- Home /
- Branches /
- Endoscopy /
- Gastroscopy of the stomach
Gastroscopy of the stomach is one of the few procedures that allows you to diagnose gastrointestinal diseases with high accuracy of results. It is also used for minimally invasive treatment of various neoplasms, bleeding and other pathologies of the gastric mucosa. Previously, the procedure caused unaccountable fear and disagreement on the part of patients, since the process was unpleasant and often painful. In the clinical hospital on Yauza, you can do a gastroscopy without swallowing a probe, without experiencing pain or discomfort.
Why is gastroscopy performed?
The doctor prescribes the procedure if there is a suspicion of the development of gastrointestinal diseases. This is one of the best methods for identifying pathologies at an early stage. The following symptoms may be the reason for gastroscopy:
- causeless weight loss;
- heartburn;
- nausea and vomiting mixed with blood;
- excessive burping;
- pain and heaviness in the stomach;
- distorted perception of taste;
- anemia.
Using a study, a specialist determines the presence or absence of gastrointestinal pathologies (ulcers, polyps, lesions, gastritis). This is one of the effective methods for diagnosing malignant and benign neoplasms at an early stage. During the procedure, you can immediately obtain a biopsy sample for research. Gastroscopy also reveals:
- disturbances in the functioning of neighboring organs;
- swallowed foreign objects;
- bleeding (and eliminated);
- evaluate the results of the therapy.
How is gastric FGSD performed for children?
Two types of anesthesia are used for the examination:
- medicated sleep;
- treatment with local anesthetic drugs.
The choice of anesthesia depends on the child’s age, body characteristics and type of operation (planned or emergency). It is difficult to explain the need for the procedure to children under 2–3 years of age, so these patients are generally provided with short-term sleep.
How is gastroscopy of the stomach done in children?:
- the child is placed in a stable position on the left side so that the right leg is bent and pulled towards the stomach, and the left is straightened;
- a special device is inserted into the oral cavity - a mouthpiece; it will prevent the baby from accidentally closing his mouth during the procedure and will prevent injuries to the palate or gums;
- the baby’s head is slightly pulled back and fixed in the desired position;
- a pre-prepared device is inserted into the throat, and when the child involuntarily swallows, it is pushed into the digestive tract.
If everything is done correctly, there is no cough or difficulty breathing. In some cases, to facilitate the passage of the gastroscope through the esophagus and to improve the quality of the image, air is supplied to the area under study. The amount is strictly dosed to prevent swelling of the internal organs. If necessary, a biopsy is performed directly during gastroscopy - the collection of biological material for further research in the laboratory.
After completing the examination and recording the results, the equipment is carefully removed, and the baby is turned over on his stomach so that air can escape from the esophagus. The child is sent under the supervision of an anesthesiologist for 2 hours.
Gastroscopy takes from 15 minutes to half an hour. After the procedure is completed, parents are given a conclusion and photographs taken during the examination.
Possible consequences of gastroscopy
Within 30–40 minutes after FGSD, slight difficulties with swallowing are possible. In some cases, there is mild numbness and tingling in the throat, which disappears after 1-2 hours. Sometimes children complain of slight discomfort and pain in the abdomen. Some patients experience numbness of the tongue.
Serious complications are very rare. These include:
- damage to the mucous membranes of the esophagus and stomach;
- esophageal rupture;
- gastric perforation;
- bleeding.
How gastroscopy is performed at the Yauza Clinical Hospital
The procedure requires preliminary preparation. It is carried out on an empty stomach, so you should not eat food 8-10 hours before gastroscopy. If pre-sedation is planned, cardiac data must be obtained. An ECG can also be performed in our clinic to evaluate your condition. You won't have to spend a lot of time on research if you do everything you need in one hospital.
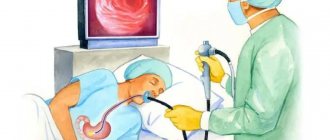
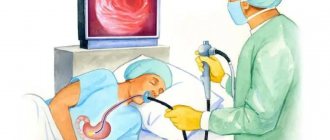
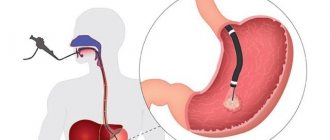
The patient's stomach is filled with air to improve vision. Next, a backlit camera on a thin and flexible cord is inserted into the esophagus. With its help, the doctor assesses the condition of the organ and records the collected data.
Often, in order to fully assess the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, gastroscopy and colonoscopy are performed. In the latter case, the examination is carried out through the intestines, inserting an endoscope into the rectum.
Gastroscopy of the stomach in Moscow at the clinical center on Yauza is carried out in the iScan expert mode. High-precision endoscopic equipment based on the ERK-i 7000 video processor allows you to obtain high-quality images and detect even small changes. The device undergoes intensive disinfection before and after the procedure.
The equipment allows you to take a targeted biopsy precisely from the lesion. In addition, if necessary, tumors and polyps can be removed using an endoscope. When using this method, the operation occurs with minimal tissue damage and does not require a long period of rehabilitation.
Video gastroscopy
In IMMA clinics, endoscopic examination of the stomach is performed using the digital video endoscopic system PENTAX EPK-1000 (Japan).
For video gastroscopy, the PENTAX EG-2490K device is used. It has an ultra-thin tube, so the patient experiences minimal discomfort. Another advantage of using a video gastroscope is that the doctor sees the endoscopic image on the monitor already during the procedure. On the distal part of the device there is a CCD matrix that converts the optical image into electronic signals and transmits them to the processor for processing. After this, the resulting image is displayed on the screen. Diagnostics takes a short time with maximum information content. In our clinics, we pay great attention to patient safety. To clean the device after video gastroscopy, we use the BANDEQ CYW-100N sterilization machine (South Korea). It provides a full cycle of leak testing, disinfection, washing, sterilization and drying of gastroscopic equipment. This is the total destruction of infections and viruses!
Is it possible to do a gastroscopy without swallowing a probe?
The Department of Gastroenterology at the Yauza Medical Center offers patients several methods for studying the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. The clinic is equipped with modern diagnostic equipment that allows you to obtain data on the condition of the stomach. As an alternative to gastroscopy, but without a probe, you can use:
- ultrasonography;
- plain radiography;
- CT and MRI.
The clinic also provides endosonography. This is a research method using ultrasound and an endoscope simultaneously.
Carrying out the procedure
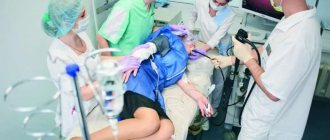
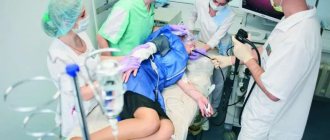
To reduce the gag reflex, the doctor suggests anesthesia. The patient lies on his left side and bends his knees. After the fibrogastroscope is inserted into the mouth, the doctor asks the patient to swallow. This is necessary to facilitate the advancement of the device along the esophagus. All received information is displayed on the monitor. If simultaneous treatment is necessary, special microsurgical instruments can be used. They are inserted into an additional channel of endoscopic equipment.
If you have any questions about the procedure, please contact our staff by phone in Moscow listed on the website. They will tell you in detail about the preparation, tell you the price for gastroscopy of the stomach, and also sign up for an examination.
Contraindications for EGDS
Like any medical procedure, gastroscopy has a number of contraindications. The decision to carry out can only be made by a qualified specialist after examining the patient’s health condition.
It is prohibited to perform gastroscopy in the following pathologies:
- acute heart attack, stroke;
- heart failure;
- psychical deviations;
- aortic aneurysm;
- narrowing of the esophagus;
- varicose veins of the esophagus;
- poor blood clotting.
There are diseases in which it is necessary to postpone research until the patient has fully recovered or the disease has gone into remission. These include inflammatory processes in the throat and exacerbation of stomach ulcers.
Fibrogastroduodenoscopy (FGDS)
FGDS or fibrogastroduodenoscopy (gastroscopy) is an endoscopic method for examining the upper parts of the gastrointestinal tract.
FGDS can be safely called the “gold standard” in the diagnosis of diseases of the esophagus and stomach. The diagnostic value of the method is invaluable, since it is possible not only to examine the walls of the stomach from the inside for diseases, but also to perform a tissue biopsy, that is, “pinch off a piece” of the affected tissue with further examination of the material under a microscope. In addition, during gastroscopy, it is possible to carry out therapeutic manipulations, for example, to stop bleeding or remove a small polyp in the mucous membrane of the organ.
Advantages of FGDS
The advantages of the method are:
- high information content,
- no tissue trauma,
- safety and almost complete absence of complications,
- painlessness,
- the ability to perform several diagnostic procedures in one procedure (for example, confirming the diagnosis of a stomach ulcer, conducting an acidity test, testing for Helicobacter pylori and taking a biopsy),
- the possibility of carrying out in a clinic, without hospitalization in a hospital, if there are no emergency indications,
- widespread equipment of modern medical institutions.
Disadvantages of FGDS
The only disadvantages include the presence of slight discomfort when swallowing the probe.
However, our clinic specialists, knowing this feature, try to reduce the patient’s discomfort.
Video FGDS
One of the types of gastroscopy is video-FGDS - this is a study in which the doctor examines the stomach cavity not only with his eyes, but also with the help of an enlarged image transmitted to the TV in the office. This allows you to better examine the smallest details in the mucous membrane, and give the video examination protocol on the hard drive to the patient.
Currently, each gastroscopy procedure is recorded by a miniature video camera at the end of the gastroscope.
Indications for FGDS
Indications for FGDS include:
- age over 40 years,
- esophagitis is an inflammatory process in the esophagus,
- gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) - reflux of acidic stomach contents into the esophagus,
- varicose veins of the esophagus with cirrhosis of the liver,
- Mallory-Weiss syndrome - bleeding on the mucous membrane of the border between the esophagus and stomach due to uncontrollable vomiting due to alcohol poisoning,
- tumors, strictures (adhesions) and adhesions of the esophagus,
- thermal and chemical burns of the esophagus,
- stomach ulcer,
- symptomatic stomach ulcers when taking certain medications (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: diclofenac, aspirin, ketorol, nise; steroid hormones: prednisolone, dexamethasone, etc.),
- acute and chronic gastritis,
- tumors and polyps of the stomach,
- stomach cancer,
- complications of peptic ulcer – gastric bleeding and perforated ulcer,
- pyloric stenosis (pyloric stenosis) – cicatricial narrowing of the gastric outlet,
- ulcers, tumors and cancer of the duodenal bulb,
- duodenitis - inflammation of the duodenal bulb,
- Papilla of Vater cancer is a malignant tumor of the formation into which the bile ducts and pancreatic duct open on the posterior wall of the duodenum.
Contraindications to FGDS
The study is not recommended for diseases such as:
- acute myocardial infarction, acute stroke,
- acute heart failure and chronic at a late stage,
- sudden paroxysm of rhythm disturbances,
- aortic aneurysm in the thoracic and abdominal region,
- hemophilia (pathology of the blood coagulation system),
- acute infectious diseases, diseases of the ENT organs - sore throat, tonsillitis, pharyngitis,
- severe emaciation or significant obesity of the patient,
- mental illness in the acute phase (however, FGDS can be carried out for urgent indications during intravenous anesthesia after consultation with a psychiatrist).
Preparation for FGDS
The examination is carried out on an empty stomach. The last meal should be no later than 7-8 hours before the test. On the morning of the FGDS, you should not even drink water.
A few days before the procedure, the patient must stop eating spicy foods and alcohol, and also stop smoking, as this has an irritating effect on the gastric mucosa.
If the patient is constantly taking any medications, for example, aspirin, non-steroidal drugs or anticoagulants (warfarin, phenylin, etc.), he should discuss with the doctor the possibility of completely stopping them for several days. This is due to the fact that when the blood is “thinned” using the above drugs, longer bleeding may occur during a biopsy, if one is needed.
How is the FGDS procedure performed?
In our clinic, a planned FGDS is more often performed with irrigation of the patient’s oropharynx with an anesthetic solution (lidocaine).
Before the study, the patient signs an informed consent (view, ). This is a document in which the patient voluntarily agrees to carry out the procedure, and also signs in the column where it is stated that he was notified about the technique and possible complications of the manipulation.
Next, the nurse or doctor asks the patient to lie down on the couch on his left side, after which the doctor irrigates the oropharynx with an anesthetic spray, for example, lidocaine. If a patient has an allergic reaction to anesthetics, he must notify the doctor about this without fail.
A couple of minutes after the anesthetic has taken effect, the doctor suggests wrapping your teeth around the mouthpiece, which prevents injury to the teeth and mucous membrane of the lips.
The next stage is the introduction of a gastroscope through the oropharynx into the esophagus. This lasts a few seconds and can cause quite noticeable gagging. At this time, the patient should, at the doctor’s command, make a swallowing movement, as if swallowing a probe, and then breathe evenly, calmly and deeply. After this, you cannot swallow without a doctor’s command, and the accumulated saliva is removed by a nurse with an electric suction.
After the probe enters the stomach, air is supplied so that the folds of the mucous membrane straighten out and it can be better seen. Next, the doctor conducts a visual examination, after which he removes the probe from the oral cavity.
Duration
The entire procedure takes no more than 5-10 minutes, unless therapeutic manipulations are performed. In these cases, gastroscopy can take up to half an hour.
After the procedure, unpleasant, raw sensations may appear in the oropharynx, which will go away on their own after a couple of hours.
The patient receives the examination protocol in his hands. If necessary, the patient can request a video protocol of the examination, which must be reported to the doctor in advance.
Price of gastroscopy in Moscow
You can get a paid gastroscopy in Moscow at the Clinical Hospital on Yauza. With us you will feel comfortable during the procedure and subsequent treatment. The clinic has its own hospital with high-class staff.
Diagnosis and treatment are carried out by doctors with extensive experience and scientific achievements. From the start of the FGDS procedure until the results are obtained, no more than an hour passes. All data is recorded and transmitted to the patient or sent to his email address.
The price of gastroscopy at the medical center is 5,400 rubles. Sedation is an additional cost. You can check the full cost with your doctor.
Sign up for the procedure
Preparation
In preparation for gastroscopy, it is necessary to stop (2-3 days in advance) from drinking alcoholic beverages and foods that irritate the mucous membrane of the digestive organs. Diagnosis is carried out on an empty stomach. Dinner on the eve of the examination should be easily digestible. If the procedure is not performed in the morning, it is recommended not to eat a few hours before it. You are allowed to drink some still water 2–3 hours before. Your doctor will tell you about all the nuances of preparing for gastroscopy during your consultation.
More detailed information about preparing for the procedure...