What may affect the results
An increase in AST levels can be observed even in healthy people if the rules for preparing for the analysis are not followed. For example, blood should not be donated if during the day the patient experienced severe emotional distress, heavy physical exertion, underwent fluorography, X-ray examination or any physiotherapeutic procedures, ultrasound or rectal examinations of any spectrum. The result can be affected by the intake of alcohol and a number of medications, in particular, antitumor and choleretic drugs, antibiotics, barbiturates, contraceptives, sedatives, vitamin A and others, as well as recent heart surgery.
What is an enzyme
AST or AST is a protein synthesized inside the cells of the human body. Its highest concentrations are observed in the tissues of the myocardium, muscles and liver. To a lesser extent, the enzyme is present in the kidneys, pancreas, cells of the central nervous system and brain. It is encoded by the GOT 1 and GOT 2 genes. In a healthy person, the level of the enzyme is quite low. Its active release into the blood begins when the heart muscle ruptures, as well as liver destruction as a result of hepatitis, cirrhosis or cancer. The enzyme is important because it contains vitamin B6, which is involved in amino acid metabolism and, accordingly, the synthesis of insulin. In tests, the indicator is measured in units per liter of blood.
Aspartate aminotransferase (in blood serum)
Blood for research is taken from a vein.
Usually, the level of another enzyme, alanine aminotransferase (ALT), is simultaneously determined, since the de Ritis coefficient (AST/ALT ratio) is considered informative for many liver conditions. You can take a blood test for AST (AST, aspartate aminotransferase, AST, SGOT, Aspartate aminotransferase) at the nearest INVITRO medical office.
A list of offices where biomaterial is accepted for laboratory research is presented in the “Addresses” section. Interpretation of study results contains information for the attending physician and is not a diagnosis. The information in this section should not be used for self-diagnosis or self-treatment. The doctor makes an accurate diagnosis using both the results of this examination and the necessary information from other sources: medical history, results of other examinations, etc.
How to prepare for analysis
To increase the reliability of the analysis, some rules and restrictions should be observed. So on the eve of the study, you should refrain from eating fatty and smoked foods, as well as confectionery. It is best if the test is performed on an empty stomach in the morning. When taking medications, you should consult your doctor about their possible withdrawal. The fact is that during a biochemical blood test, many medications can affect the results of the study. When treated with antidepressants, antibiotics, diuretics and other drugs, the test readings may be distorted. In addition, immediately before a visit to the treatment room, it is prohibited to perform ultrasound, x-ray examination and physiotherapy procedures.
Normal indicators
Units of measurement: U/l.
Reference values:
| Age, gender | ASAT, U/l | |
| < 5 days | < 97 | |
| 5 days - 6 months | < 77 | |
| 6 – 12 months | < 82 | |
| 1 – 3 years | < 48 | |
| 3 years - 6 years | < 36 | |
| 6 – 12 years | < 47 | |
| Women | 12 - 17 years old | < 25 |
| > 17 years old | < 31 | |
| Men | 12 - 17 years old | < 29 |
| > 17 years old | ||
Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) test
Table of contents
- Rules for preparing for the test
- What can affect the result?
- Analysis result
- Additional Research
- Which doctors refer you for the study?
- MEDSI cares about its patients
An aspartate aminotransferase (AST)
test is done to detect liver damage.
Biological material:
venous, capillary blood
Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) is an enzyme located in all cells of the body, but mainly in the liver and heart. Normally, its activity in the blood is very low. Indicators increase when liver or muscle tissue is damaged. In this case, AST is released into the blood.
Testing is recommended:
- To detect liver damage. The analysis is prescribed together with the study of ALT (alanine aminotransferase), which is also considered an important parameter of organ damage, or as part of a general diagnosis of the liver
- To determine the specific form of liver pathology
- To monitor the effectiveness of existing therapy
- To evaluate the health of patients who are taking drugs that are potentially toxic to the liver
It is especially important to get tested in the following cases:
- If you have symptoms of a liver disorder: fatigue and weakness, nausea and vomiting, abdominal pain, yellowing of the whites of the eyes and skin, itching, dark urine, light-colored stools
- In the presence of factors that increase the risk of developing liver diseases: previous hepatitis, alcohol abuse, hereditary predisposition, taking certain medications, diabetes, excess weight
- During the treatment of identified diseases to monitor its dynamics and effectiveness of therapy
Rules for preparing for the test
- Food.
You should refuse food 12 hours before the test - Loads.
You should refrain from physical and emotional stress half an hour before the diagnosis - Smoking.
You should stop smoking at least half an hour before the test
What can affect the result?
AST levels may decrease during pregnancy.
Increasing the indicator
aspartate aminotransferase is possible with:
- intramuscular injections of drugs
- intense physical activity
- taking dietary supplements
It's important to keep in mind
that only a doctor who is aware of the medications and dietary supplements the patient is taking, as well as pregnancy and other conditions, can correctly interpret the diagnostic results. Therefore, in many cases, it is important to consult a doctor for advice before taking the test. The test result is also assessed by the doctor in comparison with the patient’s clinical picture.
If necessary, the specialist will refer the patient for other examinations. Based on the results of a comprehensive diagnosis, an accurate diagnosis will be made.
We recommend that you consult a doctor or undergo a check-up (a full examination program).
To clarify the specifics of the test or make an appointment at the clinic, just call +7 (495) 7-800-500. A specialist will answer all questions and select the optimal time for a visit. Registration and payment for services is also possible through the SmartMed application.
Analysis result
| Age/gender | Reference values |
| 0-1 year | < 58 U/l |
| 1-4 years | < 59 U/l |
| 4-7 years | < 48 U/l |
| 7-13 years | < 44 U/l |
| 13-18 years old | < 39 U/l |
| Men over 18 years old | < 40 U/l |
| Women over 18 years old | < 32 U/l |
High AST activity is observed when:
- viral infections
- taking medications that are toxic to the liver
- diseases that slow blood flow to the organ
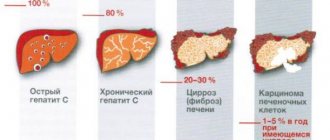
- chronic hepatitis
- bile duct obstruction
- cirrhosis
- some types of liver cancer
- muscle damage
The rate also increases after a heart attack.
Additional Research
Additionally, the patient may be referred for tests to determine:
- Alanine aminotransferase (ALT)
- Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase (gamma-GT)
- Serum total protein
- Serum albumin
- Alkaline total phosphatase
Which doctors refer you for the study?
The following can be referred for diagnosis: a therapist, a pediatrician, a general practitioner, a hepatologist, a gastroenterologist, a cardiologist, or a surgeon.
MEDSI cares about its patients
- Experienced specialists.
They professionally collect biological material and examine it, which guarantees diagnostic accuracy - All our clinics have created comfortable conditions for taking the test.
- The research is carried out using high-precision expert-class equipment
- There is an opportunity to undergo a comprehensive examination
To take an AST test and make an appointment with a doctor to interpret the result, as well as clarify its cost, call +7 (495) 7-800-500. Our specialist will answer all questions and suggest the optimal time to visit the clinic. Recording is also possible through the SmartMed application.
What do increased indicators mean?
A significant increase in AST activity is observed in myocardial infarction, insufficient blood circulation, shock, hypoxia, acute viral or toxic hepatitis, necrosis or damage to liver cells.
A moderate increase in AST activity can be detected in liver cirrhosis, obstructive jaundice, metastases, acute pancreatitis, ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke, with damage to skeletal muscles, after injuries or surgical interventions. In children, protein activity may increase in the presence of inflammatory processes in the body. An increase in aspartate aminotransferase concentrations is sometimes observed during pregnancy.
The use of hepatotoxic drugs or drugs that cause cholestasis (slowdown or complete cessation of bile secretion) can also provoke an increase in AST. Usually this condition is regarded as temporary.
Range of application of AST analysis
- In cardiology as a marker of myocardial infarction. In the heart muscle the enzyme is more than 10,000 times more active than in the blood. During a heart attack, intense release of the enzyme occurs.
- For liver pathologies. Diseases such as hepatitis and cirrhosis are certainly accompanied by the destruction of liver tissue and a sharp jump in AST values.
- For chronic alcoholism.
- In obstetrics and gynecology. During pregnancy, a woman may experience a slight increase in AST values. This is explained by the effect of the growing fetus on the mother's liver. In the first trimester, its values should not exceed 31 U/l, in the second and third – 30 U/l.
- In endocrinology for diabetes and/or excess weight.
Reasons for increased ALT
An increase in ALT levels may be due to:
- myositis;
- intrahepatic cholestasis;
- burns, severe intoxication, muscle injuries;
- autoimmune thyroiditis;
- liver pathologies (hepatitis caused by viruses and alcohol, fatty hepatosis, cancer, cirrhosis);
- heart diseases (myocarditis and other pathologies that are accompanied by damage to myocardial cells);
- acute pancreatitis.
Also, the amount of ALT can be increased in cancer, progressive leukemia and obesity of III-IV degree. During a heart attack, this indicator practically does not change.
Reasons for increased AST levels
A high titer of AST may indicate pathology of the hepatobiliary tract, which is accompanied by the destruction of hepatocytes:
- hepatitis (infectious, alcoholic, ischemic, drug);
- fatty hepatosis;
- cirrhosis;
- autoimmune cholangitis;
- primary and secondary tumors in the liver.
High levels of AST are observed against the background of other diseases:
- heart failure;
- heart attack;
- pancreatitis;
- muscle dystrophy;
- celiac disease;
- kidney pathologies.
An increase in AST titer is observed after intense strength training, massive injuries, burns, and ketoacidosis. The concentration of AST in the blood increases when taking certain dietary supplements and medications (statins, barbiturates, acetylsalicylic acid).
Indications
An AST test can be recommended by a therapist, pediatrician, hepatologist, oncologist, surgeon, gastroenterologist, or cardiologist. The main reason for prescribing the study are symptoms of liver damage, which include:
- yellowing of the sclera and mucous membranes;
- skin itching;
- stool discoloration;
- darkening of urine;
- intoxication of the body (weakness, fatigue, nausea);
- bitter taste in the mouth, bloating, constipation as a manifestation of digestive tract dysfunction.
Liver tests, including AST, are taken by people at risk of developing liver disease. The test is prescribed in the following situations:
- previous hepatitis;
- unfavorable family history;
- taking hepatotoxic drugs;
- overweight;
- diabetes;
- alcohol abuse;
- contact with persons sick with viral hepatitis.
Transaminase indicators are important not only at the stage of primary diagnosis, but are also used to monitor the condition of patients with already diagnosed diseases, tracking the dynamics of the development of pathology and assessing the effectiveness of treatment.
The study is prescribed to persons with cardiovascular pathology. A high level of aspartate aminotransferase in the blood indicates serious damage to the heart muscle (in acute failure, heart attack), which is used in the differential diagnosis of acute life-threatening conditions.