people. However, with good glycemic control, the development of such complications can be delayed.
Another endocrine disorder in which high MPV is observed is hyperthyroidism - increased production of hormones in the thyroid gland, which affect all types of metabolism in the human body. With this disease, the production of blood clotting factors is disrupted and the risk of cerebral thrombosis increases.
Early postoperative period
An increase in MPV levels in the postoperative period, after injuries and burns, is associated with significant blood loss. In order for the wounds to close, more platelets are needed. Therefore, the production of “young”, larger cells is activated in the bone marrow, which is what causes this phenomenon.
MPV usually returns to normal by the time you are discharged from the hospital. In the case of burns, this occurs by the time the wounds are completely closed.
Hereditary diseases
The average platelet volume also changes in some genetic diseases.
It is elevated in an adult or a child in the following cases:
- Giant platelet syndrome (Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome) . This disease mainly affects men (1 case per 250 thousand newborn boys). It manifests itself in the form of frequent bleeding, which is the main cause of death in patients. The diagnosis in most patients is established by 1.5 years after birth. In some patients, the disease is mild, so it may not be detected for a long time.
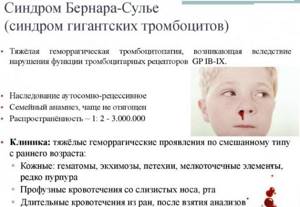
- Bernard-Soulier syndrome. In this disorder, platelets are unable to adhere to damaged blood vessel walls, making it difficult for wounds to heal normally. Genetic deviation most often occurs in consanguineous marriages (both among men and women).
- Mediterranean macrothrombocytopenia. This disorder is also characterized by bleeding, but more moderate than in previous cases. Simultaneously with the increase in platelet size, there is a decrease in their total number in the blood.
- May-Heglin syndrome. This is a rare genetic disorder associated with purpura and bleeding (from the nose, in the mouth, in the form of bruises under the skin, heavy menstruation in women). In this case, platelets reach gigantic sizes, and their structure is not disturbed.
- Epstein syndrome. Such patients are characterized not only by impaired hematopoietic function, but also by deafness and kidney pathologies. The prevalence of the disease is 1 case per 300-400 thousand newborns.
- Sebastian syndrome. Its features are hearing loss, cataracts, and kidney damage.
Genetic disorders are associated with qualitative defects in platelet production and maturation. Such patients receive mainly supportive and symptomatic treatment.
Tumors
When platelets in the bloodstream collide with substances produced by the tumor, their activation may occur. However, an increase in MPV is not the only sign of a tumor. If there is a family history of cancer, the doctor should order additional tests to rule out this diagnosis.
The localization of the tumor can be very different: lungs, endometrium in women, mammary gland, kidneys, stomach, colon and other organs.
Inflammation
The average platelet volume is increased in adults with the following infectious and inflammatory processes:
- viral respiratory diseases;
- sepsis;
- HIV;
- Epstein-Barr virus and other systemic inflammatory reactions.
The release of proinflammatory cytokines stimulates platelet activation. After treatment of the underlying disease, the MPV level returns to normal.
Malignant blood diseases
The formation of platelets is also influenced by malignant blood pathologies, such as chronic myeloid leukemia. This is a tumor disease in which the degeneration of stem cells, which give rise to all blood cells, occurs. The disorder can occur due to exposure to radiation, infections and toxins.
The prevalence of the pathology is relatively low - about 1 patient per 100 thousand adults. Most often it is diagnosed at the age of 50-59 years. At the initial stage, symptoms may be completely absent for a number of years.
Subjective factors
Other reasons for increased MPV levels may include:
- living at high altitudes above sea level;
- smoking and alcohol abuse;
- intense physical activity;
- taking oral contraceptives and certain medications that enhance bone marrow activity.
Preparation and delivery of a general blood test
To take a general blood test, standard preparation rules are used. Blood sampling is carried out in the morning on an empty stomach. On the eve of the study, you should avoid excessive physical and mental stress, and give up fatty foods. Before donating blood, you should not smoke; the patient should be completely at rest for half an hour before the test. Blood for general analysis can be taken either from a finger or from a vein.
Determination of MPV in a general blood test is carried out within two hours after collecting the material, since with a later study the result may be distorted.
A decrease in MPV may mean an enlarged spleen (splenomegaly), the presence of liver cirrhosis, hypoproteinemia, kidney disease, and thyroid pathologies.
Additional examinations
A blood test gives an approximate idea of the state of the body. It only allows us to state a fact: there is a problem. Why it arose is a different question, and the answer to it is sought using auxiliary techniques.
The examination is carried out by a hematologist. Third party specialists are brought in as needed.
- Oral interview with the patient. Complaints are informative in some cases. Symptoms indicate damage to one or another organ.
- Anamnesis collection. Lifestyle, past and current diseases, family history, genetics and other points. The doctor collects them for interpretation and determines the possible source of the problem. Its origins.
- Ultrasound of the digestive tract. First of all, specialists are interested in the liver.
- To study the functional state of the largest gland in the body, scintigraphy is prescribed. Radioisotope technique.
- A blood test for hormones helps identify thyroid diseases.
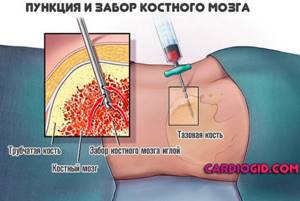
- Specific, extreme measures are possible. Bone marrow puncture, histological evaluation of the obtained material.
- If necessary, diabetes is diagnosed with special tests: sugar curve and others.
The question of examination is within the competence of the doctor. The list can be expanded or narrowed. Of necessity.
MPV in a blood test: decoding, norms in women and men
Determination of MPV is important for assessing the hematopoietic function of the body. Using the MPV platelet index in a blood test, you can detect increased platelet aggregation, thrombosis, and active blood loss (if large platelets are detected in people with iron deficiency anemia). In addition, the MPV indicator in a blood test acts as an additional marker of chronic myeloproliferative diseases (the presence of large platelets in the peripheral blood).
The MPV rate in adults is the same for women and men and is 6-13 fl. In children under one year old, the MPV norm is 7-7.9 fl, 1-5 years old - 8-8.8 fl. For children over 5 years of age, the normal values are the same as for adults.
An elevated MPV platelet index indicates the presence of large platelets in the patient's peripheral blood. If the MPV in the blood test is low, this means a predominance of small platelets.
What affects indexes
The norms are calculated for each indicator in the blood test:
- For MPV from 7 to 10 femtoliters;
- For PDW from 15 to 17%;
- For PCT from 0.108 to 0.282%.
Each index can be raised or lowered. The cause is various factors, including diseases. You need to know that various actions unrelated to ongoing diseases can lead to changes in each of these indicators and thus the blood test will contain deliberately false results.
An unreliable result when determining the average platelet volume, volume distribution width and thrombocrit may be higher or lower than normal if the following actions are taken the day before or immediately before collecting material for research:
- Eating food in the morning before the blood test is taken;
- Heavy physical labor both immediately before collecting material and during the day the day before;
- Mental work that requires a lot of concentration;
- The use of various medications in the morning before handing over the material (especially when administered intramuscularly or intravenously);
- X-ray irradiation;
- Carrying out physical procedures before blood collection.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=arLn-Z53ib0
It is possible to obtain a result that will be lowered or increased, and such a platelet value will not be considered a significant deviation from the norm. More often, such deviations can be within 1-2% of normal values, but more significant changes are possible. Most often they occur in the following situations:
- When collecting blood from young children due to incomplete maturation of the hematopoietic system;
- After surgery;
- During the recovery period after receiving numerous injuries;
- The period before menstruation in women or immediately after its end;
- After intense bleeding.
After each of these phenomena, the body intensively produces new platelets, which affects their average volume and other indicators of blood cells.
Like all elements, platelet content is measured in thousands per 1 μl of blood. The norm is a relative concept; it depends on many factors. Sometimes the indicators are higher than normal or lower. This is gender and age. Values for adults differ from those for children.
For men, the norm is considered to be about 200-400 thousand units/mcL. For women, normal values range from 180 to 320 thousand. In addition, women may experience a temporary decrease in the index, which most often occurs during pregnancy (100-310 thousand) and menstruation (up to 75-220 thousand). This is considered normal and no treatment is required.
In children, the platelet rate is distributed by age:
- in newborns - 100-420 thousand units/μl,
- for a child from 2 weeks to 12 months - 150-350 thousand.
- from 1 year to 5 years - 180-380 thousand.
- from 5 to 7 years - 180-450 thousand.
Adults and children need to have a blood test every year. This is necessary in order to determine the number of blood platelets in the biomaterial and, if a deviation from the norm occurs, prevent this process in time. This way you can prevent the development of increased or, conversely, decreased blood clotting.
When MPV in a blood test is increased and decreased
An increase in MPV may indicate the presence of thrombocytopenia, myeloproliferative diseases, posthemorrhagic anemia, hyperthyroidism, diabetes mellitus, infectious and inflammatory diseases, neoplasms, preeclampsia, idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, impaired platelet formation due to a lack of vitamin B12 or folic acid in the body, May-Hegglin anomaly , Bernard-Soulier syndrome. The index also increases after surgical removal of the spleen (splenectomy), in smoking patients with atherosclerotic changes in blood vessels, with alcoholism and taking certain medications, and in the elderly.
When the balance between the formation and destruction of platelets is disturbed, a tendency to thrombosis or increased bleeding occurs.
Decreased level and its causes
What does low platelet count mean?
Why can a woman have an increased platelet count in her blood test and what does this mean for her health?
Pathology is classified according to severity and is distinguished:
- I degree (moderately low content), in which the level of cell content in the blood varies between 50-160x109/l, and hemostasis is characterized as satisfactory;
- II degree (platelets are sharply reduced) - a decrease in platelets to the level of 20-50x109/l, which is characterized by the occurrence of hemorrhages under the skin and prolonged bleeding from wounds;
- Stage III (severe thrombocytopenia) is a condition in which the concentration of platelets in the blood is below 20x109/l. A pronounced decrease in platelets in a patient is accompanied by the development of spontaneous bleeding, both external and internal.
Thrombocytopenia is also classified according to its forms:
- Immune is the most common form of pathology that develops several weeks after an infectious disease or while taking certain groups of medications, including after vaccination;
- Heteroimmune - platelets are reduced due to disruption of the antigenic structure of cells by pathogenic microorganisms, toxins, chemicals;
- Isoimmune - platelets are reduced, mainly in children due to the transfer of cells from the fetus to the mother (identical to Rh factor incompatibility), as well as as a result of donor blood transfusion;
- Autoimmune is a pathology that consists of dysfunction of the immune mechanism, in which the production of antibodies to platelets begins.
Causes of low platelet levels
There are 3 main causes of low platelets:
- Red bone marrow dysfunction (red bone marrow does not produce the required number of platelets);
- Active production of antibodies that destroy platelets;
- Dysfunction and changes in the spleen.
The causes of moderately low platelets are:
- Abuse of alcoholic beverages, chronic alcoholism. Alcohol inhibits the functioning of the red bone marrow, leading to a lack of folic acid in the body, which is necessary for hematopoiesis. With alcoholism, platelets in the blood are reduced to 80x109/l, as evidenced by the cyanosis of the body;
- Pregnancy. A small number of platelets in pregnant women is observed due to hormonal changes, blood thinning, vitamin deficiency, etc.;
- Liver pathologies. The liver is an organ in which the synthesis of certain substances involved in the process of blood clotting occurs. A decrease in their production due to some liver diseases leads to increased bleeding and consumption of large numbers of platelets;
- Use of certain medications. The development of stage I thrombocytopenia is possible when taking diuretics, antibacterial, antitumor drugs, analgin, heparin, nitroglycerin, reserpine and vitamin K;
- Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC syndrome). A condition that develops in various pathologies and is characterized by rapid blood clotting in small vessels with the formation of blood clots in them, which consumes a large number of platelets;
- Heart failure. In heart failure, the blood supply to the organs of the heart is disrupted, which leads to stagnation of blood in the spleen. Also, platelet consumption occurs as a result of thrombus formation in the vessels.
- Radiation therapy. When treating tumor diseases, radiation is used, which, in addition to destroying cancer cells, can damage the red bone marrow, which leads to inevitable disturbances in the production of platelets and other blood cells;
A low platelet level to the point of severe thrombocytopenia can be caused by:
- Acute leukemia. In leukemia, cancer cells form in the bone red marrow, which displace physiological hematopoietic tissue, which affects the formation of platelets and red blood cells;
- Hemolytic disease of the child, the development of which is associated with incompatibility of maternal blood with fetal blood according to the group and Rh factor;
- Systemic lupus erythematosus;
- Severe form of disseminated intravascular coagulation.
Reduced platelets in the blood to critical levels are characteristic of:
- Acute radiation sickness;
- Overdose of antitumor drugs;
- Severe forms of leukemia.
What does a decrease in MPV mean?
A decrease in MPV may mean an enlarged spleen (splenomegaly), the presence of liver cirrhosis, hypoproteinemia, kidney disease, and thyroid pathologies. The platelet index decreases in aplastic anemia, septic thrombocytopenia, congenital megakaryocytic hypoplasia, Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome, X-linked thrombocytopenia with platelet microcytosis, thrombocytopenia caused by immunological destruction of cells, as well as during chemotherapy and during pregnancy. A significant decrease in MPV in the blood of a pregnant woman indicates a threat of miscarriage.
Increase in coefficient
PDW values can be increased through a number of measures. The choice of each of them lies on the shoulders of the attending physician, who sees the overall clinical picture of the patient.
Depending on the root cause of the decrease in platelet volume distribution, drug treatment is prescribed. These include:
- Sedokor.
- Vikasol.
- Derinat.
- Dicynone.
After serious interventions such as chemotherapy, the normal value of the platelet index is restored with hormonal drugs.
The creation of platelets is greatly influenced by the patient's diet. The diet should include proteins and green vegetables. The main products are:
- Red lean meat.
- Eggs.
- Sesame.
- Beetroot.
- Buckwheat, rice and beans.
- Linseed oil.
What to do if MPV is higher or lower than normal
When receiving MPV results in a general blood test that go beyond the normal range, additional tests are usually prescribed: general urinalysis, biochemical blood test, coagulogram, etc.
Treatment depends on the cause of the increase or decrease in MPV. Self-medication in this case is unacceptable, since uncontrolled use of medications can aggravate the pathology, even threatening life.
In order to prevent the development of diseases affecting the blood coagulation system, it is recommended:
- undergo regular preventive examinations;
- rational use of antiviral and other drugs (some drugs have a negative effect on platelet formation);
- eat rationally, avoid excessive consumption of animal fats, give preference to easily digestible varieties of meat (rabbit, turkey, fish);
- maintain sufficient drinking regime.
Using the MPV platelet index in a blood test, increased platelet aggregation, thrombosis, and active blood loss can be detected.
You should immediately consult a doctor if the following symptoms appear:
- change in color of the skin and/or mucous membranes;
- causeless formation of hematomas;
- frequent nose and gum bleeding;
- frequent increase in blood pressure and the appearance of tachycardia;
- sudden weight loss;
- weakness, constant fatigue, deterioration in general condition for no apparent reason and for a long time, which does not go away after proper rest.
Video from YouTube on the topic of the article:
Found an error in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
Treatment
Treatment tactics depend on the underlying disease for which this change in the blood is diagnosed. For physiological reasons, therapy is not required.
To establish a diagnosis, the doctor prescribes additional tests:
- biochemical and hormonal blood analysis;
- general urine analysis;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs;
- ECG and others.
Drugs
The main medications for treating conditions associated with elevated MPV are listed in the table below.
| Name | Purpose | Average dosage for adults per day | Average price, rub. |
| Antiplatelet drugs
| |||
| Clopidogrel | Decreased platelet activation and an increase in their average size without changing their absolute number | 75 mg | 670 |
| Plagril | 400 | ||
| Antifibrinolytic drugs | |||
| Desmopressin (synthetic analogue of the hormone vasopressin) | Preventing the destruction of blood clots and stopping severe bleeding | 0.1-0.2 mg 1-3 times a day | 1500 |
| Aminocaproic acid (5% solution for infusion) | 5 g until bleeding stops completely | 60 | |
| Medicines to control heavy menstrual bleeding in women | |||
| Levonorgestrel | Reducing blood loss during menstruation | According to the dosage regimen (daily) | 400 |
| Intrauterine device "Mirena" | — | 13 000 | |
| Iron supplements
| |||
| Totema | Treatment of iron deficiency anemia with heavy bleeding | 2-4 ampoules (100-200 mg iron) | 500 |
| Maltofer | 1-3 tablets (100-300 mg iron) | 300 | |
For severe, uncontrollable bleeding that occurs due to a bleeding disorder, platelet transfusion is indicated. This procedure is also performed after surgery. For such patients, taking Aspirin and NSAIDs (Ibuprofen, Naproxen and others) is contraindicated, as they can worsen symptoms.
Since all these drugs have side effects, their independent use is not allowed. A preliminary consultation with a doctor is required.
Diet
To reduce the risk of complications, you must adhere to the following dietary recommendations:
- Drink plenty of water and reduce the amount of table salt. Salty foods provoke an increase in blood pressure and the displacement of blood clots.
- Fatty meats and dairy products with a high percentage of fat content should be excluded from the diet. Instead, use lean meats and fish, vegetables, fruits, and cereals.
- It is also not recommended to consume spicy, smoked food and canned food, alcohol, coffee and cocoa, yeast baked goods and sweets with fatty creams.
- Omega-3 and omega-6 unsaturated acids, which are found in significant quantities in fish and seafood, contribute to the dissolution of blood clots.
- To restore iron levels, you can eat liver dishes (1-2 times a week). Preference should be given to steamed or boiled products.
If you have concomitant diseases, there may be other dietary restrictions, the need for which should be consulted with your doctor.
Traditional methods
To dissolve blood clots in folk medicine, the following recipe is used:
- Add 15 drops of horse chestnut tincture to 150 g of grapefruit juice.
- Add ½ tbsp. l. tincture of celandine, kept in vodka for 1 week (17% solution).
- Take this remedy regularly, with a break of 1 day every 6 days for 1 month.
- Then take a 2 week break.
- Continue treatment according to the same regimen, there should be 3-6 courses in total.
The following methods are used as hemostatic agents for heavy menstruation in women:
- Barberry tincture. 2 tbsp. l. crushed leaves of the plant pour 1 tbsp. boiling water and leave for 1 hour. Take 1 tbsp. l. 5 times a day.

- 1 tbsp. l. Pour a glass of boiling water over chopped nettle herb and keep on low heat for 15 minutes. Strain and take 1 tbsp. in a day.
- 1 tbsp. l. burnet roots pour 1 tbsp. boiling water, leave for half an hour. Drink 3 times a day.
The average platelet volume is used in laboratory practice for the diagnosis and control of various diseases that are associated with the blood and hematopoietic system.
If MPV is elevated in an adult, this may indicate serious pathologies that require additional diagnosis and treatment, since the platelet component of the blood is responsible for such important characteristics as clotting.
Description
Mean platelet volume (MPV) - characterizes the average value of platelet volume.
Due to the relatively short lifespan of platelets and their constant synthesis, formed elements are always present in human blood and are at different stages of their life cycle. At the same time, young and mature cells, as well as platelets, whose life cycle is already nearing completion, not only differ in size and saturation with biologically active substances, but also carry different functional loads. MPV in a blood test allows you to determine how many platelets of different sizes are in the blood at the moment.
Treatment of platelet abnormalities
It is important to understand that a high average platelet volume is not an independent disease, but only a concomitant symptom of the underlying pathology. Therefore, before starting treatment, you need to find out the reason for the increase.
If there is a slight deviation from the norm, you can correct the situation with proper nutrition. It is important to adhere to the following principles:
- Maintain drinking regime. You need to drink at least two liters of clean water per day.
- Replace animal fats with vegetable fats: preference should be given to olive and flaxseed oils.
- Replace fatty meats with dietary ones - rabbit, turkey.
- Eat lean fish.
- Eat foods that thin the blood: blueberries, cranberries, tomatoes, ginger, green tea.
Hormonal contraceptives, any alcoholic drinks, diuretics are strictly prohibited - they contribute to blood thickening and will only aggravate the problem.
Drug treatment is used to reduce platelet levels. Preparations containing acetylsalicylic acid are used.
Important! With an increased platelet volume, self-medication is unacceptable. Be sure to consult your doctor. He will find out the cause of the pathology and prescribe suitable medications.

Proper nutrition is the key to successful treatment of elevated platelets
To eliminate the problem, it is important not only to reduce the increased platelet volume, but also to influence the underlying disease that provoked it. Here are some examples:
- Thrombocytosis . The platelet level is elevated, so all efforts are aimed at lowering it. A diet and proper drinking regimen must be followed. But it is important to understand that thrombocytosis is just the tip of the iceberg; it can be caused by another disease. The doctor’s task is to find the root cause and choose the right treatment.
- Thrombocytopenia . In this condition, platelet levels are low. To treat the pathology, medications are prescribed that prevent the destruction of platelets, strengthen the walls of blood vessels and have a hemostatic effect.
- Diabetes . It is not completely curable, but can be corrected with a special diet, and in severe cases, insulin injections are used.
- Atherosclerosis . Treatment is aimed at reducing blood cholesterol through diet and medications.
An annual preventative medical examination will help you notice the problem in time and take steps to eliminate it. An increase in the average platelet volume is a serious pathology that can lead to dire consequences, including death. Therefore, timely measures will help maintain health and save life.
If you find yourself with similar symptoms, then contact your doctor, do not self-medicate or use folk therapy.
The photo shows what platelets look like in blood plasma, among erythrocytes and leukocytes.
Normal values
The norm for this indicator varies from 7.5 to 11 fL. The histogram allows you to estimate the number of platelets of different sizes. Normally, the content of mature cells should occupy 90% of the total platelet mass, young - no more than 0.8%, degenerative - 0.2%, old - 5.6%. In this case, the predominance of immature elements shifts the histogram to the left, and the predominant content of old cells shifts to the right. It is worth considering that deciphering the results can reveal certain changes in MPV (blood test) indicators even if the absolute platelet count is normal.
Symptoms
Symptoms characteristic of low MPV:
• tachycardia.
• being overweight.
• bluish tint of the skin.
• an increase in the size of blood vessels, the outlines of which are clearly visible through the skin.
• multiple subcutaneous hemorrhages, most often located on the anterior surface of the limbs, abdomen, and chest.
• frequent nosebleeds.
• women have long and heavy menstruation.
• hemorrhages in the retina.
When MPV increases.
Externally, an increase in MPV is more difficult to determine. However, there are a number of signs indicating this pathology:
• tachycardia.
• being overweight.
• bluish tint of the skin.
• an increase in the size of blood vessels, the outlines of which are clearly visible through the skin.
Blood clotting is an important property
Without blood clotting, a person simply would not survive, and platelets provide this feature of the blood. If you get hurt, an ambulance rushes in to stop the bleeding: platelets stuck together close the vessel wall. A clot, called a thrombus, forms and the bleeding stops.
MPV—mean platelet volume. Without a laboratory test, you can understand that mpv is lowered by bruising that often occurs for no apparent reason, bleeding gums, and frequent nosebleeds. The same fact will tell the specialist examining the mpv blood test about organ diseases. A deficiency in important blood elements (thrombocytopenia) leads to bacterial and viral diseases, problems associated with the bone marrow. The opposite complication - increased levels of them - is called thrombocytosis, and will also cause a number of serious disorders.
Platelet production is a constant process
Norm:
— 180 — 320 *109/l (adults);
- 100 - 420*109/l (newborns).
Depending on the research methods, these figures may vary slightly, but at the same time in healthy men and women they are at the same level. When a baby is born, the rate is significantly higher, and it becomes the same as in adults after a week.
Expectant mothers have slightly fewer platelets - 150 - 380 *109/l, because their blood volume increases, and the body does not have time to produce them in larger quantities. A decrease for no apparent reason (pregnancy, menstruation) to 150 *109/l or less causes concern among doctors, and additional examinations should be done to understand the cause.
The lifespan of platelets is 7–10 days, and the bone marrow produces them continuously. The dead cells are processed into waste by the liver and spleen. Pathological processes begin when the balance in production is disturbed for some reason. For example, if defective platelets continue to function, but there are few of them in the blood, it means that the cells are being destroyed too quickly in the spleen, and there are problems with this organ.
Possible complications
The average platelet volume is increased in an adult in the presence of disturbances in the hemostatic system. The most serious complications are bleeding and deep vein thrombosis (including the pulmonary artery).
Impaired blood clotting, for which platelets are mainly responsible, leads to the development of hemorrhagic syndrome. It can manifest itself both in a mild form, in the form of petechiae (small subcutaneous hemorrhages), and in a severe form - hemorrhages in the brain, ending in death.
Deep vein thromboembolism is also associated with high mortality. Blockage by blood clots can occur in various areas - in the veins of the lower extremities, lungs, pelvic organs (damage to the kidneys, liver) and heart. In this case, tissue infarction occurs. The risk of this complication is especially high in severe injuries, burns and in the postoperative period.