Amylase and lipase are digestive enzymes. Their quantity in the bloodstream is used to diagnose the condition of the pancreas if pancreatitis is suspected. Tests can be carried out on the direction of a doctor or at the request of the patient himself, but only a specialist can interpret the results and, if necessary, prescribe treatment. To obtain the most accurate results, special preparation is required before donating blood. For 10 hours before the tests, you must stop eating and avoid significant physical activity and stress.
Lipase test
Lipase is an enzyme that is necessary for the breakdown of fats. The results of a blood test for lipase play an important role in the diagnosis of diseases such as obstruction of the pancreatic duct and pancreatitis in acute or chronic form. Reference values for this enzyme are 13-60 IU/L. If the test results are within these values, this indicates that at the moment the pathological process does not affect the pancreas.
Increased performance
may indicate acute or chronic inflammation, neoplastic changes, traumatic damage to the pancreas, or blockage of its ducts. It is impossible to make an accurate diagnosis and select an effective treatment method based on the results of one test. For this purpose, an examination is prescribed, which may include both laboratory tests and instrumental studies.
Concentration too low
enzyme in the blood may indicate a decrease in the functional activity of the pancreas or cystic fibrosis. Determination of lipase levels has a high diagnostic value in identifying various pancreatic pathologies. The enzyme is produced only by the cells of this organ, so it can be used as a marker of its condition.
When interpreting the results, the patient’s age, clinical picture, results of other studies and other factors are taken into account.
Alpha amylase (spot urine)
Test to determine damage to the pancreas and abdominal organs. The activity and presence of amylase in the urine directly depends on its activity in the blood serum. This enzyme is produced in the pancreas and also in the salivary glands.
Alpha amylase (diastase)
- a digestive enzyme that is mainly synthesized in the pancreas and salivary glands of humans. This enzyme is involved in the breakdown and absorption of complex carbohydrates by the body. Together with other enzymes, diastase, after digestion, enters the bloodstream and is also excreted from the body in the urine.
An alpha-amylase urine test is prescribed for abdominal pain. It will be increased:
- with pancreatitis. In this case, its indicator increases several times and can reach 128–256 units, despite the fact that the norm is within the range of 16–64 units;
- with mumps (inflammation of the salivary glands);
- with cholecystitis (inflammation of the gallbladder);
- with renal failure, diabetes mellitus.
Slightly increased diastasis is determined in acute inflammatory diseases of the abdominal organs (colitis, gastritis, appendicitis, peritonitis).
Before the study, it is also worth considering that amylase has the property of instability in acidic urine.
Indications:
- damage to the parotid glands;
- damage to the pancreas;
- acute stomach;
- viral infections;
- decompensated diabetes.
Preparation
On the eve of the test, it is not recommended to eat vegetables and fruits that can change the color of urine (beets, carrots, cranberries, etc.), or take diuretics.
Collect a strictly morning portion of urine, excreted immediately after sleep. Before collecting urine, it is necessary to perform a thorough hygienic toilet of the external genitalia. When urinating for the first time in the morning, release a small amount of urine (the first 1-2 seconds) into the toilet, then collect the entire portion of urine in a clean container without interrupting urination. Pour approximately 50 ml of urine into a sterile plastic container with a screw cap. When collecting urine, it is advisable not to touch the container to your body. The container with urine must be delivered to the medical office within 2 hours from the moment the biomaterial is taken.
Women are not recommended to take a urine test during menstruation.
Interpretation of results
Units of measurement: Units/hour. Alternative units: U/l. Reference values: 1–17 U/h.
Level up:
- mumps;
- pancreatitis;
- bowel obstruction or infarction;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- perforation of a hollow organ;
- diseases of the biliary tract of all types;
- diabetic ketoacidosis;
- pancreatic cyst;
- peritonitis;
- some lung and ovarian tumors;
- renal failure;
- abdominal trauma;
- skull damage;
- viral infections;
- postoperative period;
- alcohol.
Amylase test
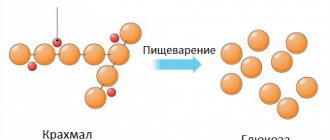
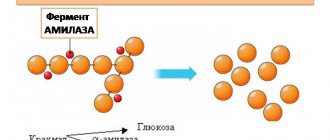
Amylase is an enzyme that is responsible for the breakdown of carbohydrates. It, unlike lipase, is produced not only by the pancreas, but also by the salivary glands. In addition, some amount of the enzyme is produced in the skeletal muscles, intestines and ovaries. A blood test for amylase is prescribed to patients with acute or chronic pancreatitis, if pathology of the ovaries or salivary glands is suspected.
In patients over 18 years of age, the enzyme level should not exceed 53 U/l. The norm for children varies depending on their age. The level of pancreatic amylase is analyzed by the doctor taking into account the total amount of enzyme. In acute pancreatitis, in most cases there is a significant increase in the amount of pancreatic enzyme. Sometimes the increase in indicators is insignificant or they remain within normal limits. The test results do not reflect the degree of damage to the pancreas, so a comprehensive examination is performed to confirm the diagnosis and develop a treatment regimen. An increase in indicators can be caused not only by pancreatitis, but also by traumatic damage to the pancreas, its oncology, blockage of the pancreatic duct, rupture of an aortic aneurysm, perforated ulcer, peritonitis, intestinal obstruction and other pathologies.
In acute pancreatitis,
amylase levels usually rise before lipase levels
. The lipase concentration remains high longer. To obtain a complete picture, a study to determine the amount of these two enzymes is carried out simultaneously.
Pancreatic amylase
Amylase is a digestive enzyme that can break down carbohydrates. The largest amount of amylase is found in the salivary and pancreas glands. Amylase, which is produced in the pancreas - pancreatic amylase (P-type) - is part of pancreatic juice. From the pancreas, pancreatic juice containing lipase passes through the pancreatic duct into the duodenum, where it helps digest food. Amylase of the salivary glands - salivary amylase (S-type) - digests food starch in the oral cavity. Normally, a small amount of amylase circulates in the blood. In this case, about 60% is salivary amylase (S-type), and the remaining 40% is pancreatic amylase. When damage to the pancreas occurs, as in pancreatitis, or if the pancreatic duct is blocked by a stone or tumor, pancreatic amylase (P-type) begins to leak into the bloodstream in large quantities. There is no increase in salivary amylase. Small amounts of amylase are also produced in the ovaries, intestines and skeletal muscles. What is analysis used for? An increase in the level of pancreatic amylase in the blood without a change in the level of salivary amylase confirms the pathology of the pancreas. For example, in acute pancreatitis, its content in the blood can increase to 90% of the total amount of amylase. For the diagnosis of pancreatitis in the postoperative period, when the level of total amylase is elevated. If pathology of the salivary glands, ovaries or bronchi is suspected. When is the test scheduled?
- When the diagnosis of “acute” or “chronic pancreatitis” is confirmed.
- If you suspect a disease of the salivary glands and ovaries.
Causes of increased pancreatic amylase levels
- Acute pancreatitis. With this disease, the level of pancreatic amylase can be significantly higher than normal and constitute a larger percentage of the level of total amylase. However, in some patients with acute pancreatitis, amylase may increase slightly or even remain normal. In general, the amount of amylase does not reflect the severity of damage to the pancreas during pancreatitis. For example, with massive pancreatitis, sometimes the death of most of the cells that produce this enzyme occurs, so its level may not be changed.
- Chronic pancreatitis. With it, the amylase level is initially moderately elevated, but then may decrease and return to normal as damage to the pancreas worsens.
- Decompensation of diabetes mellitus is diabetic ketoacidosis, both due to high sugar levels and due to the concomitant involvement of the pancreas in the pathological process.
- Trauma to the pancreas.
- Pancreas cancer.
- Blockage (stone, scar) of the pancreatic duct.
- Acute appendicitis, peritonitis.
- Perforation (perforation) of a stomach ulcer.
- Acute cholecystitis is inflammation of the gallbladder.
- Intestinal obstruction.
- Ruptured aortic aneurysm.
- Macroamylasemia is a condition where amylase binds to large proteins in the serum and therefore cannot pass through the glomeruli, accumulating in the blood.
Reasons for decreased pancreatic amylase levels
- Decreased pancreatic function.
- Cystic fibrosis (cystic fibrosis) of the pancreas is a severe hereditary disease associated with damage to the exocrine glands (lungs, gastrointestinal tract).
- Removal of the pancreas.
What can influence the result? Captopril, corticosteroids, oral contraceptives, furosemide, ibuprofen, and narcotic analgesics can increase amylase levels. Chronic renal failure sometimes leads to an increase in the concentration of pancreatic amylase. High cholesterol can cause low levels of pancreatic amylase.
Preparation for the procedure
- A biochemical blood test is taken in the morning and strictly on an empty stomach. At least 8 hours should pass between the last meal and blood collection (preferably at least 12 hours). Juice, tea, coffee, especially with sugar, cannot be drunk! You can drink water.
- It is advisable to exclude fatty and/or fried foods and alcohol from the diet 1-2 days before the examination. If there was a feast the day before, the laboratory test should be postponed for 1-2 days.
- One hour before taking blood, you must refrain from smoking.
- It is necessary to exclude factors that influence the research results: active physical activity, emotional overexcitation. Before the procedure, you need to rest for 10-15 minutes and calm down.
- Blood is taken for analysis before starting medications (for example, antibacterial and chemotherapy) or no earlier than 10-14 days after their discontinuation. You must inform your doctor about taking medications.
- Blood should not be donated after radiography, ultrasound or rectal examination, physiotherapeutic procedures, physical therapy, acupuncture (reflexology), massage.
Prices
| Pancreatic amylase | 150 ₽ |
All prices
Name in English: Amylase pancreatic
Pancreatic amylase is a digestive enzyme, a type of amylase that is produced by the pancreas and is capable of breaking down carbohydrates. The largest amount of amylase is found in the salivary and pancreas glands.
Amylase produced by the pancreas, pancreatic amylase (P-type), is part of pancreatic juice. From the pancreas, pancreatic juice containing lipase passes through the pancreatic duct into the duodenum, where it helps digest food.
Amylase of the salivary glands - salivary amylase (S-type) - digests food starch in the oral cavity.
Normally, a small amount of amylase circulates in the blood. In this case, about 60% is salivary amylase (S-type), and the remaining 40% is pancreatic amylase.
When damage to the pancreas occurs, as in pancreatitis, or if the pancreatic duct is blocked by a stone or tumor, pancreatic amylase (P-type) begins to leak into the bloodstream in large quantities. There is no increase in salivary amylase activity.
Small amounts of amylase are also produced in the ovaries, intestines and skeletal muscles.
Biochemical blood test: normal indicators
| Analysis: | Men: | Women: |
| Total protein | 64-84 g/l. | 64-84 g/l. |
| Hemoglobin | 130-160 g/l | 120-150 g/l. |
| Haptoglobin | 150-2000 mg/l | 150-2000 mg/l |
| Glucose | 3.30-5.50 mmol/l. | 3.30-5.50 mmol/l. |
| Urea | 2.5-8.3 mmol/l. | 2.5-8.3 mmol/l. |
| Creatinine | 62-115 µmol/l | 53-97 µmol/l. |
| Cholesterol | 3.5-6.5 mmol/l. | 3.5-6.5 mmol/l. |
| Bilirubin | 5-20 µmol/l. | 5-20 µmol/l. |
| AlAT (ALT) | up to 45 units/l. | up to 31 units/l. |
| ASAT (AST) | up to 45 units/l. | up to 31 units/l. |
| Lipase | 0-190 units/l. | 0-190 units/l. |
| Alpha amylase | 28-100 units/l. | 28-100 units/l. |
| Pancreatic amylase | 0-50 units/l. | 0-50 units/l. |
Peptides in blood tests
One of the convenient options for checking blood biochemistry for normal values is the corresponding table. If the C-peptide is higher, then there is a suspicion of excessive insulin synthesis, the development of tumor formation or pancreatitis. A decrease compared to the standard may occur, this is possible during inflammation or diabetes (only the first type).
Content of glucose and carbohydrate metabolism metabolites
In diabetes mellitus, glucose increases, other reasons: problems with the central nervous system, pituitary gland, thyroid gland, brain injuries. If normal blood biochemistry levels for glucose in adults are underestimated, it is worth checking the endocrine system, liver and pancreas.