Thyrotoxicosis
Hepatitis
Diabetes
49663 06 August
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. We remind you that independent interpretation of the results is unacceptable; the information below is for reference only.
Glucose (in blood) (Glucose): indications for prescription, rules for preparing for the test, interpretation of results and normal indicators.
Standard glycemic values by age
The unit of measurement for sugar levels in the Russian Federation is millimoles per liter (mmol/l). In some other countries, glucose is measured in units of milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL). 1 mmol/l = 18 mg/dl. The normal level of blood glucose in young men (from 20 to 40 years old) is 3.3-5.5 mmol/l. In boys and young men during puberty this figure may be slightly lower, in men aged 60+ it may be slightly higher. This is not a pathology, since tissue sensitivity to insulin decreases with age.
Table of glycemic indicators taking into account age-related changes
| Age category | Newborns | Boys under 14 years old | Boys and men under 60 years of age | Elderly people under 90 / over 90 |
| Glucose norm in mmol/l | 2,7 – 4,4 | 3,3 — 5,6 | 4,1 – 5,9 | 4,6 – 6,4 / 4,6 – 6,7 |
The optimal sugar content for a healthy person varies in the range of 4.2–4.6 mmol/l. Reduced glucose levels are called hypoglycemia, and increased glucose levels are called hyperglycemia. You should not self-diagnose. Only a doctor can give an objective assessment of your health status based on laboratory microscopy.
Insulin high and low
Why there is elevated insulin, what this means, you can understand by understanding what insulin . This hormone, which is one of the most important in the body, is produced by the pancreas. It is insulin that has a direct effect on lowering blood sugar, determining the process of transfer of glucose into body tissues from blood serum.
The normal level of insulin in the blood of women and men is from 3 to 20 µU/ml. In older people, the upper level of 30-35 units is considered normal. If the amount of the hormone decreases, the person develops diabetes .
With increased insulin, the processes of glucose synthesis from proteins and fats are inhibited. As a result, the patient exhibits signs of hypoglycemia .
Sometimes patients have elevated insulin with normal sugar levels; the reasons may be associated with various pathological phenomena. This may indicate the development of Cushing's disease , acromegaly , as well as diseases associated with liver dysfunction.
How to reduce insulin should be asked by a specialist who will prescribe treatment after a series of studies.
Laboratory diagnostic methods
A basic blood test for glucose is performed by collecting capillary or venous biological fluid (from a finger or from a vein). The main condition is to take the test on an empty stomach. Any food, regardless of its carbohydrate component, affects the plasma glucose level, increasing its value. Objective data can only be obtained from measurements taken on an empty stomach
Other prohibitions during preparation include:
- morning oral hygiene (toothpaste is a sugar-containing product);
- alcoholic drinks (at least three days before the analysis);
- medications (except for vital medications).
It is not recommended to chew gum because it contains sucrose. When assessing venous blood, the amount of cholesterol is analyzed in parallel. In this case, it is separately assessed how much low-density lipotropes (“bad cholesterol”) is contained in the plasma and how much high-density lipotropes (“good cholesterol”) is contained in the plasma. Diabetes mellitus is almost always accompanied by hypercholesterolemia.
Acceptable and pathological cholesterol levels
A one-time elevated glycemic level is not diabetes. To confirm or refute the suspected diagnosis, it is necessary to undergo additional laboratory testing. What factors can distort laboratory microscopy results? First of all, this is incorrect preparation on the eve of the test:
- heavy physical activity;
- excessive consumption of sweets;
- drinking alcohol;
- unstable neuropsychological state (stress).
The results of the study are also affected by therapy with hormone-containing drugs and the presence of infectious diseases.
Advanced Diagnostics
Methods for additional diagnostics of sugar in men, women and children include:
- glucose tolerance test (GTT);
- blood test for HbA1C - glycated hemoglobin (“sweet protein”).
Testing for glucose tolerance allows you to determine not only diabetes, but also the borderline state of prediabetes, when the development of the disease can be prevented. Blood is drawn twice: on an empty stomach and 2 hours after the “load”. In this way, the body's response to carbohydrates is assessed. The loading role is played by an aqueous solution of glucose. With an extended analysis, blood sampling for sugar is carried out every 30 minutes.
Results of the study
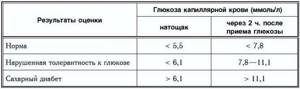
Impaired glucose tolerance means prediabetic condition
Glycosylated (glycated) hemoglobin is formed when hemoglobin and glucose are inhibited. HbA1C determines the percentage of hemoglobin and sugar in the body, that is, the amount of “sweet protein”. Norm and deviation of HbA1C indicators by age:
| Category | Norm | Satisfactory value | Overvalued |
| up to 40 years old | <6.5 | 6.5 — 7.0 | >7.0 |
| from 40 to 65 | <7.0 | 7.0 — 7.5 | >7.5 |
| 65+ | <7.5 | 7.5 — 8.0 | >8.0 |
The analysis allows you to track the sugar curve in retrospect over the lifespan of red blood cells (erythrocytes), which is 120 days. If the results are consistently elevated, the patient is referred to an endocrinologist to differentiate the type of diabetes. Additional testing is performed to determine the amount of glutamate decarboxylase antibodies (GAD antibodies).
Frequency of examination
For the adult population, medical examination is provided once every three years. A potentially healthy person receives a referral from a therapist for tests and hardware diagnostic procedures. In addition to routine examinations, men aged 50+ are recommended to monitor glycemia once a year. If you are systematically unwell, you should check your sugar without waiting for a certain period of time.
A blood test is the only reliable way to determine glucose levels
How often should a healthy person and a diabetic check their sugar?
A blood glucose test is one of those that must be taken during an annual routine examination for healthy people. Those with diabetes need to check their sugar levels frequently (especially people who take insulin injections), so it is advisable to have a glucometer at home. If you have hypertension or high blood cholesterol levels, you need to do a test at least once every six months.
Signs of deviations from the norm
Type 2 diabetes develops after age 30. The reasons may be genetic predisposition or unhealthy lifestyle. The disease does not occur suddenly, so the initial symptoms are often ignored. This behavior is especially typical for men due to a neglectful attitude towards health or the presence of bad habits.
Exceeding the permissible glucose level is indicated by the following symptoms:
- Decreased tone and performance, weakness. This is due to the body’s inability to fully absorb incoming sugar, which causes an energy deficiency.
- Severe drowsiness after eating. Eating food automatically increases glucose levels. When there is a high concentration of sugar in the blood, fatigue and a desire to sleep occur.
- Polydipsia (permanent feeling of thirst). Impaired carbohydrate metabolism provokes dehydration (dehydration), and the body strives to compensate for fluid reserves.
- Pollakiuria (frequent urge to urinate). The volume of urine increases due to a decrease in reabsorption of free fluid by the kidneys.
- Stably elevated blood pressure (BP). This is due to a violation of the composition of the blood and the circulatory process.
- Polygaffia (increased appetite). The feeling of satiety is under the control of the hypothalamus (a region of the brain) according to the criterion of qualitative and quantitative insulin production. Failure in the production and absorption of this hormone causes eating disorders. Uncontrolled eating leads to gaining extra pounds.
- Changes in the protective and regenerative qualities of the skin and thickening of the stratum corneum of the skin on the feet (hyperkeratosis). Hyperglycemia makes the skin dry and thin. Mechanical damage to the epidermis (skin) takes a long time to scar, and upon contact with pathogens, purulent processes develop. In keratinized areas, desquamation (exfoliation) is impaired. Calluses do not go away for a long time.
- Hyperhidrosis (increased sweating). An imbalance in the endocrine system disrupts the body's heat exchange.
For men, a characteristic sign may be a decrease in libido (sexual desire) and erectile capabilities. Hypoglycemia is a condition of the body in which the glucose level does not exceed 3.3 mmol/l. Symptoms of low blood sugar include:
Diet to lower blood sugar
- Regular dizziness (in some cases leading to short-term loss of consciousness). Frequent headaches. These symptoms are caused by a decrease in blood pressure.
- Involuntary contraction of leg muscles (cramps). They appear due to insufficient nutrition of the nerve fibers and capillaries of the peripheral system.
- Attacks of hunger, heaviness in the epigastric (epigastric) region, nausea after eating. They arise due to disturbances in carbohydrate metabolism and the ability to adequately absorb sugar (lack of glucose).
- Violation of thermoregulation. Due to a shortage of energy resources, a person experiences bouts of chills. Failure of blood circulation processes leads to insufficient blood supply to the extremities, which makes the hands and feet constantly cold.
Signs of decreased performance of the central nervous system (central nervous system) caused by oxygen starvation (brain hypoxia) systematically appear:
- asthenia (neuropsychic weakness);
- ataxia (impaired coordination of movements);
- absentmindedness;
- tachycardia (increased heart rate);
- hand shaking (tremor);
- decrease in cognitive functions (memory, mental performance);
- psycho-emotional instability (unreasonable irritability is replaced by an indifferent attitude to what is happening).
Many people who follow a diet to combat excess body weight experience a plateau effect (stopping weight loss) when they experience hypoglycemia. At the same time, a person consumes only permitted foods and follows the conditions of proper nutrition.
When should you get tested?
Determination of blood sugar in men and women can be prescribed by a general practitioner, gynecologist, endocrinologist or gastroenterologist if a parameter deviation from the norm is suspected.
Blood sugar levels in men and women are measured by:
- standard preventive examination of patients;
- the patient develops symptoms of diabetes mellitus;
- suspected hyperglycemia (excess) and hypoglycemia (lack). Biomaterial for research can be collected before or after meals, in critical conditions - spontaneously at any time;
- differential diagnosis of diabetes mellitus in combination with a glucose tolerance test. To make a final diagnosis, the study is repeated twice at different times of the day;
- daily monitoring for people with established diabetes mellitus. This is necessary to adjust the dosage of medications and insulin injections;
- the need to exclude gestational diabetes - a temporary increase in blood sugar levels in pregnant women. In the absence of timely treatment, gestational diabetes can lead to fading of pregnancy, damage to the nervous tissues and internal organs of the fetus, miscarriage, severe gestosis in a pregnant woman, hypoglycemia in a newborn, etc.
Symptoms of an increase in the level of simple sugars in the blood: frequent urge to urinate, severe thirst, decreased visual acuity, fatigue, drowsiness, low performance, frequent relapses of infectious diseases, dry and itchy skin, dry mucous membranes, etc.
Signs of decreased sugar include:
- increased sweating,
- excessive appetite,
- confusion of consciousness
- mental disorders,
- increased nervousness,
- feeling of restlessness and blurred vision,
- disorientation in space,
- fainting, etc.
Causes of hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia in men
The normal level of glycemia changes upward or downward under the influence of certain factors. The reasons may be external influences, lifestyle, undiagnosed pathologies.

Obesity is a factor contributing to the development of diabetes mellitus
Hyperglycemia
The main reason for increased glucose is the development of diabetes mellitus. In adult men, the disease is diagnosed according to the second type. A characteristic feature of this form of diabetes is independence from insulin injections. The pancreas does not stop producing the hormone. The accumulation of sugar in the blood occurs due to the cells’ lack of sensitivity to insulin and the ability to use it rationally.
Important! The main factors influencing the occurrence of type 2 diabetes in men are obesity and chronic alcoholism.
Other causes of hyperglycemia include chronic inflammation of the pancreas (pancreatitis), oncological processes in the body, excessive production of thyroid hormones (hyperthyroidism), pre-infarction or pre-stroke condition (history of strokes and heart attacks), taking hormone-containing drugs to treat other pathologies. The true cause of excess sugar levels can only be determined by undergoing a comprehensive medical examination.
Hypoglycemia
The development of pathological glucose deficiency can provoke:
- Poor nutrition (insufficient intake of macro- and microelements and vitamins into the body).
- Irrational consumption of simple carbohydrates. When you overeat sweets, the sugar level rises sharply, but is consumed very quickly, causing a deficiency of glucose in the blood.
- Physical activity that is disproportionate to the body’s capabilities. In this case, the glucose reserve, glycagon, is consumed, which also leads to hypoglycemia.
- Distress. Permanently being in a state of neuropsychological tension can cause both an increase and a decrease in glucose levels.
Intoxication (poisoning) and dehydration of tissues and cells can lead to a decrease in sugar.
Symptoms of high sugar
High blood sugar can be detected if a person exhibits certain symptoms. The following symptoms that appear in adults and children should alert a person:
- weakness, severe fatigue;
- increased appetite and at the same time weight loss;
- thirst and constant feeling of dry mouth;
- copious and very frequent urine output, frequent trips to the toilet at night;
- pustules , boils and other lesions on the skin, such lesions do not heal well;
- regular occurrence of itching in the groin and genitals;
- deterioration of immunity, deterioration of performance, frequent colds, allergies in adults;
- deterioration of vision, especially in people over 50 years of age.
The occurrence of such symptoms may indicate that there is increased glucose in the blood. It is important to note that signs of high blood sugar can only be expressed by some of the manifestations listed above. Therefore, even if only some symptoms of high sugar levels appear in an adult or a child, you need to get tested and determine glucose. What kind of sugar, if it is elevated, what to do - all this can be found out by consulting a specialist.

Symptoms of low sugar levels
The risk group for diabetes includes those who have a hereditary predisposition to diabetes , obesity , pancreatic disease , etc. If a person is included in this group, then a single normal value does not mean that the disease is absent. After all, diabetes mellitus very often occurs without visible signs and symptoms, in waves. Therefore, it is necessary to carry out several more tests at different times, since it is likely that in the presence of the described symptoms, elevated levels will still occur.
If such signs are present, high blood sugar during pregnancy is also possible. In this case, it is very important to determine the exact causes of high sugar. If glucose is elevated during pregnancy, your doctor should explain what this means and what to do to stabilize the levels.
It should also be taken into account that a false positive test result is also possible. Therefore, if the indicator, for example, is 6 or blood sugar is 7, what this means can be determined only after several repeated tests. What to do if in doubt, the doctor determines. For diagnosis, he may prescribe additional tests, for example, a glucose tolerance test, a sugar load test.
The effect of high blood sugar on the male body
For diabetics, a state of hypoglycemia can be dangerous due to the development of coma. In the absence of diabetes, low glucose levels are compensated by eating sugary foods in moderation and reducing physical activity. High sugar levels in men lead to more serious consequences:
- Thrombosis. With hyperglycemia, the blood becomes thicker and it is difficult for it to circulate through the vessels. Stagnation leads to the formation of blood clots.
- Heart attacks and strokes. The thick consistency of the blood, combined with cholesterol deposits on the walls of blood vessels, disrupts the blood supply to the heart and cerebral circulation.
- Problems with potency. Due to insufficient blood and oxygen supply to the genitals, men cannot achieve a full erection. In addition, hyperglycemia inhibits the production of testosterone (the main male sex hormone), which leads to suppression of sexual desire. Long-term elevated sugar levels threaten erectile dysfunction (impotence).
- Malfunction of the renal apparatus. Excessive fluid consumption with the symptom of polydipsia increases the load on the kidneys, as a result of which various pathologies of the urinary organs develop.

To avoid the consequences of unstable glycemia, it is necessary to seek medical help at the first manifestation of symptoms.
When an increase in sugar is not considered a pathology
In some cases, an increase in glucose levels is the body's response to external influences. This condition is called physiological hyperglycemia. It appears in the background:
- eating foods high in carbohydrates;
- after intense training;
- due to taking hormonal drugs (corticosteroids);
- stress;
- dousing with ice water.
When the provoking factors stop acting, glucose returns to normal.
How to keep your numbers normal
Even a one-time deviation of sugar levels from the acceptable norm should not be neglected. This may be a prerequisite for the development of an incurable endocrine pathology – diabetes mellitus. Systematically “walking” sugar indicates metabolic disorders and hormonal instability. The disease can be prevented by adhering to the rules of a healthy lifestyle.
Important points are a balanced diet based on the consumption of foods rich in fiber, dietary fiber, pectin, elimination of fatty foods and dishes prepared by the culinary method of frying from the daily menu, adherence to the drinking regime (1.5 - 2 liters of water per day), taking vitamins A, E, and B-groups, and microelements (chromium, zinc, manganese, magnesium).
Rational sports activities on a regular basis and spending time in the fresh air, avoiding alcoholic beverages and nicotine are also important. To promptly identify abnormalities in the body’s functioning, men need to regularly visit a doctor and monitor blood glucose levels.
How to prepare
In order for the analysis results to be reliable, the patient needs to know that the examination requires certain preparation:
- Blood donation occurs on an empty stomach. The last meal should be 8 hours before the start of the procedure. Therefore, the most convenient time is morning.
- It is forbidden to drink anything except plain water.
- In two days you need to eliminate fatty foods and alcoholic drinks.
- On the day of delivery, you should not brush your teeth or chew gum.
- It is prohibited to take medications 3 days before the test. This is especially true for glycemic medications. If it is impossible to cancel, then you need to inform your doctor.
- Avoid smoking on the day of delivery.
- Do not subject the body to increased mental and physical stress during the day.
- The analysis does not fail after the patient has had a massage, x-ray, or ultrasound.
- You should not donate blood if there are signs of inflammation and infection.
It is important to follow all these rules, because the amount of sugar may change. Certain foods, physical activity, and possible stressful situations can increase or decrease blood sugar.
Before donating, some patients try to reduce the monosaccharide readings in the body using folk remedies. Such actions are unacceptable, since the real picture of the condition is distorted and the results will be invalid.
Doctors' advice
Experts recommend regularly monitoring blood glucose levels and undergoing routine examinations on time. If symptoms of hyperglycemia appear, you should immediately seek advice from your family doctor or endocrinologist.
Doctors recommend leading a healthy lifestyle, eating in moderation, moving a lot and avoiding extra pounds.
Share your opinion or experience - write comments. Did you like the article? – Share it with your friends on social networks.
Blood glucose levels provide insight into how successfully the body processes carbohydrates. It is necessary to control your sugar levels by getting tested regularly. If the diagnostic result shows an excess of the norm, there is no need to self-medicate. It is important to immediately seek advice from an endocrinologist.