Infections of the genitourinary system cause discomfort and are very dangerous. It's not just about unpleasant symptoms - pain, burning, increased urination. Diseases of the urinary tract and bladder are fraught with complications. In almost half of patients, inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system occur repeatedly and have a chronic course, which leads to renal failure and disability.
This happens due to untimely and ineffective treatment. But identifying pathogens in the genitourinary tract is quite simple; just take a “bacteriological urine culture” test.
What is urine culture
This is an accurate and informative test for identifying bacteria in the genitourinary system that cause infectious diseases. Women often face this problem - their urethra is shorter and closer to the anus, and it is easy for bacteria to enter the urinary tract.
Men have an antibacterial substance in their prostate gland that reduces the likelihood of developing an infection. But even this may not save at certain moments, so urine culture for flora can also be prescribed for a man.
Preparing for diagnosis
The diagnostic results directly depend on the correctness of the study. The doctor must explain to the patient that this test will help determine the presence of a urinary tract infection. There is no need to introduce any dietary restrictions before the analysis. The patient is told in detail how to properly collect urine (an emphasis is placed on the toilet of the external genital tract immediately before the sample is taken). If necessary, a special catheter is inserted into the urinary tract. If there is a suspicion of tuberculosis, urine is collected in the morning for three days in a row. It is important to tell your doctor about taking antimicrobial medications. The patient must purchase a sterile urine collection jar and gloves from the pharmacy.
What is bioflora and why do you need to know its composition?
Flora is a complex of bacteria that inhabit a specific department or area in the body. Bioflora can be normal and pathogenic. Pathogenic composition implies the inclusion of pathogenic bacteria that have a detrimental effect on health. They can cause inflammation, destroy tissue, poison the body, or destroy beneficial flora, making room for other pathogens.
Knowing the composition of the flora in the organ, it is easy to choose an effective treatment. If pathogens are found that are resistant to most common drugs, an additional study is carried out - antibiotic sensitivity tests. The laboratory technician treats the sample with bacteria with different drugs, determining the strongest one that completely destroys the infection.
Why do you need a general urine test?
Children undergo a general urine test regularly at each medical examination. In the first days of life, at 1, 3, 6, 12 months, then at 2 and 3 years, at each examination before entering the children's group. The doctor may also prescribe this analysis during the treatment of acute respiratory viral infections and other diseases in order to know how the infection affected the functioning of the kidneys and digestive organs. Bacterial infections often disrupt the functioning of the kidneys and other organs of the genitourinary system, which is why it is so important to prevent irreversible consequences in a timely manner. Urinalysis helps diagnose various chronic diseases.
When is the test ordered?
Urine culture is a complex and highly informative study. Prescribed only by urologists or gynecologists for certain indications:
- there is a suspicion of the development of an infectious process in the body;
- treatment control is necessary ;
- confirmation of diagnosis is required ;
- a woman plans to become pregnant ;
- there was a relapse of the disease ;
- the patient has diabetes mellitus and the body is very weakened;
- sensitivity to antibiotics is established .
Based on the results obtained, the doctor draws up a treatment regimen. Pregnant women and patients with problems in the endocrine system must undergo the test. If the pregnancy progresses normally and the woman does not experience kidney problems, the test is scheduled immediately before childbirth, at the end of the third trimester.
Indications for bacteriological examination of urine
The main goals of the analysis pursued by the attending physician when prescribing urine culture are the diagnosis and monitoring of bacterial infections of the urinary tract, as well as determining the sensitivity of the pathogen to antibiotic therapy.
Sometimes bacteriological examination (bacteriological culture) of urine is used as a screening for the prevention of inflammatory diseases of the urinary tract in people at high risk (pregnant women, the elderly, patients with diabetes mellitus). The main indication for urine culture is the presence of symptoms of urinary infection.
However, according to Russian urological recommendations, if a patient has an uncomplicated urinary infection, as well as in the absence of concomitant diseases, antibacterial therapy can be prescribed empirically, without first identifying the pathogen. Empirical prescription of antibiotics achieves a positive effect in approximately 75-80% of cases.
Absolute indications for conducting a urine microflora test are:
- 1Urinary tract infections in pregnant women;
- 2Suspicion that the patient has pyelonephritis;
- 3All cases of urinary tract infection in men;
- 4Outbreaks of hospital-acquired urological infections;
- 5 Fever during prolonged catheterization of the bladder, as well as suspicion of a urological infection associated with medical procedures (cystoscopy, catheterization);
- 6 Fever above 38 C for no apparent reason in children under 3 years of age;
- 7 Recurrent urinary infections, ineffectiveness of previously conducted empirical antimicrobial therapy;
- 8Complicated urinary infections over the age of 65 years;
- 9The appearance of symptoms of urological infection in persons with impaired immune status, chronic kidney disease, diabetes mellitus, congenital anomalies of the structure of the kidneys and ureters, after kidney transplantation;
- 10The patient had taken antibacterial drugs during the previous three months, which theoretically could lead to the formation of resistant forms of pathogens.
According to the recommendations of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, mandatory screening bacteriological urine culture is regulated, even in the absence of symptoms of urinary system pathology, in the following population groups:
- 1Women during pregnancy, after the 14th week, even in the absence of any symptoms of pathology, which reduces the risk of developing pyelonephritis in pregnant women;
- 2Patients with planned surgical intervention on the organs of the urinary system;
- 3Patients with a kidney transplant during the first two months after surgery, and then with any deterioration in the functioning of the transplanted organ.
Preparation
Since the purpose of the analysis is to determine the content of microorganisms in urine, and not on the surface of organs, it is important to prevent the container for collecting urine from coming into contact with the genitals, hands, etc.
Before the procedure, you need to thoroughly wash and dry your hands and perform intimate hygiene procedures without antiseptics.
The day before the analysis, it is not advisable to perform any physical activity or eat food that has dyes. If the rules for preparing and collecting urine were violated, the results will be false and the treatment will be incorrect.
Execution technique
Russian laboratories carry out urine microflora testing in accordance with the order of the Ministry of Health No. 535 of April 22, 1985 “ON THE UNIFICATION OF MICROBIOLOGICAL (BACTERIOLOGICAL) RESEARCH METHODS USED IN CLINICAL AND DIAGNOSTIC LABORATORIES OF TREATMENT AND PREVENTIVE INSTITUTIONS”
Over the past few years, the order has been supplemented and updated several times.
A bacteriologist and a laboratory assistant (paramedic laboratory assistant) are involved in carrying out bacteriological culture. The doctor’s responsibilities include monitoring the technology of the study and directly performing all the necessary stages of diagnosis.
The laboratory assistant is responsible for receiving incoming urine samples, preparing accompanying documents for them, preparing the necessary diagnostic media and reagents, cultivating cultures, quantitatively counting grown bacterial colonies, destroying consumables and sample residues.
Several types of nutrient media are used for sowing:
- 1Universal (blood agar, CLED) – supporting the growth of both gram-positive and gram-negative microorganisms;
- 2Differential diagnostic (chromogenic) – used for differentiation of uropathogens, changing color upon contact with the products of their vital activity;
- 3Selective (Columbia agar, Endo agar, MacConkey) - allow you to separately grow gram-positive and gram-negative pathogens.
The acquisition of nutrient media for the cultivation of pathogens occurs in ready-made form or in the form of specialized dry mixtures for self-preparation. For dry mixtures, instructions are required that precisely regulate all stages of preparation.
To obtain the result of bacterial culture of urine using a non-sector method, a certain volume of the test material is applied to a Petri dish filled with a non-selective medium (in this case, exactly 1 µl of urine). Then a special microbiological loop, tated to the appropriate volume, is immersed into the sample under study.
The material is distributed over the surface in the central area in the form of several straight lines, and then horizontal strokes perpendicular to them.
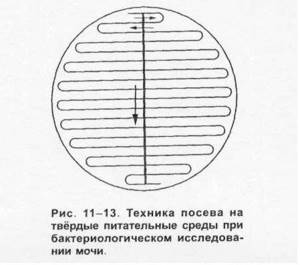
Figure 3 - Urine culture, application of material to the nutrient medium in a Petri dish
When using the sector sowing method, the Petri dish is pre-divided into 4 equal sectors, designated by letters of the alphabet. A sterile loop is used to inoculate urine in an amount of 0.005 ml, alternately in four sectors. When moving to the next sector, the loop is first burned through.
Culture of urine on non-selective media allows for quantitative culture, while selective media are used to obtain isolated colonies and primary determination of the microorganism, so urine is not applied to them evenly.
Petri dishes are kept in a thermostat at a temperature of 35-37 for 18-24 hours, after which the result is calculated. In some cases (weak growth of flora, discrepancy between the result and the clinical picture, suspicion of the presence of fungi, etc.), incubation can be extended to 2 days.
When bacterial growth is detected, using special tables, all types of grown colonies are taken into account, and their possible pathogenicity is also assessed.
When probable uropathogens are detected, they are further identified by studying cultural, biochemical, tinctorial and agglutinative properties, and the degree of their sensitivity to antimicrobial drugs is determined.
How is the analysis carried out?
The biomaterial is collected in a special cup purchased at the pharmacy. It must be clean and dry. There is no point in collecting urine in the evening and taking it to the laboratory the next morning; procedures must be done 2-4 hours before the test.
Only morning urine is used for examination; you need to take an average portion of 70 ml. The first jet washes the urinary canals, it descends, the last one is also not needed for analysis. It is important that the edge of the container does not touch the labia. When the material is selected, the lid of the container is carefully closed and the sample is taken to the laboratory.
Rules for collecting material
We will discuss below how to properly take a urine culture test during pregnancy, in adults and children. To ensure the accuracy of laboratory diagnosis of urological infection, it is important to comply with all stages of diagnosis, including its preanalytical part - the collection of urine samples and their delivery.
It is the need to determine the exact amount of bacterial agents in the test sample that places special demands on sample collection.
When conducting research in a hospital setting, the nursing staff of the hospital is responsible for preparing the patient, collecting material and transporting it to the laboratory. For such cases, laboratories have written instructions regulating all diagnostic steps.
When examined on an outpatient basis, the patient collects urine independently, without the supervision of a medical professional. In connection with the above, it is necessary to carefully instruct the patient on the technique of independently collecting the test material in order to avoid false analysis results.
- 1Urine collection must be done in a sterile disposable container specially designed for this purpose, which can be purchased at the pharmacy chain. It is not allowed to collect urine in non-sterile, previously used containers, jars or bottles;
- 2If possible, urine collection should be carried out before starting to take antibacterial drugs or in the intervals between drug courses, to avoid distortion of the information received;
- 3The most reliable study is the average morning urine sample - after a night's sleep and before breakfast;
- 4 In the evening, on the eve of urine collection, it is recommended, if possible, to refrain from taking diuretics, since when they are taken, the urine is diluted and the total number of bacteria in one milliliter is reduced;
- 5 To collect urine from infants, you should use special children's urinals with a hypoallergenic adhesive; the collected sample is subsequently poured into a urine collection container, labeled and transported to the laboratory.
Figure 1 - Sterile containers for collecting urine for analysis (without a spatula)
What the result shows
The purpose of the study is to identify the causative agent of the inflammatory process and whether the permissible limit for the number of bacteria is exceeded. Are there any among them that can cause serious harm to health? The concentration of various microorganisms (fungus, protozoa, bacteria) is taken into account, and a general assessment of the condition of the urinary system is made.
On average, results are prepared within 10 days. All this time, the bacteria grow and are studied. If no process occurs, the test will be negative - the person is healthy. Active proliferation of microorganisms indicates a positive test result. The type of bacteria affecting the genitourinary system is identified using a microscope and chemical testing. The conclusion indicates which drugs these microorganisms are sensitive to.
“What is tank analysis and why is it needed”
Date: 12/04/2019
Bak analysis (bacteriological culture) is an analysis that identifies pathogenic bacteria that depress the health of the gastrointestinal tract and cause various intestinal diseases - the causative agents of salmonellosis, dysentery, typhoid fever and other dangerous parasites. The essence of this diagnostic method is that stool samples placed in a special environment favorable for the development and reproduction of bacteria and other microorganisms. During the study, the exact time, temperature, and lighting level necessary for the development of microbes are established. Different types of bacteria have their own environment. The study is carried out in a special Petri dish. If the test material contains pathogenic microorganisms, then in a favorable environment they will begin to multiply at an active pace, and then the picture of the disease will become clearer. Based on the results of the study, the treating specialist can establish an accurate diagnosis, treatment and duration of treatment. This method also allows you to establish an antibiogram for treatment. Indications for tank analysis Bacteriological analysis of stool is prescribed under the following circumstances: If there is a suspicion of the presence of parasites or pathogenic microorganisms in the intestines. Long-term disturbances in the intestines. If intestinal disorders are being treated, tank analysis is used to evaluate the result therapy. As a general examination or before any medical procedures. After the use of antibiotics, hormonal drugs, after treatment with chemotherapy or radiation therapy. There are no contraindications for this diagnostic method
How to correctly take a bacteriological analysis of feces For the accuracy of the study, you need to follow a number of rules to avoid distortion of the results: The container in which you want to pass feces must be sterile. It is not allowed to reuse the same container for testing. Feces must be fresh and obtained only through natural bowel movements. You cannot use suppositories, laxatives, or enemas. A few days before collecting the material, it is better to follow a special diet that excludes foods that can cause stool coloration, increased gas formation, constipation, or stomach upset. These are dried fruits, dairy products, beets, cabbage, dried apricots. If a patient has individual reactions to any product, it should also be excluded from the diet. In addition to eliminating a certain type of food, you need to follow a general diet: it is recommended to exclude fried, smoked, and highly salty foods. In particular, you need to remove flour and sweet dishes. 2-3 days before the procedure, you need to stop using drugs that affect the gastrointestinal tract - antibiotics, activated charcoal, etc. During menstruation, it is better for women not to take a stool test, but if this is still required, then the vaginal opening should be closed with a tampon to avoid blood getting into the stool. 3-4 days before collecting stool, X-ray procedures should not be performed, especially using the contrast agent barium sulfate, which can discolor stool. Feces should be donated in a small, clean container, which can be purchased at any pharmacy. The kit includes a sterile sealed container and a spatula, with which you need to collect 5 - 12 grams of feces from different areas and put them in a container. It is necessary to collect stool from different places for a more accurate result, since microorganisms may not be located everywhere in the stool. Containers with samples should be submitted to the laboratory along with a referral previously taken from the therapist and a form on which the results of the study will be written. It will be better if if feces do not come into contact with the surface of the toilet. No matter how often the toilet is cleaned, bacteria and harmful substances are still present on it. You can cover the toilet hole with cling film, securing it to the sides, and defecate directly on the film. But this method is not very convenient. Test collection in clinics and laboratories starts early in the morning, so it would be better to collect the material immediately before delivery. If this is not possible for any reason, it is allowed to store feces in a tightly closed container in the refrigerator. You cannot keep containers with feces in places where the temperature is above +5 and in places exposed to sunlight. This can cause fermentation and rotting processes, which will affect the test result. Peculiarities of donation in children If you need to donate feces from a baby, it can be collected from a clean, dry diaper. Collecting feces from a diaper is not recommended, since urine may get on the feces, which is unacceptable when collecting feces in both adults and children. You need to put the baby on his back, lay a diaper under his body, and begin to lightly massage the tummy. After some time, the feces should come out onto the diaper, from where they need to be collected. If the child has defecated urine, then he should be washed and put on a new diaper. If the child is already using the potty, then tests can be taken directly from there. But before the child goes to the toilet, the potty must be thoroughly rinsed and doused with boiling water to get rid of bacteria. What is a urine culture test? In order to prescribe competent treatment, the doctor gives the patient a referral for a urine culture test. A bacteriological urine culture test is carried out in order to recognize the causative agents of infectious and inflammatory processes in the bladder and urinary tract. When a person is healthy, his bladder does not contain harmful microorganisms, that is, the urine found in the cavity of the bladder is sterile. When pathogenic microflora enters the urethra, the infection can reach the bladder area through the ascending tract and settle there. The kidneys filter water and liquid that is no longer needed in the body, becomes waste material and is excreted. It also contains bacteria that create a source of inflammation or infection in the body. . What does the method of bacterial culture of urine show? In laboratory research, urine is placed in a special environment favorable for the development and growth of microorganisms. Moreover, each microorganism needs its own habitat with the correct acid and water balance. If the bacteria do not spread over the surface of the urine, then the test is considered negative.
With increased proliferation of microorganisms, experts conclude that the results are positive. In this case, the patient needs to seriously think about his health and not delay treatment. In order to accurately determine the type of bacteria that have settled in the human body, they conduct a number of special studies. If an infection has been detected, some antibiotics are tested on it. A urine culture is taken to identify the number of pathogenic microorganisms and identify possible medications that can be used to get rid of them.
In such a study, laboratory specialists are guided by the normative indicators established for medical standards. Read about what urine analysis for cystitis says in our article. Indications for analysis Collection of urine for analysis is prescribed in the following cases: if the attending physician suspects the presence of an infectious process, occurring in the bladder, kidneys or urinary tract; to confirm or refute the diagnosis; if a patient suspects diabetes mellitus or tuberculosis; reduced immunity can also prompt a medical specialist to conduct an analysis; in order to ensure the effectiveness of the chosen treatment. Culture can identify the following pathogens : If we are talking about an analysis prescribed for a child or people with gastrointestinal diseases, then it is possible to detect dysentery and enterococcus. Chlamydia in urine. Staphylococcus. These microorganisms have a detrimental effect on the body of the expectant mother. Gonorrhea. This test is performed for those patients who suspect a sexually transmitted infection. If tuberculosis is suspected, the doctor wants to identify the presence of Koch's bacillus. The test is prescribed by a therapist, urologist, and sometimes a gynecologist. This technique identifies pathological processes occurring in the urinary system in pregnant women.
In addition to cases where there are complaints from the expectant mother and an urgent test is needed, doctors give a referral for the procedure twice during the period of gestation. Men sometimes undergo the same test in order to determine whether they have an infectious process in the bladder and other organs. Indicators of the analysis and its decoding It is not difficult to decipher the analysis if you know the unit of measurement for the number of microorganisms and the normal limits within which urine indicators are measured. The results will indicate the types of microorganisms present in the urine, as well as the presence of fungi if they are also present in the urine. Additionally, drugs that can cope with these pathogens will be indicated. The picture is clickable, click to enlarge) In the result obtained, the patient will find the abbreviation COE. It stands for colony-forming unit and is used to calculate the presence of bacteria in the body. If the size of the colony-forming unit is less than one thousand, then treatment is not required, and the number of microorganisms living in the urine is considered normal. If the colony-forming unit reaches more than one million particles, such information indicates an extensive inflammatory process or infectious lesion of the bladder. If the bacteria are slightly higher than normal, then we are talking about an inflammatory process or a focus of infection that has recently arisen in the urinary tract or bladder. Types of urine cultures A urine culture test is carried out to identify bacteriuria, that is, the presence of a certain amount of bacteria in the urine, indicating on the inflammatory process taking place in the cavity of the bladder and kidneys. In another way, bacteriuria is called pathogenic microflora. Bacteriuria most often appears in diseases such as: cystitis; bacterial sepsis; prostatitis; urethritis; diabetes mellitus. Normally, urine is sterile; when deviations from sterility occur, this condition is called bacteriuria.
Hemotest is carried out in cases where it is necessary to determine hidden food allergens in the blood. In this case, there is no need to conduct research on a urine sample. Microflora analysis involves determining, in addition to bacteria, the presence of protozoa and fungi. Yeast may be found in urine. Its presence indicates serious illnesses, a stressful situation experienced, or poor nutrition leading to this condition. Sometimes Candida fungi may appear in urine. The presence of this microorganism indicates improper hygiene or wearing synthetic underwear. They pose a danger due to rapid reproduction, leading to an allergic reaction of the body. Protozoa are often detected in urine, these primarily include Trichomonas vaginalis, amoebas that cause amoebic cystitis, as well as chlamydia. The causative agents of protozoal diseases penetrate the bladder through the blood or lymph flow, and in women the route of penetration from the anus through the urethra is possible. If detected, you must immediately visit your doctor, who will prescribe medications to eliminate it, usually these are drugs with an antiprotozoal effect.
Author: Taisha
Asem Sharafikyzy
GP on RVC Regional Infectious Diseases Hospital
bacteriological laboratory – tank
laboratory assistant
What types of urine tests are there?
There are several types of urine tests that a pediatrician or specialist can prescribe for a child:
- A general urine test, which is prescribed in tandem with a blood test. Helps evaluate the physical and chemical composition: density, color;
- Biochemical urine analysis. The content of protein, glucose, amylase, creatinine, sodium, potassium, phosphorus, magnesium, microalbumin, urea and uric acid is calculated in the urine;
- Urinalysis according to Nechiporenko. Demonstrates the number of leukocytes and erythrocytes in morning urine and allows you to diagnose pathological processes in the kidneys and urinary tract;
- Urine analysis according to Zimnitsky. Prescribed to assess kidney function. In this case, daily urine is collected, its volume, density, and the ratio of daytime and nighttime portions are assessed. The analysis is carried out when diagnosing various diseases.