When should a lipase test be done?
A doctor will usually order a lipase test if a person has signs of pancreatic disease.
The lipase test is a blood test. Preparation for the test is minimal. The doctor usually asks the patient not to eat for a certain period of time, usually 8 to 12 hours, before performing a blood test.
A person taking any drugs or supplements should tell their doctor in advance, as some compounds may interfere with the results. Drugs that may affect the results:
- codeine;
- thiazide diuretics;
- morphine.
Lipase test results are usually measured in IU/L (international unit per liter). The optimal lipase range is 7-60 IU/L. High or low lipase levels can signal different problems.
Preparing for analysis
A blood test for lipase is always prescribed in the morning, on an empty stomach. To determine the quantitative content of lipase, venous blood is required.
Before taking the lipase test, you need to do some preparation.
The day before the collection, exclude fatty, spicy, fried foods from the diet. Stop eating any food 8-12 hours before, you can only drink weak unsweetened tea and water. It is prohibited to drink alcohol the day before and 3 days before the test. In the last 24 hours, limit physical activity.
For complex diagnostics, take the test before using radiological research methods (fluorography, abdominal x-ray, etc.).
Failure to comply with the rules can provoke excessive release of the enzyme in response to fatty foods or exercise, or contribute to the suppression of pancreatic function (after exposure to radioactive radiation). Such a violation will cause an incorrect result, which will disrupt the diagnosis and selection of complex therapy.
Currently, lipase in the blood is determined by two methods:
immunochemical; enzymatic.
The latter is more often used in laboratories, as it has higher efficiency and speed.
Increased lipase in the blood - causes
If the lipase level is 5-10 times higher than normal, this indicates acute pancreatitis. Pancreatic disease causes increased lipase levels. These levels may remain elevated for up to 2 weeks. High lipase levels can also indicate other problems, such as kidney or intestinal problems.
Elevated lipase levels can indicate a number of diseases, such as:
- acute pancreatitis;
- gallstone gastroenteritis, which occurs when a virus causes; inflammation of the stomach;
- intestinal problem;
- cholecystitis or sudden inflammation of the gallbladder;
- celiac disease;
- pancreatic cancer;
- renal failure.
Acute pancreatitis
Acute pancreatitis is one of the most common problems associated with high levels of lipase in the blood. When a doctor detects this disease at an early stage, treatment may include:
- intravenous infusions;
- painkillers;
- diet.
Your doctor will prescribe treatment for underlying conditions associated with pancreatitis, such as gallstones or elevated calcium levels. Some medications can cause acute pancreatitis, in which case your doctor will change the type or dosage.
A person can reduce the risk of developing acute pancreatitis by eating a healthy diet and avoiding excessive alcohol consumption.
The lipase test is relatively non-invasive and is unlikely to cause any complications. The test results will help your doctor diagnose acute pancreatitis and other health problems affecting the pancreas. Finding and treating acute pancreatitis early can prevent the condition from getting worse.
Lipase - what is it? Protease, amylase, lipase
Laboratory diagnostics doctor (head of clinical diagnostic laboratory) Lavitskaya T.V.
A lipase test is prescribed for suspected gastrointestinal diseases. Let's take a closer look at the enzyme called lipase - what is it? What functions does it perform in the body, and what diseases is indicated by its deviation from the norm in test results?
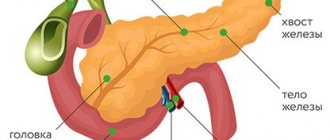
Lipase is an enzyme produced by certain organs of the human body. It dissolves, separates and digests various fractions of fats, and also performs a number of other important tasks. Pancreatic lipase is of primary importance. Its activity can be assessed when fats enter the body.
The enzyme “works” together with colipase (coenzyme) and bile acids. In addition to the pancreas, it is produced by the lungs, stomach, intestines and even leukocytes - white blood cells belonging to the immune system. There is also such a thing as “lingual lipase” . What it is?
This is an enzyme that is produced in the oral cavity of newborn children for the primary breakdown of food, that is, for the breakdown of mother's milk. Pancreatic lipase.
Its level in the blood is much higher than the level of other types of lipase. However, during pancreatectomy (removal of the pancreas), a small percentage of lipase will still remain due to its release by other organs. Lipase is normally absent in urine tests. After “birth” in the pancreas, it enters the intestines, where it performs its main function - it breaks down fats. Pancreatic lipase plays a particularly important role. It is for its determination that blood is donated, since changes in this indicator can help in the diagnosis of many diseases. We'll look at which ones below.
Functions of lipase in the body
In addition to the breakdown of fats, lipase is involved in energy metabolism, and also takes part in the absorption of polyunsaturated fatty acids and even some vitamins - in particular A, D, E, K. Hepatic lipase is responsible for regulating the content of lipids in plasma. It promotes the absorption of chylomicrons and low-density lipoproteins.
Lipase test
Lipase analysis is carried out in two cases:
-To detect pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas).
— To assess the effectiveness of treatment of pancreatitis.
A blood test for lipase is considered more informative for the diagnosis of acute pancreatitis than the determination of amylase in the blood. However, in the later stages of acute pancreatitis, lipase levels may decrease.
How to prepare for the analysis?
Blood is donated strictly on an empty stomach; you can only drink water before taking the test. At least 8-12 hours should pass after the last meal. It is better to do this before starting to take medications or 1-2 weeks after stopping them. If this is not possible, before donating blood, you should inform about what medications are being used. The day before taking blood, you should go on a light diet - exclude fatty, fried, spicy foods, alcohol, and also avoid heavy physical activity. It is recommended to donate blood before other studies - fluorography, radiography - or physiotherapeutic procedures.
Normal level of lipase in the blood
An indicator of many diseases is the enzyme lipase, the norm of which in adult men and women is almost the same. In adults, that is, persons over 18 years of age, from 0 to 190 units. In children (under 17 years of age), lipase levels from 0 to 130 units are considered acceptable.
What does an increase in the level of an enzyme called lipase indicate?
The normal level of its content indicates that everything is in order with the pancreas, but if the levels are elevated, this may indicate the following diseases:
Acute pancreatitis or exacerbation of a chronic disease.
Biliary colic.
Chronic pathologies of the gallbladder.
Injuries of the pancreas.
The presence of neoplasms in the pancreas.
Blockage of the pancreatic ducts (stone or scar).
Intrahepatic cholestasis (and decreased flow of bile into the duodenum).
Acute intestinal obstruction.
Intestinal infarction.
Peritonitis (inflammation of the peritoneum).
Perforated stomach ulcer. Perforation of a hollow organ.
Liver pathology, acute or chronic.
Epidemic parotitis (“mumps”), causing complications on the pancreas. Metabolic disorders, which is usually observed with gout, diabetes, obesity.
Cirrhosis of the liver
Reasons for low blood lipase levels
If lipase is low, this indicates problems such as:
-Development of any cancer with the exception of pancreatic cancer. — - Excess triglycerides, which occurs with poor nutrition, in particular excessive consumption of fats.
-Transition of pancreatitis to the chronic stage.
Our body produces food enzymes to digest proteins, fats and carbohydrates (the main ones are amylase, lipase and protease). However, in case of decreased enzyme production (enzyme deficiency), pancreatitis and other pancreatic diseases, doctors prescribe drugs containing animal enzymes - they are in a shell, therefore they are protected even from the increased acidity of gastric juice. Reaching the duodenum, they are activated in it. Enzymes are often prescribed in short courses, but there are cases when you have to take them for quite a long time. Long-term use of enzymes may be accompanied by some decrease in pancreatic function, but after discontinuation of the drug, the function of the organ is restored.
Of the pancreatic enzymes, Creon, Festal, Mezim, Pancreazim, Panzinorm and other drugs are usually prescribed, the main active ingredient of which is pancreatin.
It contains protease, lipase, amylase. The level of lipase in one tablet is higher than the level of other enzymes. This is due to the fact that lipase, compared to other enzymes, is produced by the body in the smallest quantities during illness. Considering that lipase is reduced in the body, its content in preparations is no less than
10,000 action units (AU).
Enzyme preparations are in most cases safe for the body . They often play the role of concomitant therapy in antibiotic treatment, along with pre- and probiotics, as well as vitamins and other agents.
Reasons for deviations from the norms
An important diagnostic indicator is an increase in the amount of lipase in the blood plasma. An increase in this indicator indicates that the following pathological processes occur in the pancreas:
- Destruction of gland cells, as a result of which a high amount of lipase, as well as other enzymes, is released into the blood;
- Retention of pancreatic juice in the ducts, resulting from stones, tumors of the duct itself or the duodenum.
But most often these processes occur either simultaneously or as a consequence of one another.
Low levels of the enzyme indicate the development of conditions such as:
- cystic fibrosis;
- stomach ulcer;
- cancerous formations;
- peritonitis;
- chronic course of pancreatitis;
- hyperlipidemia;
- diabetes;
- Crohn's disease;
- high blood pressure.
Prevention of lipase surges
Like any other malfunction in the body, lipase surges can be avoided by following some rules:
- Diet. It is useful to eat small and often, dividing portions into smaller ones. Don't skip breakfast. Compliance with sanitary and hygienic standards.
- Diet. Avoid smoked, fried, spicy, too salty foods. But fiber-rich foods can be consumed in unlimited quantities. Cabbage, legumes, radishes, mustard, and garlic cause gas formation in the intestines, so it is worth limiting their consumption.
- Don't overeat. The standard serving for an adult is 300-400 ml.
- Drink enough fluids. It is recommended to drink a glass of warm water half an hour before meals.
- Keep your body weight under control. Excess weight aggravates the course of diseases and provokes increased symptoms.
- Quitting alcohol. Many alcoholic drinks contain dyes, preservatives, sugars and flavorings, which negatively affects the functioning of the pancreas. Although conditionally safe doses of ethanol have been established, it is better to refrain from drinking it completely.
- Minimize the amount of stress, walk more, relax and get enough sleep.
- If you smoke, you should definitely give up cigarettes. Tar and nicotine significantly weaken the body and subject it to additional stress.
- Increase your level of physical activity. Swimming strengthens you well, improves intestinal motility, take advantage of every opportunity to move more often.
- If you have diabetes, monitor your blood sugar levels especially carefully.
- Follow all the recommendations of your doctor, undergo regular medical examinations, and if you have chronic diseases, regularly take tests for control.
- Taking many medications can provoke the development of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, so be sure to consult your doctor before taking it.
Timely diagnosis of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, and especially the pancreas, is the key to quickly relieving the main symptoms of the disease. And a huge role in this diagnosis belongs to lipase analysis, which helps to accurately diagnose and begin therapy as quickly as possible, avoiding serious consequences.
Purpose of lipase in the human body
So, the main mission of any type of lipase is the processing of fats, their breakdown and fractionation. Also, this substance is actively involved in energy exchange, promotes the absorption of polyunsaturated fatty acids and certain vitamins.
The most important enzyme is produced by the pancreas. Pancreatic lipase is an enzyme with the help of which lipids are absorbed completely and completely. It enters the digestive tract, where, under the influence of colipase, which is also a pancreatic enzyme, it combines with bile acids and is converted into an active form. Pancreatic lipase plays an important role - it breaks down triglycerides (neutral fats) into two components: glycerol and higher fatty acids.
Symptoms of lipase deficiency and excess
When should you be wary and consult a doctor? If the consistency of the stool changed to liquid, abdominal cramps appeared, appetite disappeared and weight began to disappear, periodic feelings of nausea, vomiting, flatulence, general weakness and low physical activity appeared. In addition, sometimes your body temperature may rise slightly.
All these symptoms indicate both an excess and a lack of lipase. The only thing is that body hyperthermia most likely indicates an excess of the enzyme level.
Lysosomal acid lipase deficiency (LALD)
Congenital and inherited deficiency of specific lysosomal enzymes causes lysosomal diseases. The incidence of such diseases is quite low, but the danger from such conditions is very high. Thus, DLCL (lysosomal acid lipase deficiency) causes Wolman's disease (develops in infancy) and cholesteryl ester storage disease (less progressive and characterized by damage to older people).
Wolman disease without enzyme replacement therapy (for example, the use of Sebelipase alfa) is fatal in the first year of life. This disease has a very rapid course, causing liver failure, enlarged spleen, and paralytic intestinal obstruction. Diseases of accumulation of cholesterol esters are distinguished by a weaker nature of development, the liver is affected and dyslipidemia develops (a condition that provokes the development of atherosclerosis).
Treatment of lysosomal diseases consists of lifelong enzyme replacement therapy, which normalizes the level of transaminases, liver and spleen volumes, and improves the number of surviving patients. The prognosis of diseases, with early diagnosis and prevention of degenerative processes in the liver, is favorable.
Article on the topic:
What is lipomatosis and pancreatic lipoma? What are the dangers and the main methods of treatment?